Steroid Alkaloids from Holarrhena africana with Strong Activity against Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Anti-Trypanosomal Activity of Crude Extracts and Alkaloid-Enriched Fractions of Holarrhena africana Leaves and Stem Bark
2.2. Bio-Activity Guided Fractionation and Isolation of Steroid Alkaloids
2.3. In Vitro Anti-Trypanosomal Activity of Isolated Compounds
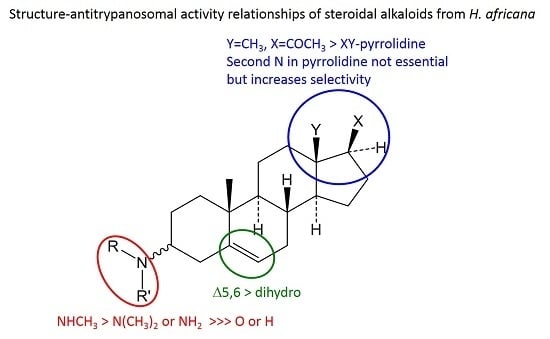
2.4. Structure-Activity and -Selectivity Relationships
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Preparation of Alkaloid-Enriched Fractions
3.4. Isolation of Steroid Alkaloids
3.4.1. Isolation of Alkaloids from the Leaf Extract
3.4.2. Isolation of Alkaloids from the Stem Bark Extract
3.4.3. Preparation of Compounds 16 and 17 by Alkaline Hydrolysis of the Esters 14 and 15
3.5. Structural Characterization of Isolated Compounds
3.6. Spectral Data of Isolated Compounds
3.7. In Vitro Biological Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hotez, P.J.; Alvarado, M.; Basáñez, M.; Bolliger, I.; Bourne, R.; Boussinesq, M.; Brooker, S.J.; Brown, A.S.; Buckle, G.; Budke, C.M.; et al. The Global Burden of Disease Study 2010: Interpretation and Implications for the Neglected Tropical Diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fèvre, E.M.; Odiit, M.; Coleman, P.G.; Welburn, S.C.; Woolhouse, M.E.J. Estimating the burden of rhodesiense sleeping sickness during an outbreak in Serere, eastern Uganda. BMC Public Health 2008, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fèvre, E.M.; Wissmann, B.V.; Welburn, S.C.; Lutumba, P. The Burden of Human African Trypanosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.G. Stigma and the social burden of neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, K.H.; Cunningham, L.V.; Bromel, M.C.; Schermeister, L.J.; Khalil, S.K. In vitro antitrypanosomal activity of certain alkaloids against Trypanosma lewisi. Lloydia 1976, 39, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoet, S.; Stévigny, C.; Block, S.; Opperdoes, F.; Colson, P.; Baldeyrou, B.; Lansiaux, A.; Bailly, C.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Alkaloids from Cassytha filiformis and related aporphines: Antitrypanosomal activity, cytotoxicity, and interaction with DNA and topoisomerases. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nibret, E.; Sporer, F.; Asres, K.; Wink, M. Antitrypanosomal and cytotoxic activities of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-producing plants of Ethiopia. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotti, M.T.; Speck-Planche, A.; Tavares, J.F.; da Silva Sobral, M.; Natália, M.; Cordeiro, D.S.; Scotti, L. Virtual Screening of Alkaloids from Apocynaceae with Potential Antitrypanosomal Activity. J. Curr. Bioinform. 2015, 10, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merschjohann, K.; Sporer, F.; Steverding, D.; Wink, M. In Vitro Effect of Alkaloids on Bloodstream Forms of Trypanosoma brucei and T. congolense. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toriizukaa, Y.; Kinoshitaa, E.; Kogurea, N.; Kitajimaa, M.; Ishiyamab, A.; Otogurob, K.; Yamadab, H.; Ōmurab, S.; Takayama, H. New lycorine-type alkaloid from Lycoris traubii and evaluation of antitrypanosomal and antimalarial activities of lycorine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 10182–10189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Phillipson, J.D.; Croft, S.L.; Rock, P.; Marshall1, S.J.; Schiff, P.L., Jr. In-vitro activity of Triclisia patens and some bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids against Leishmania donovani and Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, G.; Hoerr, V.; Holzgrabe, U.; Stich, A. Antitrypanosomal naphthylisoquinoline alkaloids and related compounds. Die Pharm. 2003, 58, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Murebwayirea, S.; Frédérichb, M.; Hannaertc, V.; Jonvilleb, M.C.; Duez, P. Antiplasmodial and antitrypanosomal activity of Triclisia sacleuxii (Pierre) Diels. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Davis, R.A.; Sykes, M.L.; Avery, V.M.; Carroll, A.R.; Camp, D.; Quinn, R.J. Anti-trypanosomal pyridoacridine alkaloids from the Australian ascidian Polysyncraton echinatum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 2477–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.J.; Khalid, S.A.; Romanha, A.J.; Alves, T.M.; Biayatti, M.W.; Brun, R.; Da Costa, F.B.; de Castro, S.L.; Ferreira, V.F.; de Lacerda, M.V.; et al. The potential of secondary metabolites from plants as drugs or leads against protozoan neglected diseases-Part II. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2176–2228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raffauf, R.F.; Flagler, M.B. Alkaloids of the Apocynaceae. Econ. Bot. 1960, 14, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bever, B.O. Medicinal plants in tropical West Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1982, 5, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogne, K.P.; Penlap, B.V.; Lontsi-David, E.F. Antibacterial activities of the extracts and conessine from Holarrhena floribunda G. DON. (Apocynaceae). Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2007, 4, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fotie, J.; Scott, B.D.; MaraLeimanis, L.; Elias, G.; Geoffrey, R.; Nkenfack, E. Lupeol long-chain fatty acid esters with antimalarial activity from Holarrhena floribunda. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwodo, N.J.; Brun, R.; Osadebe, P.O. In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of the antitrypanosomal activity of fractions of Holarrhena africana. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, T.; Sim, K.; Koyano, K.; Toyoshima, M.; Hayashi, M.; Komiyama, K. Cytotoxic and Leishmanicidal Aminoglycosteroids and Aminosteroids from Holarrhena curtisii. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasal, A.; Budesinsky, M.; Griffiths, W.J. Spectroscopic Methods of Steroid Analysis. In Steroid Analysis, 2nd ed.; Makin, H.L.J., Gower, D.B., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media B.V.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 90. [Google Scholar]
- Zirihi, G.N.; Grellier, P.; Guede-Guina, F.; Bodo, B.; Mambu, L. Isolation, characterization and anti-plasmodial activity of steroidal alkaloids from Funtumia elastica (Preuss) Stapf. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2637–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Su, J.; Ge, X.; Dong, T.; Li, X.; Wen, H.; Sun, B. Compounds with inhibitory activity on peristalsis from the seeds of Holarrhena antidysenterica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.D.; Duan, D.Z.; Xue, W.W.; Yao, X.J.; Li, S. Steroidal alkaloids from Holarrhena antidysenterica as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and the investigation for structure-activity relationships. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, B.S.; Usmani, S.B.; Begum, S.; Siddiqui, C. Steroidal alkaloids and an androstane derivative from the bark of Holarrhena pubescens. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerny, V.; Sorm, F. Steroid Alkaloids: Alkaloids of apocynaceae and buxaceae. In The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 9, pp. 305–426. [Google Scholar]
- Hitchin, J.R.; Hamilton, N.M.; Jordan, A.M.; Lyons, A.J.; Ogilvie, D.J. A novel scalable and stereospecific synthesis of 3α- and 3β-amino-5α-androstan-17-ones and 3α- and 3β-amino-5α-pregnan-20-ones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn, J.; Monneret, C.; Khuong-Huu, Q. Alcaloïdes des feuilles de l’Holarrhena crassifolia. Phytochemistry 1972, 11, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Seegert, K.; Sonnenbichler, H.; Ilyas, M.; Odenthal, K.P. Steroidal alkaloids of Funtumia africana. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicha, J.; Malon, M.; Vesela, P.; Humpa, O.; Strnad, M.; Marek, R. 1H-, 13C-, and 15N- NMR chemical shifts for selected glucosides and ribosides of aromatic cytokinins. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, V.; Skobridis, K.; Tzakos, A.G.; Ragoussis, V. A simple method for the alkaline hydrolysis of esters. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 8230–8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, A.M.M.; Khalid, S.A.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Abdallah, W.E.; Schmidt, T.J. The Antiprotozoal Activity of Sixteen Asteraceae Species Native to Sudan and Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Xanthanolides from Xanthium brasilicum. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 3, 8, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19 are available from the authors. |


