Cytotoxicity of Different Excipients on RPMI 2650 Human Nasal Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
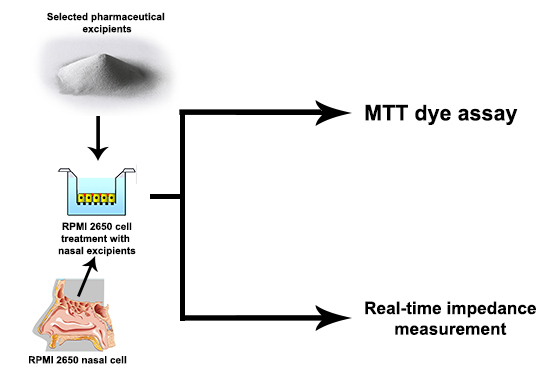
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. MTT Dye Assay
3.2.2. Real-Time Impedance Measurement
3.2.3. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costantino, H.R.; Illum, L.; Brandt, G.; Johnson, P.H.; Quay, S.C. Intranasal delivery: Physicochemical and therapeutic aspects. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkus, F.W.H.M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Marttin, E.; Romeijn, S.G.; van der Kuy, P.H.M.; Hermens, W.A.J.J.; Schipper, N.G.M. Cyclodextrins in nasal drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 1999, 36, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, M.I.; Agu, R.U.; Verbeke, N.; Kinget, R. Nasal mucoadhesive drug delivery: Background, applications, trends and future perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1640–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deli, M.A. Potential use of tight junction modulators to reversibly open membranous barriers and improve drug delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 892–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvát, S.; Fehér, A.; Wolburg, H.; Sipos, P.; Veszelka, S.; Tóth, A.; Kis, L.; Kurunczi, A.; Balogh, G.; Kürti, L.; et al. Sodium hyaluronate as a mucoadhesive component in nasal formulation enhances delivery of molecules to brain tissue. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrus, R.; Pomázi, A.; Réti-Nagy, K.; Fenyvesi, F.; Vecsernyés, M.; Szabó-Révész, P. Cytotoxicity testing of carrier-based microcomposites for DPI application. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kürti, L.; Veszelka, S.; Bocsik, A.; Dung, N.T.K.; Ózsvári, B.; Puskás, L.G.; Kittel, Á.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Deli, M.A. The effect of sucrose esters on a culture model of the nasal barrier. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kürti, L.; Veszelka, S.; Bocsik, A.; Ózsvári, B.; Puskás, L.G.; Kittel, Á.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Deli, M.A. Retinoic acid and hydrocortisone strengthen the barrier function of RPMI 2650 cells, a model for human nasal epithelial permeability. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMerlis, C.C.; Schoneker, D.R. Review of the oral toxicity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Fenyvesi, F.; Pásztor, N.; Fehér, P.; Váradi, J.; Kocsán, R.; Szente, L.; Fenyvesi, E.; Szabó, G.; Vecsernyés, M.; et al. Cytotoxicity of different types of methylated beta-cyclodextrins and ionic derivatives. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leitnera, V.M.; Guggia, D.; Kraulanda, A.H.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Nasal delivery of human growth hormone: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a thiomer/glutathione microparticulate delivery system. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Iwakura, Y.; Morisaka, K.; Ohashi, Y.; Nakai, Y. Effects of viscous hyaluronate-sodium solutions on the nasal absorption of vasopressin and an analogue. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, F.; Ohta, R.; Machida, Y.; Nagai, T. In vitro and in vivo nasal mucoadhesion of some water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 134, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkus, F.W.; Verhoef, J.C.; Romeijn, S.G.; Schipper, N.G.M. Absorption enhancing effect of cyclodextrins on intranasally administered insulin in rats. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, N.G.M.; Romeijn, S.G.; Verhoef, J.C.; Merkus, F.W. Nasal insulin delivery with dimethyl-beta-cyclodextrin as an absorption enhancer in rabbits: Powder more effective than liquid formulations. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, R.; Zia, H.; Needham, T. The influence of tonicity and viscosity on the intranasal absorption of salmon calcitonin in rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 147, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.


| Excipient | Role in Nasal Form | Concentration | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-d-mannitol | osmotic additive | 12% w/v | [11] |
| sodium hyaluronate | absorption enhancer | 0.1%–1.5% w/v | [12] |
| polyvinyl alcohol | viscosity-increasing material | 4% w/v | [13] |
| α-cyclodextrins | absorption enhancer | 5% w/v | [14] |
| β-cyclodextrins | absorption enhancer | 5%–30% w/v | [15] |
| methylcellulose | viscosity enhancing agent | 0.1%–1% w/v | [16] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horváth, T.; Bartos, C.; Bocsik, A.; Kiss, L.; Veszelka, S.; Deli, M.A.; Újhelyi, G.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Ambrus, R. Cytotoxicity of Different Excipients on RPMI 2650 Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050658
Horváth T, Bartos C, Bocsik A, Kiss L, Veszelka S, Deli MA, Újhelyi G, Szabó-Révész P, Ambrus R. Cytotoxicity of Different Excipients on RPMI 2650 Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Molecules. 2016; 21(5):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050658
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorváth, Tamás, Csilla Bartos, Alexandra Bocsik, Lóránd Kiss, Szilvia Veszelka, Mária A. Deli, Gabriella Újhelyi, Piroska Szabó-Révész, and Rita Ambrus. 2016. "Cytotoxicity of Different Excipients on RPMI 2650 Human Nasal Epithelial Cells" Molecules 21, no. 5: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050658
APA StyleHorváth, T., Bartos, C., Bocsik, A., Kiss, L., Veszelka, S., Deli, M. A., Újhelyi, G., Szabó-Révész, P., & Ambrus, R. (2016). Cytotoxicity of Different Excipients on RPMI 2650 Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. Molecules, 21(5), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050658