A Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Formation of Smooth Muscle Foam Cells Which Transdifferentiate to Macrophage-Like State
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LD Formation Induced by MT-III in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
2.2. PLIN2 and PLIN3 Co-Localize with LDs in MT-III-Stimulated VSMCs
2.3. Acyl CoA: Diacylglycerolacyltransferase (DGAT) and Acyl-CoA:Cholesterolacyltransferase (ACAT) Contribute to LD Formation Induced by MT-III
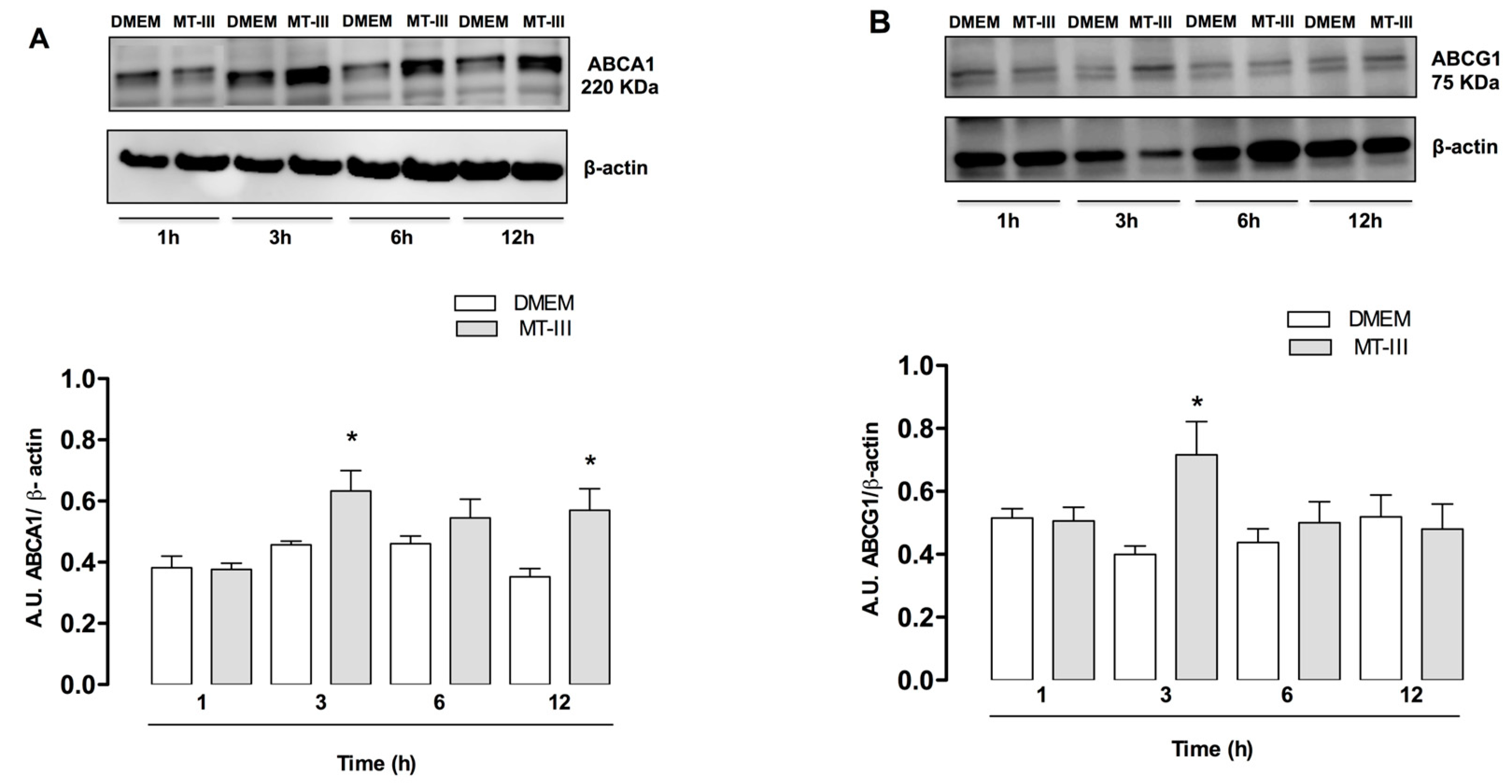
2.4. MT-III Induces Increased Protein Expression of ABC Lipid Transporters
2.5. MT-III Induces Protein Expression and Translocation of PPAR-γ and PPAR-δ/β in VSMCs
2.6. MT-III Upregulates SR-A1 and LOX-1 But Not CD36 Protein Expression. None of These Receptors Are Involved in Lipid Accumulation Induced by MT-III
2.7. MT-III Increases acLDL Uptake by VSMCs
2.8. Macropinocytosis But Not Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis is Involved in MT-III-Induced LDs Formation
2.9. MT-III Increases VSMC Phagocytic Activity and Upregulates Macrophage-Related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Phospholipase A2
4.3. Cell Isolation and Culture
4.4. Stimulation and Treatment of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
4.5. Lipid Droplet Staining and Quantification
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Quantification of Phagocytosis
4.8. Quantification of acLDL Uptake
4.9. Immunocytochemistry Analysis
4.10. Real-Time PCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torella, D.; Laconetti, C.; Catalucci, D.; Ellison, G.M.; Leone, A.; Waring, C.D.; Bochicchio, A.; Vicinanza, C.; Aquila, I.; Curcio, A.; et al. MicroRNA-133 controls vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch in vitro and vascular remodeling in vivo. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, G.K.; Kumar, M.S.; Wamhoff, B.R. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 767–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacolley, P.; Regnault, V.; Nicoletti, A.; Li, Z.; Michel, J.B. The vascular smooth muscle cell in arterial pathology: A cell that can take on multiple roles. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinert, S.; Poitz, D.M.; Auffermann-Gretzinger, S.; Eger, L.; Herold, J.; Medunjanin, S.; Schmeisser, A.; Strasser, R.H.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C. The lysosomal transfer of LDL/cholesterol from macrophages into vascular smooth muscle cells induces their phenotypic alteration. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 97, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, A.C.; Meller, N.; McNamara, C.A. Role of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozza, P.T.; Magalhães, K.G.; Weller, P.F. Leukocyte lipid bodies—Biogenesis and functions in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, R.C.; D’Avila, H.; Wan, H.C.; Bozza, P.T.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Lipid bodies in inflammatory cells: Structure, function, and current imaging techniques. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robenek, H.; Hofnagel, O.; Buers, I.B.; Robenek, M.J.; Troyer, D.; Severs, N.J. Adipophilin-enriched domains in the ER membrane are sites of lipid droplet biogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 4215–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulankina, A.V.; Deggerich, A.; Wenzel, D.; Mutenda, K.; Wittmann, J.G.; Rudolph, M.G.; Burger, K.N.; Höning, S. TIP47 functions in the biogenesis of lipid droplets. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Itabe, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Homma, K.J.; Onoduka, J.; Mori, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Makita, M.; Higashi, Y.; Yamashita, A.; et al. Involvement of ACSL in local synthesis of neutral lipids in cytoplasmic lipid droplets in human hepatocyte HuH7. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekiya, M.; Osuga, J.; Igarashi, M.; Okazaki, H.; Ishibashi, S. The role of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolysis in macrophage foam cells. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tontonoz, P.; Nagy, L.; Alvarez, J.G.; Thomazy, V.A.; Evans, R.M. PPAR-gamma promotes monocyte/macrophage differentiation and uptake of oxidized LDL. Cell 1998, 93, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijas, C.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Rubio, J.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Phospholipase A2 regulation of lipid droplet formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romano, M.; Romano, E.; Björkerud, S.; Hurt-Camejo, E. Ultrastructural localization of secretory type II phospholipase A2 in atherosclerotic and nonatherosclerotic regions of human arteries. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Gelb, M.H. Secretory phospholipase A2: A multifaceted family of proatherogenic enzymes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2009, 11, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, F.F.; Dennis, E.A. Evolutionary relationships and implications for the regulation of phospholipase A2 from snake venom to human secreted forms. J. Mol. Evol. 1990, 31, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipase A2 myotoxins from Bothrops snake venoms. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1405–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.M.; Zamuner, S.R.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Teixeira, C.F.P. Activation of cellular functions in macrophages by venom secretory Asp-49 and Lys-49 phospholipases A(2). Toxicon 2005, 46, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda, A.Q.; Rodríguez, I.G.; Arantes, E.C.; Setúbal, S.S.; Calderon, L.A.; Zuliani, J.P.; Stábeli, R.G.; Soares, A.M. Biochemical characterization, action on macrophages, and superoxide anion production of four basic phospholipases A2 from Panamanian Bothrops asper snake venom. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 789689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khelef, N.; Buton, X.; Beatini, N.; Wang, H.; Meiner, V.; Chang, T.Y.; Farese, R.V.J.; Maxfield, F.R.; Tabas, I. Immunolocalization of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol O-acyltransferase in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 11218–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.J.; Levin, M.C.; Zhou, P.; Han, J.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V. The endoplasmic reticulum enzyme DGAT2 is found in mitochondria-associated membranes and has a mitochondrial targeting signal that promotes its association with mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5352–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvan-Charvet, L.; Ranalletta, M.; Wang, N.; Han, S.; Terasaka, N.; Li, R.; Welch, C.; Tall, A.R. Combined deficiency of ABCA1 and ABCG1 promotes foam cell accumulation and accelerates atherosclerosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q. Class A1 scavenger receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 5523–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarra, T.; del Turco, S.; Berti, S.; Basta, G. The lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 and its soluble form: Cardiovascular implications. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, H.; Kume, N.; Sawamura, T.; Aoyama, T.; Hoshikawa, H.; Ochi, H.; Nishi, E.; Masaki, T.; Kita, T. Ligand specificity of LOX-1, a novel endothelial receptor for oxidized low density lipoprotein. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, J.; Walduck, A.K.; Thomas, S.R.; Glaros, E.N.; Hooker, E.U.; Guida, E.; Sobey, C.G.; Drummond, G.R. Accumulation of serum lipids by vascular smooth muscle cells involves a macropinocytosis-like uptake pathway and is associated with the downregulation of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Arch. Pharmacol. 2013, 386, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellan, B.; Reardon, C.A.; Getz, G.S.; Bowman, M.A.H. Enzymatically Modified Low-Density Lipoprotein Promotes Foam Cell Formation in Smooth Muscle Cells via Macropinocytosis and Enhances Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rong, J.X.; Shapiro, M.; Trogan, E.; Fisher, E.A. Transdifferentiation of mouse aortic smooth muscle cells to a macrophage-like state after cholesterol loading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 11, 13531–13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucer, A.; Brglez, V.; Payré, C.; Pungerčar, J.; Lambeau, G.; Petan, T. Group X secreted phospholipase A(2) induces lipid droplet formation and prolongs breast cancer cell survival. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiguez, E.; Giannotti, K.C.; Moreira, V.; Matsubara, M.H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Balsinde, J.; Teixeira, C. Critical role of TLR2 and MyD88 for functional response of macrophages to a group IIA-secreted phospholipase A2 from snake venom. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 93741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Ye, H.; Serrero, G. Stimulation of adipose differentiation related protein (ADRP) expression in adipocyte precursors by long-chain fatty acids. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 182, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gruia-Gray, J.