Chrysin Induces Antidiabetic, Antidyslipidemic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Athymic Nude Diabetic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
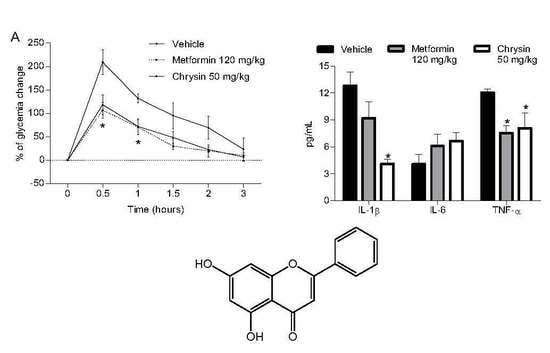
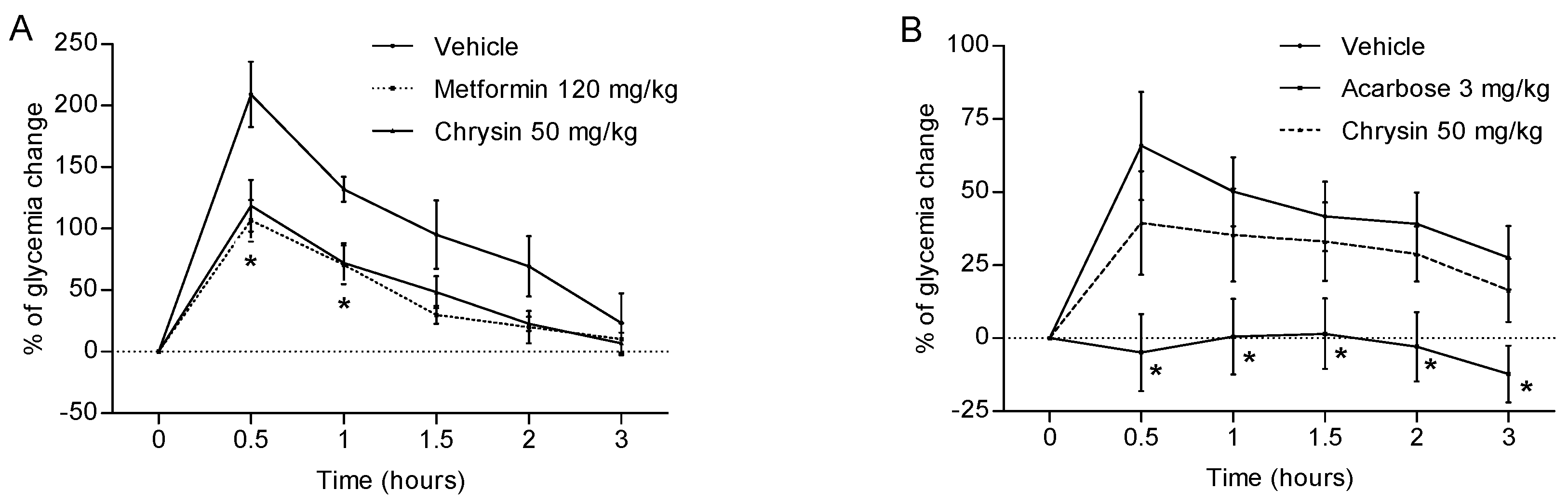
2.1. Antihyperglycaemic Activity
2.2. Glucose Determination and Biochemical Analysis after Sub-Acute Treatment with Chrysin
2.3. Anti-Proinflammatory Effect
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Drugs
3.2. Animals
3.3. Oral Glucose and Sucrose Tolerance Tests
3.4. Induction of Hyperglycaemic Condition
3.5. Orally Sub-Acute Treatment and Glucose Determination
3.6. Determination of Blood Parameters
3.7. Quantification of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α Cytokines
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Fact Sheet #312. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/index.html (accessed on 16 October 2016).
- Kaur, J. A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2014, 943162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2014 Report: Medicines in Development for Diabetes—PhRMA. Available online: www.phrma.org/sites/default/files/pdf/diabetes2014.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2016).
