A Beta/ZSM-22 Zeolites-Based-Mixed Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Method for the Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Eight Compounds with Different Polarities in Viticis Fructus by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.4. HPLC Analysis
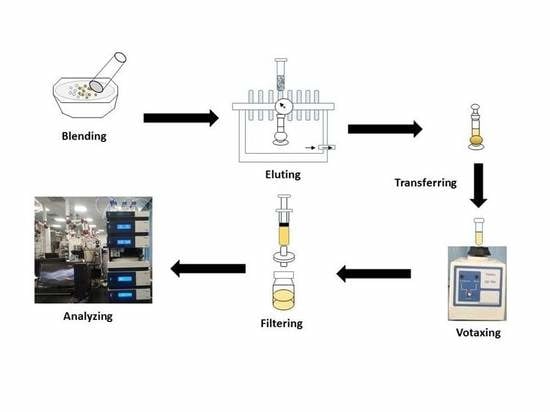
2.5. B/Z-MMSPD Procedure
2.6. Heating Reflux Extraction
2.7. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of B/Z-MMSPD Method
3.1.1. Type of Sorbent
3.1.2. Mass Ratio of Beta to ZSM-22
3.1.3. Mass Ratio of Matrix to Sorbent
3.1.4. Grinding Time
3.1.5. The Organic Part of Elution Solvent
3.2. Method Validation
3.2.1. Selectivity and Linearity
3.2.2. Limits of Detection and Quantification
3.2.3. Reproducibility
3.2.4. Precision, Stability and Recovery
3.3. Application
3.4. Comparison with Other Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, L. Analysis of accumulation dynamics of vitexicarpin in fruit and leaf of Vitex trifolia. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao 2012, 23, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Bao, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, L. Status quo and prospects of studies on fructus viticis of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 37, 673–675. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, A.; Zhang, G. The evolution and modern research of Fructus Viticis and its processed products. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 37, 673–675. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission: Beijing, China, 2015; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, J.; Xu, C.; Zheng, H.; He, S.; Wang, S. An Integrated Strategy to Qualitatively Differentiate Components of Raw and Processed Viticis Fructus Based on NIR, HPLC and UPLC - MS Analysis. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papers, O.; Naohiro, O.; Sayaka, M.; Ryuta, S.; Kanae, Y.; Hiroshi, M.; Emi, S.; Yutaka, T.; Tadahiro, Y.; Masato, W.; et al. Identification of New Diterpenes as Putative Marker Compounds Distinguishing Agnus Castus Fruit (Chaste Tree) from Shrub Chaste Tree Fruit (Viticis Fructus). Planta Med. 2016, 82, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Zou, H.; Cao, J.; Cui, Y.; Sun, S.; Ren, K.; Song, Z. A candidate Chinese medicine preparation-Fructus Viticis Total Flavonoids inhibits stem-like characteristics of lung cancer stem-like cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.M.; Park, H.; Park, B.; Kim, H. Vitex rotundifolia Fruit Suppresses the Proliferation of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells through Down-regulation of Cyclin D1 and CDK4 Via Proteasomal-Dependent Degradation and Transcriptional Inhibition. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xin, H.L.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zheng, H.C.; Rahman, K.; Qin, L.P. Anti-nociceptive and anti-hyperprolactinemia activities of Fructus Viticis and its effective fractions and chemical constituents. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Im, M.; Ma, J.Y. SRVF, a novel herbal formula including Scrophulariae Radix and Viticis Fructus, disrupts focal adhesion and causes detachment- induced apoptosis in malignant cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Yin, Y.P.; Jun, L.; Xuan, L.J. Halimane-type diterpenoids from Vitex rotundifolia and their anti-hyperlipidemia activities. Phytochemistry 2018, 146, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Jung, K.H.; Ji, E.S.; Bae, H. Pyranopyran-1, 8-dione, an Active Compound from Vitices Fructus, Attenuates Cigarette-Smoke Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Lee, J.W.; Jin, Q.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.; Hwang, B.Y. Anti-inflammatory constituents from the fruits of Vitex rotundifolia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6010–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruüzüm-Uz, A.; Ströch, K.; Demirezer, L.Ö.; Zeeck, A. Glucosides from Vitex agnus-castus. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiligira, E.; Viljoen, A.M.; Başer, K.H.C.; Ózek, T.; Van Vuuren, S.F. Essential oil composition and in vitro antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity of South African Vitex species. S. Afr. J. Botany 2004, 70, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojković, D.S.; Živković, J.; Soković, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Janković, T.; Maksimović, Z. Antibacterial activity of Veronica montana L. extract and of protocatechuic acid incorporated in a food system. