4-Hydroxyisoleucine from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Effects on Insulin Resistance Associated with Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
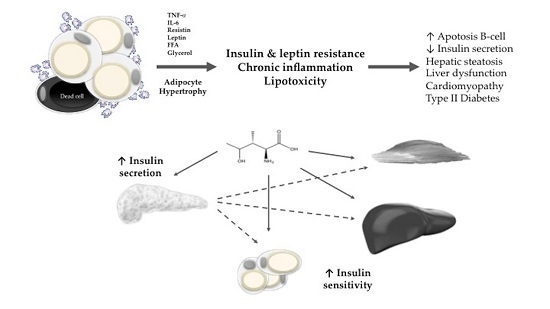
2. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Lipotoxicity
3. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.)
4. Pharmacological Effects of 4-Hydroxyisoleucine (4-OHIle)
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2009. Available online: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/publications/facts/obesity/en/ (accessed on 28 May 2016).
- Caballero, B. The global epidemic of obesity: An overview. Epidemiol. Rev. 2007, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, P.; Kawar, B.; El Nahas, M. Obesity and Diabetes in the Developing World—A Growing Challenge. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.P.; Lin, C.C.; Li, C.I.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, W.Y.; Hwang, K.L.; Yang, S.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Li, T.C. Cardiovascular Risk Factors Increase the Risks of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Taiwan Diabetes Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, A.F.; Rees, J.M.; Schiff, M.; Hujoel, P. Total body weight and waist circumference associated with chronic periodontitis among adolescents in the United States. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2006, 160, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, P. Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes—Role of the adipokines. Curr. Mol. Med. 2005, 5, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plutzky, J. Emerging concepts in metabolic abnormalities associated with coronary artery disease. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2000, 15, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, H.K.; Innes, K.E.; Vincent, K.R. Oxidative stress and potential interventions to reduce oxidative stress in overweight and obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 813–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastard, J.P.; Maachi, M.; Lagathu, C.; Kim, M.J.; Caron, M.; Vidal, H.; Capeau, J.; Feve, B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulou, M.; Savopoulos, C.; Michalakis, K.; Coppack, S.; Dardavessis, T.; Hatzitolios, A. Age, weight and obesity. Maturitas 2012, 71, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couillard, C.; Mauriège, P.; Imbeault, P.; Prud’homme, D.; Nadeau, A.; Tremblay, A.; Bouchard, C.; Després, J.-P. Hyperleptinemia is more closely associated with adipose cell hypertrophy than with adipose tissue hyperplasia. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, J.W.; Cześnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Brzozowski, T.; Sito, E.; Konturek, S.J. Neuro-hormonal control of food intake: Basic mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 56 (Suppl. 6), 5–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.E.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, J.E. Lipotoxicity: When tissues overeat. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, U.; Cao, Q.; Yilmaz, E.; Lee, A.H.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Ozdelen, E.; Tuncman, G.; Görgün, C.; Glimcher, L.H.; Hotamisligi, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 2004, 306, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Davis, K.E.; Scherer, P.E. Mechanisms of obesity and related pathologies: The macro- and microcirculation of adipose tissue. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5738–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wood, I.S. Adipokines: Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganami, T.; Tanimoto-Koyama, K.; Nishida, J.; Itoh, M.; Yuan, X.; Mizuarai, S.; Kotani, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Miyake, K.; Aoe, S.; et al. Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kappaB pathway in saturated fatty acid-induced inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyna, S.M.; Ghosh, S.; Tantiwong, P.; Meka, C.S.; Eagan, P.; Jenkinson, C.P.; Cersosimo, E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Coletta, D.K.; Sriwijitkamol, A.; et al. Elevated toll- like receptor 4 expression and signaling in muscle from insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jialal, I.; Huet, B.A.; Kaur, H.; Chien, A.; Devaraj, S. Increased toll-like receptor activity in patients with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain-Godefroy, O.; Le Bacquer, O.; Plancq, P.; Lecoeur, C.; Pattou, F.; Fruhbeck, G.; Froguel, P. Inflammatory role of Toll-like receptors in human and murine adipose tissue. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 823486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Favelyukis, S.; Nguyen, A.K.; Reichart, D.; Scott, P.A.; Jenn, A.; Liu-Bryan, R.; Glass, C.K.; Neels, J.G.; Olefsky, J.M. A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35279–35292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, R.H.; Orci, L. Lipotoxic diseases of nonadipose tissues in obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24 (Suppl. 