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Londos, C.; Kimmel, A.R. The murine perilipin gene: The lipid droplet-associated perilipins derive from tissue-specific, mRNA splice variants and define a gene family of ancient origin. Mamm. Genome 2001, 12, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruit, J.K.; Wijesekara, N.; Westwell-Roper, C.; Vanmierlo, T.; de Haan, W.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Tang, R.; Wellington, C.L.; LütJohann, D.; Johnson, J.D.; et al. Loss of both ABCA1 and ABCG1 results in increased disturbances in islet sterol homeostasis, inflammation, and impaired β-cell function. Diabetes 2012, 61, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, S.; Murao, K.; Imachi, H.; Cao, W.M.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Nishiuchi, T.; Ahmed, R.A.; Wong, N.C.; et al. Platelet derived growth factor regulates ABCA1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4371–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W.; Wan, Z.; Chen, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Z. 17β-estradiol promotes cholesterol efflux from vascular smooth muscle cells through a liver X receptor α-dependent pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Barak, Y.; Nagy, L.; Liao, D.; Tontonoz, P.; Evans, R.M. PPAR-gamma dependent and independent effects on macrophage-gene expression in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasceri, V.; Wu, H.D.; Willerson, J.T.; Yeh, E.T. Modulation of vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activators. Circulation 2000, 101, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdian, S.; Chehroudi, A.C.; McManus, B.M.; Abraham, T.; Francis, G.A. Contribution of intimal smooth muscle cells to cholesterol accumulation and macrophage-like cells in human atherosclerosis. Circulation 2014, 129, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, S.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Lukowski, R.; Essmann, F.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schaller, M.; Feil, R. Transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells to macrophage-like cells during atherogenesis. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, I.I.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Plummer, D.; Aird, S.D.; Odell, G.D. The amino acid sequence of a myotoxic phospholipase from the venom of Bothrops asper. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 278, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Obando, D.; Díaz, C.; Angulo, Y.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Role of enzymatic activity in muscle damage and cytotoxicity induced by Bothrops asper Asp49 phospholipase A2 myotoxins: Are there additional effector mechanisms involved? PeerJ 2014, 2, e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, R.P.; Patterson, J.L.; Wilson, E. Vascular smooth muscle cells: Isolation, culture, and characterization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 843, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of compounds are not available from the authors. |









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannotti, K.C.; Weinert, S.; Viana, M.N.; Leiguez, E.; Araujo, T.L.S.; Laurindo, F.R.M.; Lomonte, B.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.; Teixeira, C. A Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Formation of Smooth Muscle Foam Cells Which Transdifferentiate to Macrophage-Like State. Molecules 2019, 24, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183244
Giannotti KC, Weinert S, Viana MN, Leiguez E, Araujo TLS, Laurindo FRM, Lomonte B, Braun-Dullaeus R, Teixeira C. A Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Formation of Smooth Muscle Foam Cells Which Transdifferentiate to Macrophage-Like State. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183244
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannotti, Karina Cristina, Sönke Weinert, Mariana Nascimento Viana, Elbio Leiguez, Thaís L. S. Araujo, Francisco R. M. Laurindo, Bruno Lomonte, Rüdiger Braun-Dullaeus, and Catarina Teixeira. 2019. "A Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Formation of Smooth Muscle Foam Cells Which Transdifferentiate to Macrophage-Like State" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183244
APA StyleGiannotti, K. C., Weinert, S., Viana, M. N., Leiguez, E., Araujo, T. L. S., Laurindo, F. R. M., Lomonte, B., Braun-Dullaeus, R., & Teixeira, C. (2019). A Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Formation of Smooth Muscle Foam Cells Which Transdifferentiate to Macrophage-Like State. Molecules, 24(18), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183244





