Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Preservation of Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
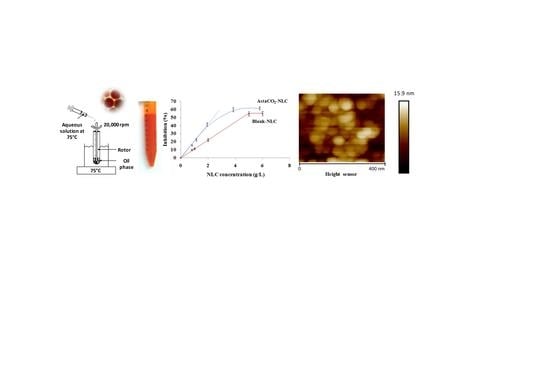
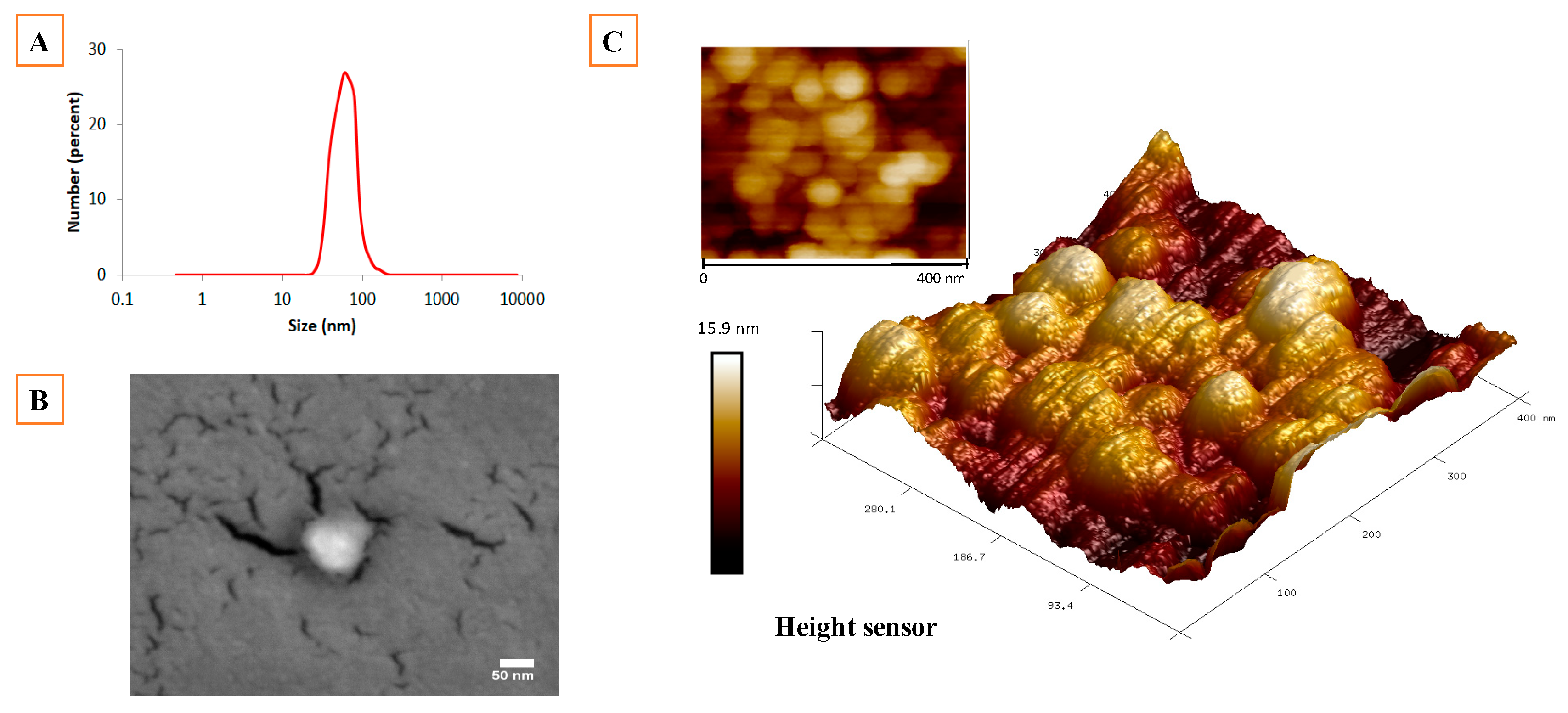
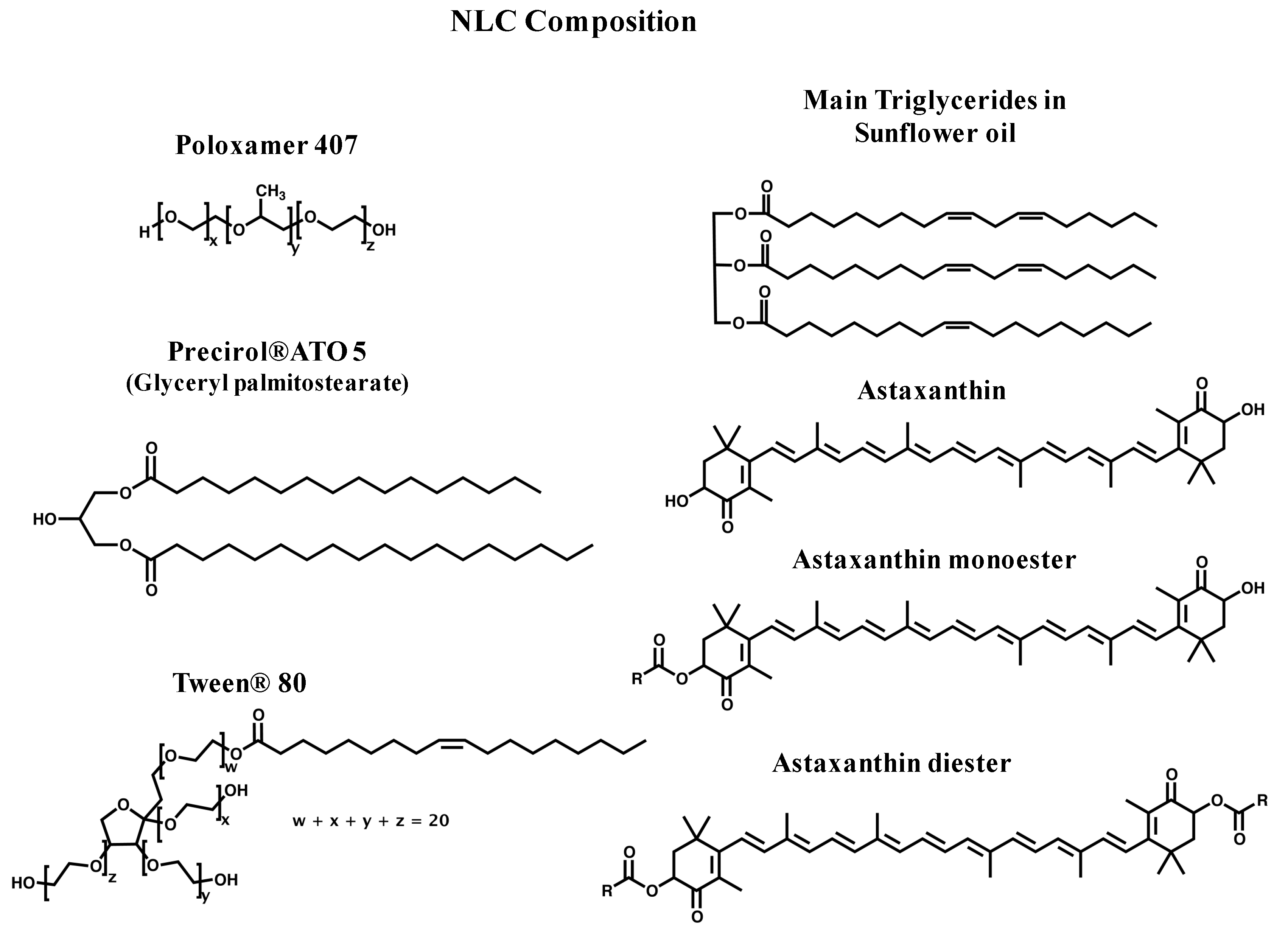
2.1. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of NLC
2.2. Evaluation of Astaxanthin Content in AstaCO2 and AstaCO2-NLC
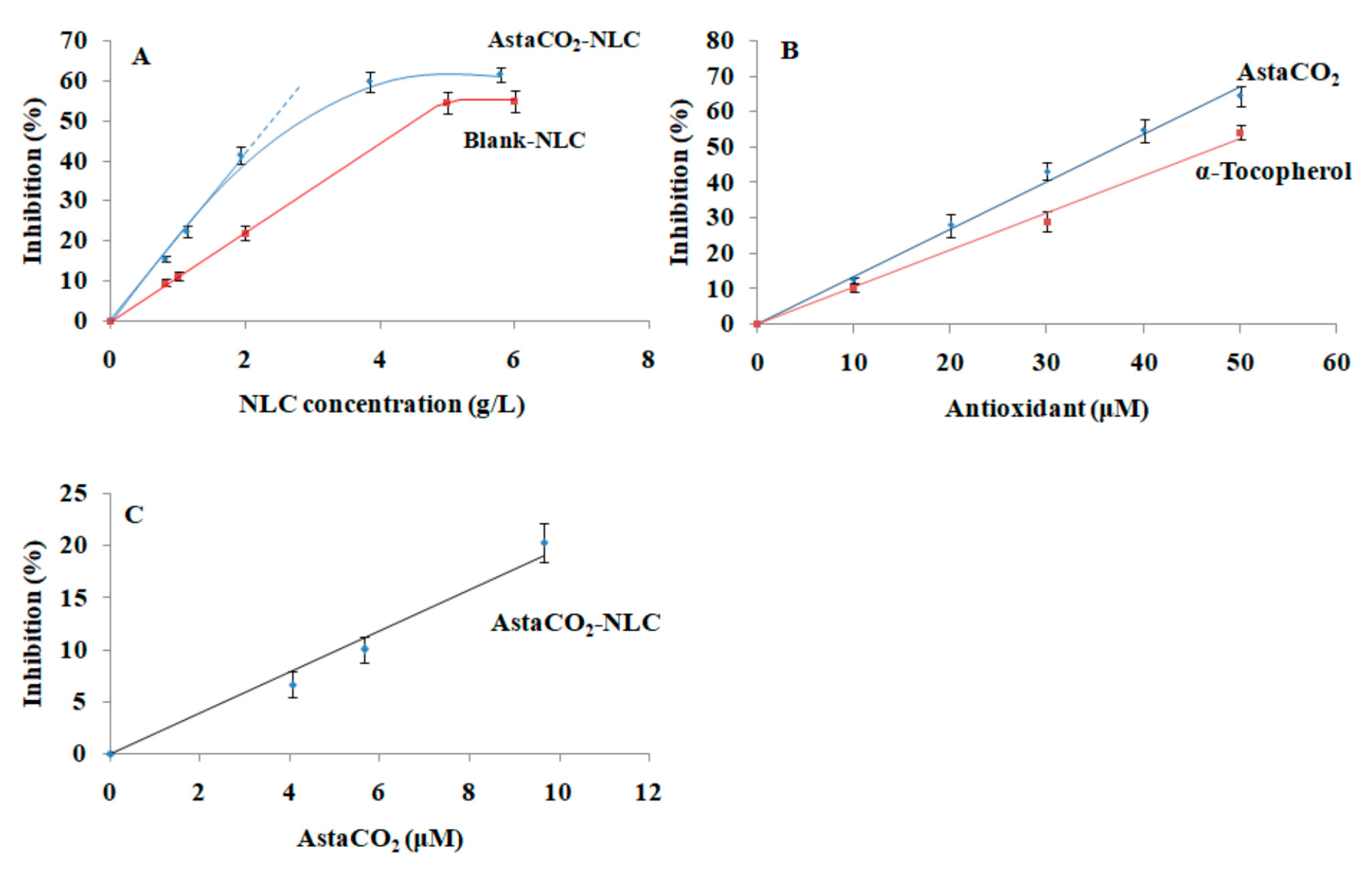
2.3. Antioxidant Activity of AstaCO2-NLC by Lipophilic ABTS Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algae Material
3.2. Chemicals
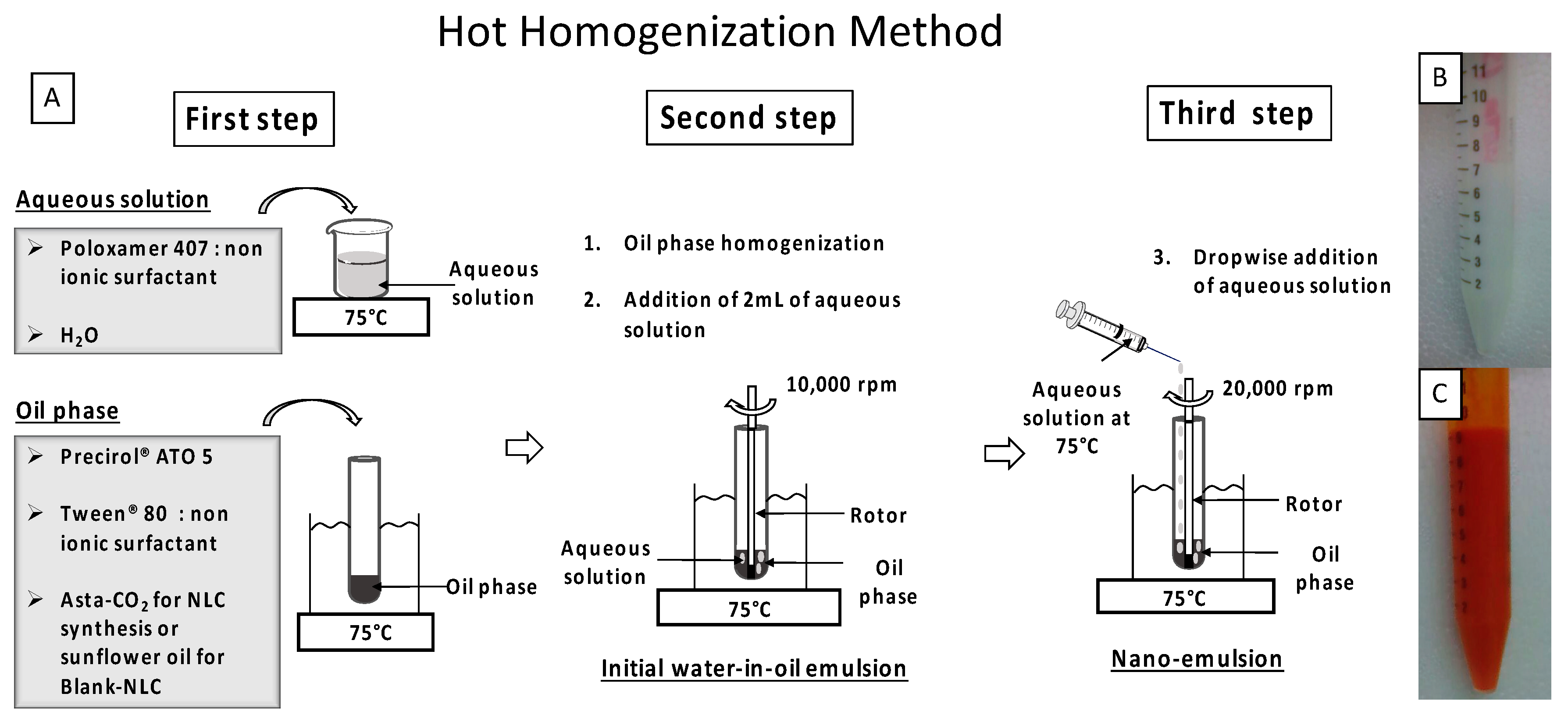
3.3. Synthesis of AstaCO2-Loaded NLC (AstaCO2-NLC) by Hot Homogenization (HH) Method
3.4. Particle Size Analysis and Zeta Potential
3.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.7. Quantification of NLC
3.8. Beer–Lambert Law Parameters
3.9. Determination of the Astaxanthin Concentration in AstaCO2 and AstaCO2-NLC
3.10. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of AstaCO2-NLC by α-TEAC Assay
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambati, R.R.; Moi, P.S.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R.G. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—A review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhuge, F.; Zhan, L.; Nagata, N.; Tsutsui, A.; Nakanuma, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regnier, P.; Bastias, J.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, V.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Caballo, C.; Sicilia, D.; Fuentes, A.; Maire, M.; Crepin, M.; Letourneur, D.; et al. Astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis Prevents Oxidative Stress on Human Endothelial Cells without Toxicity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2857–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Ni, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Astaxanthin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Mice