4), S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, R.H.; Zhou, Y.T. Lipotoxicity of β-Cells in Obesity and in Other Causes of Fatty Acid Spillover. Diabetes 2001, 5 (Suppl. 1), S118–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navina, S.; Acharya, C.; DeLany, J.P.; Orlichenko, L.S.; Baty, C.J.; Shiva, S.S.; Durgampudi, C.; Karlsson, J.M.; Lee, K.; Bae, K.T.; et al. Lipotoxicity Causes Multisystem Organ Failure and Exacerbates Acute Pancreatitis in Obesity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 107ra110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: The missing links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1270–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K. Role of Obesity and Lipotoxicity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 711.e6–725.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.E.; Harris, K.P.G.; Walls, J.; Furness, P.N.; Brunskill, N.J. Fatty acids exacerbate tubule interstitial injury in protein-overload proteinuria. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2012, 283, F640–F647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.; Gargallo, M.; Millán, A.; Moreno, B. Drugs in the treatment of obesity: Sibutramine, orlistat and rimonabant. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Garza, A.L.; Milagro, F.I.; Bloke, N.; Campion Martinez, J.A. Natural inhibitors of pancreatic lipase as new players in obesity treatment. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 733–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeman, W.; Griffin, S.; Johnston, M.; Kinmonth, A.L.; Wareham, N.J. Interventions to prevent weight gain: A systematic review of psychological models and behaviour change methods. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, R.J.; Tschöp, M.H.; Wilding, J.P.H. Anti-obesity drugs: Past, present and future. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, D.; Bloom, S. The obesity pipeline: Current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargent, B.J.; Moore, N.A. New central targets for the treatment of obesity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birari, R.; Bhutani, K. Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources: Unexplored potential. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumantran, V. Experimental approaches for studying uptake and action of herbal medicines. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Sung, M.K. Effects of dietary mulberry, Korean red ginseng, and banaba on glucose homeostasis in relation to PPAR-a, PPAR-c, and LPL mRNA expressions. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 3344–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kudo, H.; Sassa, S.; Nomura, M.; Sakamoto, S. Effects of three Chinese herbal medicines on plasma and liver lipids in mice fed a high fat diet. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.A.; Hocht, C.; Puyo, A.; Taira, C.A. Recent advances in obesity pharmacotherapy. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, J.; Gupta, D.; Rao, A.R.; Yadava, P.K.; Baquer, N.Z. TSP foenum-graecum (fenugreek) seed powder improves glucose homeostasis in alloxan diabetic rat tissues by reversing the altered glycolytic, gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 224, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, K. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): A review of health beneficial physiological effects. Food Rev. Int. 2006, 22, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalki, L.; M’hamed, S.B.; Bennis, M.; Chait, A.; Sokar, Z. Evaluation of the developmental toxicity of the aqueous extract from Trigonella foenum-graecum (L.) in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 15, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Max, B. This and That: The essential pharmacology of herbs and spices. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 13, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, J.W. The Spice Handbook; Chemical Publishing Co.: Brooklyn, NY, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, P.; Sauvaire, Y.; Ponsin, G.; Manteghetti, M.; Fave, A.; Ribes, G. Effect of a fenugreek seed extract on feeding behaviour in the rat: Metabolic-endocrine correlates. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1993, 45, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardon, P.; Bessiere, J.M.; Baccou, J.C.; Sauvaire, Y. Volatile constituents of fenugreek seeds. Planta Med. 1985, 6, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.D. Effect of fenugreek seeds and leaves on blood glucose and serum insulin responses in human subjects. Nutr. Res. 1986, 6, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvaire, Y.; Baccou, J.S. Nutritional value of the proteins of leguminous seed, fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Nutr. Rep. Int. 1976, 14, 527–535. [Google Scholar]
