Preparation of Silica Aerogels by Ambient Pressure Drying without Causing Equipment Corrosion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
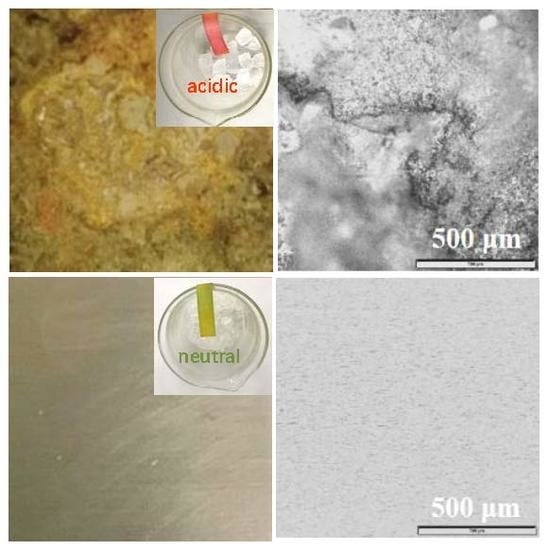
2.1. Corrosion Behaviour under Different Drying Atmosphere
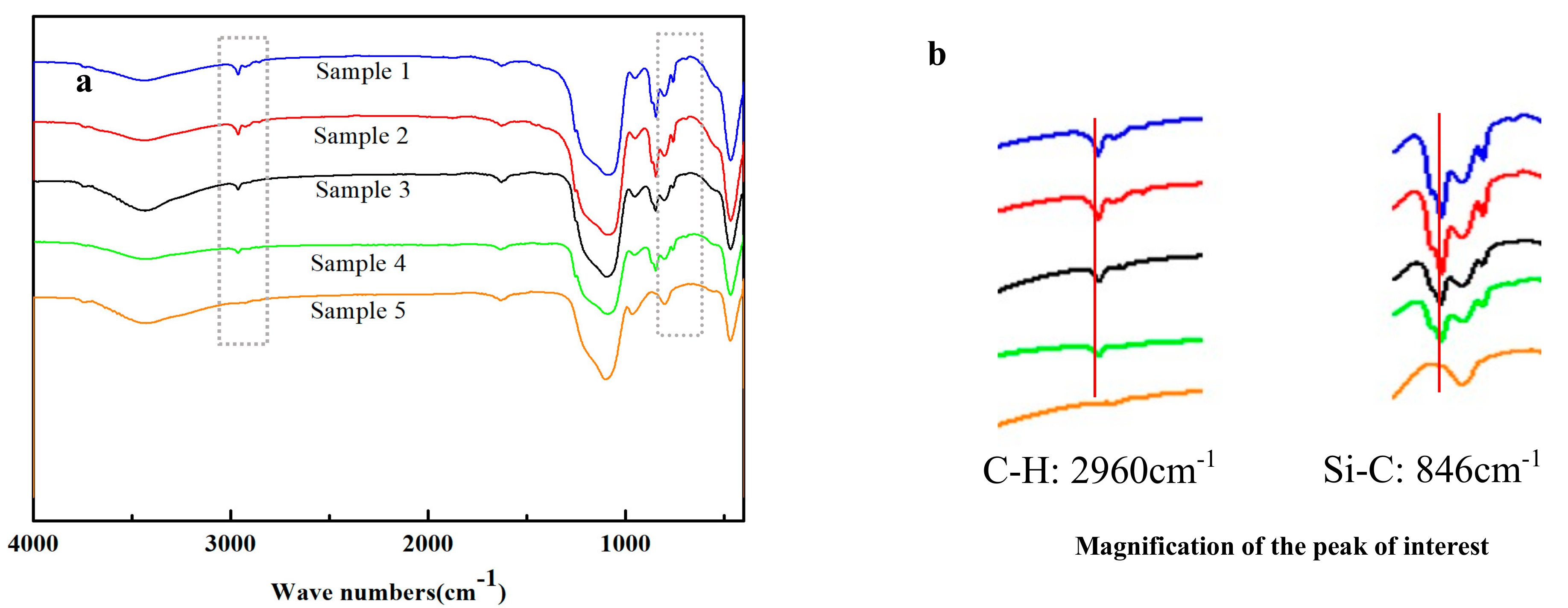
2.2. Pore Structure
2.3. Morphology and Hydrophobicity
2.4. Thermal Conductivity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thapliyal, P.C.; Singh, K. Aerogels as promising thermal insulating materials: An overview. J. Mater. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.F.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.Y. Preparation and characterization of silica aerogel microspheres. Materials 2017, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, J.; Milow, B.; Ratke, L. Aerogel-aerogel composites for normal temperature range thermal insulations. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2016, 441, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M. Aerogel-based thermal superinsulation: An overview. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miros, A.; Psiuk, B.; Szpikowska-Sroka, B. Aerogel insulation materials for industrial installation: properties and structure of new factory-made products. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.F.; Chen, X.H.; Song, H.H.; Hu, Z.J.; Cao, B. The influence of thermal treatment on the microstructure and thermal insulation performance of silica aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2017, 470, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estok, S.K.; Hughes, T.A.; Carroll, M.K.; Anderson, A.M. Fabrication and characterization of TEOS-based silica aerogels prepared using rapid supercritical extraction. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.W.; Zhou, B.; Du, A.; Shen, J.; Yu, Q.J. Effect of the thermal treatment on microstructure and physical properties of low-density and high transparency silica aerogels via acetonitrile supercritical drying. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingale, S.V.; Wagh, P.B.; Tripathi, A.K.; Kamble, V.S.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, S.C. Physico-chemical properties of silica aerogels prepared from TMOS/MTMS mixtures. J. Porous Mater. 2011, 18, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.P.; Rao, A.V. Microstructural and physical properties of the ambient pressure dried hydrophobic silica aerogels with various solvent mixtures. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2008, 354, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.P.; Rao, A.V.; Pajonk, G.M. Hydrophobic and physical properties of the ambient pressure dried silica aerogels with sodium silicate precursor using various surface modification agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 6032–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.P.; Rao, A.V. Improvement in optical transmission of the ambient pressure dried hydrophobic nanostructured silica aerogels with mixed silylating agents. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2009, 355, 2260–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.M.; Liu, D.R.; Zou, H.F.; Zou, L.C.; Gan, S.C. Preparation of silica aerogel from oil shale ash by fluidized bed drying. Powder Technol. 2010, 197, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, J.X.; Song, K.; Wang, Z.Y. Cost-effective synthesis of silica aerogels from fly ash via ambient pressure drying. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2010, 356, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazriati, N.; Setyawan, H.; Affandi, S.; Yuwana, M.; Winardi, S. Using bagasse ash as a silica source when preparing silica aerogels via ambient pressure drying. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2014, 400, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadjarodi, A.; Haghverdi, M.; Mohammadi, V. Preparation and characterization of nano-porous silica aerogel from rice husk ash by drying at atmospheric pressure. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, T.B.; Anderson, A.M.; Carroll, M.K. Analysis of a rapid supercritical extraction aerogel fabrication process: Prediction of thermodynamic conditions during processing. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2008, 354, 3685–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; He, X.; Niu, Z.; Huang, T.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Ambient pressure dried shape-controllable sodium silicate based composite silica aerogel monoliths. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 162, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Li, Z.; Gong, L.; Zhang, H. Rapid synthesis of ambient pressure dried monolithic silica aerogels using water as the only solvent. Mater. Lett. 2017, 204, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzov, S.; Danchova, N.; Karakashev, S.I.; Khristov, M.; Ivanova, J.; Ulbikas, J. Preparation and thermal properties of chemically prepared nanoporous silica aerogels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parale, V.G.; Mahadik, D.B.; Mahadik, S.A.; Kavale, M.S.; Rao, A.V.; Wagh, P.B. Wettability study of surface modified silica aerogels with different silylating agents. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Peng, K.C.; Tsai, H.S.; Chen, J.R.; Huang, C.T.; Ho, K.; Lien, W. Preparation of silica aerogel/polyurethane composites for the application of thermal insulation. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, J.L.; Rao, A.V.; Nadargi, D.Y. Study of thermal conductivity and effect of humidity on HMDZ modified TEOS based aerogel dried at ambient pressure. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 50, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.P.; Rao, A.V. Modifying the surface energy and hydrophobicity of the low-density silica aerogels through the use of combinations of surface-modification agents. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Shewale, P.M.; Rao, A.V.; Gurav, J.L.; Rao, A.P. Synthesis and characterization of low density and hydrophobic silica aerogels dried at ambient pressure using sodium silicate precursor. J. Porous Mater. 2009, 16, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, H.Y.; Parale, V.G.; Jung, H.N.