Water Extraction Kinetics of Bioactive Compounds of Fucus vesiculosus
Abstract
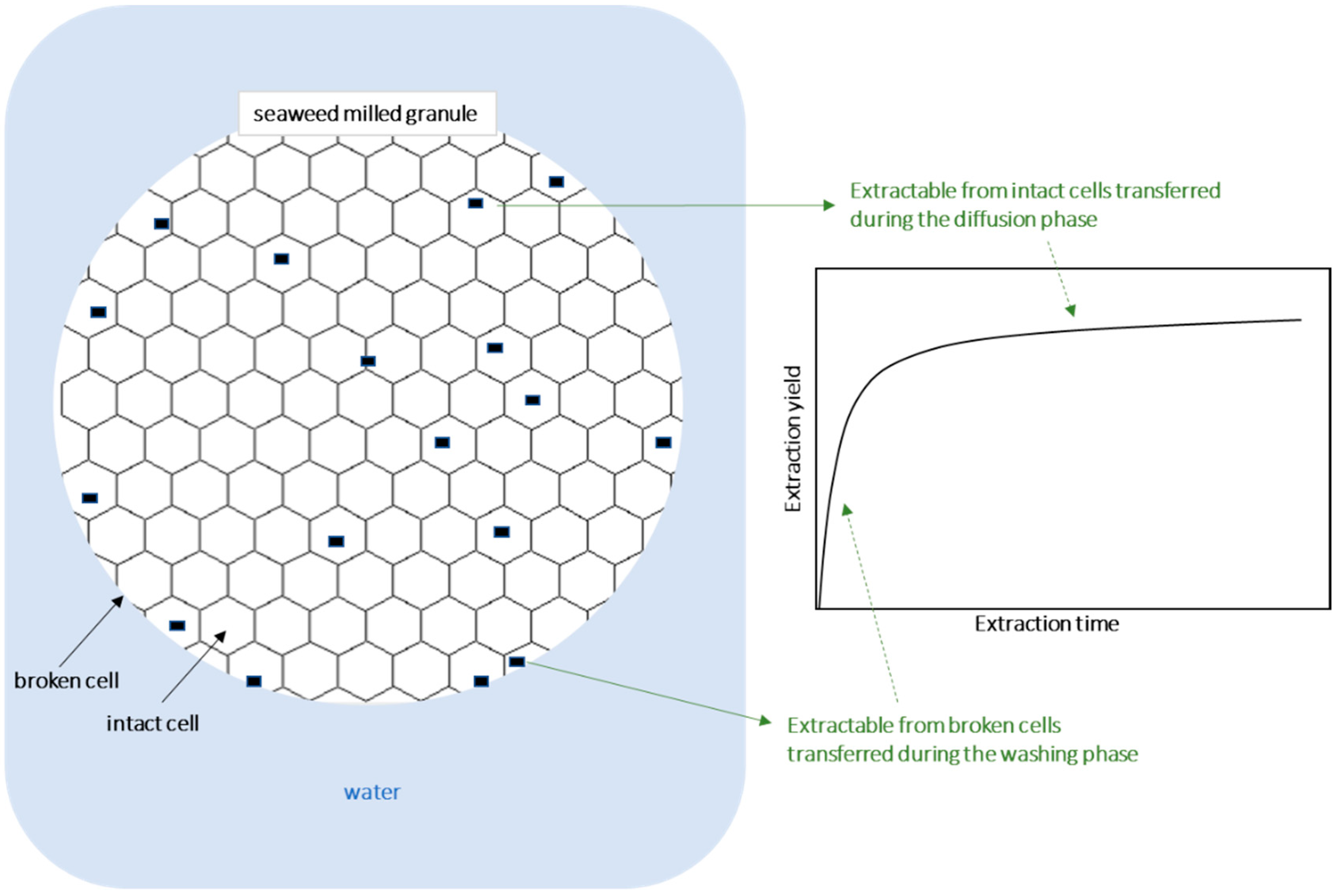
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mass Yield of the Aqueous Extracts
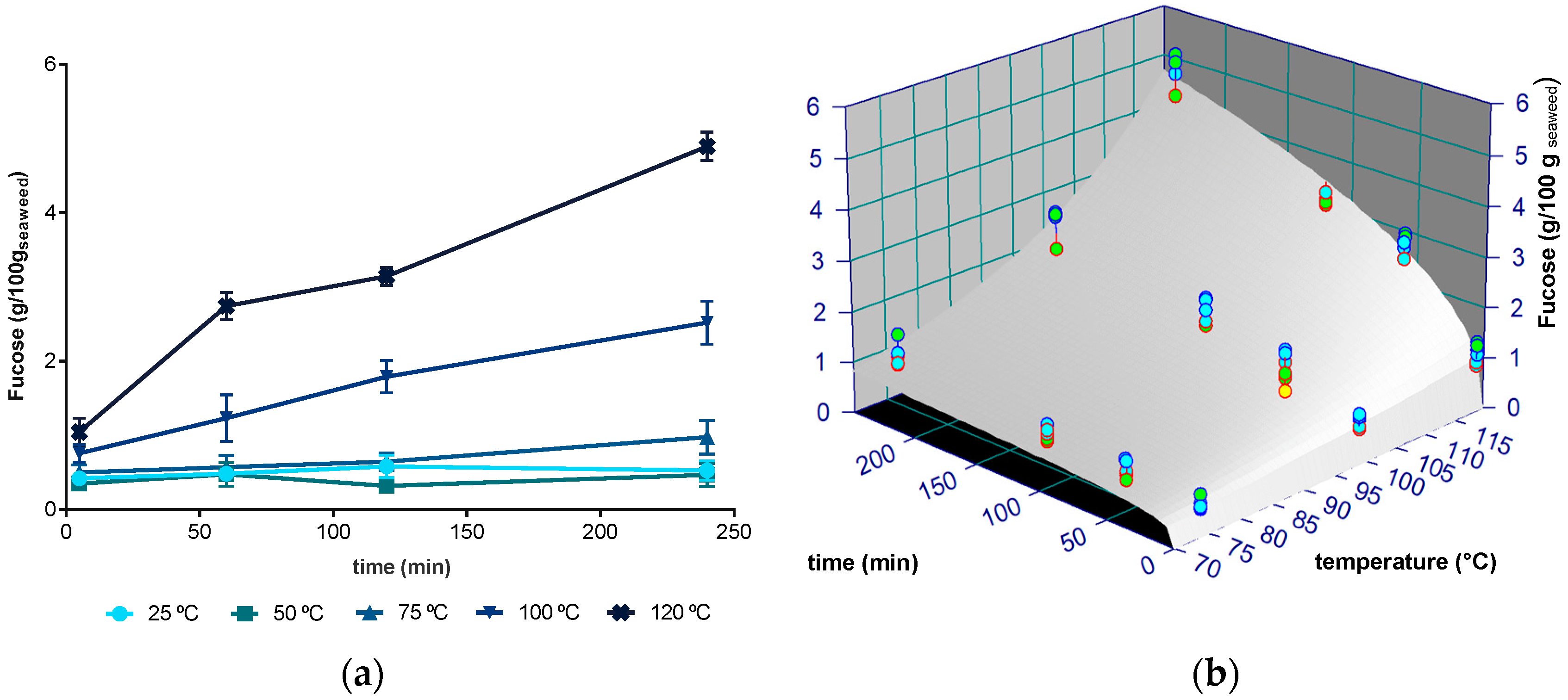
2.2. Fucose
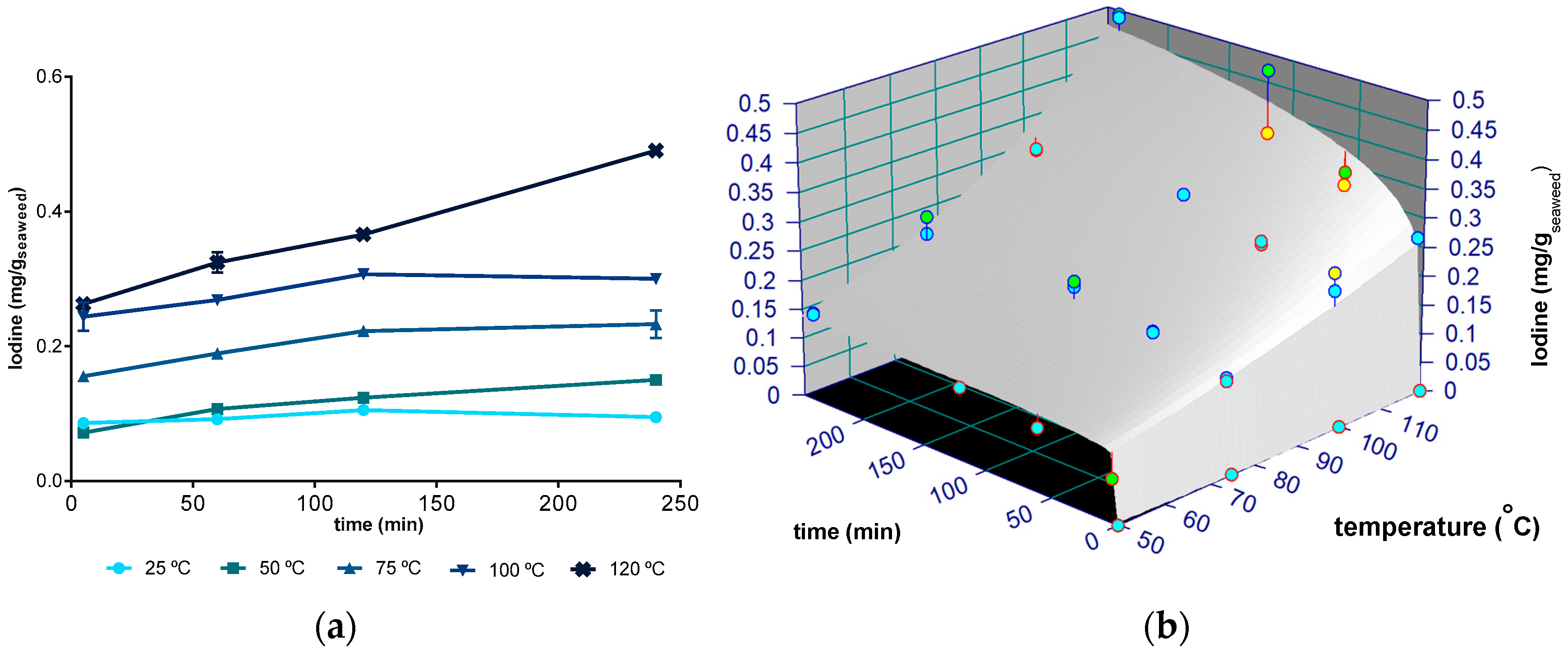
2.3. Iodine
2.4. Phlorotannins
2.5. 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-Sulphonic Acid (ABTS•+) Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Extraction Experiments
3.3. Chemical Analysis
3.3.1. Fucose
3.3.2. Assisted Alkaline Digestion
3.3.3. Iodine
3.3.4. Determination of Total Phlorotannin Content
3.3.5. ABTS•+ Discoloration Assay
3.4. Statistical Analysis and Mathematical Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wheeler, T.A.; Anderson, M.G.; Russell, S.A.; Woodward, J.E.; Mullinix, B.G. How to Feed the World in 2050. 2009, 42, 128–137. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-X.; Wijesekara, I.; Kim, S.K.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.X. Phlorotannins as bioactive agents from brown algae. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, D.C.; Scapagnini, G.; Willcox, B.J. Healthy aging diets other than the Mediterranean: A focus on the Okinawan diet. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.M.; Pereira, O.R.; Seca, A.M.L.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Seaweeds as preventive agents for cardiovascular diseases: From nutrients to functional foods. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6838–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Thomas, N.V.; Li, X. Anticancer compounds from marine macroalgae and their application as medicinal foods. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier Inc.: Busan, Korea, 2011; Volume 64, pp. 213–224. ISBN 9780123876690. [Google Scholar]