- Baccou, J.C.; Sauvaire, Y.; Ollie, V.; Petit, L.J. L’huile de fenugreec, composition, properties, possibilities d’utilisation dans l’industrie des peintures et vernis. Rev. Fr. Corps Gras 1978, 25, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mahdy, A.R.; El-Sebaiy, L.A. Proteolytica activity, amino acid composition, protein quality of fermented fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum-graecum). Food Chem. 1985, 18, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayasekhara Rao, P.; Sharma, R.D. An evaluation of protein quality of fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum-graecum) and their supplementary effects. Food Chem. 1987, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Anis, M.; Aminuddin, E. Estimation of diosgenin in seeds of induced autoploid Trigonella foenum-graecum. Fitoterapia 1985, 56, 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Brenac, P.; Sauvaire, Y. Accumulation of sterols and steroidal sapogenins in developing fenugreek pods: Possible biosynthesis in situ. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Srivastava, R.S.; Chatterjee, D.C.; Dutta, S.K. Extractives of Trigonella-1. Fenugreekine, a new steroidal sapogenin-peptide ester of Trigonella foenum-graecum. Phytochemistry 1974, 13, 2247–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvaire, Y.; Baissac, Y.; Leconte, O.; Petit, P.; Ribes, G. Steroid saponins from fenugreek and some of their biological properties. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 405, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.D. Hypocholesterolaemic activity of fenugreek (T. foenum-graecum): An experimental study in rats. Nutr. Rep. Int. 1984, 30, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, P.R.; Sauvaire, Y.D.; Hillaire-Buys, D.M.; Leconte, O.M.; Baissac, Y.G.; Ponsin, G.R.; Ribes, G.R. Steroid saponins from fenugreek seed: Extraction, purification and pharmacological investigation on feeding behaviour and plasma cholesterol. Steroids 1995, 60, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishkinsky, J.; Joseph, B.; Sulman, F. Hypoglycaemic effect of trigonelline. Lancet 1967, 290, 1311–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankara Rao, D.S.; Deosthale, Y.G. Mineral composition of four Indian food legumes. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 1962–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Hemavathy, J.; Prabhakar, J.V. Lipid composition of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) seeds. Food Chem. 1989, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, I.P.; Sharma, S.C. Saponins XXXII Trigonella foenum-graecum seeds. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 1996, 43, 564–567. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan, C.; Rama Shatsri, B.V.; Balasubramanyan, S.C. Nutritive Value of Indian Foods; National Institute of Nutrition: Hyderabad, India, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvaire, Y.; Girardon, P.; Baccou, J.C.; Risterucci, A.M. Changes in growth, proteins and free amino acids of developing seed and pod of fenugreek. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.N.; Chopra, I.C.; Honda, K.L.; Kapur, L.D. Chopra’s Indigenous Drugs of India; Academic Publishers: Calcutta, India, 1982; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- Fazli, F.R.Y.; Hardman, R. The spice, fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Its commercial varieties of seed as a source of diosgenin. Trop. Sci. 1968, 10, 66–78. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, R.; Abdul-Ghani, A.S.; Suleiman, M.S. Intestinal absorption. In: Proceedings of the 47th Annual Meeting of the American Diabetes Association (Indianapolis U.S.A.). Diabetes 1987, 36, 211. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Meshal, I.A.; Parmar, N.S.; Tariq, M.; Aqeel, A.M. Gastric anti-ulcer activity in rats of Trigonella foenum-graecum (Hu-Lu-Pa). Fitoterapia 1985, 56, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, P.C.; Gupta, R.K.; Joshi, L.D. Hypocholesterolaemic effect of Trigonella foenum-graecum (Methi). Curr. Sci. 1982, 51, 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.D.; Sarkar, A.; Hazar, D.K.; Misra, B.; Singh, J.B.; Maheshwari, B.B. Toxicological evaluation of fenugreek seeds: A long term feeding experiment in diabetic patients. Phytother. Res. 1996, 10, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, J.K.; Yadav, S.; Vats, V. Medicinal plants of India with anti-diabetic potential. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 81, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Stevens, M.; Wiley, J.W. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Evidence for apoptosis and associated mitochondrial dysfunction. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broca, C.; Gross, R.; Petit, P.; Sauvaire, Y.; Manteghetti, M.; Tournier, M.; Masiello, P.; Gomis, R.; Ribes, G. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine: Experimental evidence of its insulinotropic and antidiabetic properties. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, E617–E623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broca, C.; Manteghetti, M.; Gross, R.; Baissac, Y.; Jacob, M.; Petit, P.; Sauvaire, Y.; Ribes, G. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine: Effects of synthetic and natural analogues on insulin secretion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 390, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, U.C.S.; Moorthy, K.; Baquer, N.Z. Effects of sodium orthovanadate and Trigonella foenum-graecum seeds on hepatic and renal lipogenic enzymes and lipid profile during alloxan diabetes. J. Biosci. 2004, 29, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, U.C.S.; Moorthy, K.; Baquer, N.Z. Combined Treatment of Sodium orthovanadate and Momordica charantia fruit extract prevents alterations in lipid profile and lipogenic enzymes in alloxan diabetic rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 268, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flammang, A.; Cifone, M.; Erexson, G.; Stankowski, L. Genotoxicity testing of a fenugreek extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 11, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, S.; Stephens, J.M. Diosgenin, 4-Hydroxyisoleucine, and Fiber from Fenugreek: Mechanism of Actions and potential Effects on Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Fang, K.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.; Hu, M.; Lu, F. Effect of fenugreek on hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetes and prediabetes: A meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajimehdipoor, H.; Sadat-Ebrahimi, S.E.; Izaddoost, M.; Amin, G.R.; Givi, E. Identification and quantitative determination of blood lowering sugar amino acid in Fenugreek. Planta Med. 2008, 74, PH12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narender, T.; Puri, A.; Khaliq, T.; Saxena, R.; Bhatia, G.; Chandra, R. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine an unusual amino acid as antidyslipidemic and antihyperglycemic agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrafarin, A.; Qaderi, A.; Rezazadeh, S.H.; Naghdi-Badi, H.; Noormohammadi, G.H.; Zand, E. Bioengineering of important secondary metabolites and metabolic pathways in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). J. Med. Plant. 2010, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvaire, Y.; Petit, P.; Broca, C.; Manteghetti, M.; Baissac, Y.; Fernandez-Alvarez, J.; Gross, R.; Roye, M.; Leconte, A.; Gomis, R.; et al. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine: A novel amino acid potentiator of insulin secretion. Diabetes 1998, 47, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowden, L.; Pratt, H.M.S.; Mith, A. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from seed of Trigonella foenum-graecum. Phytochemistry 1973, 12, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaltsa, H. Chemical constituents. In Fenugreek—The genus Trigonella; Petropoulos, G.A., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2002; pp. 132–163. [Google Scholar]
- Broca, C.; Breil, V.; Cruciani-Guglielmacci, C.; Manteghetti, M.; Rouault, C.; Derouet, M.; Rizkalla, S.; Pau, B.; Petit, P.; Ribes, G.; et al. Insulinotropic agent ID-1101 (4-hydroxyisoleucine) activates insulin signaling in rat. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E463–E471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S.N.; Thomas, J.E.; Basu, S.K. Fenugreek, an alternative crop for semi-arid regions of North America. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquer, N.Z.; Taha, A.; Kumar, P.; McLean, P.; Cowsik, S.M.; Kale, R.K.; Singh, R.; Sharma, D. A metabolic and functional overview of brain aging linked to neurological disorders. Biogerontology 2009, 10, 377–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, S.; Taha, A.; Akhtar, K.; Bamezai, R.N.; Baquer, N.Z. In vivo effect of Trigonella foenum-graecum on the expression of Pyruvate kinase, Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and distribution of glucose transporter (GLUT4) in alloxan diabetic rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2006, 84, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Rangari, V. Enhancement of anti-diabetic activity of 4-hydroxyisoleucine in combination with natural bioavailability enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Haeri, M.R.; Izaddoost, M.; Ardekani, M.R.S.; Nobar, M.R.; White, K.N. The effect of fenugreek 4-hydroxyisoleucine on liver function biomarkers and glucose in diabetic and fructose-fed rats. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.B.; Tamarkar, A.K.; Narender, T.; Srivastava, A.K. Antihyperglycaemic effect of an unusual amino acid (4-hydroxyisoleucine) in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeri, M.R.; Limaki, H.K.; White, C.J.; White, K.N. Non-insulin dependent anti-diabetic activity of (2S,3R,4S)4-hydroxyisoleucine of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) in streptozotocin-induced type I diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, N.; Maurya, C.K.