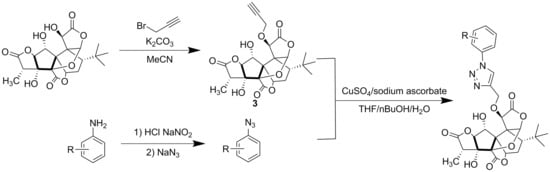
3.1.3. General Procedures for the Preparation of 10-Substituted 1,2,3-triazole-Ginkgolide Derivatives
Sodium ascorbate (0.03 mmol) and CuSO4 (0.01 mmol) were added in single portions to a solution of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide 3, 3′ or 3″ (0.1 mmol) and corresponding azide 4 (0.11 mmol) in 1:1:1 t-BuOH/ H2O/THF (3 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 48 h under an argon atmosphere and then was extracted with EtOAc three times. The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by chromatography (SiO2, PE/EtOAc 1:3 stepwise elution to EtOAc) to afford the appropriate compound 5.
10-O-(1-Phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5a). Following the described procedure, 42.3 mg (73%) of compound 5a were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.798 (1H, s), 7.88 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.50–7.64 (m, 3H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.52 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 6.8 Hz, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.6 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (ddd, J = 14.0 Hz, 13.6 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J =14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.32, 172.51, 170.12, 143.76, 136.46, 129.96 (2C), 128.94, 121.59, 120.23 (2C), 109.68, 98.88, 92.62, 82.47, 78.49, 75.16, 73.77, 71.96, 67.34, 63.00, 48.73, 41.56, 36.54, 31.73, 28.64 (3C), 7.84. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31N3O10 [M + H]+: 582.2082, found 582.2062.
10-O-(1-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5b). Following the described procedure, 21.0 mg (34%) of compound 5b were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.78 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.58–7.71 (m,2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.50 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 5.46 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.33–5.35 (m, 2H), 4.97 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (dd, J = 13.6 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.85 (ddd, J = 14.4 Hz, 13.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz,1H), 1.12 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H), 176.30, 172.47, 170.10, 142.91, 134.30, 131.77, 130.60, 128.52, 128.39, 128.31, 125.43, 109.67, 98.86, 92.58, 82.46, 78.47, 75.25, 73.74, 71.93, 67.32, 63.07, 48.72, 41.55, 36.51, 31.72, 28.65 (3C), 8.57 (s,1H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ7.82, 7.80 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H). HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H30ClN3O10 [M + H]+: 616.1692, found 616.1670.
10-O-(1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5c). Following the described procedure, 40.1 mg (65%) of compound 5c were obtained as method 1, from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3).1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.87 (s, 1H), 8.02 (s, 1H), 7.59–7.91 (m, 3H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.43–5.46 (m, 2H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 4.20 (dd, J = 7.0 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.0 Hz, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 1.86 (ddd, J = 14.2 Hz, 13.4 Hz, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.12(d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.46, 170.08, 143.82, 137.48, 134.20, 131.69, 128.74, 121.91, 120.02, 118.84, 109.66, 98.88, 92.60, 82.47, 78.45, 75.14, 73.75, 71.93, 67.29, 62.90, 48.71, 41.53, 36.51, 31.70, 28.62 (3C), 7.82. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H30ClN3O10 [M + H]+: 616.1692, found 616.1674.
10-O-(1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5d). Following the described procedure, 20.3 mg (33%) of compound 5d were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ8.82 (s,1H), 7.68–7.94 (dd, 4H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.43–5.48 (m, 2H), 5.32–5.33 (m, 2H), 4.92 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.20 (dd, J = 7.0 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.0 Hz, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (ddd, J = 14.4 Hz, 13.2Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.46, 170.08, 143.87, 135.24, 133.19, 129.91 (2C), 121.90 (2C), 121.73, 109.66, 98.87, 92.60, 82.46, 78.45, 75.16, 73.74, 71.92, 67.30, 62.93, 48.70, 41.53, 36.51, 31.70, 28.62 (3C), 7.81. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H30ClN3O10 [M + H]+: 616.1692, found 616.1671.
10-O-(1-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5e). Following the described procedure, 34.5 mg (53%) of compound 5e were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ8.54 (s,1H), 7.68–7.81(m, 3H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.47 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.32–5.54 (m, 2H), 5.24 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 4.99 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.19 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.87 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.13 (dd, J = 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (ddd, J = 14.2 Hz, 13.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.03 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.27, 172.38, 170.07, 143.11, 133.04, 132.58 (2C), 132.42, 129.26 (2C), 125.88, 109.68, 98.82, 92.40, 82.48, 78.45, 75.51, 73.74, 71.91, 67.28, 63.20, 48.68, 41.54, 36.50, 31.74, 28.69 (3C), 7.80. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H29Cl2N3O10 [M + H]+: 650.1303, found 650.1287.
