Physicochemical Aspects and Sensory Profiles as Various Potential Factors for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha Produced from Rhamnus heterophylla Oliv.
Abstract
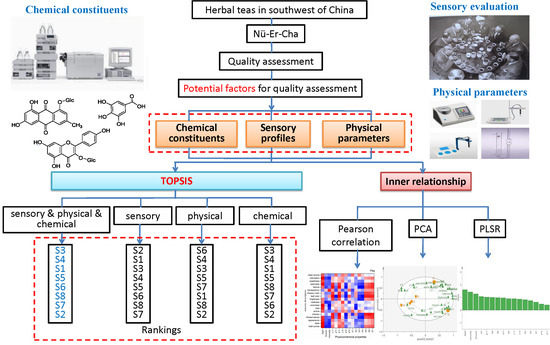
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis on Sensory Profiles, Physical Parameters and Chemical Constituents of Nü-Er-Cha
2.1.1. Sensory Profiles, a Potential Factor for the Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha
2.1.2. Physical Parameters, Another Potential Factor for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha
2.1.3. Chemical Constituents, the Potential Factor for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha
2.2. The Inner Relationship among Physical Parameters, Chemical Constituents and Sensory Profiles Based On Multiple Statistics Analysis Approaches
2.2.1. The Analysis Based on Pearson Correlation Coefficients
2.2.2. The Analysis Based On PCA
2.2.3. The Analysis Based On PLSR
2.3. Comprehensive Evaluation of Nü-Er-Cha by TOPSIS Method
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Sensory Evaluation of Nü-Er-Cha
3.4. Physicochemical Measurements
3.4.1. Viscosity, Conductivity, pH and Color
3.4.2. Establishment of HPLC Fingerprint and HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS Analysis
3.5. TOPSIS Comprehensive Evaluation Method
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, L.; Li, X.B.; Tian, D.Q.; Fang, X.P.; Yu, Y.M.; Zhu, H.Q.; Ge, Y.Y.; Ma, G.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Xiao, W.F.; et al. Antioxidant properties and color parameters of herbal teas in China. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 87, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Cunningham, A.B.; Towns, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, J.W.; Yang, X.F. A billion cups: The diversity, traditional uses, safety issues and potential of Chinese herbal teas. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 222, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.Q.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, P.G. Systematic research on Chinese non-camellia tea. Mod. Chin. Med. 2013, 15, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonte, T.T.; Kock, H.L.D. Descriptive sensory evaluation of cooked stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.) leaves and leaf infusions: Effect of using fresh or oven-dried leaves. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 110, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Bian, M.X.; Mi, R.F.; Hu, X.S.; Wu, J.H. Quality identification and evaluation of Pu-erh teas of different grade levels and various ages through sensory evaluation and instrumental analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.Y. The qualitative and quantitative assessment of tea quality based on E-nose, E-tongue and E-eye combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, C.; Yang, R.J.; Zheng, T.T.; Zhao, M.M.; Ma, L.; Yan, L. Comparison of volatile profiles and bioactive components of sun-dried Pu-erh tea leaves from ancient tea plants on Bulang Mountain measured by GC-MS and HPLC. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2019, 20, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teresa, H.; Yolanda, A.; Miguel, R.H.; Elena, B.; Vanesa, B.; Nuria, M.S.; Silvia, M.A.; María, D.D.C.; María, A.M.C. Teas and herbal infusions as sources of melatonin and other bioactive non-nutrient components. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.C.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.Y.; Niu, Y.W.; Xiao, Z.B. Evaluation of the synergism among volatile compounds in Oolong tea infusion by odour threshold with sensory analysis and E-nose. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.M. Effects of solution viscosity on perceived saltiness and sweetness. Percept. Psychophy. 1980, 28, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, J.A.; Fan, Z.H. Influence of green tea soup pH on its color and anti-oxidative activity. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 11, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Shi, Z.P. The Evaluation and Analysis of Tea, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.F.; Zhang, Y.N.; Du, Q.Z.; Chen, J.X.; Yuan, H.B.; Xu, Y.Q. Effect of Ca2+ concentration on the tastes from the main chemicals in green tea infusions. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attributes Decision Making Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Cai, Z.Q.; Cai, W.; Ji, T.; Pan, P. Comprehensive Evaluation on Medicinal Quality of Platycodon grandiflorus from different origin by TOPSIS Model. Ginseng Res. 2019, 31, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, O.; Atalar, I.; Mortas, M.; Saricaoglu, F.T.; Yazici, F. Application of TOPSIS methodology to determine optimum hazelnut cake concentration and high pressure homogenization condition for hazelnut milk production based on physicochemical, structural and sensory properties. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, G.M.; Guo, Z.Q.; Lv, H.N.; She, D.M. New flavonoid glycosides from Elsholtzia rugulosa Hemsl. Molecules 2009, 14, 4190–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, G.M.; Wang, D.; Zeng, S.F.; Yang, C.R.; Zhang, Y.J. New phenylethanoids glycosides and sugar esters from Ku-Ding-Cha, a herbal tea produced from ligustrum purpurascens. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, C476–C481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, T.; Chang, Y.L.; Fan, S.S.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.P.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.R.; et al. Correlation analysis between HPLC fingerprint and free radical-scavenging activity of Rhamnus heterophylla Oliv. Chin. J. Exper. Trad. Med. Formulae 2018, 20, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, Z. Research progress in influencing factors of crude tea color. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2017, 7, 2687–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.Z.; Chen, P.; Harnly, J.M. New phenolic components and chromatographic profiles of green and fermented teas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8130–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xia, T.; Gao, L.P.; Zhao, C.; Dai, Q.Y.; Li, Z. Study on the determination of flavonols and its glycosides and their effects on the color of green tea infusion. Food Ferment. Ind. 2009, 35, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, H.; Naes, T. Multivariate Calibration; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Chichester, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z. Food Sensory Inspection Technology, 1st ed.; China Quality and Standards Publishing & Media Company: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.F.; Liang, Z.S.; Shan, C.J.; Viernstein, H.; Unger, F. Comprehensive evaluation of natural antioxidants and antioxidant potentials in Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. spinosa (bunge) Hu ex H. F. Chou fruits based on geographical origin by TOPSIS method. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |





| Samples | DpH B | Dcond. C (μs/cm) | Viscosity (m2/s) | Color | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves D | Infusions E | ||||||||
| L*1 | a*1 | b*1 | L*2 | a*2 | b*2 | ||||
| S1 | 0.74 ± 0.05 a | 47 ± 12 cd | 1.53 ± 0.19 b | 33.29 ± 0.01 ab | 2.78 ± 0.02 a | 19.02 ± 0.01 c | 98.32 ± 0.00 a | 0.59 ± 0.00 abc | 6.08 ± 0.00 c |
| S2 | 0.65 ± 0.04 b | 40 ± 7 d | 1.53 ± 0.05 b | 34.05 ± 0.01 ab | 2.10 ± 0.02 c | 18.52 ± 0.04 d | 98.08 ± 0.00 ab | 0.69 ± 0.01 abc | 6.28 ± 0.01 bc |
| S3 | 0.61 ± 0.02 bc | 41 ± 6 cd | 1.56 ± 0.09 ab | 43.28 ± 0.02 ab | 1.22 ± 0.00 f | 26.76 ± 0.05 a | 97.51 ± 0.00 abc | −2.69 ± 0.01 bc | 13.19 ± 0.02 abc |
| S4 | 0.57 ± 0.02 c | 56 ± 8 cd | 1.57 ± 0.04 ab | 43.41 ± 0.00 a | −0.58 ± 0.01 h | 24.82 ± 0.02 b | 95.73 ± 0.01 bc | −2.54 ± 0.01 bc | 18.35 ± 0.04 a |
| S5 | 0.59 ± 0.02 bc | 61 ± 7 bc | 1.55 ± 0.06 ab | 33.34 ± 0.01 ab | 1.09 ± 0.02 g | 17.59 ± 0.02 f | 96.07 ± 0.00 abc | 0.32 ± 0.00 abc | 14.95 ± 0.02 abc |
| S6 | 0.60 ± 0.01 bc | 113 ± 6 a | 1.58 ± 0.33 ab | 36.35 ± 0.01 ab | 1.59 ± 0.01 e | 17.61 ± 0.03 f | 95.33 ± 0.00 c | 0.88 ± 0.01 ab | 17.58 ± 0.02 ab |
| S7 | 0.50 ± 0.01 c | 77 ± 5 b | 1.56 ± 0.05 ab | 32.55 ± 0.01 ab | 2.44 ± 0.02 b | 18.08 ± 0.03 e | 97.60 ± 0.00 abc | 0.72 ± 0.00 abc | 7.49 ± 0.00 abc |
| S8 | 0.43 ± 0.02 d | 66 ± 3 bc | 1.60 ± 0.03 a | 28.68 ± 0.42 b | 1.78 ± 0.02 d | 16.04 ± 0.03 g | 96.88 ± 0.00 abc | 2.03 ± 0.00 a | 8.18 ± 0.01 abc |
| Common Peaks | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.5926 | 5.0868 | 0.2053 | 0.3683 | 2.1660 | 3.9654 | 1.5900 | 3.0771 |
| X2 | 0.0290 | 0.1588 | 0.0348 | 0.0314 | 0.0812 | 0.1189 | 0.1600 | 0.2555 |
| X3 | 0.7450 | 1.5302 | 0.1738 | 0.1919 | 1.3710 | 2.3854 | 1.4628 | 2.2161 |
| X4 | 0.6424 | 1.4100 | 0.0536 | 0.0662 | 1.5070 | 2.7684 | 1.6495 | 2.0251 |
| X5 | 0.0650 | 0.0987 | 0.0736 | 0.0651 | 0.0627 | 0.1103 | 0.0867 | 0.1200 |
| X6 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| X7 | 0.2055 | 0.2393 | 0.1535 | 0.1906 | 0.1574 | 0.2434 | 0.1593 | 0.2050 |
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 0.696 | 0.801 | 0.829 | 0.893 | 0.810 | 0.910 | 0.849 | 0.888 |
| S2 | 0.696 | 1 | 0.400 | 0.514 | 0.910 | 0.879 | 0.806 | 0.906 | 0.915 |
| S3 | 0.801 | 0.400 | 1 | 0.988 | 0.536 | 0.427 | 0.561 | 0.467 | 0.548 |
| S4 | 0.829 | 0.514 | 0.988 | 1 | 0.618 | 0.518 | 0.627 | 0.556 | 0.634 |
| S5 | 0.893 | 0.910 | 0.536 | 0.618 | 1 | 0.950 | 0.953 | 0.975 | 0.989 |
| S6 | 0.810 | 0.879 | 0.427 | 0.518 | 0.950 | 1 | 0.948 | 0.953 | 0.963 |
| S7 | 0.910 | 0.806 | 0.561 | 0.627 | 0.953 | 0.948 | 1 | 0.964 | 0.971 |
| S8 | 0.849 | 0.906 | 0.467 | 0.556 | 0.975 | 0.953 | 0.964 | 1 | 0.987 |
| R | 0.888 | 0.915 | 0.548 | 0.634 | 0.989 | 0.963 | 0.971 | 0.987 | 1 |