H22 Hepatoma Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2152–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuluaga, M.; Gueguen, V.; Letourneur, D.; Pavon-Djavid, G. Astaxanthin-antioxidant impact on excessive Reactive Oxygen Species generation induced by ischemia and reperfusion injury. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 279, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, M.; Huntley, M.E.; Olaizola, M. Haematococcus astaxanthin: Applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Design and characterization of astaxanthin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 26, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Stability of astaxanthin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers in beverage systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L.; Lai, F.; Offerta, A.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Micicchè, L.; Maccioni, A.M.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M. From nanoemulsions to nanostructured lipid carriers: A relevant development in dermal delivery of drugs and cosmetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Zimmer, A.; Pardeike, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for pulmonary application: A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasodomska, O.; Paolicelli, P.; Cesa, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Jungnickel, C. Protection and viability of fruit seeds oils by nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) nanosuspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 479, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchow, M.; Maincent, P.; Muller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles with a solid matrix (SLN, NLC, LDC) for oral drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garces, A.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Formulations based on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for cutaneous use: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xia, N.; Xia, Q. Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) as a strategy for encapsulation of quercetin and linseed oil: Preparation and in vitro characterization studies. J. Food Eng. 2017, 215, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonogi, S.; Riangjanapatee, P. Physicochemical characterization of lycopene-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier formulations for topical administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, N.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mehramuz, B.; Kafil, H.S. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Physicochemical Properties of Turmeric Extract-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier (NLC). Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2018, 22, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhuang, P.; Luan, L.; Sun, Q.; Cao, F. Preparation and characterization of novel nanocarriers containing krill oil for food application. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Préat, V. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Promising drug delivery systems for future clinics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Smith, E. Experimental design for the optimization of lipid nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nanoemulsion templates—A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Egea, M.A.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, E.B. Design and ocular tolerance of flurbiprofen loaded ultrasound-engineered NLC. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 81, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ng, W.K.; Kanaujia, P.; Kim, S.; Tan, R.B.H. Formulation design, preparation and physicochemical characterizations of solid lipid nanoparticles containing a hydrophobic drug: Effects of process variables. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 88, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zahi, M.R.; Yuan, Q.; Tian, F.; Liang, H. Preparation and stability of astaxanthin solid lipid nanoparticles based on stearic acid. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, C.M.; Kovačević, A.; Müller, R.H.; Savić, S.; Vuleta, G.; Milić, J. Formulation of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): The value of different alkyl polyglucoside surfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, C.; Sánchez-Hernández, N.; García-Montoya, E.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Ticó, J.R.; Suñé, C.; Miñarro, M. DNA delivery via cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeranachaideekul, V.; Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H.; Junyaprasert, V.B. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro release studies of ascorbyl palmitate-loaded semi-solid nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC gels). J. Microencapsul. 2008, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.-M.; Zhang, J.-P.; Skibsted, L.H. Reaction dynamics of flavonoids and carotenoids as antioxidants. Molecules 2012, 17, 2140–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, A.; Skibsted, L.H.; Sampson, J.; Rice-Evans, C.; Everett, S.A. Comparative mechanisms and rates of free radical scavenging by carotenoid antioxidants. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Focsan, A.L.; Pan, S.; Kispert, L.D. Electrochemical study of astaxanthin and astaxanthin n-octanoic monoester and diester: Tendency to form radicals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsavova, J.; Misurcova, L.; Ambrozova, J.V.; Vicha, R.; Mlcek, J. Fatty Acids Composition of Vegetable Oils and Its Contribution to Dietary Energy Intake and Dependence of Cardiovascular Mortality on Dietary Intake of Fatty Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12871–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Apak, R.; Gorinstein, S.; Böhm, V.; Schaich, K.M.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K. Methods of measurement and evaluation of natural antioxidant capacity/activity (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 957–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Porter, N.A. Free Radical Lipid Peroxidation: Mechanisms and Analysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5944–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinova, M.; Hewitt, M.; Brezova, V.; Madden, J.C.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Valko, M. Antioxidant properties of carotenoids: QSAR prediction of their redox potentials. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2007, 26, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuluaga, M.; Barzegari, A.; Letourneur, D.; Gueguen, V.; Pavon-Djavid, G. Oxidative Stress Regulation on Endothelial Cells by Hydrophilic Astaxanthin Complex: Chemical, Biological, and Molecular Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8073798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.H.; Mader, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Theile, K.; Bohm, V. In vitro antioxidant activity of tocopherols and tocotrienols and comparison of vitamin E concentration and lipophilic antioxidant capacity in human plasma. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Sample | Z-Average (nm) 1 | PDI 1 | ZP (mV) 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 30 | Day 1 | Day 30 | Day 1 | Day 30 | |
