A Highlight of Recent Advances in Aptamer Technology and Its Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction



2. Aptamer Modifications and Improved Strategies in SELEX Technology
2.1. Aptamer Modifications
2.2. Improved Strategies in SELEX Technology
2.2.1. Design of Oligonucleotide Pool
2.2.2. Partitioning
2.2.3. Amplification
2.2.4. Sequencing
3. Improvement in Applications
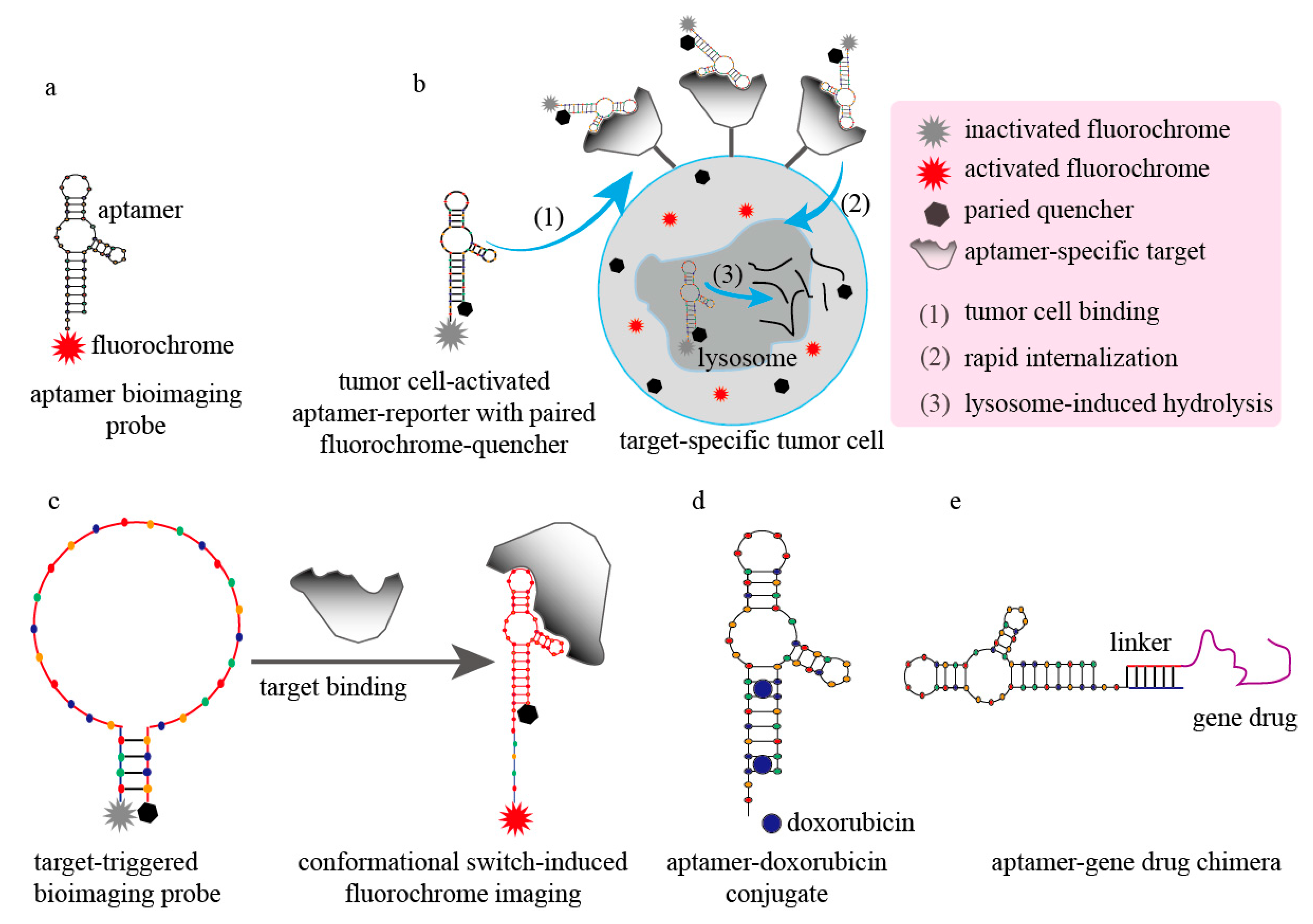
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberian-Borujeni, M.; Johari-Ahar, M.; Hamzeiy, H.; Barar, J.; Omidi, Y. Nanoscaled aptasensors for multi-analyte sensing. BioImpacts:BI 2014, 4, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, T.; Patel, D.J. Adaptive recognition by nucleic acid aptamers. Science 2000, 287, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimjee, S.M.; Rusconi, C.P.; Sullenger, B.A. Aptamers: An emerging class of therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Med. 2005, 56, 555–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.O.; Kolonias, D.; Pastor, F.; Mittler, R.S.; Chen, L.; Giangrande, P.H.; Sullenger, B.; Gilboa, E. Multivalent 4-1BB binding aptamers costimulate CD8+ T cells and inhibit tumor growth in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, B. Pegaptanib for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyetech Study Group. Preclinical and phase 1A clinical evaluation of an anti-VEGF pegylated aptamer (EYE001) for the treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2002, 22, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ireson, C.R.; Kelland, L.R. Discovery and development of anticancer aptamers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Y.H.; Phua, K.K.; Leong, K.W. Aptamer nanomedicine for cancer therapeutics: Barriers and potential for translation. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2235–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.; Shigdar, S.; Qiao, G.; Wang, T.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Zhou, S.F.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Pu, C.; Duan, W. Nucleic acid aptamer-guided cancer therapeutics and diagnostics: The next generation of cancer medicine. Theranostics 2015, 5, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesiolka, J.; Gorski, J.; Yarus, M. Selection of an RNA domain that binds Zn2+. RNA 1995, 1, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Goldstein, I.J.; Mei, H.Y.; Engelke, D.R. DNA ligands that bind tightly and selectively to cellobiose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5462–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltenburg, R.; Nikolaus, N.; Strehlitz, B. Capture-SELEX: Selection of DNA Aptamers for Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012, 415697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Duan, J.H.; Song, Y.M.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.D.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.D. Novel HER2 aptamer selectively delivers cytotoxic drug to HER2-positive breast cancer cells in vitro. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cao, Z.C.; Chen, H.W.; Mallikaratchy, P.; Sefah, K.; Yang, C.J.; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11838–11843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, H.; Ding, H.; Huang, Y.; Cao, X.