| Compounds | Molecular Formula | Observed Mass (m/z) | Expected Mass (m/z) | Mass Error (ppm) | RT (min) | [M − H]− (m/z) | MS/MS Fragment Ions (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| flavonoids | |||||||
| 3′,5,7-Trihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone 7-O-rutinoside | C28H32O15 | 608.1738 | 608.1741 | −0.49 | 46.779 | 607.1699 | 461.6880, 299.0577, 152.016, 148.6852 |
| quercetin | C15H10O7 | 302.0429 | 302.0427 | 0.91 | 48.095 | 301.0316 | 152.0082, 153.0085, 121.0286 |
| quercetin 3-methyl ether | C16H12O7 | 316.0588 | 316.0583 | 1.3 | 54.461 | 315.0529 | 300.0259, 272.0315, 152.0128 |
| rhamnezin | C17H14O7 | 330.0738 | 330.074 | −0.41 | 67.703 | 329.0734 | 314.0509, 299.0226, 271.0245, 227.0336 |
| kaempferol | C15H10O6 | 286.0484 | 286.0477 | 1.62 | 54.037 | 285.0414 | 257.0445, 229.0508, 121.026, 93.0356, 65.00333 |
| rhamnocitrin | C16H12O6 | 300.0636 | 300.0634 | 1.01 | 67.449 | 299.0624 | 271.0607, 243.0695, 166.0197 |
| quercetin galactoside(3-O;7-O) | C21H20O12 | 464.0953 | 464.0955 | 0.2 | 32.434 | 463.088 | 301.0325, 273.0334, 245.0515, 136.9104 |
| kaempferol 3-O-glucoside/galactoside | C21H20O11 | 448.1011 | 448.1006 | 0.51 | 37.484 | 285.0333 | 257.0445, 229.0511, 152.0099 |
| quercetin diglycoside with a rhamnose and a galactose/glucose) | C27H30O16 | 610.1532 | 610.1534 | −0.36 | 31.288 | 609.1523 | 301.0313, 273.0802, 152.8107, 136.9585 |
| quercetin triglycoside with a galactose/glucose and two rhamnoses (X5) | C33H40O20 | 756.2144 | 756.2113 | 0.88 | 30.906 | 755.2144 | 301.0349, 463.0765, 152.4898, 137.3381 |
| quercetin 3-methyl ether 7-O-galactopyranoside | C22H22O12 | 478.1106 | 478.1111 | −0.34 | 51.788 | 477.1018 | 315.0430, 300.0189, 165.0141, 137.5443, 109.0301 |
| kaempferol triglycoside with a galactose/glucose and two rhamnoses (X6) | C33H40O19 | 740.2158 | 740.2164 | 0.07 | 32.901 | 739.2122 | 285.0403, 57.0435, 229.0946, 152.0061, 120.0288 |
| rhamnocitrin diglycoside with a rhamnose and a galactose/glucose) | C28H32O15 | 608.1738 | 608.1741 | −0.83 | 47.012 | 607.1597 | 299.0577, 255.7552, 165.5555, 119.9104 |
| rhamnocitrin triglycoside with a galactose/glucose and two rhamnoses (X7) | C34H42O19 | 754.2335 | 754.232 | 1.01 | 40.015 | 753.2289 | 299.0507, 271.0618, 255.0335, 165.0185 |
| rhamnazin triglycoside with a galactose/glucose and two rhamnoses | C35H44O20 | 784.2431 | 784.2426 | 0.71 | 46.822 | 783.236 | 329.0661, 314.0414, 286.0448, |
| rhamnazin diglycoside with a rhamnose and a galactose/glucose) | C29H34O16 | 638.1852 | 638.1847 | 0.61 | 47.586 | 637.1799 | 329.0737, 314.0414, 299.0407 |
| rhamnetin triglycoside with a galactose/glucose and two rhamnoses | C34H42O20 | 770.2276 | 770.2269 | 0.48 | 34.280 | 769.2203 | 315.0507, 300.0245, 272.0272, 165.5149, 137.721 |
| anthroquainones | |||||||
| emodin | C15H10O5 | 270.053 | 270.0528 | 0.49 | 64.562 | 269.0462 | 225.0574, 241.0480, |
| emodin-3-O-rhamnoside | C21H20O9 | 416.1109 | 416.1107 | 0.4 | 64.605 | 415.1148 | 269.0459, 241.0525, 197.0590 |
| emodin glucoside(1-O;8-O) | C21H20O10 | 432.1065 | 432.1056 | 2.01 | 49.708 | 431.094 | 269.0461, 240.0423, 241.0514, 225.0562 |
| emodin 3-O-(di-O-acety) rhamnoside | C25H24O11 | 500.1321 | 500.1319 | 0.48 | 58.069 | 499.1353 | 269.0411, 240.0461, 212.0476 |
| organic acids | |||||||
