Purification and Characterization of Antioxidant Peptides of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
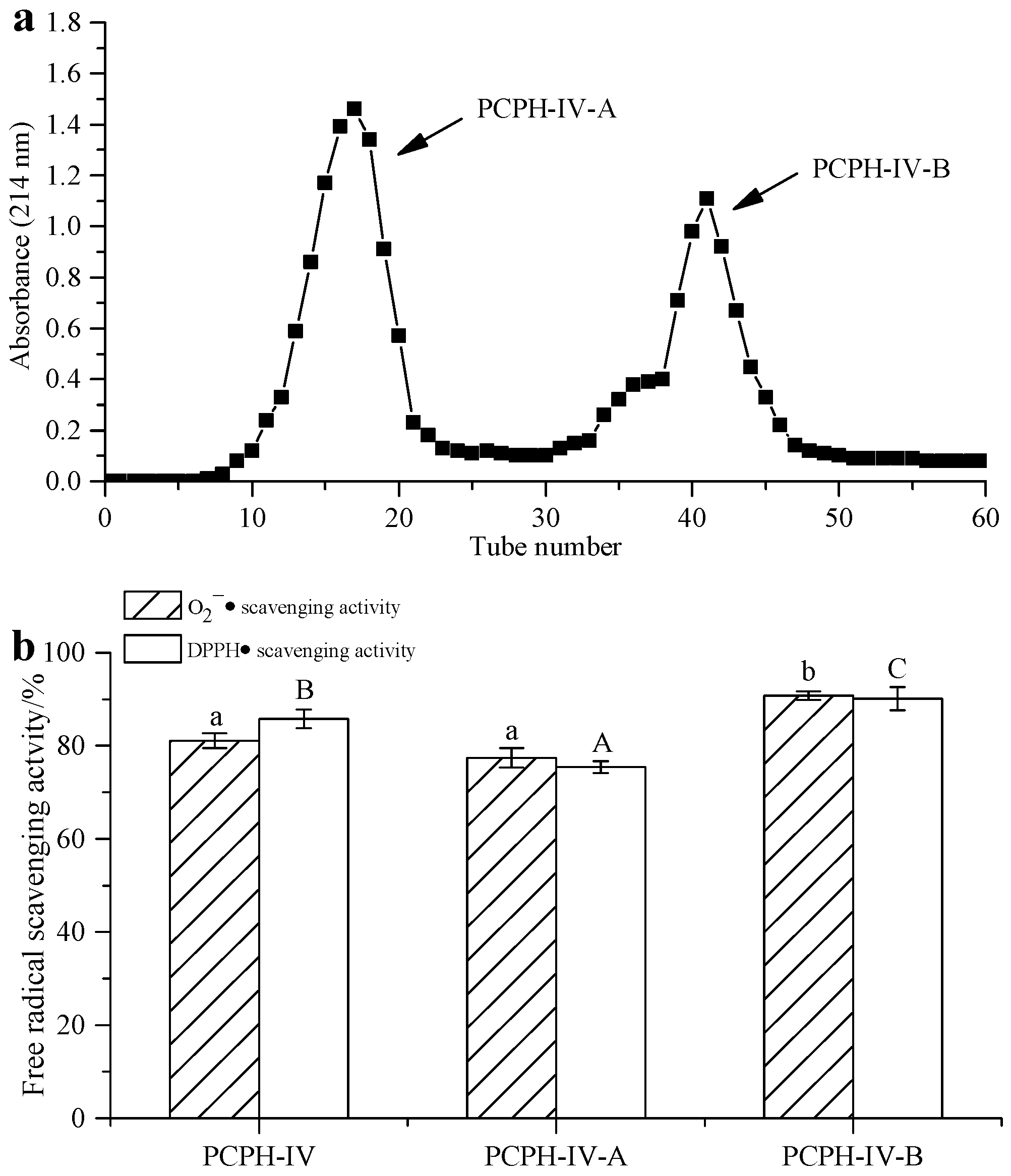
2.1. Free Radical Scavenging Ability of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates (PCPH) after Ultrafiltration
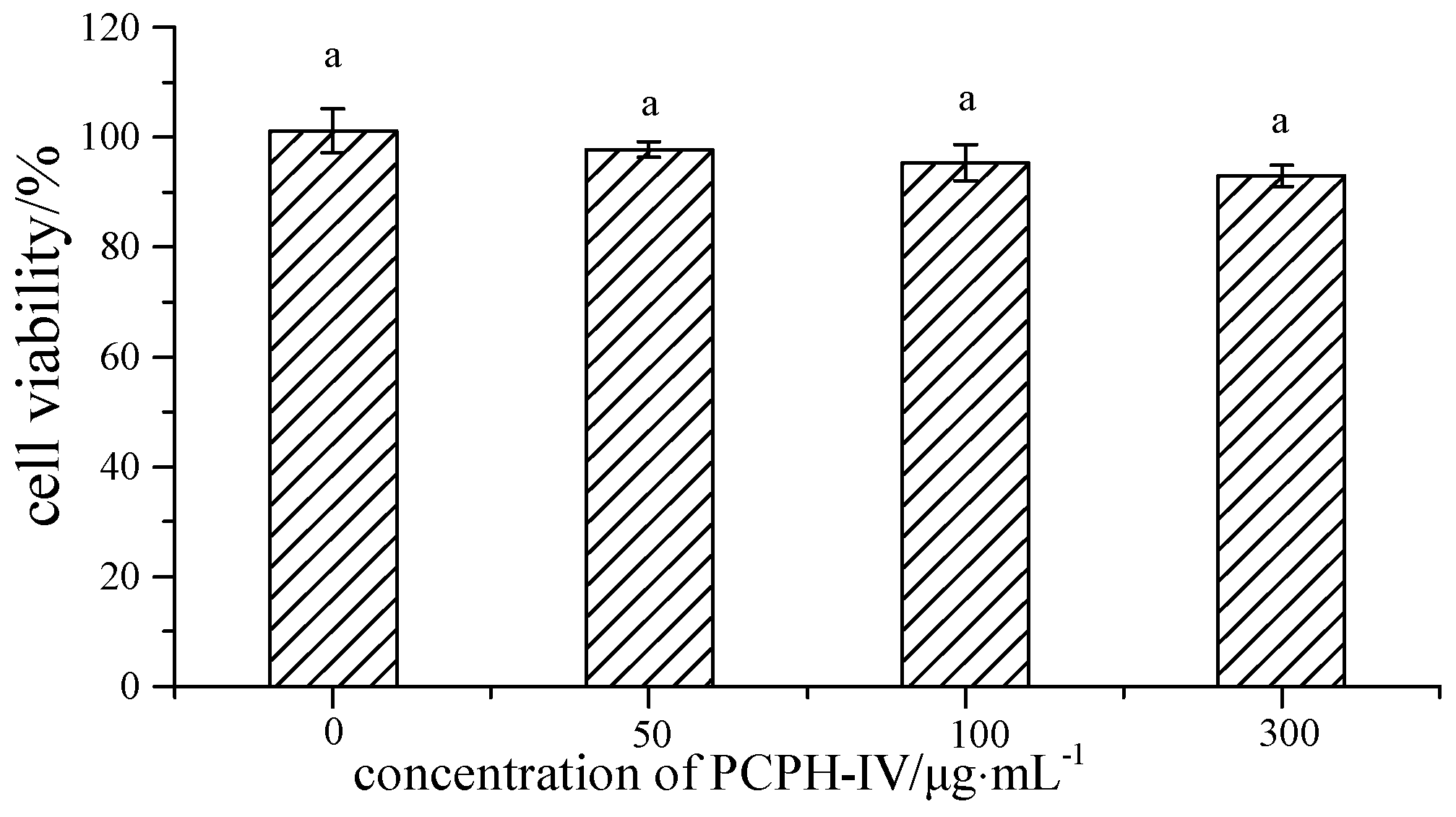
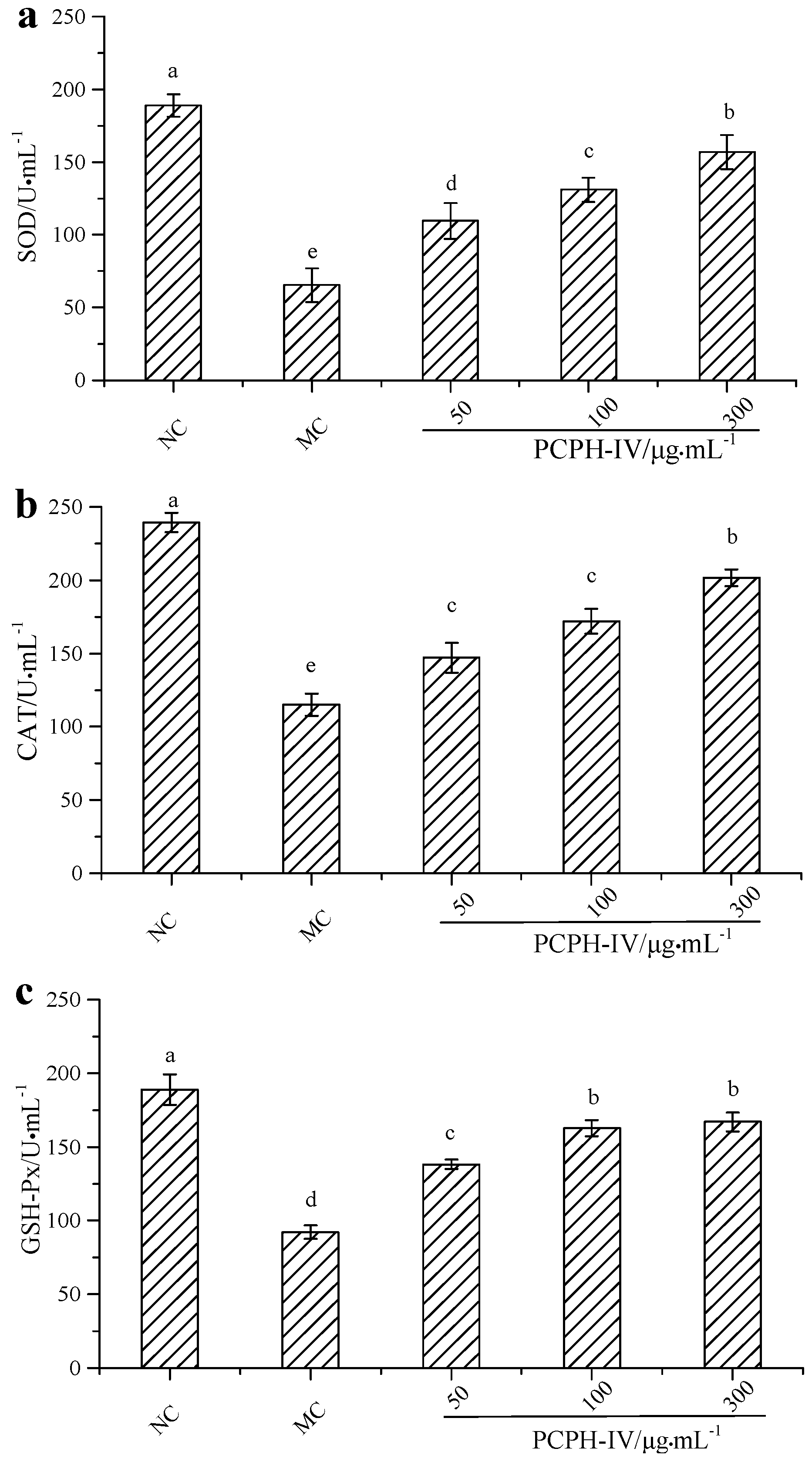
2.2. Effect of PCPH-IV on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in HepG2 Cells
2.3. Peptide Separation by Ion Exchange Chromatography and Sephadex G-15 Gel Chromatography
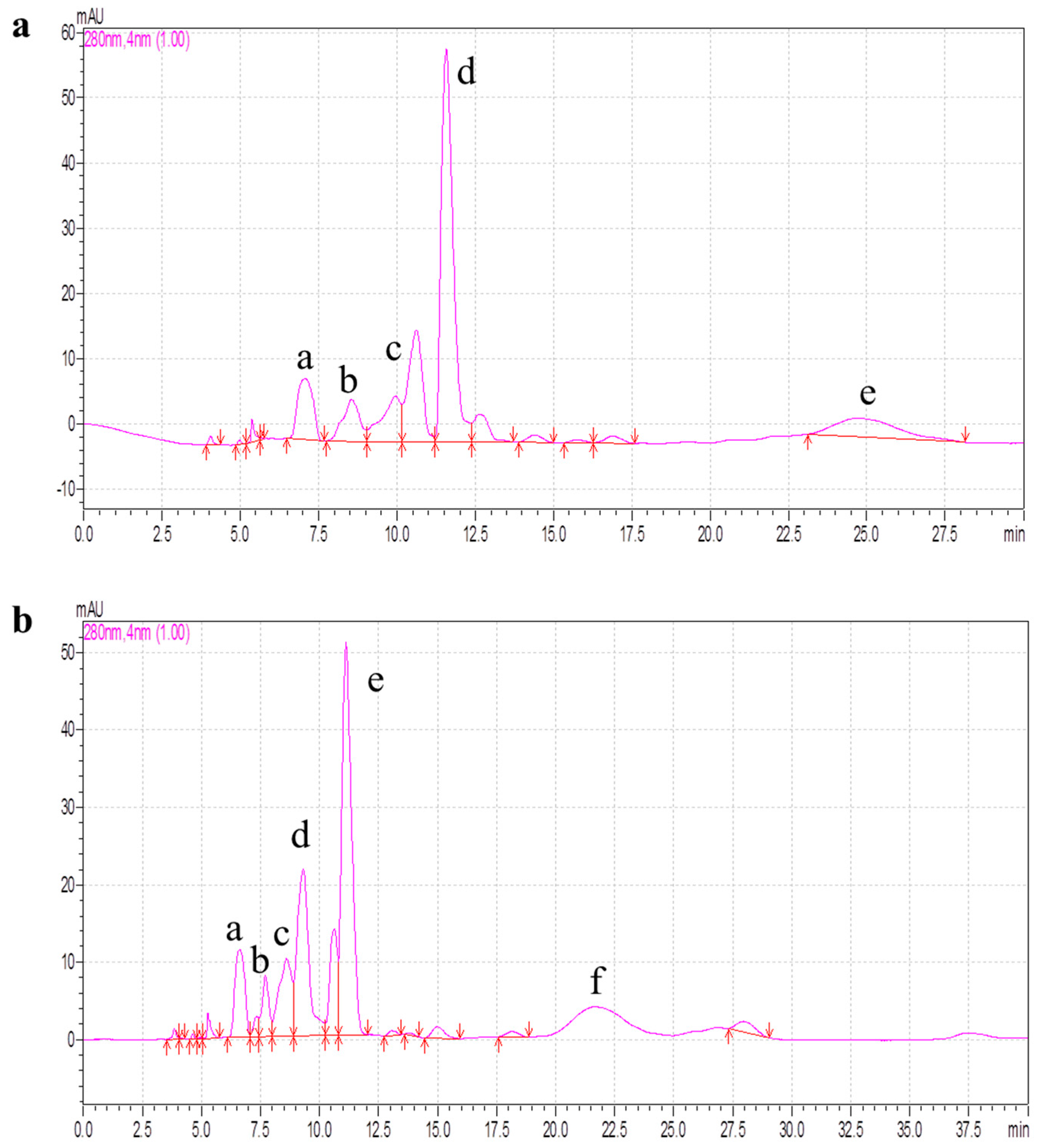
2.4. Purification of Antioxidant Peptides by RP-HPLC
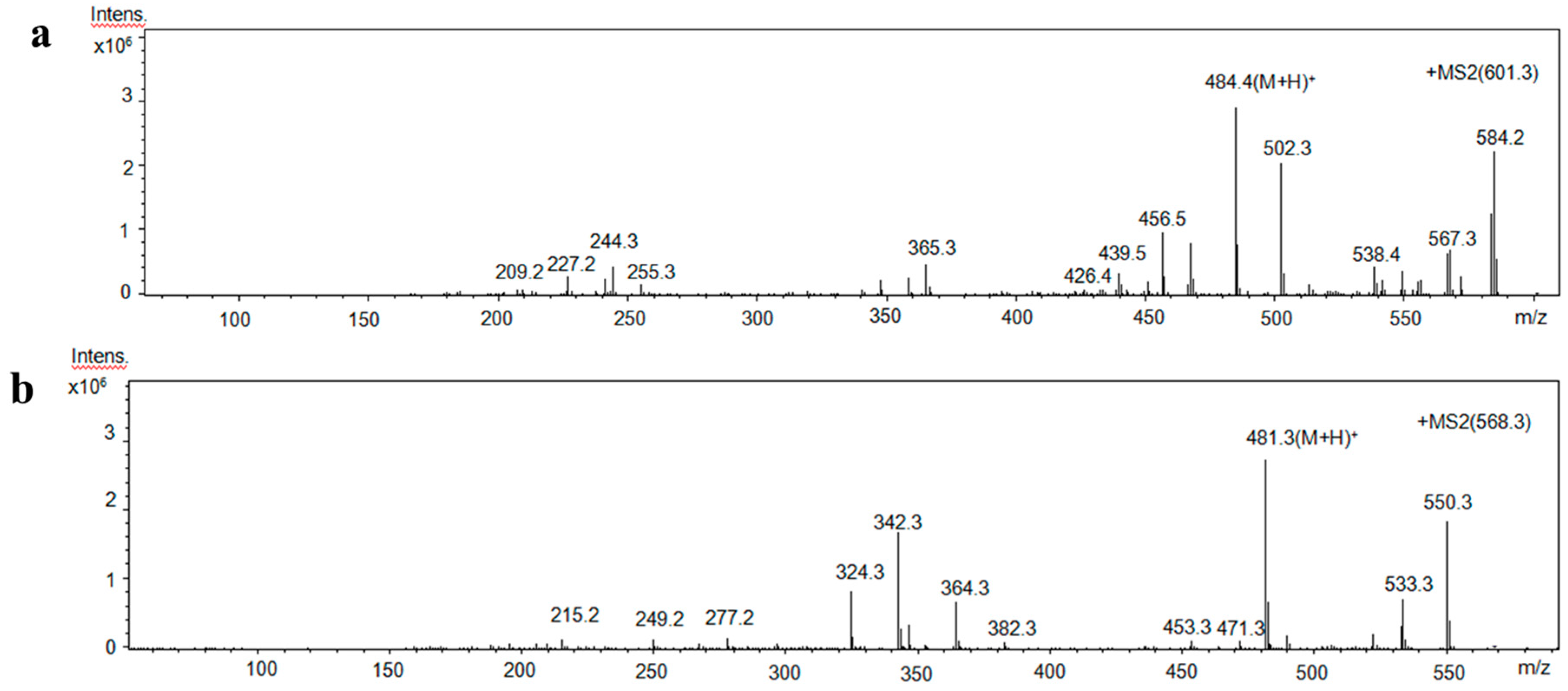
2.5. Identification of Amino Acid Sequence of Antioxidant Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation and Fractionation of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates (PCPH)
3.3. Free Radical Scavenging Activity
3.4. Assessment of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in HepG2 Cells
3.4.1. Cell Culture
3.4.2. Cell Viability
3.4.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Assays in H2O2 Challenged HepG2 Cells
3.5. Purification of Antioxidant Peptides from PCPH
3.5.1. Ion Exchange Chromatography
3.5.2. Gel Filtration Chromatography (GFC)
3.5.3. RP-HPLC
3.6. Amino Acid Sequencing of Purified Peptides
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S.; Luximon-Ramma, A.; Aruoma, O.L.; Bahourun, T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: Mechanism and actions. Mutat. Res. 2005, 579, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.B.; Kim, J.B.; Je, J.Y. Purification and antioxidant properties of ocapeptide from salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, H.; Joshi, R.; Gupta, M. Isolation, purification and characterization of antioxidative peptide of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Zhao, M.M.