- Holdt, S.L.; Kraan, S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 543–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Mateus, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Optimization of phlorotannins extraction from Fucus vesiculosus and evaluation of their potential to prevent metabolic disorders. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, B. Functional foods market size, share & trends analysis report by ingredient (carotenoids, prebiotics & probiotics, fatty acids, dietary fibers), by product, by application, and segment forecasts, 2019–2025; Research and Markets: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 7215. [Google Scholar]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Fucaceae: A source of bioactive phlorotannins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L. Edible Seaweeds of the World; CRC Press: Coimbra, Portugal, 2016; ISBN 9781498730471. [Google Scholar]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phycochemical constituents and biological activities of Fucus spp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circuncisão, A.R.; Catarino, M.D.; Cardoso, S.M.; Silva, A.M.S. Minerals from macroalgae origin: Health benefits and risks for consumers. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted from Laminaria japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbs, T.I.; Skriptsova, A.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Antioxidant activity of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides obtained from Fucus evanescens by different extraction methods. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 27, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, C.K.; Josephine, A.; Preetha, S.P.; Varalakshmi, P. Beneficial role of sulfated polysaccharides from edible seaweed Fucus vesiculosus in experimental hyperoxaluria. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, H.D.; Thuy, T.T.T.; Huong, T.T.; Ly, B.M.; Van, T.T.T. Structure and hypolipidaemic activity of fucoidan extracted from brown seaweed Sargassum henslowianum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wen, K.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y. Hypolipidemic effect of fucoidan from Laminaria japonica in hyperlipidemic rats. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, X.; He, Y.; Song, Y. Hypolipidemic effects of sulfated fucoidan from Kjellmaniella crassifolia through modulating the cholesterol and aliphatic metabolic pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 51, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Yoon, K.Y.; Lee, B.Y. Fucoidan regulate blood glucose homeostasis in C57BL/KSJ m+/+db and C57BL/KSJ db/db mice. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Liu, X.; Hao, J.; Cai, C.; Fan, F.; Dun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Yu, G. In vitro and in vivo hypoglycemic effects of brown algal fucoidans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth Kumar, T.; Lakshmanasenthil, S.; Geetharamani, D.; Marudhupandi, T.; Suja, G.; Suganya, P. Fucoidan—A α-d-glucosidase inhibitor from Sargassum wightii with relevance to type 2 diabetes mellitus therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.M.; Carvalho, L.G.; Silva, P.J.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Pereira, O.R.; Pereira, L. Bioproducts from seaweeds: A review with special focus on the Iberian Peninsula. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 896–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.P.; Sidana, J. Phlorotannins. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Jónsdóttir, R.; Liu, H.; Gu, L.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Raghavan, S.; Ólafsdóttir, G. Antioxidant capacities of phlorotannins extracted from the brown algae Fucus vesiculosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5874–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K. Sodium, potassium, blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease in humans. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truus, K.; Vaher, M.; Taure, I. Algal biomass from Fucus vesiculosus (Phaeophyta): Investigation of the mineral and alginate components. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. Chem. 2001, 50, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner, R. Recent data on iodine intake in Germany and Europe. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 37, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important determinants for fucoidan bioactivity: A critical review of structure-function relations and extraction methods for fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: An update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machmudah, S.; Diono, W.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Supercritical fluids extraction of valuable compounds from algae: Future perspectives and challenges. Eng. J. 2018, 22, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Jasso, R.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of sulphated polysaccharides extracted from Fucus vesiculosus using different hydrothermal processes. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agregán, R.; Munekata, P.E.; Domínguez, R.; Carballo, J.; Franco, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Proximate composition, phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity of aqueous extracts of the seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum, Bifurcaria bifurcata and Fucus vesiculosus. Effect of addition of the extracts on the oxidative stability of canola oil unde. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, B.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Smyth, T.J.; Ahmed, A.M.; Sweeney, T. A cold water extract of Fucus vesiculosus inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced pro-inflammatory responses in the porcine colon ex-vivo model. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Yusoff, R.; Ngoh, G.C. Modeling and kinetics study of conventional and assisted batch solvent extraction. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, G.C.; Macdonald, D.G. Kinetics of oil extraction from canola (rapeseed). Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1986, 64, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcel, J.A.; García-Pérez, J.V.; Mulet, A.; Rodríguez, L.; Riera, E. Ultrasonically assisted antioxidant extraction from grape stalks and olive leaves. Phys. Procedia 2010, 3, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An introduction to statistical learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781461471370. [Google Scholar]