- Gambelunghe, C.; Rossi, R.; Sommavilla, M.; Ferranti, C.; Rossi, R.; Ciculi, C. Effects of chrysin on urinary testosterone levels in human males. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandian, S.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Samini, F.; Farkhondeh, T. Chrysin treatment improves diabetes and its complications in liver, brain and pancreas in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 94, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Piedra, M.; Ortiz-Andrade, R.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Singh, N.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Webster, S.P.; Binnie, M.; Navarrete-Vázquez, Ç.; Estrada-Soto, S. A comparative study of flavonoid analogues on streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats: Quercetin as a potential antidiabetic agent acting via 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibition. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, F.L.; Zhao, G.B.; Li, J. Chrysin suppressed inflammatory responses and the inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12270–12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiao, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, R.; Hao, J. Chrysin protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20913–20926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Xiong, H.; Du, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Autoantibodies against β1-adrenoceptor induce blood glucose enhancement and insulin insufficient via T lymphocytes. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Andrade, R.; Sánchez-Salgado, J.C.; Navarrete-Vázquez, G.; Webster, S.P.; Binnie, M.; García-Jiménez, S.; León-Rivera, I.; Cigarroa-Vázquez, P.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Estrada-Soto, S. Antidiabetic and toxicological evaluations of naringenin in Normoglycemic And NIDMM rat models and its implications on extra-pancreatic glucose regulation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bassossy, H.M.; Abo-Warda, S.M.; Fahmy, A. Chrysin and luteolin alleviate vascular complications associated with insulin resistance mainly through PPAR-γ activation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Hayashida, S.; Matsumoto, K. Luteolin, a flavone, does not suppress postprandial glucose absorption through an inhibition of alpha-glucosidase action. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 6, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, J.L.; Francini, F.; Schinella, G.R. Natural products for the treatment of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 975–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Yu, C.S.; Yang, J.S.; Lu, C.C.; Chiang, J.H.; Lin, J.P.; Kuo, C.L.; Chung, J.G. Chrysin, a natural and biologically active flavonoid, influences a murine leukemia model in vivo through enhancing populations of T-and B-cells, and promoting macrophage phagocytosis and NK cell cytotoxicity. In Vivo 2012, 26, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Coudriet, G.M.; Hyun Kim, D.; Lu, Y.; Perdomo, G.; Qu, S.; Slusher, S.; Tse, H.M.; Piganelli, J.; Giannoukakis, N.; et al. FoxO1 links insulin resistance to proinflammatory cytokine IL-1beta production in macrophages. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2624–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulthess, F.T.; Paroni, F.; Sauter, N.S.; Shu, L.; Ribaux, P.; Haataja, L.; Strieter, R.M.; Oberholzer, J.; King, C.C.; Maedler, K. CXCL10 impairs beta cell function and viability in diabetes through TLR4 signaling. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Cai, Y.; Hu, J.; Yu, C.; Li, J.; Feng, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; et al. Inhibition of high glucose-induced inflammatory response and macrophage infiltration by a novel curcumin derivative prevents renal injury in diabetic rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maedler, K.; Sergeev, P.; Ris, F.; Oberholzer, J.; Joller-Jemelka, H.I.; Spinas, G.A.; Kaiser, N.; Halban, P.A.; Donath, M.Y. Glucose-induced beta cell production of IL-1beta contributes to glucotoxicity in human pancreatic islets. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, T.; Shigematsu, N.; Maruki, R.; Urano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Shimaya, A.; Shimokawa, T.; Shibasaki, M. Discovery of novel forkhead box O1 inhibitors for treating type 2 diabetes: Improvement of fasting glycemia in diabetic db/db mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Du, C.; Zheng, Q.; Peng, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of metformin on serum interleukin-6 levels in polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review. BMC Womens Health 2014, 5, 14–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.B.; Qian, X.C.; Huang, P.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, J.S.; Yang, G.M.; Cai, B.C. Simultaneous determination of ten flavonoids of crude and wine-processed Radix Scutellariae aqueous extracts in rat plasma by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS and its application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Flores, A.; Hidalgo-Figueroa, S.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Ibarra-Barajas, M.; Bazán-Perkins, B.; Navarrete-Vázquez, G.; Estrada-Soto, S. Relaxant effect of structurally related flavonoids on isolated tracheal rat rings: A SAR study. Med. Chem. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Espinosa, J.J.; García-Jiménez, S.; Rios, M.Y.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; López-Vallejo, F.; Webster, S.P.; Binnie, M.; Ibarra-Barajas, M.; Ortiz-Andrade, R.; Estrada-Soto, S. Antihyperglycemic and sub-chronic antidiabetic actions of morolic and moronic acids, in vitro and in silico inhibition of 11β-HSD 1. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St. Louis, D.; Romero, R.; Plazyo, O.; Arenas-Hernandez, M.; Panaitescu, B.; Xu, Y.; Bhatti, G.; Mi, Q.S.; Drewlo, S.; Tarca, A.L.; et al. Invariant NKT cell activation induces late preterm birth that is attenuated by rosiglitazone. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


| Parameter (mg/dL) | Vehicle (1 mL) | Metformin (120 mg/kg) | Chrysin (50 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLU | 172 ± 2 | 153 ± 13 | 132 ± 10 * |
| CHO | 210 ± 4 | 208 ± 7 | 201 ± 7 |
| TG | 223 ± 13 | 167 ± 12 * | 167 ± 14 * |
| HDL | 101 ± 3 | 118 ± 9 * | 104 ± 4 |
| LDL | 27 ± 1 | 43 ± 4 * | 42 ± 5 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Espinosa, J.J.; Saldaña-Ríos, J.; García-Jiménez, S.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Ávila-Villarreal, G.; Rodríguez-Ocampo, A.N.; Bernal-Fernández, G.; Estrada-Soto, S. Chrysin Induces Antidiabetic, Antidyslipidemic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Athymic Nude Diabetic Mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010067
Ramírez-Espinosa JJ, Saldaña-Ríos J, García-Jiménez S, Villalobos-Molina R, Ávila-Villarreal G, Rodríguez-Ocampo AN, Bernal-Fernández G, Estrada-Soto S. Chrysin Induces Antidiabetic, Antidyslipidemic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Athymic Nude Diabetic Mice. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Espinosa, Juan José, Johann Saldaña-Ríos, Sara García-Jiménez, Rafael Villalobos-Molina, Gabriela Ávila-Villarreal, Angélica Nallelhy Rodríguez-Ocampo, Germán Bernal-Fernández, and Samuel Estrada-Soto. 2018. "Chrysin Induces Antidiabetic, Antidyslipidemic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Athymic Nude Diabetic Mice" Molecules 23, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010067
APA StyleRamírez-Espinosa, J. J., Saldaña-Ríos, J., García-Jiménez, S., Villalobos-Molina, R., Ávila-Villarreal, G., Rodríguez-Ocampo, A. N., Bernal-Fernández, G., & Estrada-Soto, S. (2018). Chrysin Induces Antidiabetic, Antidyslipidemic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Athymic Nude Diabetic Mice. Molecules, 23(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010067