10-O-(1-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5f). Following the described procedure, 29.3 mg (45%) of compound 5f were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.57 (s,1H), 8.02(d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.76(m, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.43–5.48 (m, 2H), 5.33–5.40 (m, 2H), 4.96 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.20 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.8Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (ddd, J = 14.2 Hz, 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.12(d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H).13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.27, 172.44, 170.07, 143.02, 135.51, 133.34, 130.16, 129.64, 129.49, 128.65, 125.51, 109.65, 98.85, 92.58, 82.45, 78.44, 75.27, 73.71, 71.91, 67.30, 63.03, 59.71, 48.69, 41.53, 36.49, 31.71, 28.64 (3C), 7.81. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H29Cl2N3O10 [M + H]+: 650.1303, found 650.1289.
10-O-(1-(3,5-Dichlorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5g). Following the described procedure, 38.3 mg (34%) of compound 5g were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.92 (s,1H), 8.05 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 2H), 7.80 (t, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.44 (d, J = 12.0 Hz,1H), 5.36 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 5.32–5.35 (m, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.20 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.6Hz, 1H), 2.87 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (ddd, J = 14.4 Hz, 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.43, 170.08, 143.90, 138.05, 135.26 (2C), 128.27, 122.22, 118.98, 118.88, 109.66, 98.91, 92.60, 82.49, 78.44, 75.17, 73.75, 71.93, 67.28, 62.84, 48.71, 41.52, 36.51, 31.71, 28.62 (3C), 7.84. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H29Cl2N3O10 [M + H]+: 650.1303, found 650.1287.
10-O-(1-(3-Fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5h). Following the described procedure, 32.4 mg (54%) of compound 5h were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3).1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.16–7.54 (m, 4H), 6.01 (s, 1H), 5.67 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 5.53 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 5.05 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 4.96 (s, 1H), 4.91 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (dd, J = 7.6 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 3.07 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.84 (s, 1H), 2.28 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 2.05 (ddd, J = 16.8 Hz, 10.8 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.98 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.30 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.13 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.46, 170.08, 143.86, 137.64, 131.93, 121.85, 116.14, 115.66, 109.66, 107.83, 107.62, 92.60, 82.47, 78.45, 75.17, 73.75, 71.93, 67.30, 62.92, 48.71, 41.53, 36.51, 31.71, 28.62 (3C), 7.82. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31FN3O10 [M + H]+: 600.1993, found 600.2014.
10-O-(1-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5i). Following the described procedure, 27.9 mg (41%) of compound 5i were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.07 (s,1H), 7.70–8.09 (m, 3H), 6.01 (s, 1H,), 5.65 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 5.52 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 4.97 (s, 1H), 4.91 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 4.38 (dd, J = 7.6 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 3.07 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.98 (s, 1H), 2.28 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 2.04 (ddd, J = 14.0 Hz, 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.95 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.30 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.12 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.27, 172.44, 170.07, 143.99, 135.40, 133.39, 130.69, 128.15, 127.83, 125.51, 122.25, 119.60, 109.66, 98.88, 92.56, 82.47, 78.43, 75.19, 73.74, 71.93, 67.28, 62.84, 48.70, 41.53, 36.50, 31.70, 28.62 (3C), 7.82. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H29ClF3N3O10 [M + H]+: 684.1566, found 684.1544.
10-O-(1-(4-Trifluoromethoxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5j). Following the described procedure, 20.6 mg (31%) of compound 5j were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.83 (s,1H), 8.03 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.43–5.49 (m, 2H), 5.32–5.34 (m, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (ddd, J = 14.2 Hz, 13.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.13(d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.46, 170.08, 148.02, 143.91, 135.30, 122.63 (2C), 122.30 (2C), 121.97, 121.00, 109.66, 98.87, 92.61, 82.46, 78.45, 75.17, 73.74, 71.93, 67.30, 62.94, 48.71, 41.53, 36.51, 31.70, 28.62 (3C), 7.81. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H30F3N3O11 [M + H]+: 666.1905, found 666.1887.
10-O-(1-(3,5-Ditrifluoromethylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5k). Following the described procedure, 32.3 mg (45%) of compound 5k were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.14 (s, 1H), 8.62 (s, 2H), 8.31 (s, 1H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.21 (s, 1H), 5.47 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.35 (s, 1H), 5.30–5.33 (m, 2H), 4.96 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (dd, J = 12.8 Hz, 4.0 Hz,1H), 1.71–1.87 (m, 2H), 1.13 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H), 1.03 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.44, 170.07, 144.01, 137.73, 132.00 (2C), 131.73 (2C), 123.81, 122.64, 121.64, 121.07, 109.68, 98.90, 92.54, 82.49, 78.42, 75.22, 73.77, 71.94, 62.78, 48.71, 41.53, 36.50, 31.71, 28.63 (3C), 7.83. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H29F6N3O10 [M + H]+: 718.1830, found 718.1808.
