Nanoemulsion Formulations of Fungicide Tebuconazole for Agricultural Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
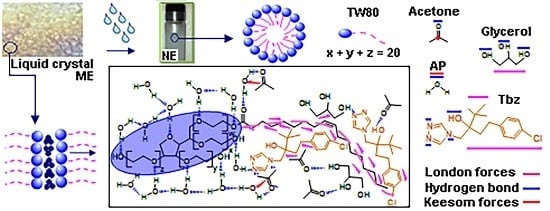
2.2. Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams
3.3. Nanoemulsion Preparation
3.4. Characterization of MEs and NEs
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD-FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook. Expect Slower Global Agricultural Production Growth. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/newsroom/oecd-fao-expect-slower-global-agricultural-production-growth.htm (accessed on 30 September 2013).
- Alonso, M.L.; Laza, J.M.; Alonso, R.M.; Jiménez, R.M.; Villas, J.L.; Fañanás, R. Pesticides microencapsulation. A safe and sustainable industrial process. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditta, A. How helpful is nanotechnology in agriculture? Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo-Medina, E. Nanotechnology and nanoencapsulation of pesticides. Ra Ximhai 2010, 6, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kah, M.; Hofmann, T. Nanopesticide research: Current trends and future priorities. Environ. Int. 2013, 63, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Gonzalez, C.; Maestro, A.; Solé, I.; Pey, C.M.; Nolla, J. Nano-emulsions: New applications and optimization of their preparation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface 2008, 13, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; Izquierdo, P.; Nolla, J.; Azemar, N.; Garcia-Celma, M.J. Nano-emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface 2005, 10, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez, G.; Parra, I.; Luzardo, M.; Bravo, B.; Delgado, N.; Márquez, N. Influencia de variables de formulación en la viscosidad de emulsiones de surfactante aniónico-aceite-agua. Quím. Nova 2014, 37, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, K. Microencapsulation of pesticides and their improved handling safety. J. Microencapsul. 2001, 18, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceschin, C.; Roques, J.; Malet-Martino, M.C.; Lattes, A. Fluorocarbon microemulsions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1985, 35, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates-A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.J.; Warisnoicharoen, W. Recent Advances in Microemulsions as Drug Delivery Vehicles. In Nanoparticulates as Drug Carriers; Torchilin, V.P., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2006; Chapter 7; pp. 125–160. ISBN 1-86094-630-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, T.G.; Wilking, J.N.; Meleson, K.; Chang, C.B.; Graves, S.M. Nanoemulsions: Formation, structure, and physical properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 635–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjali, C.H.; Sudheer-Khan, S.; Margulis-Goshen, K.; Magdassi, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Formulation of water-dispersible nanopermethrin for larvicidal applications. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, J.H.; Qian, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Wu, Q.H. Stability of triazophos in self-nanoemulsifying pesticide delivery system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 350, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.; Izquierdo, R.; Esquena, J.; Solans, C. Formation and stability of nano-emulsions. Adv. Colloids Interface Sci. 2004, 108, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.L.; Li, X.G.; Zhu, F.; Lei, C.L. Structural Characterization of Nanoparticles Loaded with Garlic Essential Oil and Their Insecticidal Activity against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10156–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessler-Blank, S.; Scheuermann, R.; Venzmer, J.; Lindsay, D. Nanoemulsions and Processes for Their Preparation, and Their Use as Formulations of Plant Protection Agents and/or Pesticides and/or Cosmetic Preparations. US 20100041629A1, 18 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Cano, L.; Togores, J. Tratado de Viticultura, 4th ed.; Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 2011; ISBN 9788484764243. [Google Scholar]
- Marrs, T.; Ballentyne, B. Pestice Toxicology and International Regulation, 1st ed.; Wiley: London, UK, 2004; ISBN 0-471-49644-8. [Google Scholar]
- Morell, I.; Hernández, F. El Agua en Castellón: un Reto Para el Siglo XXI, 1st ed.; Universitat Jaume I: Castellon, Spain, 2000; ISBN 8480213337. [Google Scholar]
