SnO2 Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: Influence of Al Incorporation on the Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SnO:Al | Al-doped tin oxide |
| ITO | Sn-doped indium oxide |
| FTO | F-doped tin oxide |
| AZO | Al-doped zinc oxide |
| TCO | Transparent conducting oxide |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive spectroscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| EDX | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared Spectroscopy |
| ALD | Atomic layer deposition |
| CVD | Chemical vapor deposition |
| EPMA | Electron probe micro-analyzer |
| SIMS | Secondary ion mass spectroscopy |
| AES | Auger electron spectroscopy |
| RBS | Rutherford back scattering |
References
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginley, D.S.; Bright, C. Transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 2000, 25, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, Ç.; Zunger, A. Origins of coexistence of conductivity and transparency in SnO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 095501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, K.; Major, S.; Pandya, D. Transparent conductors—A status review. Thin Solid Film. 1983, 102, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göpel, W.; Schierbaum, K.D. SnO2 sensors: Current status and future prospects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmakov, A.; Klenov, D.; Lilach, Y.; Stemmer, S.; Moskovits, M. Enhanced gas sensing by individual SnO2 nanowires and nanobelts functionalized with Pd catalyst particles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snaith, H.J.; Ducati, C. SnO2-based dye-sensitized hybrid solar cells exhibiting near unity absorbed photon-to-electron conversion efficiency. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Jennings, J.R.; Koh, Z.Y.; Wang, Q. Carrier generation and collection in CdS/CdSe-sensitized SnO2 solar cells exhibiting unprecedented photocurrent densities. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3172–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcántara, R.; Fernández-Madrigal, F.; Pérez-Vicente, C.; Tirado, J.; Jumas, J.C.; Olivier-Fourcade, J. Preparation, sintering, and electrochemical properties of tin dioxide and Al-doped tin dioxides obtained from citrate precursors. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3044–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Lou, X.W. SnO2-based nanomaterials: Synthesis and application in lithium-ion batteries. Small 2013, 9, 1877–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yan, J.; Liao, M.; Wu, L.; Fang, X. Ultrahigh external quantum efficiency from thin SnO2 nanowire ultraviolet photodetectors. Small 2011, 7, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, S.; Fonstad, C. Defect structure and electronic donor levels in stannic oxide crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 4618–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjerna, B.; Olsson, E.; Granqvist, C. Optical and electrical properties of radio frequency sputtered tin oxide films doped with oxygen vacancies, F, Sb, or Mo. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 3797–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Brezesinski, T.; Antonietti, M.; Smarsly, B. Ordered mesoporous Sb-, Nb-, and Ta-doped SnO2 thin films with adjustable doping levels and high electrical conductivity. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, Y. Defect chemistry of the metal cation defects in the p-and n-doped SnO2 nanocrystalline films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 18097–18109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Fuchigami, J.; Kishikawa, M.; Seiyama, T. Interactions of tin oxide surface with O2, H2O and H2. Surf. Sci. 1979, 86, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAleer, J.; Moseley, P.; Norris, J.; Williams, D.; Taylor, P.; Tofield, B. Tin oxide based gas sensors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1987, 17, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, G.; Consonni, V.; Puyoo, E.; Bellet, D. High performance ZnO-SnO2: F nanocomposite transparent electrodes for energy applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14096–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyu, G.K.; Hunka, J.; Roussel, H.; Brötz, J.; Bellet, D.; Klein, A. Electrical