10-O-(1-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5l). Following the described procedure, 35.0 mg (55%) of compound 5l were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.75 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.62 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.58 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (ddd, J = 14.4 Hz, 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 1.33 (s, 9H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.01 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.29, 172.50, 170.08, 150.60, 143.60, 134.13, 126.64 (2C), 121.49, 119.98 (2C), 109.65, 98.84, 92.60, 82.43, 78.46, 75.09, 73.73, 71.93, 67.32, 62.97, 48.71, 41.54, 36.51, 34.50, 31.70, 30.95 (3C), 28.62 (3C), 7.80. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C33H39N3O10 [M + H]+: 638.2708, found 638.2689.
10-O-(1-(3-Bromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5m). Following the described procedure, 38.3 mg (58%) of compound 5m were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.87 (s, 1H), 8.14 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (dd, J = 8.2 Hz, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.43–5.46 (m, 2H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.20 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (ddd, J = 14.4 Hz, 13.2 Hz, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.01 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.28, 172.46, 170.08, 143.79, 137.55, 131.90, 131.66, 122.77, 122.43, 121.92, 119.23, 109.66, 98.88, 92.60, 82.47, 78.45, 75.13, 73.75, 71.93, 67.29, 62.89, 48.71, 41.53, 36.51, 31.70, 28.62 (3C), 7.83. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31BrN3O10 [M + H]+: 660.1193, found 660.1207.
10-O-(1-(2-Methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5n). Following the described procedure, 39.3 mg (66%) of compound 5n were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.46 (s, 1H), 7.52–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.46–7.41 (m, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20(s, 1H), 5.57 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.35–5.33 (m, 2H), 4.97 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.89 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.15 (s, 3H), 2.13 (dd, J = 13.7, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.91–1.80 (m, 1H), 1.75 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.03 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.83, 173.02, 170.63, 143.35, 136.56, 133.54, 131.90, 130.45, 127.53, 126.45, 125.28, 110.16, 99.33, 93.08, 82.94, 79.01, 75.62, 74.23, 72.43, 67.83, 63.57, 49.20, 41.90, 37.01, 32.22, 29.14 (3C), 17.84, 8.32. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H34N3O10 [M + H]+: 596.2244, found 596.2249.
10-O-(1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5o). Following the described procedure, 22.1 mg (37%) of compound 5o were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.59 (s, 1H), 8.51 (s, 1H), 7.60 (dd, J = 7.9, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (ddd, J = 8.2, 7.5, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (td, J = 7.8, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.64 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.34–5.32 (m, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (dd, J = 7.2, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.92–2.84 (m, 1H), 2.12 (dd, J = 13.3 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.3 Hz, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.74, 171.96, 169.55, 149.06, 141.97, 129.74, 124.60, 124.12, 123.73, 118.97, 116.45, 109.07, 98.23, 91.99, 81.83, 77.91, 74.66, 73.13, 71.35, 66.74, 62.61, 48.10, 40.98, 35.93, 31.15, 28.07 (3C), 7.23. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H32N3O11 [M + H]+: 598.2037, found 598.2051.
10-O-(1-(2-Cyanophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5p). Following the described procedure, 25.5 mg (42%) of compound 5p were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.74 (s, 1H), 8.16 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (td, J = 7.9, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.90–7.86 (m, 1H), 7.79 (td, J = 7.7, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.48 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 2H), 5.37–5.30 (m, 2H), 4.99 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.92–2.85 (m, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.5, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.86 (dt, J = 13.7, 7.0 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.81, 172.97, 170.63, 144.21, 138.10, 135.41, 135.30, 130.92, 126.18, 124.91, 116.22, 110.16, 107.43, 99.41, 93.18, 82.97, 79.00, 75.76, 74.22, 72.41, 67.82, 63.48, 49.20, 42.04, 37.01, 32.22, 29.13 (3C), 8.35. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H31N4O10 [M + H]+: 607.2040, found 607.2050.
10-O-(1-(3-Methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5q). Following the described procedure, 26.8 mg (45%) of compound 5q were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.78 (s, 1H), 7.72 (t, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.63 (m, 1H), 7.50 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.50 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.22–4.18 (m, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.42 (s, 3H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.72, 171.93, 169.53, 143.06, 139.14, 135.83, 129.16, 128.93, 120.98, 120.04, 116.73, 109.08, 98.26, 92.00, 81.87, 77.89, 74.53, 73.16, 71.35, 66.72, 62.36, 48.11, 40.97, 35.93, 31.13, 28.04 (3C), 20.32, 7.25. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H34N3O10 [M + H]+: 596.2244, found 596.2255.