| malic acid (X1) | C4H6O5 | 134.0216 | 134.0215 | 0.76 | 3.701 | 133.0128 | 115.0039, 71.047, |
| gallic acid (X2) | C7H6O5 | 170.0213 | 170.0215 | −1.48 | 5.992 | 169.0127 | 152.0945, 125.0271 |
| protocatechuic acid (X3) | C7H6O4 | 154.0264 | 154.0266 | −1.74 | 10.391 | 153.0181 | 109.0283, 91.0185, 63.0259 |
| salicylic acid (X4) | C7H6O3 | 138.0318 | 138.0317 | −1.02 | 15.435 | 137.0245 | 93.0348, 65.0386,51.0226 |
| Rankings | Sensory and Physicochemical Parameters | Physical Parameters | Chemical Constituents | Sensory Profiles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S3 | S6 | S3 | S2 |
| 2 | S4 | S4 | S4 | S1 |
| 3 | S1 | S3 | S1 | S3 |
| 4 | S5 | S5 | S5 | S4 |
| 5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S5 |
| 6 | S8 | S1 | S7 | S6 |
| 7 | S7 | S8 | S6 | S8 |
| 8 | S2 | S2 | S2 | S7 |
| Rankings | Samples | D+ | D− | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S3 | 0.28362 | 0.57927 | 0.67131 |
| 2 | S4 | 0.42034 | 0.33637 | 0.44451 |
| 3 | S1 | 0.47427 | 0.27501 | 0.36703 |
| 4 | S5 | 0.53332 | 0.26859 | 0.33493 |
| 5 | S6 | 0.57201 | 0.27990 | 0.32855 |
| 6 | S8 | 0.57241 | 0.23610 | 0.29202 |
| 7 | S7 | 0.56961 | 0.21190 | 0.27114 |
| 8 | S2 | 0.59041 | 0.21846 | 0.27008 |
| No. | Location | Batches Number | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Zhennanshan | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S2 | Zhennanshan | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S3 | yangjiaba | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S4 | yangjiaba | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S5 | Sizhuya | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S6 | Sizhuya | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S7 | Matongmiao | 6 | 2015.05 |
| S8 | Matongmiao | 6 | 2015.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, X.; Shan, D.; Xiao, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Physicochemical Aspects and Sensory Profiles as Various Potential Factors for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha Produced from Rhamnus heterophylla Oliv. Molecules 2019, 24, 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183211
Wang L, Fan S, Wang X, Wang X, Yan X, Shan D, Xiao W, Ma J, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Physicochemical Aspects and Sensory Profiles as Various Potential Factors for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha Produced from Rhamnus heterophylla Oliv. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183211
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Le, Shusheng Fan, Xiaoping Wang, Xiuhuan Wang, Xin Yan, Dongjie Shan, Wuqing Xiao, Jiamu Ma, Yanran Wang, Xiao Li, and et al. 2019. "Physicochemical Aspects and Sensory Profiles as Various Potential Factors for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha Produced from Rhamnus heterophylla Oliv." Molecules 24, no. 18: 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183211
APA StyleWang, L., Fan, S., Wang, X., Wang, X., Yan, X., Shan, D., Xiao, W., Ma, J., Wang, Y., Li, X., Xu, X., & She, G. (2019). Physicochemical Aspects and Sensory Profiles as Various Potential Factors for Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Nü-Er-Cha Produced from Rhamnus heterophylla Oliv. Molecules, 24(18), 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183211