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Identification of an aptamer targeting hnRNP A1 by tissue slide-based SELEX. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmostuk, M.; Rimpelova, S.; Gbelcova, H.; Ruml, T. Current approaches in SELEX: An update to aptamer selection technology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, W.; Jia, S.; Guan, Z.; Yang, C.J.; Zhu, Z. Microfluidic approaches to rapid and efficient aptamer selection. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 041501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, L.; Ayers, D.; Bertino, J.; Bock, C.; Bock, A.; Brody, E.N.; Carter, J.; Dalby, A.B.; Eaton, B.E.; Fitzwater, T.; et al. Aptamer-based multiplexed proteomic technology for biomarker discovery. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elle, I.C.; Karlsen, K.K.; Terp, M.G.; Larsen, N.; Nielsen, R.; Derbyshire, N.; Mandrup, S.; Ditzel, H.J.; Wengel, J. Selection of LNA-containing DNA aptamers against recombinant human CD73. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, D.A.; Chen, H.; Hicke, B.J.; Swiderek, K.M.; Gold, L. A tenascin-C aptamer identified by tumor cell SELEX: systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15416–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefah, K.; Shangguan, D.; Xiong, X.; O’Donoghue, M.B.; Tan, W. Development of DNA aptamers using Cell-SELEX. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibiel, A.; Dupont, D.M.; Duconge, F. Methods To Identify Aptamers against Cell Surface Biomarkers. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 1216–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerchia, L.; de Franciscis, V. Targeting cancer cells with nucleic acid aptamers. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, J.G. Predicting the Uncertain Future of Aptamer-Based Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Molecules 2015, 20, 6866–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.W.; Adamis, A.P. Anti-VEGF aptamer (pegaptanib) therapy for ocular vascular diseases. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1082, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, X.; Lu, P.Y.; Rosato, R.R.; Tan, W.; Zu, Y. Oligonucleotide aptamers: New tools for targeted cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, S.E.; Matsumura, I.; Ellington, A.D. Aptamers as therapeutic and diagnostic reagents: Problems and prospects. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1997, 1, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovall, G.M.; Bedenbaugh, R.S.; Singh, S.; Meyer, A.J.; Hatala, P.J.; Ellington, A.D.; Hall, B. In vitro selection using modified or unnatural nucleotides. Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2014, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, P.E.; Lewis, S.D.; Silva, R.F.; Preiss, J.R.; Horwitz, L.R.; Pendergrast, P.S.; McCauley, T.G.; Kurz, J.C.; Epstein, D.M.; Wilson, C.; et al. Direct in vitro selection of a 2′-O-methyl aptamer to VEGF. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proske, D.; Gilch, S.; Wopfner, F.; Schatzl, H.M.; Winnacker, E.L.; Famulok, M. Prion-protein-specific aptamer reduces PrPSc formation. Chembiochem 2002, 3, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckman, J.; Green, L.S.; Beeson, J.; Waugh, S.; Gillette, W.L.; Henninger, D.D.; Janjic, N.; Claesson-Welsh, L. 2′-Fluoropyrimidine RNA-based aptamers to the 165-amino acid form of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165). Inhibition of receptor binding and VEGF-induced vascular permeability through interactions requiring the exon 7-encoded domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20556–20567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Cload, S.T. SELEX with modified nucleotides. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Yang, X.; Gharpure, K.M.; Hatakeyama, H.; Egli, M.; McGuire, M.H.; Nagaraja, A.S.; Miyake, T.M.; Rupaimoole, R.; Pecot, C.V.; et al. 2′-OMe-phosphorodithioate-modified siRNAs show increased loading into the RISC complex and enhanced anti-tumour activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wang, D.; Zhu, F.G.; Bhagat, L.; Dai, M.; Kandimalla, E.R.; Agrawal, S. Modifications incorporated in CpG motifs of oligodeoxynucleotides lead to antagonist activity of toll-like receptors 7 and 9. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5108–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, C.; Zydek, M.; Rothkegel, M.; Wu, Z.; Gallin, C.; Gessner, R.; Lisdat, F.; Furste, J.P. Properties of an LNA-modified ricin RNA aptamer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, V.B.; Taylor, A.I.; Cozens, C.; Abramov, M.; Renders, M.; Zhang, S.; Chaput, J.C.; Wengel, J.; Peak-Chew, S.Y.; McLaughlin, S.H.; et al. Synthetic genetic polymers capable of heredity and evolution. Science 2012, 336, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eulberg, D.; Klussmann, S. Spiegelmers: Biostable aptamers. Chembiochem 2003, 4, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, P.; Kamble, S.; Zhao, N.; Zeng, Z.; Portier, B.P.; Zu, Y. Immunotherapy of CD30-expressing lymphoma using a highly stable ssDNA aptamer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8909–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.J.; Ventura, D.A.; Brasier, A.R.; Gorenstein, D.G. Novel combinatorial selection of phosphorothioate oligonucleotide aptamers. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 16489–16493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, B.E. The joys of in vitro selection: Chemically dressing oligonucleotides to satiate protein targets. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1997, 1, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.R.; Gelinas, A.D.; Zhang, C.; Rohloff, J.C.; Carter, J.D.; O’Connell, D.; Waugh, S.M.; Wolk, S.K.; Mayfield, W.S.; Burgin, A.B.; et al. Unique motifs and hydrophobic interactions shape the binding of modified DNA ligands to protein targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19971–19976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, S.; Vaught, J.D.; Bock, C.; Gold, L.; Katilius, E.; Keeney, T.R.; Kim, N.; Saccomano, N.A.; Wilcox, S.K.; Zichi, D.; et al. From SOMAmer-based biomarker discovery to diagnostic and clinical applications: A SOMAmer-based, streamlined multiplex proteomic assay. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimoto, M.; Yamashige, R.; Matsunaga, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Hirao, I. Generation of high-affinity DNA aptamers using an expanded genetic alphabet. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Pai, S.; Ellington, A. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T.; Choe, W.S.; Su, X. PEGylated anti-MUC1 aptamer-doxorubicin complex for targeted drug delivery to MCF7 breast cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghdisi, S.M.; Danesh, N.M.; Sarreshtehdar Emrani, A.; Tabrizian, K.; Zandkarimi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K. Targeted delivery of Epirubicin to cancer cells by PEGylated A10 aptamer. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macugen, A.M.D.S.G.; Apte, R.S.; Modi, M.; Masonson, H.; Patel, M.; Whitfield, L.; Adamis, A.P. Pegaptanib 1-year systemic safety results from a safety-pharmacokinetic trial in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Basile, A.S.; Hutmacher, M.; Nickens, D.; Nielsen, J.; Kowalski, K.; Whitfield, L.; Masayo, O.; Nakane, M. Population pharmacokinetics of pegaptanib in patients with neovascular, age-related macular degeneration. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 1186–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiang, Y.C.; Ou, C.M.; Chen, S.J.; Ou, T.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Highly efficient inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by aptamers functionalized gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2756–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Sefah, K.; Liu, H.; Wang, R.; Tan, W. DNA aptamer-micelle as an efficient detection/delivery vehicle toward cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.; Micheletti, J.M.; Satya, P.; Ogle, K.; Pollard, J.; Ellington, A.D. Design, synthesis, and amplification of DNA pools for in vitro selection. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbachinskiy, A.V. Methods for selection of aptamers to protein targets. Biochem. Biokhimiia 2007, 72, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.G. A review of therapeutic aptamer conjugates with emphasis on new approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallikaratchy, P.R.; Ruggiero, A.; Gardner, J.R.; Kuryavyi, V.; Maguire, W.F.; Heaney, M.L.; McDevitt, M.R.; Patel, D.J.; Scheinberg, D.A. A multivalent DNA aptamer specific for the B-cell receptor on human lymphoma and leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2458–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VEGF Inhibition Study in Ocular Neovascularization (V.I.S.I.O.N.) Clinical Trial Group; Chakravarthy, U.; Adamis, A.P.; Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Goldbaum, M.; Guyer, D.R.; Katz, B.; Patel, M. Year 2 efficacy results of 2 randomized controlled clinical trials of pegaptanib for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 1508 e1–e25. [Google Scholar]
- Ibach, J.; Dietrich, L.; Koopmans, K.R.; Nobel, N.; Skoupi, M.; Brakmann, S. Identification of a T7 RNA polymerase variant that permits the enzymatic synthesis of fully 2′-O-methyl-modified RNA. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosh, B.; Yadava, P.K. Nucleic acid aptamers: Research tools in disease diagnostics and therapeutics. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 540451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclair, S.; Gautam, A.; Ellington, A.; Prasad, V.R. High-affinity RNA Aptamers Against the HIV-1 Protease Inhibit Both in Vitro Protease Activity and Late Events of Viral Replication. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennarz, S.; Alich, T.C.; Kelly, T.; Blind, M.; Beck, H.; Mayer, G. Selective aptamer-based control of intraneuronal signaling. Angew. Chem. 2015, 54, 5369–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, H.; Ou, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Development of a fraction collection approach in capillary electrophoresis SELEX for aptamer selection. Analyst 2015, 140, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezovski, M.; Drabovich, A.; Krylova, S.M.; Musheev, M.; Okhonin, V.; Petrov, A.; Krylov, S.N. Nonequilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures: A universal tool for development of aptamers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3165–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolle, F.; Wilke, J.; Wengel, J.; Mayer, G. By-product formation in repetitive PCR amplification of DNA libraries during SELEX. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yufa, R.; Krylova, S.M.; Bruce, C.; Bagg, E.A.; Schofield, C.J.; Krylov, S.N. Emulsion PCR significantly improves nonequilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures-based aptamer selection: allowing for efficient and rapid selection of aptamer to unmodified ABH2 protein. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, E.; Foley, J.H.; Conway, E.M.; Haynes, C. Hi-Fi SELEX: A high-fidelity digital-PCR based therapeutic aptamer discovery platform. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunniger, T.; Wessels, H.; Fischer, C.; Paschke-Kratzin, A.; Fischer, M. Just in time-selection: A rapid semiautomated SELEX of DNA aptamers using magnetic separation and BEAMing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10940–10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, H.; Wu, F.; Su, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, D. Indirect purification method provides high yield and quality ssDNA sublibrary for potential aptamer selection. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 476, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.M.; Kong, K.W.; Brown, C.J.; Quah, S.T.; Yeo, H.L.; Hoon, S.; Seow, Y. Identification and Characterization of an eIF4e DNA Aptamer That Inhibits Proliferation With High Throughput Sequencing. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, R.M.; Shallcross, J.A.; Mael, L.E.; Mears, K.S.; Minkoff, L.; Scoville, D.J.; Whelan, R.J. Selection of DNA aptamers for ovarian cancer biomarker HE4 using CE-SELEX and high-throughput sequencing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Satheesan, S.; Li, H.; Weinberg, M.S.; Morris, K.V.; Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. Cell-specific RNA aptamer against human CCR5 specifically targets HIV-1 susceptible cells and inhibits HIV-1 infectivity. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoinka, J.; Berezhnoy, A.; Sauna, Z.E.; Gilboa, E.; Przytycka, T.M. AptaCluster—A Method to Cluster HT-SELEX Aptamer Pools and Lessons from its Application. In Research in Computational Molecular Biology, Proceedings of the Annual International Conference, RECOMB, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2–5 April 2014; Volume 8394, pp. 115–128.
- Hoinka, J.; Berezhnoy, A.; Dao, P.; Sauna, Z.E.; Gilboa, E.; Przytycka, T.M. Large scale analysis of the mutational landscape in HT-SELEX improves aptamer discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AptaTools. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/CBBresearch/Przytycka/index.cgi#aptatools (accessed on 06 Jun 2015).