Properties of Low-Temperature Processed Sn-Doped In2O3 Thin Films: The Role of Microstructure and Oxygen Content and the Potential of Defect Modulation Doping. Materials 2019, 12, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, M.; Jia, J.; Shigesato, Y.; Klein, A. Comparative study of sputter-deposited SnO2 films doped with antimony or tantalum. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 2016, 253, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, M.; Fuchs, A.; Bayer, T.J.; Rachut, K.; Schnell, P.; Deyu, G.K.; Klein, A. Defect Modulation Doping. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1807906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körber, C.; Ágoston, P.; Klein, A. Surface and bulk properties of sputter deposited undoped and Sb-doped SnO2 thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 139, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormunda, M.; Fischer, D.; Hertwig, A.; Beck, U.; Sebik, M.; Esser, N. Preparation of pulsed DC magnetron deposited Fe-doped SnO2 coatings. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2016, 213, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.; Bierwagen, O.; Tsai, M.; Speck, J. Electron transport properties of antimony doped SnO2 single crystalline thin films grown by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 093704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Su, C.; Chuu, D. Growth of highly oriented tin oxide thin films by laser evaporation deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1990, 57, 1879–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, J.; Schweizer, H.; Kern, W. Chemical Vapor Deposition of Antimony-Doped Tin Oxide Films Formed from Dibutyl Tin Diacetate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1976, 123, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Choi, J.M.; Lim, J.H.; Park, J.; Park, J.S. A study on the thermoelectric properties of ALD-grown aluminum-doped tin oxide with respect to nanostructure modulations. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 1978–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Rey, G.; Roussel, H.; Doisneau, B.; Blanquet, E.; Bellet, D. Preferential orientation of fluorine-doped SnO2 thin films: The effects of growth temperature. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneaux, J.; Cachet, H.; Froment, M.; Messad, A. Correlation between structural and electrical properties of sprayed tin oxide films with and without fluorine doping. Thin Solid Film. 1991, 197, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Rouvière, J.L.; Consonni, V.; Roussel, H.; Rapenne, L.; Pernot, E.; Muñoz-Rojas, D.; Klein, A.; Bellet, D. High quality epitaxial fluorine-doped SnO2 films by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis: Structural and physical property investigation. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, W.; Gee, M.A. Mechanics of film formation during the spray pyrolysis of tin oxide. Thin Solid Film. 1988, 165, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Ray, S.; Manna, I. Effect of Al doping on structural, optical and electrical properties of SnO2 thin films synthesized by pulsed laser deposition. Philos. Mag. 2014, 94, 3507–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M.; Shokooh-Saremi, M. The influence of Al doping on the electrical, optical and structural properties of SnO2 transparent conducting films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, K.; Thirumurugan, K. Type inversion and certain physical properties of spray pyrolysed SnO2: Al films for novel transparent electronics applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Khan, S.; Ghosh, P.; Mitra, M.; Chattopadhyay, K. Effect of Al doping on the conductivity type inversion and electro-optical properties of SnO2 thin films synthesized by sol-gel technique. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tamaki, J.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. Promotion of tin oxide gas sensor by aluminum doping. Talanta 1991, 38, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, G.; Ternon, C.; Modreanu, M.; Mescot, X.; Consonni, V.; Bellet, D. Electron scattering mechanisms in fluorine-doped SnO2 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 183713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammelselg, V.; Aarik, J.; Aidla, A.; Kasikov, A.; Heikinheimo, E.; Peussa, M.; Niinist, L. Composition and thickness determination of thin oxide films: comparison of different programs and methods. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1999, 14, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messad, A.; Bruneaux, J.; Cachet, H.; Froment, M. Analysis of the effects of substrate temperature, concentration of tin chloride and nature of dopants on the structural and electrical properties of sprayed SnO2 films. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 5095–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharrami, F.; Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.; Azimi-Juybari, H.; Shokooh-Saremi, M. Structural, electrical, optical, thermoelectrical and photoconductivity properties of the SnO2–Al2O3 binary transparent conducting films deposited by the spray pyrolysis method. Phys. Scr. 2011, 85, 015703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Cho, E.; Lee, H.S.; Seol, K.S.; Han, S. Comparative study of electronic structures and dielectric properties of alumina polymorphs by first-principles methods. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 245110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponja, S.D.; Parkin, I.P.; Carmalt, C.J. Synthesis and material characterization of amorphous and crystalline (α-) Al2O3 via aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102956–102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurugan, K.; Ravichandran, K.; Mohan, R.; Snega, S.; Jothiramalingam, S.; Chandramohan, R. Effect of solvent volume on properties of SnO2:Al films. Surf. Eng. 2013, 29, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, A.R.; Ashcroft, N.W. Vegard’s law. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 43, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, L.V.U.H. Untersuchungen über Mischkristalle und Legierungen. Z. Für Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 1928, 67, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agashe, C.; Takwale, M.; Marathe, B.; Bhide, V. Structural properties of SnO2:F films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Sol. Energy Mater. 