| Tested Substance | Leaves | Stem bark | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tbr | Cytotox. L6 | SI | Tbr | Cytotox. L6 | SI | |
| Crude extract | 4.70 c | 87.5 c | 18.6 | 0.708 ± 0.013 | >100 | >100 |
| Alk. fraction | 0.905 ± 0.405 | 43.8 c | 48.4 | 0.143 ± 0.091 | 16.85 ± 1.344 | 117.8 |
| Polar fraction | 54.4 c | n.t. | n.a. | 35.2 ± 25.4 | >100 | n.a. |
| Fraction 11 | 1.87 ± 1.8 | n.t. | n.a. | 0.960 ± 0.325 a | >100 | >100 |
| Fraction 12 | 0.191 ± 0.001 | n.t. | n.a. | 0.225 ± 0.012 b | >100 | >100 |
| Fraction 13 | 0.031 ± 0.005 | n.t. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Fraction 14 | 0.219 ± 0.004 | n.t. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Pos. control | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | n.a. | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | n.a. |
| Compounds | Tbr (STIB900) | Cytotoxicity L6 Cells | SI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | IC50 (µM) | IC50 (µg/mL) | IC50 (µM) | |||
| 3β-Holaphyllamine | (1) | 0.127 ± 0.088 | 0.402 ± 0.281 | 1.61 ± 0.21 | 5.10 ± 0.65 | 12.6 |
| Holaphyllamine acetamid | (2) | 1.73 ± 0.47 | 4.83 ± 1.33 | 5.49 ± 0.33 | 15.4 ± 0.9 | 3.2 |
| N-methylholaphyllamine | (3) | 0.025 ± 0.001 | 0.075 ± 0.004 | 0.829 ± 0.124 | 2.48 ± 0.44 | 33.2 |
| 3α-Holaphyllamine | (4) | 0.117 ± 0.050 | 0.370 ± 0.159 | 5.00 ± 0.37 | 15.87 ± 1.17 | 42.9 |
| 3β-Dihydroholaphyllamine | (5) | 0.213 ± 0.008 | 0.672 ± 0.027 | 5.51 ± 0.43 | 17.37 ± 1.36 | 25.8 |
| 3α-Dihydroholaphyllamine | (6) | 0.382 ± 0.238 | 1.21 ± 0.75 | 5.38 ± 0.39 | 17.0 ± 1.2 | 14.1 |
| Holadienine | (7) | 4.81 ± 0.68 | 14.9 ± 2.1 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. |
| Holonamine | (8) | 2.82 ± 0.76 | 8.67 ± 2.33 | 21.1 ± 7.5 | 64.9 ± 23.1 | 7.5 |
| Cona-4,6-dienin-3-one | (9) | 5.69 ± 0.07 | 17.5 ± 0.2 | 41.9 ± 19.9 | 129 ± 61 | 7.4 |
| Cona-3,5-dienin-7-one | (10) | 2.40 ± 0.30 | 7.37 ± 0.94 | 13.6 ± 6.2 | 41.7 ± 18.9 | 5.7 |
| Conessimine | (11) | 0.057 ± 0.028 | 0.167 ± 0.083 | 17.3 ± 4.0 | 50.4 ± 11.8 | 302 |
| Isoconessimine | (12) | 0.056 ± 0.038 | 0.166 ± 0.112 | 9.38 a | 27.4 | 168 |
| Conessine | (13) | 0.149 ± 0.031 | 0.419 ± 0.087 | 21.8 a | 61.2 | 146 |
| Holarrhesine | (14) | 0.054 ± 0.038 | 0.119 ± 0.084 | 6.51 a | 14.3 | 121 |
| Holarrhetine | (15) | 0.777 ± 0.182 | 1.66 ± 0.39 | 45.8 a | 97.7 | 58.9 |
| Holarrheline | (16) | 2.94 ± 0.37 | 8.21 ± 1.03 | 64.8 ± 14.2 | 181 ± 40 | 22.0 |
| Holarrhenine | (17) | 7.78 ± 2.23 | 20.9 ± 6.0 | 46.4 ± 12.8 | 125 ± 34 | 6.0 |
| kurchinin | (18) | 3.64 ± 0.21 | 12.1 ± 0.7 | n.t. | n.t. | n.a. |
| Isopentenyl adenine | (19) | 5.03 ± 0.54 | 24.78 ± 0.84 | 61.30 ± 4.24 | 302 ± 6.80 | 12.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nnadi, C.O.; Nwodo, N.J.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Schmidt, T.J. Steroid Alkaloids from Holarrhena africana with Strong Activity against Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Molecules 2017, 22, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071129
Nnadi CO, Nwodo NJ, Kaiser M, Brun R, Schmidt TJ. Steroid Alkaloids from Holarrhena africana with Strong Activity against Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Molecules. 2017; 22(7):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071129
Chicago/Turabian StyleNnadi, Charles Okeke, Ngozi Justina Nwodo, Marcel Kaiser, Reto Brun, and Thomas J. Schmidt. 2017. "Steroid Alkaloids from Holarrhena africana with Strong Activity against Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense" Molecules 22, no. 7: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071129
APA StyleNnadi, C. O., Nwodo, N. J., Kaiser, M., Brun, R., & Schmidt, T. J. (2017). Steroid Alkaloids from Holarrhena africana with Strong Activity against Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Molecules, 22(7), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071129