10-O-(1-(3-Isopropylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5r). Following the described procedure, 34.3 mg (55%) of compound 5r were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.81 (s, 1H), 7.75 (t, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.68–7.67 (m, 1H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.50 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.54 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 5.34 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 2H), 4.94 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 3.06–2.99 (m, 1H), 2.89 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.27 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.83, 173.02, 170.63, 150.14, 144.04, 136.99, 130.39, 127.50, 122.12, 118.67, 118.27, 110.16, 99.35, 93.06, 82.94, 78.99, 75.60, 74.25, 72.44, 67.81, 63.41, 49.19, 42.04, 37.00, 33.87, 32.20, 29.11 (3C), 24.11 (2C), 8.32. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C32H38N3O10 [M + H]+: 624.2557, found 624.2565.
10-O-(1-(3-Ethylcarboxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5s). Following the described procedure, 17.6 mg (27%) of compound 5s were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.40 (s, 1H), 8.18 (dd, J = 8.1, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.08 (dd, J = 7.8, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (s, 1H), 6.21 (s, 1H), 5.48 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.46 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.36–5.31 (m, 2H), 4.95 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.38 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 4.22 (dd, J = 7.1, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.89 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.36 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.81, 173.00, 170.61, 165.21, 144.41, 137.17, 132.08, 131.16, 129.77, 125.17, 122.46, 120.88, 110.16, 99.37, 93.11, 82.96, 78.98, 75.64, 74.23, 72.43, 67.80, 63.39, 61.85, 49.20, 42.04, 37.00, 32.21, 29.12 (3C), 14.59, 8.34. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C32H36N3O12 [M + H]+: 654.2299, found 654.2309.
10-O-(1-(3-Carboxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5t). Following the described procedure, 15.6 mg (25%) of compound 5t were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 13.45 (s, 1H), 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.38 (s, 1H), 8.16–8.14 (m, 1H), 8.11–7.99 (m, 1H), 7.76 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.21 (s, 1H), 5.47–5.44 (m, 2H), 5.35–5.28 (m, 2H), 4.94 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.89 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.81, 173.01, 170.62, 166.75, 144.21, 136.99, 133.01, 130.95, 129.88, 124.72, 122.30, 120.85, 110.07, 99.24, 92.99, 82.94, 78.93, 75.54, 74.21, 72.38, 67.74, 63.34, 49.20, 42.04, 36.74, 32.20, 29.12 (3C), 8.26. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H32N3O12 [M + H]+: 626.1986, found 626.1998.
10-O-(1-(4-Methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5u). Following the described procedure, 31.5 mg (53%) of compound 5u were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.75 (s, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.42 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 6.46 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.53 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 2H), 4.92 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 175.72, 171.94, 169.52, 142.94, 137.81, 133.34, 129.57 (2C), 120.81, 119.40 (2C), 109.01, 98.21, 91.97, 81.84, 77.84, 74.37, 73.03, 71.26, 66.65, 62.28, 47.99, 40.81, 35.83, 30.92, 28.04 (3C), 19.99, 7.01. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H34N3O10 [M + H]+: 596.2244, found 596.2251.
10-O-(1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5v). Following the described procedure, 20.8 mg (34%) of compound 5v were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.69 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 7.15 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.57 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 4.92 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.83, 173.02, 170.63, 159.92, 144.00, 130.31, 122.40 (2C), 121.94, 115.42 (2C), 110.16, 99.34, 93.08, 82.93, 79.00, 75.43, 74.13, 72.34, 67.75, 63.27, 55.84, 49.09, 41.96, 36.94, 32.01, 28.95 (3C), 8.19. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H34N3O11 [M + H]+: 612.2193, found 612.2205.
10-O-(1-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5w). Following the described procedure, 13.5 mg (22%) of compound 5w were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.69 (s, 1H), 7.93–7.89 (m, 2H), 7.49–7.44 (m, 2H), 6.64 (s, 1H), 6.19 (s, 1H), 5.63 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H), 5.46 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.37 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 5.31 (s, 1H), 4.97 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 4.65 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.24 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.14 (dd, J = 13.5 Hz, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.86 (td, J = 13.9 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.75 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.15 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.03 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.01, 172.98, 170.81, 162.28 (d, JC-F = 246.4 Hz), 144.27, 133.33 (d, JC-F = 2.5 Hz), 123.18 (d, JC-F = 8.9 Hz, 2C), 122.14, 117.30 (d, JC-F = 23.3 Hz, 2C), 110.18, 99.41, 93.08, 82.95, 79.16, 75.63, 74.28, 72.44, 67.85, 63.41, 49.21, 42.02, 36.95, 32.11, 29.03 (3C), 7.94. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31FN3O10 [M + H]+: 600.1993, found 600.2010.
10-O-(1-(4-Bromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5x). Following the described procedure, 18.5 mg (28%) of compound 5x were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.83 (s, 1H), 7.88–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.85–7.81 (m, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.47 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.80, 172.99, 170.60, 144.39, 136.14, 133.35 (2C), 122.63 (2C), 122.20, 122.09, 110.16, 99.36, 93.10, 82.96, 78.97, 75.65, 74.23, 72.42, 67.79, 63.33, 49.02, 41.91, 36.81, 32.10, 28.98 (3C), 8.26. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31BrN3O10 [M + H]+: 660.1193, found 660.1208.