1988, 17, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo, G.; Moreno, L.; De la Cruz, W.; Teheran, P. Preparation and characterization of SnO2 thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis from SnCl2 and SnCl4 precursors. Thin Solid Film. 1994, 252, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, M.; Torriani, I.; Constantino, C. Influence of the substrate on the crystalline properties of sprayed tin dioxide thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 1986, 74, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, E.; Fabbri, E.; Bi, L.; Rupp, J.L.; Lippert, T.; Pergolesi, D.; Traversa, E. Effect of dopant–host ionic radii mismatch on acceptor-doped barium zirconate microstructure and proton conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9739–9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumoorthi, M.; Prakash, J.T.J. Effect of F doping on physical properties of (211) oriented SnO2 thin films prepared by jet nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 89, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, G.F.; Cavallaro, A.; McComb, D.W.; Skinner, S.J.; Kilner, J.A. The effects of lattice strain, dislocations, and microstructure on the transport properties of YSZ films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 14319–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, G.X. Quantitative measurement of preferred orientation in rolled uranium bars. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1952, 43, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.V. Structure evolution during processing of polycrystalline films. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 2000, 30, 159–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, W. The FTIR studies of SnO2:Sb (ATO) films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1204–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Mishra, N.; Kumar, A.; Bhatt, M.; Chaudhary, P.; Singh, R. Structural investigation of nanomixed xSnO2–Al2O3 synthesized by sol–gel route. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, T.J.; Young, D.L.; Li, X. Characterization of transparent conducting oxides. Mrs Bull. 2000, 25, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Pique, A. Transparent conducting Sb-doped SnO2 thin films grown by pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, A.; Dal Maschio, R.; Dire, S.; Raccanelli, A. Electrical conductivity of tin oxide films prepared by the sol-gel method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1990, 121, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.A. The nature of semiconductivity in polycrystalline tin oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1972, 119, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ágoston, P.; Albe, K.; Nieminen, R.M.; Puska, M.J. Intrinsic n-type behavior in transparent conducting oxides: A comparative hybrid-functional study of In2O3, SnO2, and ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 245501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, J.E.; Williamson, B.A.; Whittles, T.J.; Birkett, M.; Featherstone, T.J.; Peng, N.; Abbott, A.; Farnworth, M.; Cheetham, K.J.; Warren, P.; et al. Self-compensation in transparent conducting F-doped SnO2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1701900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, C.G. Electrical properties and gas-sensing behavior of SnO2 films prepared by chemical vapor deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 2408–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferron, J.; Arce, R. Anomalous incorporation of fluorine in tin oxide films produced with the pyrosol method. Thin Solid Films 1991, 204, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K. Past achievements and future challenges in the development of optically transparent electrodes. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Mientus, R. Carrier transport in polycrystalline transparent conductive oxides: A comparative study of zinc oxide and indium oxide. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischbier, M.V.; Wardenga, H.F.; Weidner, M.; Bierwagen, O.; Jia, J.; Shigesato, Y.; Klein, A. Influence of dopant species and concentration on grain boundary scattering in degenerately doped In2O3 thin films. Thin Solid Films 2016, 614, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