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Sukanya, P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Narender, T.; Tamrakar, A.K. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine stimulates glucose uptake by increasing surface GLUT4 level in skeletal muscle cells via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent pathway. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, C.K.; Singh, R.; Jaiswal, N.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Narender, T.; Tamrakar, A.K. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine ameliorates fatty acid-induced insulin resistance and inflammatory response in skeletal muscle cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 395, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Lu, F.R.; Xie, J.; Zheng, N.; Qin, Y.; Gao, F.; Du, W.; Jian, L.M. Effect of trigonella foenum-graecum 4-hydroxyisoleucine on high-glucose induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes of mice. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2013, 33, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.I.; Du, W.; Cai, Q.; Shafqat, R.A.; Lu, F. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine improves insulin resistance in HepG2 cells by decreasing TNF-α and regulating the expression of insulin signal transduction proteins. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6555–6560. [Google Scholar]
- Olaiya, O.C.; Soetan, O.K. A review of the health benefits of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.): Nutritional, Biochemical and pharmaceutical perspectives. Am. J. Soc. Issues Humanit. 2014, SPECIAL ISSUE: MARCH/APRIL 2014. 3–12. Available online: http://www.ajsih.org/index.php/ajsih/article/view/120 (accessed on 28 May 2016). [Google Scholar]



| Model | Experimental results | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro studies | Isolated human and rat pancreas | Increase of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion | [89] |
| Normal and type II diabetic rats, isolated rat islets | Increased oral glucose tolerance, increased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion | [82] | |
| Isolated rat islets | Increased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion | [83] | |
| Skeletal muscle (L6 myocytes) | Increased glucose uptake, increased Akt phosphorylation on Ser 473 (pAkt), increased PI3K, increased glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) | [103] | |
| Insulin-resistant skeletal muscle (L6 myocytes) | Increased insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation (pIRS-1), increased PI3K, increased pAkt, decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS), decreased NF-kB, decreased c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1/2 (JNK), decreased p38 MAPK | [104] | |
| Insulin-resistant 3T3-L1 adipocytes | Decreased TNF-α, increased glucose uptake | [105] | |
| Insulin-resistant HepG2 cells | Reduced TNF-α, stimulated expression of IRS-1 and GLUT4, inhibited expression of p-IRS-1 (Ser307) | [106] | |
| In vivo studies | Zucker fa/fa rats, high fat + sucrose fed rats | Increased glucose tolerance, increased insulin sensitivity, reduced hepatic glucose production, increased phosphatidylinositide-3 kinase (PI3K), reduced fasting insulin | [93] |
| Hamsters | Decreased serum triglycerides, decreased serum total cholesterol, decreased free fatty acids, increased HDL:TC ratio | [95] | |
| Type II diabetic rats | Decreased blood glucose, increased serum HDL, decreased alanine aminotransferase, decreased aspartate aminotransferase | [100] | |
| C57BL/db/db mice | Decreased blood glucose, decreased serum triglycerides, total cholesterol and LDL, increased serum HDL | [101] | |
| Type I diabetic rats | Decreased blood glucose, decreased serum total cholesterol, decreased serum LDL, decreased serum triglycerides, increased serum HDL | [102] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avalos-Soriano, A.; De la Cruz-Cordero, R.; Rosado, J.L.; Garcia-Gasca, T. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Effects on Insulin Resistance Associated with Obesity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111596
Avalos-Soriano A, De la Cruz-Cordero R, Rosado JL, Garcia-Gasca T. 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Effects on Insulin Resistance Associated with Obesity. Molecules. 2016; 21(11):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111596
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvalos-Soriano, Anaguiven, Ricardo De la Cruz-Cordero, Jorge L. Rosado, and Teresa Garcia-Gasca. 2016. "4-Hydroxyisoleucine from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Effects on Insulin Resistance Associated with Obesity" Molecules 21, no. 11: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111596
APA StyleAvalos-Soriano, A., De la Cruz-Cordero, R., Rosado, J. L., & Garcia-Gasca, T. (2016). 4-Hydroxyisoleucine from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum): Effects on Insulin Resistance Associated with Obesity. Molecules, 21(11), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111596