Hydrazone Derivatives Enhance Antileishmanial Activity of Thiochroman-4-ones
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
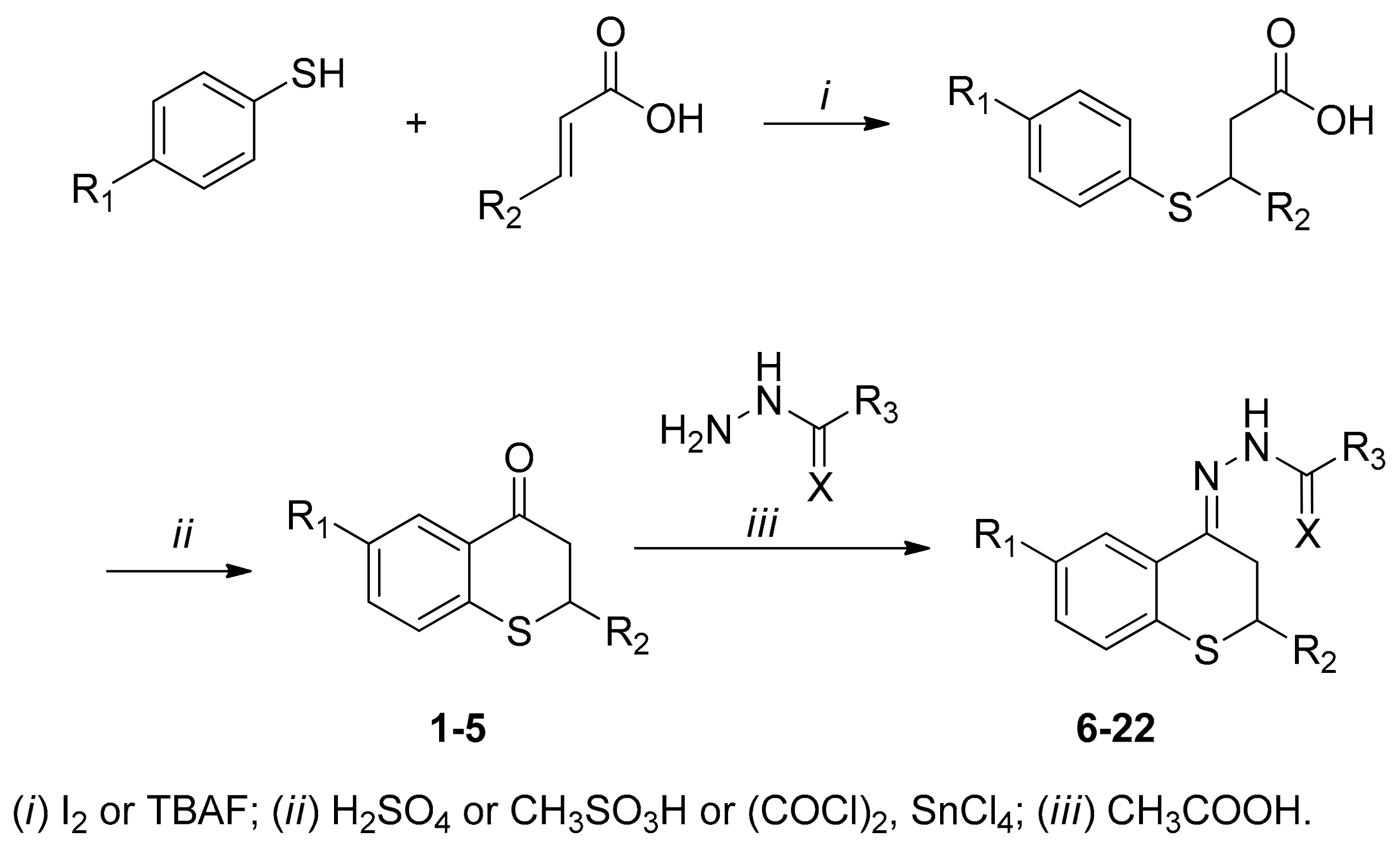
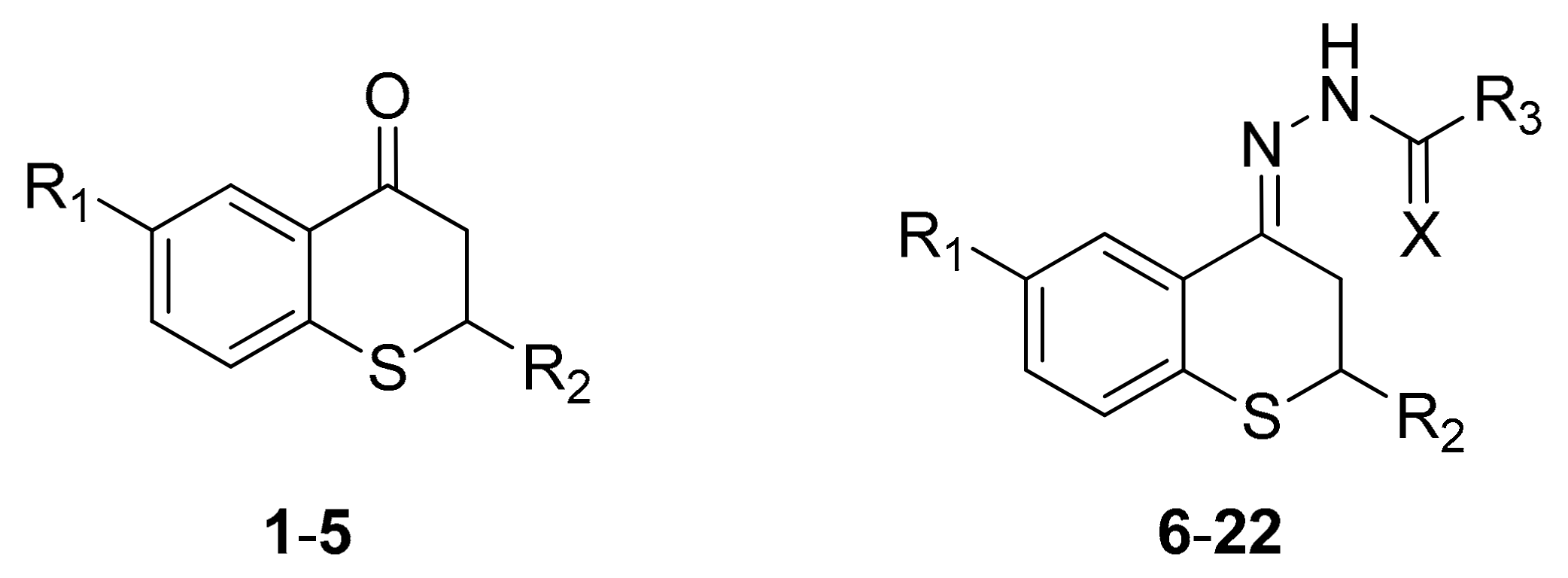
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Antileishmanial and Cytotoxic Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. General
4.1.2. Synthesis of Thiochroman-4-ones and Thioflavanone
4.1.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of Acyl Hydrazone Derivatives
4.2. Biological Activity
4.2.1. Cytotoxic Activity
4.2.2. Antileishmanial Activity
4.2.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Leishmaniasis fact sheet. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs375/en/ (accessed on 5 November 2016).
- Kaye, P.; Scott, P. Leishmaniasis: Complexity at the host–pathogen interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputto, M.E.; Ciccarelli, A.; Frank, F.; Moglioni, A.G.; Moltrasio, G.Y.; Vega, D.; Lombardo, E.; Finkielsztein, L.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of some novel 1-indanone thiazolylhydrazone derivatives as anti-Trypanosoma cruzi agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Silva, A.; Guimarães, P.P.G.; Tavares, C.A.P.; Sinisterra, R.D. New perspectives for leishmaniasis chemotherapy over current anti-leishmanial drugs: A patent landscape. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, M.E.; Snyder, S.A.; Stockwell, B.R. Privileged scaffolds for library design and drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keri, R.S.; Budagumpi, S.; Pai, R.K.; Balakrishna, R.G. Chromones as a privileged scaffold in drug discovery: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 340–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, S.; Ghanbarimasir, Z. Recent advances of chroman-4-one derivatives: Synthetic approaches and bioactivities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 93, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollas, S.; Küçükgüzel, S.G. Biological activities of hydrazone derivatives. Molecules 2007, 12, 1910–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, G.; Marella, A.; Shaquiquzzaman, M.; Akhtar, M.; Ali, M.R.; Alam, M.M. A review exploring biological activities of hydrazones. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; Secci, D.; Bizzarri, B.; Chimenti, P.; De Monte, C.; Guglielmi, P.; Campestre, C.; Rivanera, D.; Bordón, C.; Jones-Brando, L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity of a novel scaffold of thiazolidinone derivatives. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, E.S.; Antinarelli, L.M.R.; Da Silva, A.D.; Bispo, M.L.F.; Kaiser, C.R.; De Souza, M.V.N. 7-Chloro-4-quinolinyl hydrazones: A promising and potent class of antileishmanial compounds. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kahraman, Y.M.S.A.; Yasinzai, M.; Singh, G.S. Evaluation of some classical hydrazones of ketones and 1,2-diketones as antileishmanial, antibacterial and antifungal agents. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemma, S.; Giovani, S.; Brindisi, M.; Tripaldi, P.; Brogi, S.; Savini, L.; Fiorini, I.; Novellino, E.; Butini, S.; Campiani, G.; et al. Quinolylhydrazones as novel inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum serine protease PfSUB1. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5317–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.; Baharudin, M.S.; Ismail, N.H.; Khan, K.M.; Jaafar, F.M.; Samreen; Siddiqui, S.; Choudhary, M.I. Synthesis of 2-methoxybenzoylhydrazone and evaluation of their antileishmanial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3463–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.B.; Loback, V.B.; Salomão, K.; De Castro, S.L.; Wardell, J.L.; Wardell, S.M.S.V.; Costa, T.E.M.M.; Penido, C.; De Oliveira Henriques, M.D.G.M.; Carvalho, S.A.; et al. Synthesis and trypanocidal activity of novel 2,4,5-triaryl-N-hydroxylimidazole derivatives. Molecules 2013, 18, 3445–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.V.; Patny, A.; Sabnis, Y.; Tekwani, B.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.; Srivastava, A.; Avery, M. Identification of novel parasitic cysteine protease inhibitors using virtual screening. 1. The ChemBridge Database. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6609–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.V.; Patny, A.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Tekwani, B.; Srivastava, A.; Avery, M. Identification of novel parasitic cysteine protease inhibitors by use of virtual screening. 2. The Available Chemical Directory. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez, J.; Cavalcanti De Queiroz, A.; Correia, I.; Alves, M.A.; Alexandre-Moreira, M.S.; Barreiro, E.J.; Lima, L.M.; Varela, J.; González, M.; Cerecetto, H.; et al. New oxidovanadium(IV) N-acylhydrazone complexes: Promising antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöder, J.; Noack, S.; Marhöfer, R.J.; Mottram, J.C.; Coombs, G.H.; Selzer, P.M. Identification of semicarbazones, thiosemicarbazones and triazine nitriles as inhibitors of Leishmania mexicana cysteine protease CPB. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77460. [Google Scholar]