- Ahmad Raston, N.H.; Gu, M.B. Highly amplified detection of visceral adipose tissue-derived serpin (vaspin) using a cognate aptamer duo. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Oh, S.S.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; Radeke, M.J.; Eisenstein, M.; Coffey, P.J.; Thomson, J.A.; Soh, H.T. Array-based discovery of aptamer pairs. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Y.H.; Chiang, H.Y.; Yang, D.K.; Peck, K.; Chen, L.C. Selection of aptamers targeting the sialic acid receptor of hemagglutinin by epitope-specific SELEX. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8719–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Soo Oh, S.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; Eisenstein, M.; Chambers, J.; Marth, J.D.; Walker, F.; Thomson, J.A.; Soh, H.T. Quantitative selection and parallel characterization of aptamers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18460–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Lv, B.; Feng, X.; Li, C. A new application of aptamer: One-step purification and immobilization of enzyme from cell lysates for biocatalysis. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 203, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Goggins, S.; Frost, C.G.; Estrela, P. A novel immobilization strategy for electrochemical detection of cancer biomarkers: DNA-directed immobilization of aptamer sensors for sensitive detection of prostate specific antigens. Analyst 2015, 140, 2628–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsager, O.A.; Kumar, S.; Zhu, B.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; McNatty, K.P.; Hodgkiss, J.M. Ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of 17beta-estradiol: The effect of shortening DNA aptamer sequences. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4201–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. A signal-on fluorescent aptasensor based on single-stranded DNA-sensitized luminescence of terbium (III) for label-free detection of breast cancer cells. Talanta 2015, 138, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viraka Nellore, B.P.; Kanchanapally, R.; Pramanik, A.; Sinha, S.S.; Chavva, S.R.; Hamme, A., 2nd; Ray, P.C. Aptamer-conjugated graphene oxide membranes for highly efficient capture and accurate identification of multiple types of circulating tumor cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.C.; Wu, W.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Hsieh, H.H.; Lee, C.H.; Chang, H.T. Aptamer-Conjugated Polymeric Nanoparticles for the Detection of Cancer Cells through “Turn-On” Retro-Self-Quenched Fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4925–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Z. Aptamer-functionalized barcode particles for the capture and detection of multiple types of circulating tumor cells. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7333–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, H.; Her, J.; Ban, C. Dual aptamer-functionalized silica nanoparticles for the highly sensitive detection of breast cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, N.; Zeng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Tung, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Zu, Y. Using an RNA aptamer probe for flow cytometry detection of CD30-expressing lymphoma cells. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, N.; Sheehan, A.M.; Tung, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Zu, Y. Using oligonucleotide aptamer probes for immunostaining of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, P.; Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, G.; Yang, C.J.; Liu, H.; Tan, W. Using DNA aptamer probe for immunostaining of cancer frozen tissues. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Qiang, W.; Xu, D. Multifunctional aptamer-silver conjugates as theragnostic agents for specific cancer cell therapy and fluorescence-enhanced cell imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, O.; Yan, X.; Niu, G.; Weiss, I.D.; Ma, Y.; Szajek, L.P.; Shen, B.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. PET Imaging of Tenascin-C with a Radiolabeled Single-Stranded DNA Aptamer. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Parekh, P.; Li, Z.; Shi, Z.Z.; Tung, C.H.; Zu, Y. Specific and sensitive tumor imaging using biostable oligonucleotide aptamer probes. Theranostics 2014, 4, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kang, H.J.; Jang, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Ali, B.A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Kim, S. Simultaneous imaging of two different cancer biomarkers using aptamer-conjugated quantum dots. Sensors 2015, 15, 8595–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melancon, M.P.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, C.; Allen, P.; Wen, X.; Huang, Q.; Wallace, M.; Myers, J.N.; Stafford, R.J.; et al. Selective uptake and imaging of aptamer- and antibody-conjugated hollow nanospheres targeted to epidermal growth factor receptors overexpressed in head and neck cancer. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4530–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Chen, T.; Ocsoy, I.; Yasun, E.; Wu, C.; Zhu, G.; You, M.; Han, D.; Jiang, J.; Yu, R.; et al. A cell-targeted, size-photocontrollable, nuclear-uptake nanodrug delivery system for drug-resistant cancer therapy. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.X.; Chuang, E.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Ho, Y.C.; Lin, K.J.; Cheng, P.Y.; Chen, K.J.; Wei, H.J.; Sung, H.W. An AS1411 aptamer-conjugated liposomal system containing a bubble-generating agent for tumor-specific chemotherapy that overcomes multidrug resistance. J. Controll. Release 2015, 208, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Guo, B.; Wu, H.; Shao, N.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Dang, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; et al. Aptamer-functionalized lipid nanoparticles targeting osteoblasts as a novel RNA interference-based bone anabolic strategy. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Bagaria, H.G.; Wong, M.S.; Zu, Y. A nanocomplex that is both tumor cell-selective and cancer gene-specific for anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Lin, C.; Guo, L.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G. Electrochemiluminescence biosensor for ultrasensitive determination of ochratoxin A in corn samples based on aptamer and hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Tian, T.; Jia, S.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, C.J. Target-responsive DNA hydrogel mediated “stop-flow” microfluidic paper-based analytic device for rapid, portable and visual detection of multiple targets. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Mao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zeng, L. A sensitive lateral flow biosensor for Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection based on aptamer mediated strand displacement amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.F.; Zhao, Y.J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.T.; Xie, Z.Y.; Zhao, X.W.; Gu, Z.Z. Colorimetric photonic hydrogel aptasensor for the screening of heavy metal ions. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5998–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Aptamers: Active targeting ligands for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Theranostics 2015, 5, 322–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.; Shigdar, S.; Qiao, G.; Zhou, S.F.; Li, Y.; Wei, M.Q.; Qiao, L.; Shamaileh, H.A.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, C.; et al. Aptamer-mediated cancer gene therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015, 15, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zu, Y. Aptamers and Their Applications in Nanomedicine. Small 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Cell-type-specific, Aptamer-functionalized Agents for Targeted Disease Therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Yang, S. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, F.; Mei, Z.; Yao, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Peng, C.; et al. Recent trends in SELEX technique and its application to food safety monitoring. Mikrochim. Acta 2014, 181, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Aptamer based electrochemical sensors for emerging environmental pollutants. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, D.; Cao, Z.; Meng, L.; Mallikaratchy, P.; Sefah, K.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Tan, W. Cell-specific aptamer probes for membrane protein elucidation in cancer cells. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Shangguan, D.; Wang, K.; Shi, H.; Sefah, K.; Mallikratchy, P.; Chen, H.W.; Li, Y.; Tan, W. Selection of aptamers for molecular recognition and characterization of cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4900–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallikaratchy, P.; Tang, Z.; Kwame, S.; Meng, L.; Shangguan, D.; Tan, W. Aptamer directly evolved from live cells recognizes membrane bound immunoglobin heavy mu chain in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Mol. Cell. Proteomics MCP 2007, 6, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Meyer, S.; Propson, N.E.; Nie, J.; Jiang, P.; Stewart, R.; Thomson, J.A. Characterization and target identification of a DNA aptamer that labels pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Tikoo, K. Ets1 identified as a novel molecular target of RNA aptamer selected against metastatic cells for targeted delivery of nano-formulation. Oncogene 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoglu, B.; Chaouch, A.; Lochmuller, H.; Politano, L.; Bertini, E.; Spitali, P.; Hiller, M.; Niks, E.H.; Gualandi, F.; Ponten, F.; et al. Affinity proteomics within rare diseases: A BIO-NMD study for blood biomarkers of muscular dystrophies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 918–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux-Dalvai, F.; Gonzalez de Peredo, A.; Simo, C.; Guerrier, L.; Bouyssie, D.; Zanella, A.; Citterio, A.