- Seaman, D. Trends in the formulation of pesticides-an overview. Pestic. Sci. 1990, 29, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, G.Y.; Dong, J.F.; Eastoe, J. Oil-in-water nanoemulsions for pesticide formulations. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2007, 314, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, H.; Araque, P.; Ortiz, C. Nicotine Carboxylate Insecticide Emulsions: Effect of the Fatty Acid Chain Length. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9949–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglia, F.; Barbato, F.; De Rosa, G.; Granata, E.; Miro, A.; La Rotonda, M. Reduction of the Environmental Impact of Pesticides: Waxy Microspheres Encapsulating the Insecticide Carbaryl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4808–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solè, I.; Solans, C.; Maestro, A.; González, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Study of nano-emulsion formation by dilution of microemulsions. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2012, 376, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobarzo, E.; Cebey, M.; Fontenla, J.A.; Otero, F.; Torres, J.J.; González, H.; Grillo, R.; Fernández, L. Oxoisoadorphine Nanocapsules for Treating Depression. WO 2013050637 A1, 2 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mouri, A.; Diat, O.; El Ghzaoui, A.; Bauer, C.; Maurel, J.C.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Dorandeu, C.; Legrand, P. Phase behavior of reverse microemulsions based on Peceol®. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2014, 416, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forgiarini, A.; Marquez, L.; Salager, J.L. Nanoemulsiones—Formación con baja energía. In Nanopartículas: Fundamentos y Aplicaciones, 1st ed.; Universidad de Los Andes: Mérida, Venezuela, 2015; Chaper. 16; pp. 273–293. [Google Scholar]
- García, G.M.; Molinero, L.M. Formulación Magistral, 1st ed.; Paraninfo: Madrid, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Riera, B.J.; Salcedo, R.C.; López, A.P. Química y Bioquímica de los Alimentos; Universidad de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbig, J.; Ma, Q.; Davidson, P.M.; Weiss, J.; Zhong, Q. Physical and antimicrobial properties of cinnamon bark oil co-nanoemulsified by lauric arginate and Tween 80. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 233, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G. Handbook of Pesticides; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-8493-2447-5. [Google Scholar]
- TECTO® 60; SYNGENTA: México City, Mexico, 2016.
- TWEEN® 80; Sigma-Aldrich: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2016.
- Agnique BL 9754; BASF EMG30541205: Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany, 2016.
- Acetone, J.T.Baker®; VWR: Center Valley, PA, USA, 2016.
- Glycerol; Sigma-Aldrich: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2016.
- Chávez, G.; Parra, I.; Luzardo, M.; Bravo, B.; Márquez, N. Caracterización de cristales líquidos por microscopía óptica en sistemas surfactante polietoxilado-alcano-agua. Quím. Nova 2013, 36, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesamony, J.; Zachar, C.L.; Jung, R.; Williams, F.E.; Nauli, S. Preparation, characterization, sterility validation, and in vitro cell toxicity studies of microemulsions possessing potential parenteral applications. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds one (each NE) are available from the authors.










| OP//TW80//AP | OP//AG54//AP | RO/S a | OP (wt %) | S (wt %) | AP (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | A1 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 90.0 |
| T2 | A2 | 1.0 | 49.0 | 49.0 | 2.0 |
| T3 | A3 | 1.5 | 30.0 | 20.0 | 50.0 |
| T4 | A4 | 1.5 | 58.0 | 38.7 | 3.3 |
| T5 | A5 | 3.0 | 60.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 |
| T6 | A6 | 3.0 | 74.0 | 24.7 | 1.3 |
| T7 | A7 | 6.0 | 50.0 | 8.3 | 41.7 |
| T8 | A8 | 6.0 | 60.0 | 10.0 | 30.0 |
| T9 | A9 | 6.0 | 70.0 | 11.7 | 18.3 |
| T10 | A10 | 10.0 | 80.0 | 8.0 | 12.0 |
| T11 | A11 | 10.0 | 90.0 | 9.0 | 1.0 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Blancas, V.; Medina, D.I.; Padilla-Ortega, E.; Bortolini-Zavala, R.; Olvera-Romero, M.; Luna-Bárcenas, G. Nanoemulsion Formulations of Fungicide Tebuconazole for Agricultural Applications. Molecules 2016, 21, 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101271
Díaz-Blancas V, Medina DI, Padilla-Ortega E, Bortolini-Zavala R, Olvera-Romero M, Luna-Bárcenas G. Nanoemulsion Formulations of Fungicide Tebuconazole for Agricultural Applications. Molecules. 2016; 21(10):1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101271
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Blancas, Vianney, Dora I. Medina, Erika Padilla-Ortega, Raquel Bortolini-Zavala, Melissa Olvera-Romero, and Gabriel Luna-Bárcenas. 2016. "Nanoemulsion Formulations of Fungicide Tebuconazole for Agricultural Applications" Molecules 21, no. 10: 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101271
APA StyleDíaz-Blancas, V., Medina, D. I., Padilla-Ortega, E., Bortolini-Zavala, R., Olvera-Romero, M., & Luna-Bárcenas, G. (2016). Nanoemulsion Formulations of Fungicide Tebuconazole for Agricultural Applications. Molecules, 21(10), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101271