- Kishore Kumar, G.D.; Chavarria, G.E.; Charlton-Sevcik, A.K.; Arispe, W.M.; MacDonough, M.T.; Strecker, T.E.; Chen, S.-E.; Siim, B.G.; Chaplin, D.J.; Trawick, M.L.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent thiosemicarbazone based cathepsin L inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jones, L.M.; Kumar, G.D.K.; Conner, E.S.; Bayeh, L.; Chavarria, G.E.; Charlton-Sevcik, A.K.; Chen, S.-E.; Chaplin, D.J.; Trawick, M.L.; et al. Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of thiochromanone thiosemicarbazone analogues as inhibitors of cathepsin L. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siles, R.; Chen, S.-E.; Zhou, M.; Pinney, K.G.; Trawick, M.L. Design, synthesis, and biochemical evaluation of novel cruzain inhibitors with potential application in the treatment of Chagas’ disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4405–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, E.N.; Song, J.; Kishore Kumar, G.D.; Odutola, S.O.; Chavarria, G.E.; Charlton-Sevcik, A.K.; Strecker, T.E.; Barnes, A.L.; Sudhan, D.R.; Wittenborn, T.R.; et al. Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of benzoylbenzophenone thiosemicarbazone analogues as potent and selective inhibitors of cathepsin L. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6974–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jones, L.M.; Chavarria, G.E.; Charlton-Sevcik, A.K.; Jantz, A.; Johansen, A.; Bayeh, L.; Soeung, V.; Snyder, L.K.; Lade, S.D.; et al. Small-molecule inhibitors of cathepsin L incorporating functionalized ring-fused molecular frameworks. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuno, K.; Burrows, J.N.; Duncan, K.; Van Huijsduijnen, R.H.; Kaneko, T.; Kita, K.; Mowbray, C.E.; Schmatz, D.; Warner, P.; Slingsby, B.T. Hit and lead criteria in drug discovery for infectious diseases of the developing world. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, J.; Raines, R.T. Hydrolytic stability of hydrazones and oximes. Angew. Chemie 2008, 120, 7633–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scior, T.; Garces-Eisele, S. Isoniazid is not a lead compound for its pyridyl ring derivatives, isonicotinoyl amides, hydrazides, and hydrazones: A critical review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautio, J.; Kumpulainen, H.; Heimbach, T.; Oliyai, R.; Oh, D.; Jarvinen, T.; Savolainen, J. Prodrugs: Design and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornada, D.; Dos Santos Fernandes, G.; Chiba, D.; De Melo, T.; Dos Santos, J.; Chung, M. The prodrug approach: A successful tool for improving drug solubility. Molecules 2016, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, V.M.; Cedeño, D.L.; Muñoz, D.L.; Jones, M.A.; Lash, T.D.; Young, A.M.; Constantino, M.H.; Esposito, N.; Vélez, I.D.; Robledo, S.M. In vitro and in vivo studies of the utility of dimethyl and diethyl carbaporphyrin ketals in treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4755–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, S.A.; Muñoz, D.L.; Restrepo, A.M.; Mesa, C.V.; Alzate, J.F.; Vélez, I.D.; Robledo, S.M. Improvement of the green fluorescent protein reporter system in Leishmania spp. for the in vitro and in vivo screening of antileishmanial drugs. Acta Trop. 2012, 122, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, D.J. Statistical Method in Biological Assay; Charles Griffin & Company: Cambridge, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the acyl-hydrazone compounds are available from the authors. |