- Bicking, M.K.L. EXTRACTION | Analytical Extractions. In Encyclopedia of Separation Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 1371–1382. ISBN 9780122267703. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, S.H. Properties of polysaccharides in several seaweeds from Atlantic Canada and their potential anti-influenza viral activities. J. Ocean Univ. China 2012, 11, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupérez, P.; Ahrazem, O.; Leal, J.A. Potential antioxidant capacity of sulfated polysaccharides from the edible marine brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Designed optimization of a single-step extraction of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from Sargassum sp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romarís-Hortas, V.; Bianga, J.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Szpunar, J. Speciation of iodine-containing proteins in Nori seaweed by gel electrophoresis laser ablation ICP-MS. Talanta 2014, 127, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandgirard, J.; Poinsot, D.; Krespi, L.; Nénon, J.P.; Cortesero, A.M. Costs of secondary parasitism in the facultative hyperparasitoid Pachycrepoideus dubius: Does host size matter? Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 103, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gu, L. Phlorotannins from brown algae (Fucus vesiculosus) inhibited the formation of advanced glycation endproducts by scavenging reactive carbonyls. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivikko, R.; Loponen, J.; Honkanen, T.; Jormalainen, V. Contents of soluble, cell-wall-bound and exuded phlorotannins in the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus, with implications on their ecological functions. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steevensz, A.J.; MacKinnon, S.L.; Hankinson, R.; Craft, C.; Connan, S.; Stengel, D.B.; Melanson, J.E. Profiling Phlorotannins in Brown Macroalgae by Liquid Chromatography–High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, M.S.; Smyth, T.J.; Rai, D.K.; Soler-Vila, A.; Croft, A.K.; Brunton, N. Enrichment of polyphenol contents and antioxidant activities of Irish brown macroalgae using food-friendly techniques based on polarity and molecular size. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Duan, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. Extraction and identification of phlorotannins from the brown alga, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boi, V.N.; Cuong, D.X.; Vinh, P.T.K. Effects of extraction conditions over the phlorotannin content and antioxidant activity of extract from brown algae Sargassum serratum (Nguyen Huu Dai 2004). Free Radic. Antioxid. 2017, 7, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, D.X.; Boi, V.N.; Van, T.T.T.; Hau, L.N. Effect of storage time on phlorotannin content and antioxidant activity of six Sargassum species from Nhatrang Bay, Vietnam. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.W.F.; Ho, C.W.; Yong, W.T.L.; Abas, F.; Tan, T.B.; Tan, C.P. Extraction of phenolic antioxidants from four selected seaweeds obtained from Sabah. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Lack, E.B. Simándi Supercritical fluid extraction and fractionation from solid materials. In Industrial Chemistry Library; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 537–575. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez–Hernández, G.B.; Castillejo, N.; Carrión–Monteagudo, M.D.M.; Artés, F.; Artés-Hernández, F. Nutritional and bioactive compounds of commercialized algae powders used as food supplements. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Romarís-Hortas, V.; García-Sartal, C.; del Carmen Barciela-Alonso, M.; Domínguez-González, R.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. Bioavailability study using an in-vitro method of iodine and bromine in edible seaweed. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, G.W.; Peppas, N.A. Analysis of non-fickian transport in polymers using simplified exponential expressions. J. Memb. Sci. 1984, 17, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanović, S.; Milenović, D.; Veljković, V.B. Empirical kinetic models for the resinoid extraction from aerial parts of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A.; Cravotto, G. Green extraction of natural products: Concept and principles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples from the extracts are available from the authors. |

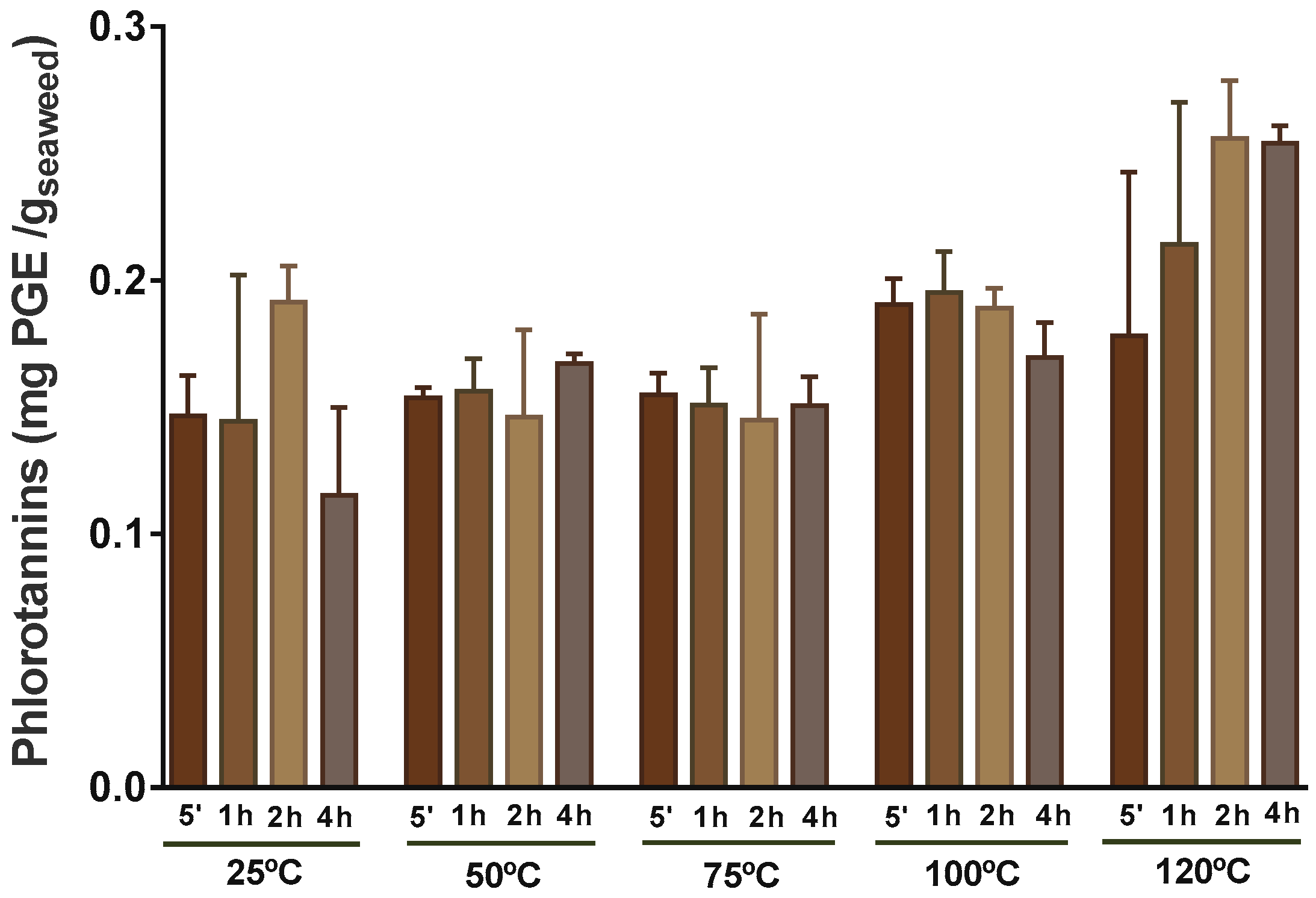
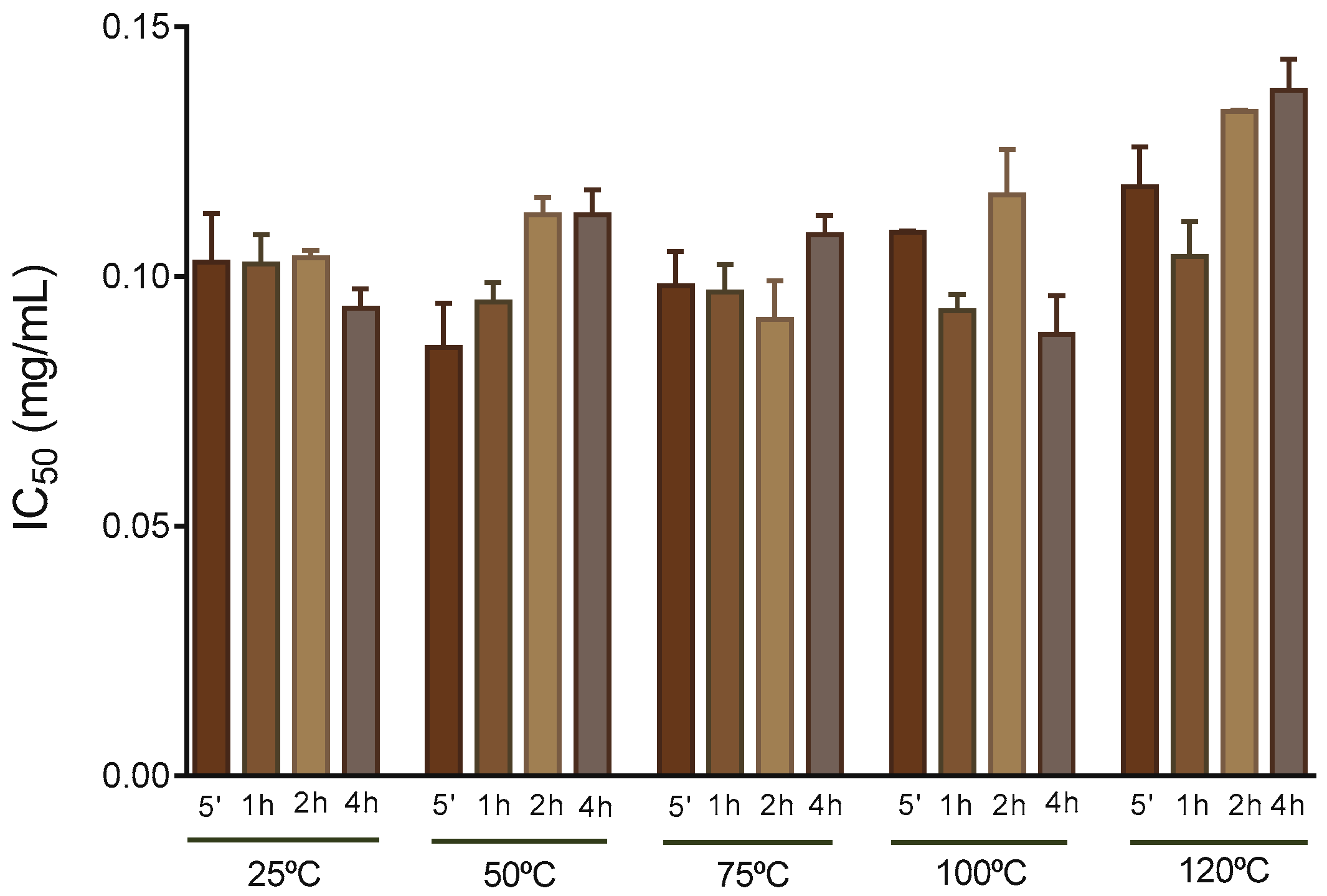
| T Range (°C) | k0 (g/100 g Seaweed) | Eak (kJ/mol) | n0 | Ean (kJ/mol) | R2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract yield | 75–120 | 76.05 | ±36.70 | 3.17 | ±1.47 | 1668 | ±2186 | 30.62 | ±4.22 | 0.9818 |
| Fucose | 75–120 | 36.1 | ±66.8 | 14.1 | ±5.9 | 37.9 | ±47.7 | 14.8 | ±4.1 | 0.9532 |
| Iodine | 50–120 | 3.19 × 10−3 | ±2.48 × 10−3 | 9.2 | ±2.3 | 35.7 | ±62.5 | 17.7 | ±5.6 | 0.9655 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, R.M.; Ramalho Ribeiro, A.; Patinha, C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M.; Costa, R. Water Extraction Kinetics of Bioactive Compounds of Fucus vesiculosus. Molecules 2019, 24, 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183408
Ferreira RM, Ramalho Ribeiro A, Patinha C, Silva AMS, Cardoso SM, Costa R. Water Extraction Kinetics of Bioactive Compounds of Fucus vesiculosus. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183408
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Ricardo M., Ana Ramalho Ribeiro, Carla Patinha, Artur M. S. Silva, Susana M. Cardoso, and Rui Costa. 2019. "Water Extraction Kinetics of Bioactive Compounds of Fucus vesiculosus" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183408
APA StyleFerreira, R. M., Ramalho Ribeiro, A., Patinha, C., Silva, A. M. S., Cardoso, S. M., & Costa, R. (2019). Water Extraction Kinetics of Bioactive Compounds of Fucus vesiculosus. Molecules, 24(18), 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183408