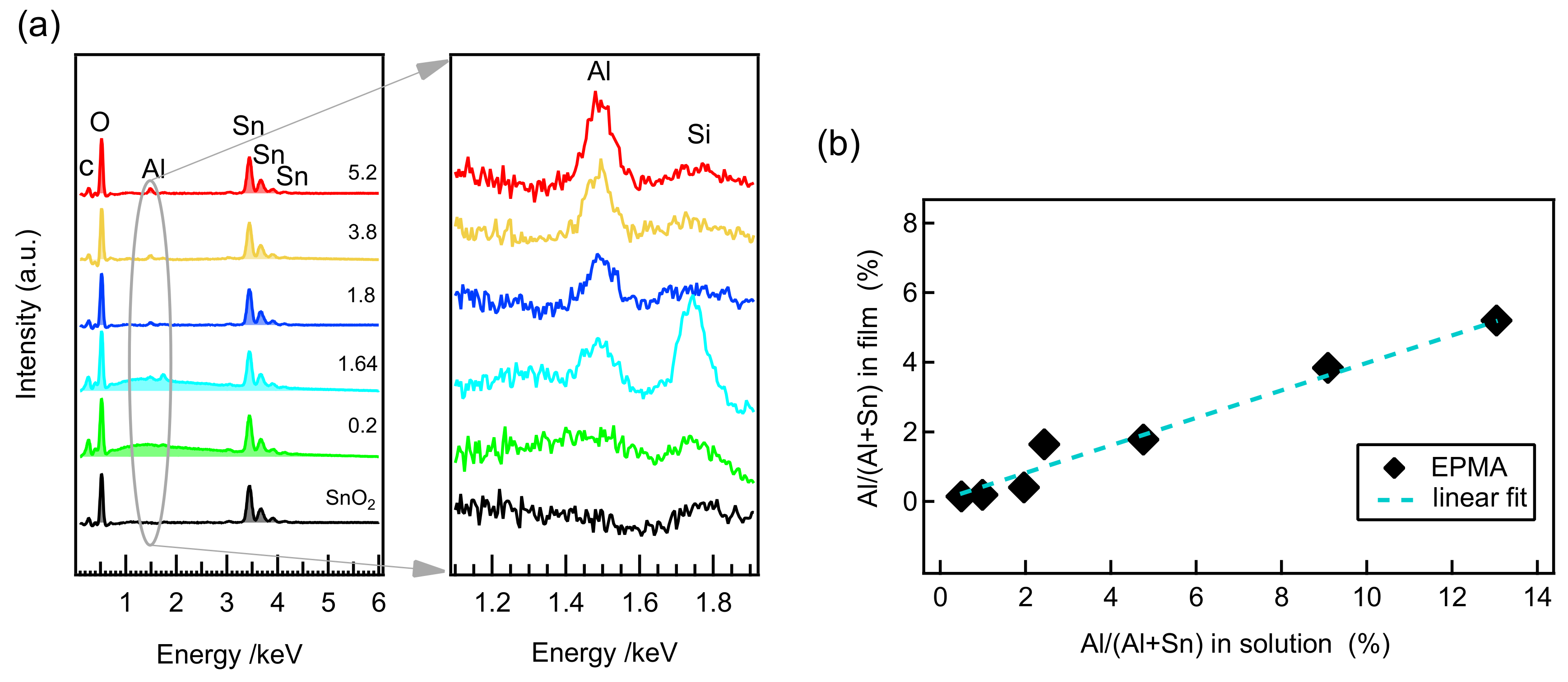
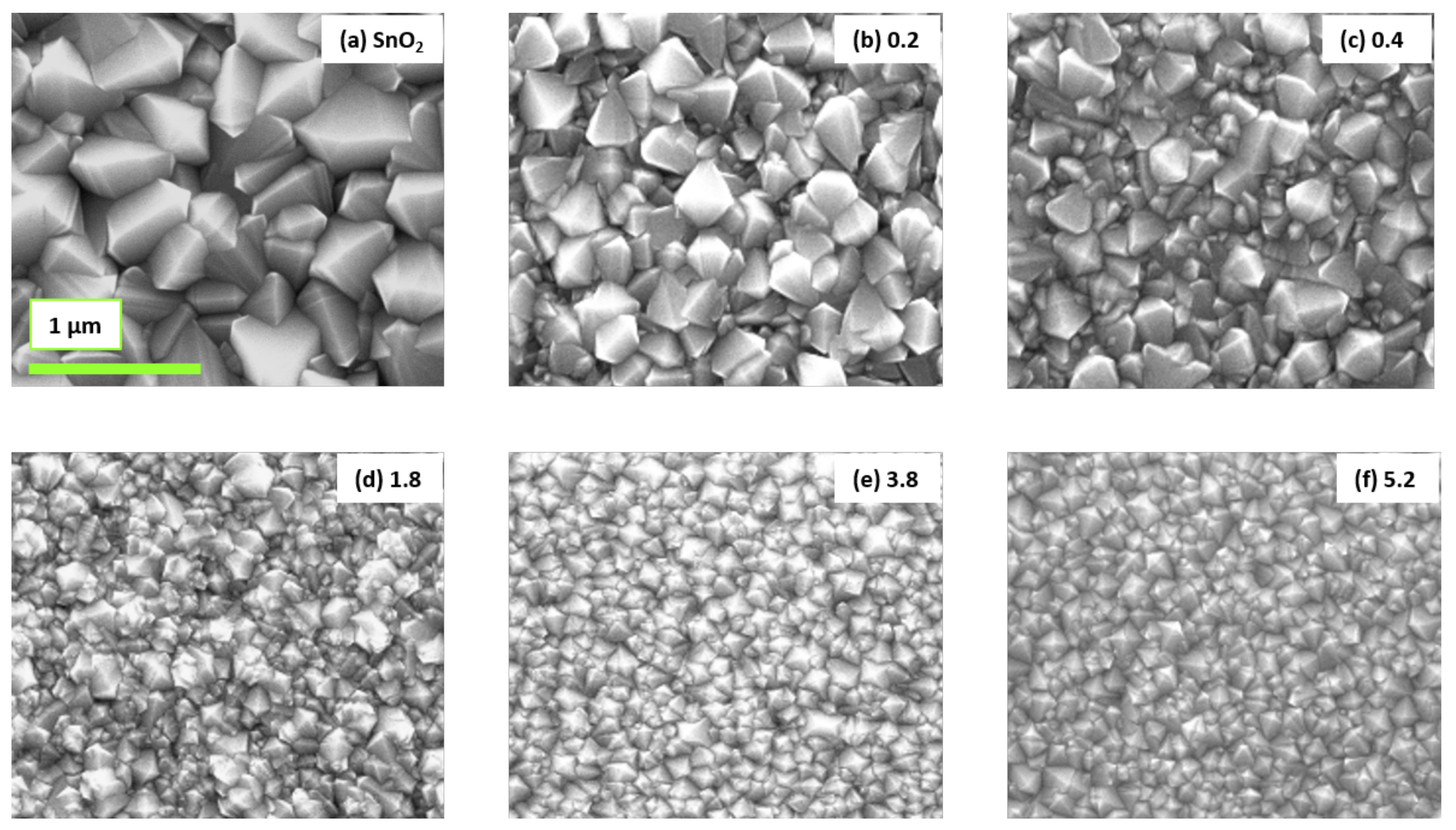
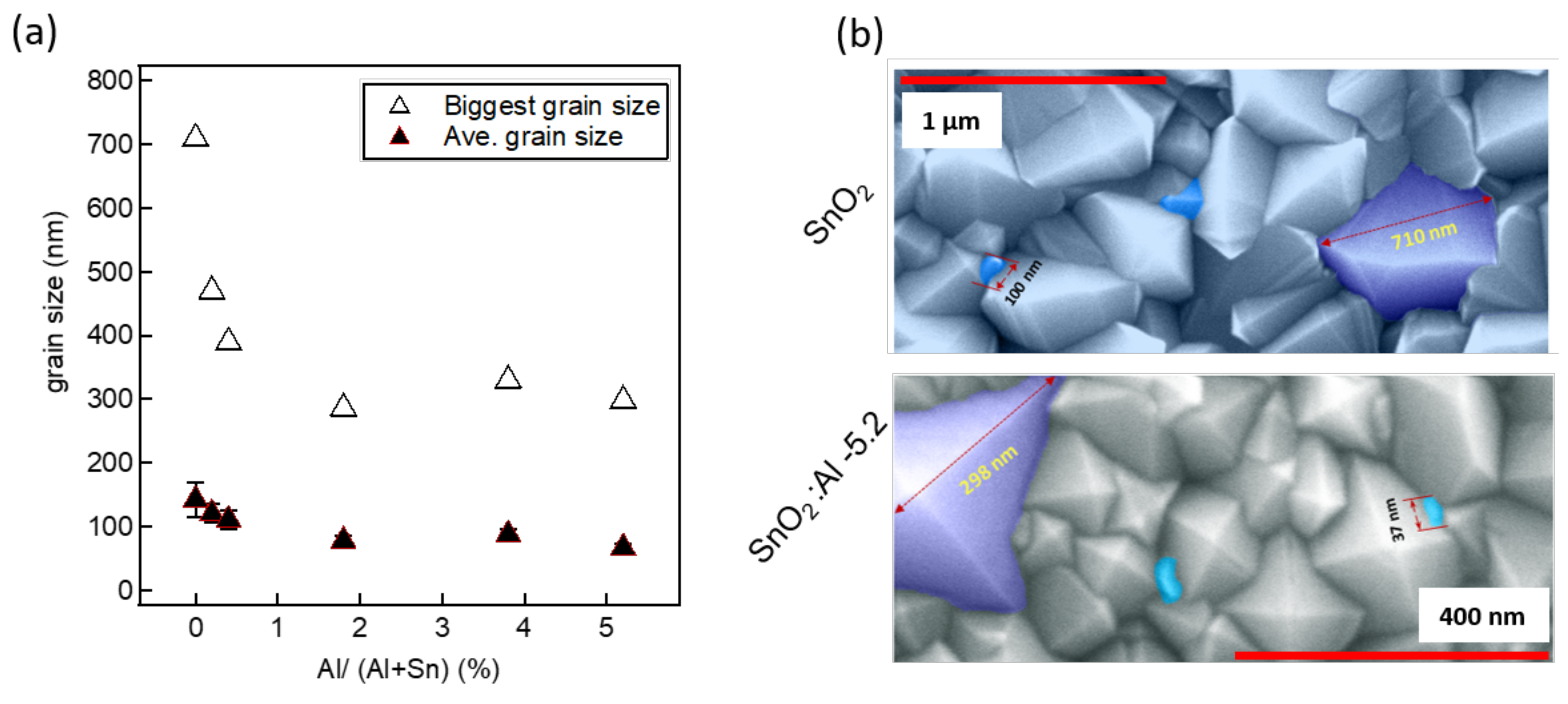
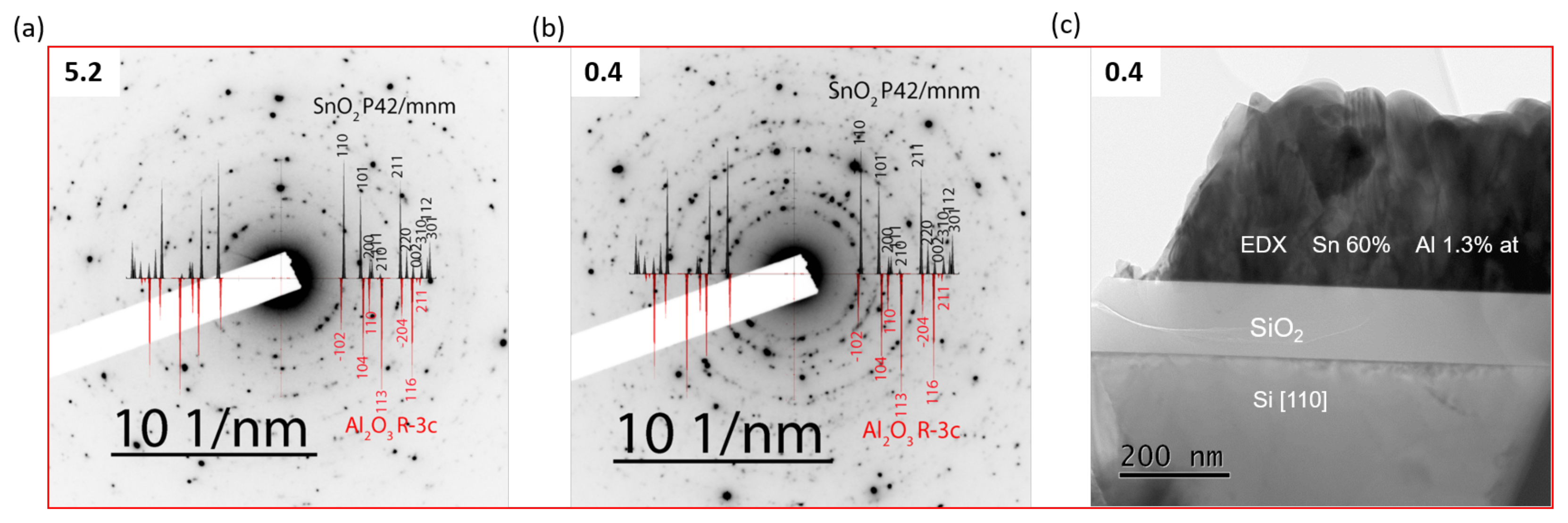
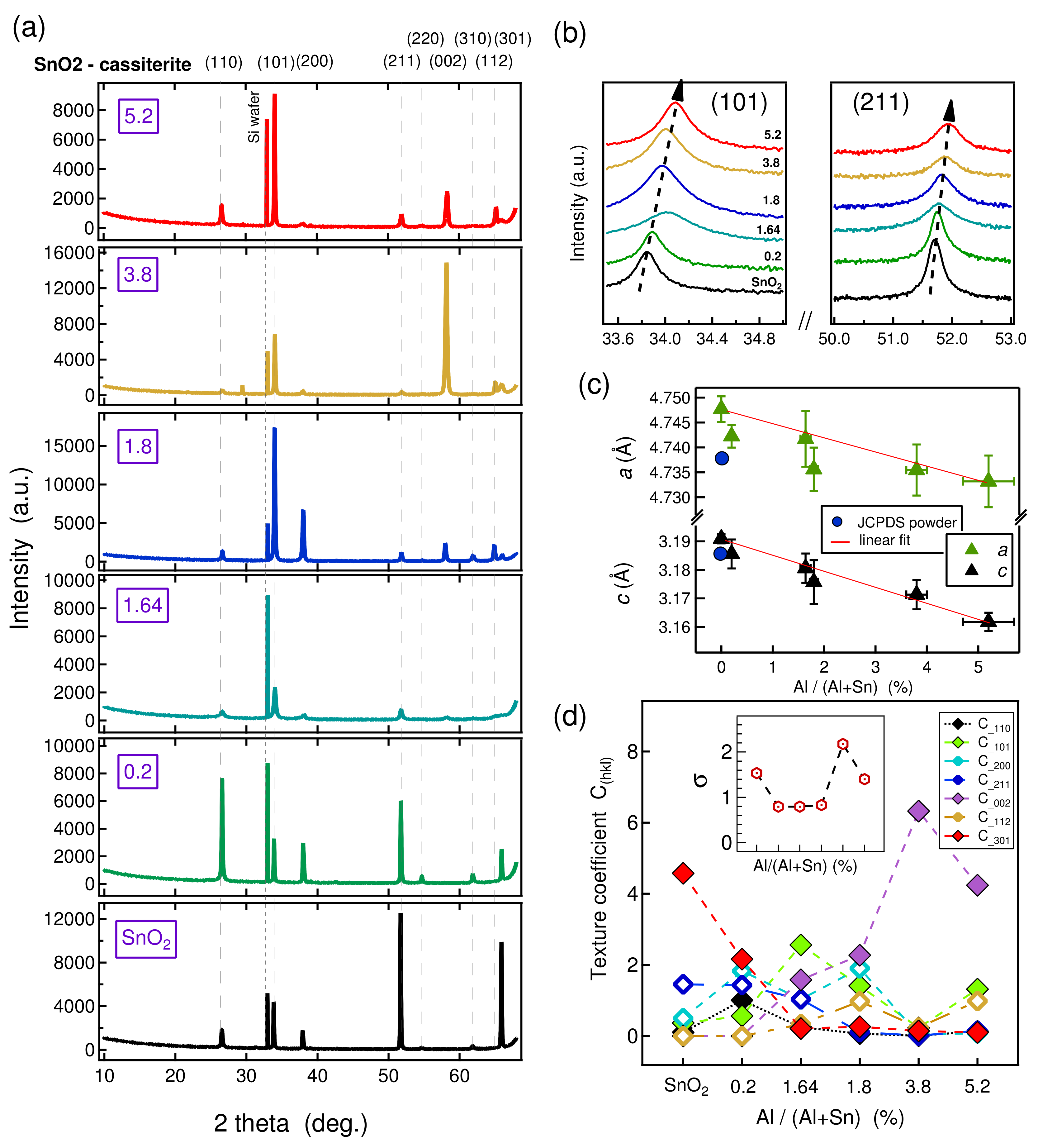
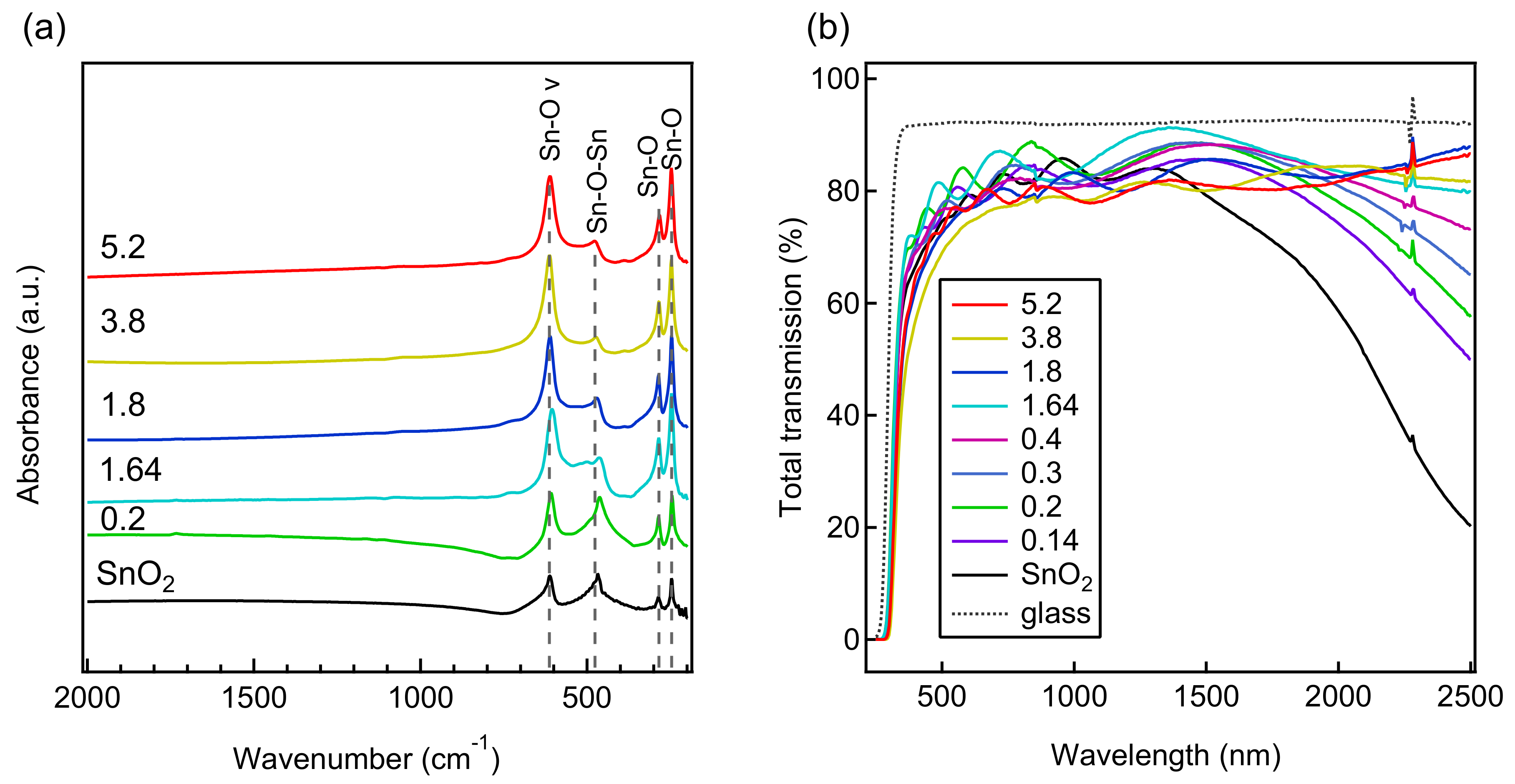
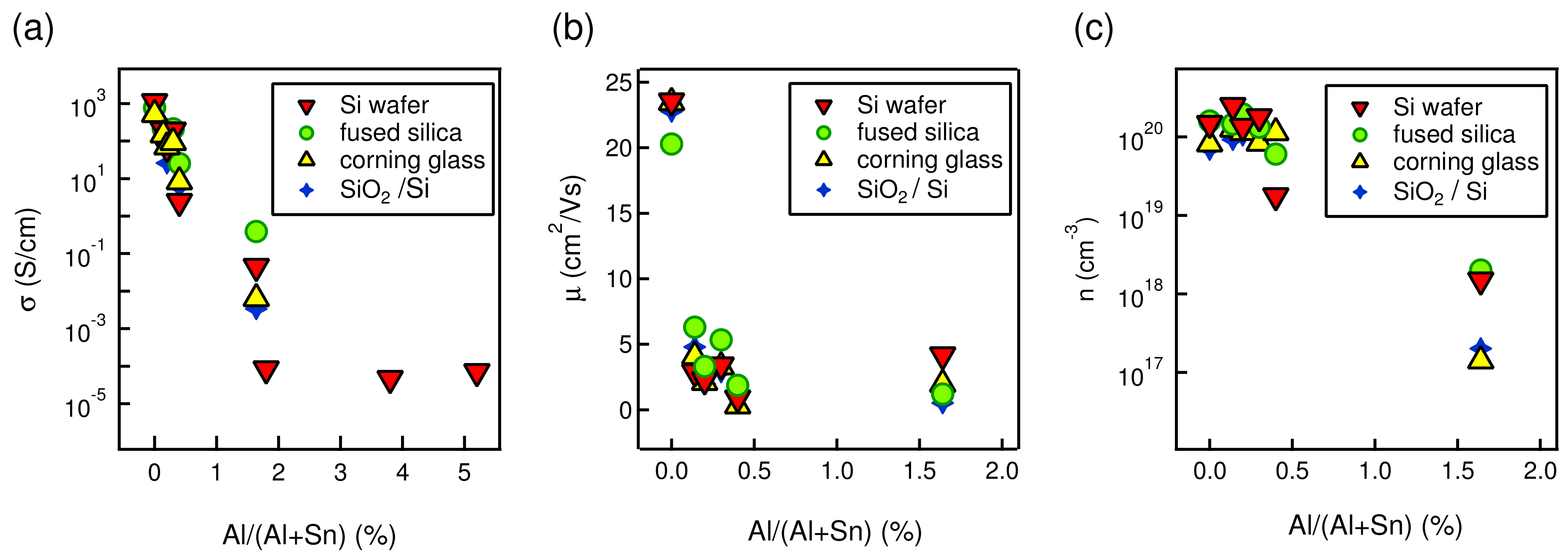
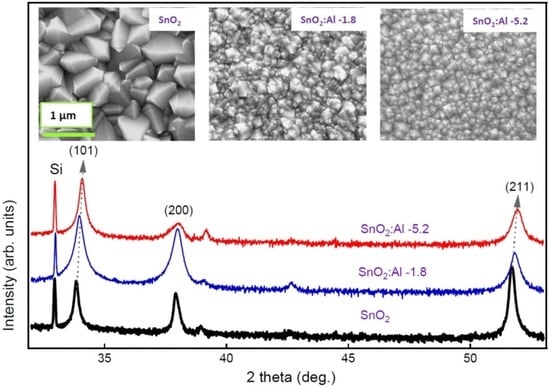
| Al/(Al+Sn) Solution | Al/(Al+Sn) Film | Film Thickness | Deposition Time | Deposition Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (nm) | (min) | (nm/min) |
| 0 | - | 670 | 45 | 15 |
| 0.5 | 0.15 | 260 | 25 | 10.4 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 340 | 30 | 11.3 |
| 1.37 | 0.3 | 260 | 25 | 10.4 |
| 1.96 | 0.4 | 290 | 25 | 11.6 |
| 2.44 | 1.64 ± 0.08 | 200 | 30 | 6.7 |
| 4.76 | 1.8 ± 0.08 | 660 | 45 | 14.66 |
| 9.1 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 800 | 45 | 17.7 |
| 13.04 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 580 | 45 | 13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deyu, G.K.; Muñoz-Rojas, D.; Rapenne, L.; Deschanvres, J.-L.; Klein, A.; Jiménez, C.; Bellet, D. SnO2 Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: Influence of Al Incorporation on the Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152797
Deyu GK, Muñoz-Rojas D, Rapenne L, Deschanvres J-L, Klein A, Jiménez C, Bellet D. SnO2 Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: Influence of Al Incorporation on the Properties. Molecules. 2019; 24(15):2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152797
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeyu, Getnet Kacha, David Muñoz-Rojas, Laetitia Rapenne, Jean-Luc Deschanvres, Andreas Klein, Carmen Jiménez, and Daniel Bellet. 2019. "SnO2 Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: Influence of Al Incorporation on the Properties" Molecules 24, no. 15: 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152797
APA StyleDeyu, G. K., Muñoz-Rojas, D., Rapenne, L., Deschanvres, J.-L., Klein, A., Jiménez, C., & Bellet, D. (2019). SnO2 Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis: Influence of Al Incorporation on the Properties. Molecules, 24(15), 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152797