10-O-(1-(4-Trifluoromethylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole)ginkgolide B (5y). Following the described procedure, 20.1 mg (31%) of compound 5y were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.95 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.02 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.21 (s, 1H), 5.47 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.35–5.32 (m, 2H), 4.95 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.89 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.81, 172.98, 170.61, 144.59, 139.72, 129.34 (q, JC-F = 32.1 Hz), 127.78 (q, JC-F = 3.6 Hz, 2C), 124.27 (q, J = 270.5 Hz), 122.50, 121.21 (2C), 110.16, 99.38, 93.12, 82.97, 78.97, 75.68, 74.24, 72.42, 67.80, 63.39, 49.19, 42.04, 37.01, 32.21, 29.12 (3C), 8.34. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H31F3N3O10 [M + H]+: 650.1962, found 650.1967.
10-O-(1-(4-Nitrophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5z). Following the described procedure, 21.9 mg (35%) of compound 5z were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.00 (s, 1H), 8.49–8.47 (m, 2H), 8.23–8.20 (m, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.20 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H), 5.46 (t, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.40 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.36–5.32 (m, 2H), 4.95 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.93–2.84 (m, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.79, 172.97, 170.60, 147.38, 144.82, 141.16, 126.13 (2C), 122.76, 121.30 (2C), 110.16, 99.39, 93.14, 82.98, 78.96, 75.74, 74.23, 72.41, 67.79, 63.37, 49.19, 42.04, 37.01, 32.22, 29.13 (3C), 8.35. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31N4O12 [M + H]+: 627.1938, found 627.1948.
10-O-(1-(4-Methylcarboxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5aa). Following the described procedure, 18.5 mg (29%) of compound 5aa were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3), 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.20–8.16 (m, 2H), 8.09–8.06 (m, 2H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.21 (s, 1H), 5.46 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.42 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.36–5.28 (m, 2H), 4.94 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (s, 3H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.80, 172.98, 170.60, 165.79, 144.58, 140.11, 131.53 (2C), 130.08, 122.40, 120.57 (2C), 110.16, 99.38, 93.12, 82.97, 78.97, 75.71, 74.23, 72.42, 67.79, 63.41, 52.64, 49.03, 42.04, 36.70, 32.12, 28.90 (3C), 8.29. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H34N3O12 [M + H]+: 640.2142, found 640.2154.
10-O-(1-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5bb). Following the described procedure, 16.3 mg (26%) of compound 5bb were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.88 (s, 1H), 8.16 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.16 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.50 (s, 1H), 6.19 (s, 1H), 5.49–5.44 (m, 2H), 5.35–5.32 (m, 2H), 4.94 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.84, 172.98, 170.50, 166.86, 144.40, 139.78, 131.60 (2C), 131.29, 122.20, 120.28 (2C), 109.95, 99.28, 93.09, 82.95, 79.01, 75.55, 74.25, 72.32, 67.76, 63.29, 49.16, 41.92, 36.87, 32.10, 29.11 (3C), 8.25. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H32N3O12 [M + H]+: 626.1986, found 626.1998.
10-O-(1-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5cc). Following the described procedure, 22.5 mg (35%) of compound 5cc were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.79 (s, 1H), 7.05 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 6.63 (t, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (s, 1H), 6.18 (s, 1H), 5.52 (s, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 5.43 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.34 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 5.32 (s, 1H), 4.92 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.22 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (s, 6H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.87, 173.00, 170.66, 161.70 (2C), 144.08, 138.40, 122.15, 110.17, 100.86, 99.37, 98.98 (2C), 93.05, 82.94, 79.03, 75.60, 74.26, 72.43, 67.81, 63.37, 56.21 (2C), 49.20, 42.03, 36.98, 32.17, 29.09 (3C), 8.31. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H36N3O12 [M + H]+: 642.2299, found 642.2308.
10-O-(1-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5dd). Following the described procedure, 29.2 mg (46%) of compound 5dd were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.83 (s, 1H), 8.20–8.18 (m, 1H), 8.00–7.88 (m, 1H), 7.75–7.60 (m, 1H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.46–5.41 (m, 2H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 4.93 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.23–4.17 (m, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (dd, J = 13.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.83 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.73 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H30ClFN3O10 [M + H]+: 634.1604, found 634.1619.