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Jiang, Y.M. Antioxidant properties of papain hydrolysates of wheat gluten in different oxidation systems. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from hoki (Johnius belengerii) frame protein by gastrointestinal digestion. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Je, J.Y.; Qian, Z.J.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Purification and antioxidant properties of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) dark muscle peptide on free radical-mediated oxidative systems. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; He, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Sun, L. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) frame protein. Molecules 2012, 17, 12836–12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.J.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolyzate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) muscle. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Yu, W.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Kou, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and antioxidative properties of a Rapeseed (Brassica napus) protein hydrolysate and three peptide fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5287–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoh, Y.Y.; Gan, C.Y. Enzyme-assisted extraction and identification of antioxidative and α-amylase inhibitory peptides from Pinto beans (Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Pinto). Food Chem. 2016, 190, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yan, J.; Lin, S.; Jones, G.S.; Feng, C. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from egg white protein and their antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimalaratne, C.; Bandara, N.; Wu, J. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed chicken egg white. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohata, M.; Uchida, S.; Zhou, L.; Arihara, K. Antioxidant activity of fermented meat sauce and isolation of an associated antioxidant peptide. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Han, K.H. Current development situation and countermeasure of large yellow crocker industry in China. J. Fujian Fish. 2011, 33, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, X. Coating effects of tea polyphenol and rosemary extract combined with chitosan on the storage quality of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Control 2012, 25, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. Stability of antioxidant peptides prepared from the large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Curr. Top. Nutraceuticals Res. 2016, 14, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Je, J.Y.; Qian, Z.J.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of an antioxidant peptide obtained from tuna backbone protein by enzymatic hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moure, A. Antioxidant properties of ultrafiltration-recovered soy protein fractions from industrial effluents and their hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Gao, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) albumin hydrolysates. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chi, Y.J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Lv, L. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from egg white protein hydrolysate. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Hong, S.; Jhoo, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Chin, N.L. Effect of acetone extract from stem bark of Acacia species (A. dealbata, A. ferruginea and A. leucophloea) on antioxidant enzymes status in hydrogen peroxide-induced HepG2 cells. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Nie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Mao, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Xiao, J.; Wan, C. Reactive oxygen species mediate nitric oxide production through ERK/JNK MAPK signaling in HAPI microglia after PFOS exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2015, 288, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Qi, J.P.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; He, L.C. Ferulic acid inhibits H2O2-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells via inhibition of the NADPH oxidase and NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, M.J.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.S. Antioxidant and hepatoprotetive effects of the red ginseng essential oil in H2O2-treated HepG2 cells and CCl4-treated mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Free radicals and antioxidants: A personal view. Nutr. Rev. 1994, 52, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valéry, A.; Romuald, C.; Dragoslav, M.; Pascal, C.; Abderrahim, L. Reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutases: Role in joint diseases. Joint Bone Spine 2007, 74, 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Oberley, L.W.; Oberley, T.D.; Yan, T.; Domann, F.E.; St Clair, D.K. Inhibition of cell growth and sensitization to oxidative damage by overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase in rat glioma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1996, 7, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.C.; Franklin, G.; Dias, A.C.P.; Lima, C.F. Methanolic extract of Hypericum perforatum cells elicited with Agrobacterium tumefaciens provides protection against oxidative stress induced in human HepG2 cells. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 59, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéguineur, B.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S.; Martín, M.A.; Mateos, R.; Bravo, L. Phloroglucinol: Antioxidant properties and effects on cellular oxidative markers in human HepG2 cell line. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 28866–28893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.J.; Zhao, M.M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ren, J. Purification and identification of antioxidative peptides from loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) protein hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.E.; Pattison, D.I.; Davies, M.J. Quantification of hydroxyl radical-derived oxidation products in peptides containing glycine, alanine, valine and proline. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 328–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Prior, R.L. The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiga, A.; Tanabe, S.; Nishmura, T. Antioxidant activity of peptides obtained from porcine myofibrillar proteins by protease treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3661–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.Z.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Kang, Z.L.; Yin, Y. Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides from Jinhua Ham. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alashi, A.M.; Blanchard, C.L.; Mailer, R.J.; Agboola, S.O.; Mawson, A.J.; He, R.; Girgih, A.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant properties of Australian canola meal protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siow, H.L.; Gan, C.Y. Extraction of antioxidative and antihypertensive bioactive peptides from Parkia speciosa seeds. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3435–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Chahal, B.; Majumder, K.; You, S.J.; Wu, J. Identification of novel antioxidative peptides derived from a thermolytic hydrolysate of ovotransferrin by LC-Ms/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7664–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.


© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, B. Purification and Characterization of Antioxidant Peptides of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates. Molecules 2017, 22, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010057
Zhang N, Zhang C, Chen Y, Zheng B. Purification and Characterization of Antioxidant Peptides of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ningning, Chong Zhang, Yuanyuan Chen, and Baodong Zheng. 2017. "Purification and Characterization of Antioxidant Peptides of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates" Molecules 22, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010057
APA StyleZhang, N., Zhang, C., Chen, Y., & Zheng, B. (2017). Purification and Characterization of Antioxidant Peptides of Pseudosciaena crocea Protein Hydrolysates. Molecules, 22(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010057