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Lim, C.H.; Yang, S.K.; Park, H.H. Role of oxalic acid in structural formation of sodium silicate-based silica aerogel by ambient pressure drying. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 85, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadik, S.A.; Pedraza, F.; Parale, V.G.; Park, H.H. Organically modified silica aerogel with different functional silylating agents and effect on their physico-chemical properties. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2016, 453, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.H.; Wei, Q.; Nie, Z.R.; Cui, S.P.; Liu, S.W.; Li, Q.Y. A rapid and low solvent/silytion agent-consumed synthsis, pore structure and property of silica aerogeis from dislodged sludge. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Z. Preparation of hydrophobic silica aerogel with kaolin dried at ambient pressure. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 501, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ding, Y.L.; Nie, Z.R.; Liu, X.G.; Li, Q.Y. Wettability, pore structure and performance of perfluorodecyl-modified silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Wei, Q.; Cui, S.P.; Nie, Z.R.; Du, M.H.; Li, Q.Y. Hydrophobic silica aerogel derived from wheat husk ash by ambient pressure drying. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, F.; Nie, Z.R.; Song, C.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Q.Y. Highly hydrothermally stable microporous silica membranes for hydrogen separation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 9354–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.H.; Bi, C.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, W.Q. Thermal transport in nano-porous insulation of aerogel: Factors, models and outlook. Energy 2015, 90, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquard, R.; Baillis, D.; Grigorova, V.; Enguehard, F.; Quenard, D.; Levitz, P. Modelling of the conductive heat transfer through nano-structured porous silica materials. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2013, 363, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Maskara, A.; Boes, U. Aerogel-based thermal insulation. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 1998, 225, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajlan, S.A. Measurements of thermal properties of insulation materials by using transient plane source technique. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.W.; Jung, H.H.; Hyun, S.H.; Ahn, Y.S. Effective preparation of crack-free silica aerogels via ambient drying. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples 1–5 are available from the authors. |






| Precursor | Drying Process | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m∙K)) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEOS | SD | 3.93–4.25 | 25–75 | 0.008–0.030 | [6] |
| TMOS | SD | - | 10–25 | 0.021–0.065 | [8] |
| Sodium silicate | APD | 1.42–2.10 | 5–30 | 0.059–0.098 | [10] |
| Oil shale ash | APD | 2.37–2.77 | 13.1–14.1 | - | [13] |
| Fly ash | APD | 0.078–4.875 | 7.69–24.09 | - | [14] |
| Bagasse ash | APD | 0.75–2.13 | 3.40–3.89 | - | [15] |