10-O-(1-(3-Pyridinyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5ee). Following the described procedure, 45.7 mg (67%) of compound 5ee were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.13 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 8.88 (s, 1H), 8.71 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 8.35–8.30 (m, 1H), 7.68 (dd, J = 8.4, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 6.49 (s, 1H), 6.21 (s, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 5.47 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.34 (d, J = 3.2 Hz, 2H), 4.95 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.12 (dd, J = 13.5 Hz, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 1.85 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.74 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.03 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.80, 172.99, 170.59, 150.41, 144.45, 141.84, 133.59, 128.59, 125.10, 122.47, 110.07, 99.32, 92.92, 82.84, 78.99, 75.45, 73.96, 72.07, 67.61, 63.29, 48.94, 42.04, 36.71, 31.75, 29.12 (3C), 8.16. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C28H31N4O10 [M + H]+: 583.2040, found 583.2056.
10-O-(1-Benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5ff). Following the described procedure, 42.8 mg (72%) of compound 5ff were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.17 (s, 1H), 7.41–7.30 (m, 5H), 6.47 (s, 1H), 6.17 (s, 1H), 5.64 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 5.61 (s, 2H), 5.35–5.31 (m, 2H), 5.27 (s, 1H), 4.84 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.62 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.17 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.09 (dd, J = 12.9 Hz, 3.9 Hz, 1H), 1.77 (td, J = 13.8 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 1.70 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.98 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.83, 172.99, 170.62, 143.50, 136.17, 129.26 (2C), 128.69, 128.48 (2C), 123.01, 109.77, 98.98, 92.78, 82.56, 78.85, 75.51, 74.03, 72.28, 67.54, 63.16, 53.19, 48.92, 41.92, 36.77, 31.99, 28.81 (3C), 8.15. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H34N3O10 [M + H]+: 596.2244, found 596.2266.
10-O-(((Anthracen-2-yloxy)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide B (5gg). Following the described procedure, 43.5 mg (70%) of compound 5gg were obtained from 46.2 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide B (3). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.22 (s, 1H), 7.93 (dd, J = 7.8 Hz, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (td, J = 7.7 Hz, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (td, J = 7.7 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 7.9 Hz, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (s, 1H), 6.17 (s, 1H), 5.83 (s, 2H), 5.58 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.36 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.31 (d, J = 3.9 Hz, 1H), 5.28 (s, 1H), 4.86 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.61 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.17 (dd, J = 7.2 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 4.03 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.87 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.50 (s, 2H), 2.09 (dd, J = 13.0 Hz, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 1.99 (s, 2H), 1.83–1.68 (m, 2H), 1.18 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 0.98 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.91, 172.97, 170.70, 143.52, 138.80, 134.36, 133.90, 130.22, 129.89, 124.13, 117.45, 111.79, 110.15, 99.32, 82.87, 79.06, 75.62, 74.19, 72.42, 67.81, 63.54, 60.34, 51.71, 49.15, 42.02, 36.92, 32.12, 29.04(3C), 8.25. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H32N4O10 [M + H]+: 621.2198, found 621.2170.
10-O-(1-Phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide A (5′a). Following the described procedure, 36.2 mg (64%) of compound 5′a were obtained from 44.6 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide A (3′). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.51 (s, 1H), 7.48 (s, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 16.7 Hz, 2H), 6.45–6.32 (m, 1H), 6.15 (s, 1H), 5.36 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 5.23 (s, 1H), 4.95 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 4.89 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 1H), 4.83 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, 7.3 Hz, 1H), 3.85–3.71 (m, 2H), 3.62–3.56 (m, 1H), 3.17 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 2.95 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.75 (dd, J = 15.1 Hz, 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.04 (dd, J = 13.6 Hz, 5.0 Hz, 1H), 2.01–1.91 (m, 2H), 1.91–1.80 (m, 2H), 1.79–1.70 (m, 3H), 1.70–1.63 (m, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.98, 173.22, 171.05, 144.45, 130.41(2C), 122.91, 120.67(2C), 110.14, 100.81, 87.96, 86.50, 85.31, 75.74, 68.63, 66.81, 66.19, 63.35, 49.16, 36.78, 36.45, 33.62, 32.19, 29.17(3C), 23.75, 8.59. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31N3O9 [M + H]+: 566.2133, found 566.2111.
10-O-(1-(2-Methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide A (5′n). Following the described procedure, 40.0 mg (69%) of compound 5′n were obtained from 44.6 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide A (3′). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.51 (s, 1H), 7.52–7.48 (m, 2H), 7.44 (dd, J = 2.2, 1.0 Hz, 2H), 6.40 (s, 1H), 6.15 (s, 1H), 5.40–5.33 (m, 2H), 5.23 (s, 1H), 4.95 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 4.89 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 1H), 4.83 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 3.82–3.75 (m, 2H), 3.60 (s, 1H), 3.17 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 2.95 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.75 (dd, J = 15.1 Hz, 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.15 (s, 3H), 1.97 (s, 1H), 1.78–1.69 (m, 3H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.97, 173.19, 171.05, 143.65, 136.71, 133.55, 131.87, 130.34, 127.50, 126.51, 126.03, 110.13, 100.79, 97.64, 87.94, 86.50, 85.35, 75.74, 67.49, 63.53, 49.07, 41.66, 40.47, 36.78, 32.20, 29.16(3C), 17.87, 8.59. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H33N3O9 [M + H] +: 580.2197, found 580.2266.