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | X | EC50 (µM) a | LC50 (µM) a | IS b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | - | - | 343.8 ± 75.6 | >1000 | <2.9 |
| 2 | F | H | - | - | >109.9 | >706.0 ± 34.6 | <6.5 |
| 3 | H | CH3 | - | - | 444.6 ± 7.3 | 604.2 ± 86.4 | 1.4 |
| 4 | F | CH3 | - | - | 422.0 ± 9.2 | 578.9 ± 59.1 | 1.4 |
| 5 | H | C6H5 | - | - | 44.1 ± 0.9 | >41.61 | >0.9 |
| 6 | H | H |  | O | 63.7 ± 9.2 | 248.3 ± 49.6 | 3.9 |
| 7 | H | H | 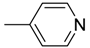 | O | 56.8 ± 4.54 | 705.8 | >12.4 |
| 8 | H | H |  | O | 91.5 ± 33.4 | 637.2 ± 37.9 | 7.0 |
| 9 | H | H |  | S | 55.7 ± 22.1 | >842.6 | >15.1 |
| 10 | F | H |  | O | 37.3 ± 3.3 | >665.9 | >17.6 |
| 11 | F | H |  | O | 39.9 ± 5.3 | >663.7 | >16.6 |
| 12 | F | H | 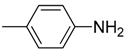 | O | 95.5 ± 6.9 | >634.2 | >6.6 |
| 13 | H | CH3 |  | O | 38.1 ± 16.2 | 150.1 ± 24.3 | 3.9 |
| 14 | H | CH3 |  | O | 56.6 ± 0.7 | >672.5 | >11.9 |
| 15 | H | CH3 |  | O | 91.8 ± 13.5 | 102.1 ± 15.1 | 1.1 |
| 16 | F | CH3 |  | O | 43.9 ± 4.5 | >636.2 | 14.5 |
| 17 | F | CH3 |  | O | 98.9 ± 19.3 | 203.3 ± 25.4 | 2.1 |
| 18 | F | CH3 |  | O | 160.7 ± 2.4 | 31.0 ± 7.0 | 0.2 |
| 19 | H | C6H5 |  | O | 5.4 ± 1.0 | 100.2 ± 19.8 | 18.6 |
| 20 | H | C6H5 |  | S | 5.1 ± 1.3 | 50.1 ± 4.1 | 9.8 |
| 21 | H | C6H5 |  | O | 28.5 ± 2.8 | 528.6 ± 7.0 | 19.6 |
| 22 | H | C6H5 |  | O | 16.4 ± 3.6 | >556.4 | >33.9 |
| thiosemicarbazide | >266.7 | >1000 | - | ||||
| Amphotericin B | - | - | - | - | 0.32 ± 1.04 | 39.6 ± 8.7 | 132.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vargas, E.; Echeverri, F.; Upegui, Y.A.; Robledo, S.M.; Quiñones, W. Hydrazone Derivatives Enhance Antileishmanial Activity of Thiochroman-4-ones. Molecules 2018, 23, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010070
Vargas E, Echeverri F, Upegui YA, Robledo SM, Quiñones W. Hydrazone Derivatives Enhance Antileishmanial Activity of Thiochroman-4-ones. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010070
Chicago/Turabian StyleVargas, Esteban, Fernando Echeverri, Yulieth A. Upegui, Sara M. Robledo, and Wiston Quiñones. 2018. "Hydrazone Derivatives Enhance Antileishmanial Activity of Thiochroman-4-ones" Molecules 23, no. 1: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010070
APA StyleVargas, E., Echeverri, F., Upegui, Y. A., Robledo, S. M., & Quiñones, W. (2018). Hydrazone Derivatives Enhance Antileishmanial Activity of Thiochroman-4-ones. Molecules, 23(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010070