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Boschetti, E.; Righetti, P.G.; et al. Extensive analysis of the cytoplasmic proteome of human erythrocytes using the peptide ligand library technology and advanced mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics MCP 2008, 7, 2254–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathout, Y.; Brody, E.; Clemens, P.R.; Cripe, L.; DeLisle, R.K.; Furlong, P.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Hache, L.; Henricson, E.; Hoffman, E.P.; et al. Large-scale serum protein biomarker discovery in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7153–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Target-cancer-cell-specific activatable fluorescence imaging probes: Rational design and in vivo applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Tung, C.H.; Zu, Y. A cancer cell-activatable aptamer-reporter system for one-step assay of circulating tumor cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, J.F.; Liu, X.; Eschbacher, J.; Nichols, J.; Mooney, M.A.; Joy, A.; Spetzler, R.F.; Feuerstein, B.G.; Preul, M.C.; Anderson, T.; et al. Use of a conformational switching aptamer for rapid and specific ex vivo identification of central nervous system lymphoma in a xenograft model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Phillips, J.A.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Tan, W. Regulation of singlet oxygen generation using single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10856–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusconi, C.P.; Scardino, E.; Layzer, J.; Pitoc, G.A.; Ortel, T.L.; Monroe, D.; Sullenger, B.A. RNA aptamers as reversible antagonists of coagulation factor IXa. Nature 2002, 419, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.G.; Purdy, D.A.; Rossi, J.S.; Grinfeld, L.R.; Myles, S.K.; Aberle, L.H.; Greenbaum, A.B.; Fry, E.; Chan, M.Y.; Tonkens, R.M.; et al. First clinical application of an actively reversible direct factor IXa inhibitor as an anticoagulation strategy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation 2010, 122, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, N.; Raghunathan, V.; Kanwar, J.R.; Kanwar, R.K.; Elchuri, S.V.; Khetan, V.; Krishnakumar, S. Target-specific delivery of doxorubicin to retinoblastoma using epithelial cell adhesion molecule aptamer. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.D. Novel MUC1 aptamer selectively delivers cytotoxic agent to cancer cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagalkot, V.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R.; Jon, S. An aptamer-doxorubicin physical conjugate as a novel targeted drug-delivery platform. Angew. Chem. 2006, 45, 8149–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, N.; Kanwar, J.R.; Akilandeswari, B.; Kanwar, R.K.; Khetan, V.; Krishnakumar, S. Chimeric nucleolin aptamer with survivin DNAzyme for cancer cell targeted delivery. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6940–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.O., 2nd; Andrechek, E.R.; Wang, Y.; Viles, K.D.; Rempel, R.E.; Gilboa, E.; Sullenger, B.A.; Giangrande, P.H. Cell type-specific delivery of siRNAs with aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, K.W.; Hernandez, L.I.; Dassie, J.P.; Thiel, W.H.; Liu, X.; Stockdale, K.R.; Rothman, A.M.; Hernandez, F.J.; McNamara, J.O., 2nd; Giangrande, P.H. Delivery of chemo-sensitizing siRNAs to HER2+-breast cancer cells using RNA aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6319–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shan, N.; Chen, Y. The anti-chemoresistant effect and mechanism of MUC1 aptamer-miR-29b chimera in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.L.; Cerchia, L.; Catuogno, S.; de Vita, G.; Dassie, J.P.; Santamaria, G.; Swiderski, P.; Condorelli, G.; Giangrande, P.H.; de Franciscis, V. Multifunctional aptamer-miRNA conjugates for targeted cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ribas, J.; Chowdhury, W.H.; Castanares, M.; Zhang, Z.; Laiho, M.; DeWeese, T.L.; Lupold, S.E. Prostate-targeted radiosensitization via aptamer-shRNA chimeras in human tumor xenografts. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucleic Acid Aptamers for Diagnostics and Therapeutics: Global Markets. Available online: http://www.marketresearch.com/BCC-Research-v374/Nucleic-Acid-Aptamers-Diagnostics-Therapeutics-8412378/ (accessed on 25 May 2015).
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Zu, Y. A Highlight of Recent Advances in Aptamer Technology and Its Application. Molecules 2015, 20, 11959-11980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711959
Sun H, Zu Y. A Highlight of Recent Advances in Aptamer Technology and Its Application. Molecules. 2015; 20(7):11959-11980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711959
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Hongguang, and Youli Zu. 2015. "A Highlight of Recent Advances in Aptamer Technology and Its Application" Molecules 20, no. 7: 11959-11980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711959
APA StyleSun, H., & Zu, Y. (2015). A Highlight of Recent Advances in Aptamer Technology and Its Application. Molecules, 20(7), 11959-11980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200711959