10-O-(1-(2-Cyanophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide A (5′p)., Following the described procedure, 34.3 mg (58%) of compound 5′p were obtained from 446 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide A (3′). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.82 (s, 1H), 8.16 (dd, J = 7.9, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (td, J = 7.9, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (td, J = 7.7, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.41 (s, 1H), 6.16 (s, 1H), 5.41 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 1H), 5.39–5.35 (m, 2H), 5.26 (s, 1H), 4.97–4.87 (m, 2H), 4.82 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 2.95 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.79–2.72 (m, 1H), 1.40 (s, 3H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.04 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 174.85, 171.03, 168.75, 142.36, 133.25, 133.10, 128.73, 128.69, 124.10, 123.44, 110.75, 108.04, 108.01, 98.77, 95.53, 85.83, 84.40, 83.30, 73.77, 66.57, 64.74, 61.33, 47.05, 39.68, 34.68, 34.37, 31.51(3C), 8.07. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H30N4O9 [M + H] +: 591.2093, found 591.2062.
10-O-(1-Benzyl -1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide A (5′ff). Following the described procedure, 39.4 mg (68%) of compound 5′ff were obtained from 44.6 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide A (3′). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.25 (s, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 8.0, 6.4 Hz, 2H), 7.34–7.22 (m, 3H), 6.40 (s, 1H), 6.12 (s, 1H), 5.61 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H), 5.24 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 5.16 (s, 1H), 4.92 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 4.82 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 4.76 (d, J = 11.6 Hz, 1H), 4.03 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.94 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.65 (dd, J = 15.1 Hz, 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.50 (p, J = 1.8 Hz, 3H), 2.05–1.99 (m, 1H), 1.99 (s, 1H), 1.90 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 1.84 (dd, J = 15.1, 8.4 Hz, 1H), 1.70 (dd, J = 14.1, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.17 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 1.12 (dd, J = 7.1, 4.0 Hz, 3H), 0.98 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.20, 173.13, 171.32, 136.27, 129.28(2C), 128.74, 128.39, 124.82, 110.16, 110.03, 101.11, 88.10, 86.53, 85.77, 75.61, 68.76, 66.93, 63.50, 63.40, 53.55, 53.35, 49.15, 40.86, 36.82, 32.04, 29.02(3C), 8.71. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H33N3O9 [M + H] +: 580.2297, found 580.2267.
10-O-(((Anthracen-2-yloxy)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide A (5′gg). Following the described procedure, 36.9 mg (61%) of compound 5′gg were obtained from 44.6 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide A (3′). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.29 (s, 1H), 7.92 (dd, J = 7.7, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.82–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.57 (td, J = 7.7, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.44–7.26 (m, 1H), 6.40 (s, 1H), 6.13 (s, 1H), 5.83 (s, 2H), 5.27 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 1H), 5.18 (s, 1H), 4.90 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 4.83 (dd, J = 8.2 Hz, 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.78 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 1H), 4.03 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 19H), 2.95 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.66 (dd, J = 15.2 Hz, 7.2 Hz, 1H), 2.51 (p, J = 1.8 Hz, 4H), 1.90–1.82 (m, 2H), 1.72 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, 4.7 Hz, 2H), 1.40 (s, 3H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 0.99 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.93, 173.14, 170.81, 143.66, 139.26, 134.29, 133.85, 129.91, 129.68, 125.44, 117.45, 111.68, 110.09, 100.82, 87.90, 86.50, 85.33, 75.74, 68.63, 66.81, 63.47, 60.22, 51.47, 49.03, 40.89, 36.40, 32.14, 29.10(3C), 8.56. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H32N4O9 [M + H] +: 605.2249, found 605.2219.
10-O-(1-Phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide C (5″a). Following the described procedure, 31.1 mg (52%) of compound 5″a were obtained from 47.8 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide C (3″). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.83 (s, 1H), 7.88 (dt, J = 7.9, 1.1 Hz, 2H), 7.63 (dd, J = 8.8, 7.2 Hz, 3H), 7.53 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.23 (s, 1H), 5.64 (t, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 5.46 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.32 (s, 1H), 4.99 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 2H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 4.32 (s, 1H), 4.17 (dd, J = 7.0 Hz, 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.98–2.78 (m, 1H), 1.99 (s, 1H), 1.57 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 1H), 1.43–1.35 (m, 2H), 1.32–1.27 (m, 1H), 1.24 (s, 2H), 1.17 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 1.10 (s, 3H), 1.07 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.79, 172.94, 170.86, 162.28, 144.14, 136.89, 130.50, 122.14, 120.73, 110.04, 99.08, 93.14, 82.93, 75.47, 74.09, 67.05, 64.03, 63.52, 60.84, 49.35, 42.03, 35.12, 32.08, 19.09(3C), 14.32, 8.34. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C29H31N3O11 [M + H] +: 598.2039, found 598.2003.