| Blank-NLC | 66 ± 17 | 61 ± 15 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | −23.3 ± 1.0 | −25.9 ± 0.4 |
| AstaCO2-NLC | 60 ± 7 | 57 ± 10 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 0.37 ± 0.05 | −25.5 ± 0.7 | −23.7 ± 0.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Ruiz, V.; Salatti-Dorado, J.Á.; Barzegari, A.; Nicolas-Boluda, A.; Houaoui, A.; Caballo, C.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Sicilia, D.; Bastias Venegas, J.; Pauthe, E.; et al. Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Preservation of Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102601
Rodriguez-Ruiz V, Salatti-Dorado JÁ, Barzegari A, Nicolas-Boluda A, Houaoui A, Caballo C, Caballero-Casero N, Sicilia D, Bastias Venegas J, Pauthe E, et al. Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Preservation of Antioxidant Activity. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102601
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Ruiz, Violeta, José Ángel Salatti-Dorado, Abolfazl Barzegari, Alba Nicolas-Boluda, Amel Houaoui, Carmen Caballo, Noelia Caballero-Casero, Dolores Sicilia, Jorge Bastias Venegas, Emmanuel Pauthe, and et al. 2018. "Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Preservation of Antioxidant Activity" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102601
APA StyleRodriguez-Ruiz, V., Salatti-Dorado, J. Á., Barzegari, A., Nicolas-Boluda, A., Houaoui, A., Caballo, C., Caballero-Casero, N., Sicilia, D., Bastias Venegas, J., Pauthe, E., Omidi, Y., Letourneur, D., Rubio, S., Gueguen, V., & Pavon-Djavid, G. (2018). Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Preservation of Antioxidant Activity. Molecules, 23(10), 2601. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102601