| Rice husk ash | APD | 0.46–0.78 | 8.3–9.8 | - | [16] |
| Component | SiO2 | MgO | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | SO3 | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (wt %) | 99.37 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Samples | Si:TMCS:HMDS (Molar Ratio) | Pb (g/cm3) | SBET (m2/g) | V (cm3/g) | DP (nm) | λ (W/(m∙K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:1:0 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 372 ± 2 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 18.2 | 0.030 ± 0.001 |
| 2 | 1:0.5:0.5 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 406 ± 4 | 3.5 ± 0.2 | 17.6 | 0.030 ± 0.001 |
| 3 | 1:0.375:0.375 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 410 ± 5 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 18.5 | 0.031 ± 0.001 |
| 4 | 1:0.25:0.25 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 319 ± 2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 14.7 | 0.044 ± 0.002 |
| 5 | 1:0.125:0.125 | - | 457 ± 3 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 7.1 | 0.087 ± 0.001 |
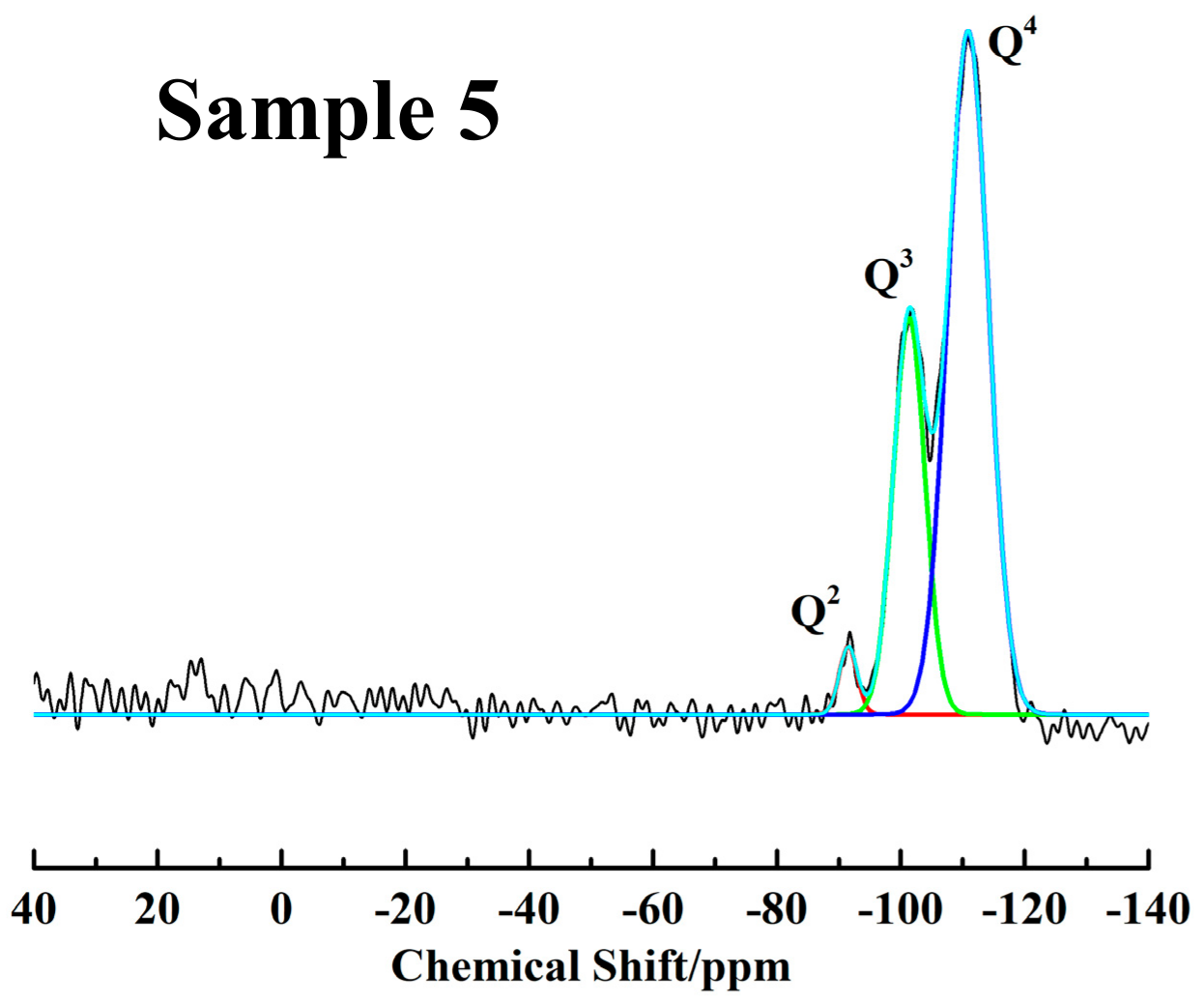
| Sample | IM (mol %) | IQ4 (mol %) | IQ3 (mol %) | IQ2 (mol %) | [OH] (mmol/g) | [CH3] (mmol/g) | WCA (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.9 ± 0.1 | 67.1 ± 0.1 | 14.0 ± 0.1 | 0 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 147.3 ± 1.1 |
| 2 | 18.6 ± 0.1 | 64.2 ± 0.1 | 17.2 ± 0.1 | 0 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 8.5 ± 0.1 | 145.6 ± 1.4 |
| 3 | 16.8 ± 0.1 | 67.6 ± 0.1 | 15.6 ± 0.1 | 0 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 144.2 ± 1.1 |
| 4 | 15.0 ± 0.1 | 64.6 ± 0.1 | 20.4 ± 0.1 | 0 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.1 | 136.3 ± 0.9 |
| 5 | 0 | 66.8 ± 0.1 | 30.3 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Materials/Medium. | Thermal Conductivity * (W/(m∙K)) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Static dry air | 0.025 | [35] |
| Perlite | 0.052–0.056 | [36] |
| Glass fiber | 0.042–0.046 | [36] |
| Rock wool | 0.040–0.049 | [36] |
| Sample 3 | 0.030–0.032 | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cui, S.; Yang, F.; Nie, Z.; Li, Q.; Wei, Q. Preparation of Silica Aerogels by Ambient Pressure Drying without Causing Equipment Corrosion. Molecules 2018, 23, 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081935
Zhu L, Wang Y, Cui S, Yang F, Nie Z, Li Q, Wei Q. Preparation of Silica Aerogels by Ambient Pressure Drying without Causing Equipment Corrosion. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081935
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Lixiao, Yali Wang, Suping Cui, Feihua Yang, Zuoren Nie, Qunyan Li, and Qi Wei. 2018. "Preparation of Silica Aerogels by Ambient Pressure Drying without Causing Equipment Corrosion" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081935
APA StyleZhu, L., Wang, Y., Cui, S., Yang, F., Nie, Z., Li, Q., & Wei, Q. (2018). Preparation of Silica Aerogels by Ambient Pressure Drying without Causing Equipment Corrosion. Molecules, 23(8), 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081935