10-O-(1-(2-Methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide C (5″n). Following the described procedure, 28.7 mg (47%) of compound 5″n were obtained from 47.8 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide C (3″). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.47 (s, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 7.44 (d, J = 1.4 Hz, 2H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.23 (s, 1H), 5.68 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H), 5.66 (dd, J = 6.2 Hz, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 5.49–5.43 (m, 1H), 5.32 (s, 1H), 5.02–5.00 (m, 2H), 5.00–4.96 (m, 1H), 4.65–4.61 (m, 1H), 4.17 (dd, J = 7.0 Hz, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 2.16 (s, 3H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 1.10 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 6H), 1.08 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.81, 172.95, 170.89, 143.24, 136.51, 133.52, 131.93, 130.49, 127.57, 126.41, 125.27, 110.03, 99.05, 93.12, 82.92, 79.36, 75.41, 74.07, 69.35, 67.06, 64.05, 60.27, 49.38, 42.03, 32.10, 21.23(3C), 17.86, 8.34. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H33N3O11 [M + H] +: 612.2195, found 612.2157.
10-O-(1-(2-Cyanophenyl) -1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide C (5″p). Following the described procedure, 24.3 mg (39%) of compound 5″p were obtained from 47.8 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide C (3″). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.78 (s, 1H), 8.17 (dd, J = 7.7, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (td, J = 7.8 Hz, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (dd, J = 8.2 Hz, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (td, J = 7.7 Hz, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 6.23 (s, 1H), 5.64 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 5.60 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 1H), 5.32 (s, 1H), 5.03 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 1H), 5.01 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 4.63 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 4.17 (dd, J = 7.0 Hz, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 3.97 (ddd, J = 12.5 Hz, 6.1 Hz, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 1.57 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 1H), 1.13 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.08 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.78, 172.90, 170.87, 143.98, 135.47, 126.10, 124.92, 116.26, 110.05, 107.36, 99.11, 93.18, 82.95, 79.34, 75.46, 74.18, 74.07, 67.04, 64.02, 63.40, 60.25, 49.37, 42.03, 32.10, 27.01, 22.55, 21.24(3C), 8.35. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H30N4O11 [M + H] +: 623.1991, found 623.1956.
10-O-(1-Benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide C (5″ff). Following the described procedure, 26.9 mg (44%) of compound 5″ff were obtained from 47.8 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide C (3″). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.19 (s, 1H), 7.40–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.32 (m, 3H), 6.46 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.73 (s, 1H), 5.62 (s, 3H), 5.35 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.25 (s, 1H), 4.97 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 4.87 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 4.61 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.13 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 2.84 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 1.55 (dd, J = 12.5 Hz, 5.2 Hz, 1H), 1.17 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 1.10–1.09 (m, 2H), 1.03 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.81, 172.93, 170.87, 143.32, 136.15, 129.29(2C), 128.75, 128.56, 123.60, 110.01, 98.96, 93.02, 82.83, 79.33, 75.34, 74.01, 67.04, 64.00, 63.56, 60.27, 53.51, 49.30, 42.03, 32.04, 29.07, 21.23(3C), 8.27. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H33N4O11 [M + H]+: 612.2195, found 612.2156.
10-O-(((Anthracen-2-yloxy)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole) ginkgolide C (5″gg). Following the described procedure, 32.5 mg (51%) of compound 5″gg were obtained from 47.8 mg (0.1 mmol) of 10-O-propargylated ginkgolide C (3″). 1H-NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.25 (s, 1H), 7.93 (dd, J = 7.7, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (td, J = 7.7 Hz, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (td, J = 7.7 Hz, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 7.8 Hz, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 6.46 (s, 1H), 6.20 (s, 1H), 5.84 (s, 2H), 5.70 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 5.62 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 5.37 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, 1H), 5.26 (s, 1H), 4.98 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 4.90 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 1H), 4.61 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 4.13 (dd, J = 7.1 Hz, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (dt, J = 12.4 Hz, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.84 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 2.50 (s, 3H), 1.55 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 1H), 1.18 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H), 1.04 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 176.83, 172.94, 170.92, 143.37, 138.90, 134.36, 133.88, 130.11, 129.85, 124.19, 117.47, 111.82, 110.02, 98.99, 82.84, 79.33, 75.38, 74.15, 74.01, 67.05, 64.01, 63.53, 60.27, 51.69, 49.33, 42.03, 32.04, 21.22 (3C), 8.28. HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H32N4O11 [M + H]+: 637.2148, found 637.2117