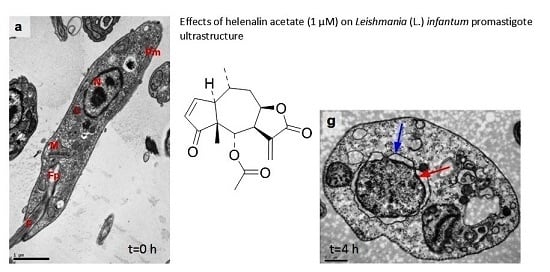
Investigation of the Anti-Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum Activity of Some Natural Sesquiterpene Lactones
Abstract
Share and Cite
Wulsten, I.F.; Costa-Silva, T.A.; Mesquita, J.T.; Lima, M.L.; Galuppo, M.K.; Taniwaki, N.N.; Borborema, S.E.T.; Da Costa, F.B.; Schmidt, T.J.; Tempone, A.G. Investigation of the Anti-Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum Activity of Some Natural Sesquiterpene Lactones. Molecules 2017, 22, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050685
Wulsten IF, Costa-Silva TA, Mesquita JT, Lima ML, Galuppo MK, Taniwaki NN, Borborema SET, Da Costa FB, Schmidt TJ, Tempone AG. Investigation of the Anti-Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum Activity of Some Natural Sesquiterpene Lactones. Molecules. 2017; 22(5):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050685
Chicago/Turabian StyleWulsten, Imke F., Thais A. Costa-Silva, Juliana T. Mesquita, Marta L. Lima, Mariana K. Galuppo, Noemi N. Taniwaki, Samanta E. T. Borborema, Fernando B. Da Costa, Thomas J. Schmidt, and Andre G. Tempone. 2017. "Investigation of the Anti-Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum Activity of Some Natural Sesquiterpene Lactones" Molecules 22, no. 5: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050685
APA StyleWulsten, I. F., Costa-Silva, T. A., Mesquita, J. T., Lima, M. L., Galuppo, M. K., Taniwaki, N. N., Borborema, S. E. T., Da Costa, F. B., Schmidt, T. J., & Tempone, A. G. (2017). Investigation of the Anti-Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum Activity of Some Natural Sesquiterpene Lactones. Molecules, 22(5), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050685