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhoosh, R.; Johnny, S.; Asnaashari, M.; Molaahmadibahraseman, N.; Sharif, A. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of o-hydroxyl, o-methoxy, and alkyl ester derivatives of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillarisetti, P.; Myers, K.A. Identification and characterization of agnuside, a natural proangiogenic small molecule. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 160, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, E.; Fujimori, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Deyama, T. Pharmacologically active components of viticis fructus (Vitex rotundifolia). II. The components having analgesic effects. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1998, 46, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Shimada, A.; Suemitsu, S.; Murakami, S.; Kitamura, N.; Wani, K.; Ishihara, T. Comprehensive behavioral study of the effects of vanillin inhalation in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Khan, H.; Fratantonio, D.; Hasan, M.M.; Sharifi, S.; Fathi, N.; Ullah, H.; Rastrelli, L. Apoptosis induced by luteolin in breast cancer: Mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Heo, D.R.; Lee, J.; Park, J.S.; Baek, M.G.; Yi, J.M.; Bang, O.S. 5,3′-Dihydroxy-6,7,4′-trimethoxyflavanone exerts its anticancer and antiangiogenesis effects through regulation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 225, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.; Chou, H.; Chou, H.; Lu, H.; Chu, Y.; Shang, H.; Chung, J. Casticin impairs cell migration and invasion of mouse melanoma B16F10 cells via PI3K/AKT and NF-κ B signaling pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2097–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Dhanani, T.; Kumar, S. Validated HPLC method for identification and quantification of p -hydroxy benzoic acid and agnuside in Vitex negundo and Vitex trifolia. J. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 3, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidin, L.; Mujeeb, M.; Mir, S.R.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, A. Comparative assessment of extraction methods and quantitative estimation of luteolin in the leaves of Vitex negundo Linn. by HPLC. Asian Pac. J. Trop Med. 2014, 7, S289–S293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Optimization of the Microwave - assisted Extraction and Purification Technology of Total Flavonoids in Fructus Viticis by Orthogonal Experiment. China Pharmacy 2009, 20, 1867–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fu, S. Quantitative Determination of Luteolin from Seeds of Vitex trifolia var. simplicifolia. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao 2005, 16, 609–610. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Xiong, W.; Li, X. Optimization for Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Vitex rotundifolia oil by Response Surface Method. Jiangxi Food Ind. 2008, 3, 20–21, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, C. Analysis of chemical constituents of the essential oil from Vitex trifolia L. var. simplicifolia Cham. by SPME-GC-MS. J. Henan Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2006, 25, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Zhong, M.; Zhong, X. Content Determination of Vitexicarpin in Vitex trifolia from Different Producing Areas of Jiangxi Province by HPLC. China Pharmacy 2011, 22, 4489–4490. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, S.A.; Long, A.R.; Short, C.R. Isolation of drug residues from tissues by solid phase dispersion. J. Chromatogr. A 1989, 475, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Cao, J.; Ye, L.H.; Xu, J.J.; Hu, S.S.; Peng, L.Q. Synthesis and application of mesoporous molecular sieve for miniaturized matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of bioactive flavonoids from toothpaste, plant, and saliva. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 2951–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Peng, L.Q.; Xu, J.J.; Du, L.J.; Zhang, Q.D. Simultaneous microextraction of inorganic iodine and iodinated amino acids by miniaturized matrix solid-phase dispersion with molecular sieves and ionic liquids. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1477, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Yang, R.; Ye, L.H.; Cao, J.; Cao, W.; Hu, S.S.; Peng, L.Q. Application of ionic liquids for elution of bioactive flavonoid glycosides from lime fruit by miniaturized matrix solid-phase dispersion. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Wei, M.; Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; He, Z.; Cao, J.; Yan, J. Micro-matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with MEEKC for quantitative analysis of lignans in Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus using molecular sieve TS-1 as a sorbent. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1063, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.J.; Huang, J.P.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.D. Carbon molecular sieve based micro-matrix-solid-phase dispersion for the extraction of polyphenols in pomegranate peel by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, X.; Hu, Y.H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, S.L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.H. Calixarene and ionic liquid assisted matrix solid-phase dispersion microextraction of organic acids from fruit. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 360131, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Montoro, P.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination of chemical markers and principal component analysis of Vitex agnus-castus L. fruits (Verbenaceae) and derived food supplements. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Geng, X.; Li, Y.; Zha, Z.; Cui, S.; Yang, J. Magnetic adsorbent based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for magnetic solid phase extraction of pyrethroid pesticides in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1598, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Bagheri, A.R. Column packing elimination in matrix solid phase dispersion by using water compatible magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for recognition of melamine from milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1594, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.B.R.; Soares, K.L.; Caldas, S.S.; Primel, E.G. Sample as solid support in MSPD: A new possibility for determination of pharmaceuticals, personal care and degradation products in sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, N.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Grande Casas, M.; Mayoral, A.; Moreno, A. Preparation of mesoporous Beta zeolite by fluoride treatment in liquid phase. Textural, acid and catalytic properties. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 284, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, N.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Mondragón, F.; Moreno, A. Generation of hierarchical porosity in beta zeolite by post-synthesis treatment with the cetyltrimethylammonium cationic surfactant under alkaline conditions. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 280, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Study on adsorption of rhodamine B onto Beta zeolites by tuning SiO2/Al2O3 ratio. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugushe, A.S.; Nqombolo, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. Application of Response Surface Methodology and Desirability Function in the Optimization of Adsorptive Remediation of Arsenic from Acid Mine Drainage Using Magnetic Nanocomposite: Equilibrium Studies and Application to Real Samples. Molecules 2019, 1792, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.J.B.; de Sousa, L.V.; Quintela, P.H.L.; Alencar Júnior, N.R.; Alencar, S.L.; Maciel, P.A.M.; Silva, A.O.S. Preparation of ZSM-22 zeolite with hierarchical pore structure. Mater. Lett. 2018, 218, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, agnuside, 10-O-vanilloylaucubin, vanillin, luteolin, 5,3′-dihydroxy-6,7,4′-trimethoxyflavanone and casticin are available from the authors. |



| Compounds | Regressive Equation | Linear Range (µg/g) | r | LOD (µg/g) | LOQ (µg/g) | Repeatability RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | Y = 0.4676x − 0.0088 | 9–2250 | 0.9999 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.68 |
| PHBA | Y = 0.6944x − 0.0011 | 9–2300 | 0.9999 | 1 | 4 | 3.33 |
| Agnuside | Y = 0.2439x − 0.0213 | 29–7300 | 0.9999 | 2 | 7 | 1.96 |
| VA | Y = 0.1547x − 0.0016 | 7.5–1900 | 0.9999 | 1 | 3 | 4.54 |
| Vanillin | Y = 0.4982x − 0.0033 | 10–2500 | 0.9999 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 4.76 |
| Luteolin | Y = 0.2433x + 0.0084 | 10–500 | 0.9997 | 2 | 7 | 3.57 |
| DHTMF | Y = 0.1561x + 0.0095 | 20–2500 | 0.9992 | 5.5 | 16 | 2.57 |
| Casticin | Y = 0.5268x − 0.0073 | 16–4000 | 0.9999 | 1 | 2.5 | 2.79 |
| Compounds | Concentration (µg/mL) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Stability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| PCA | 2 | 2.0 | 97.4 | 1.2 | 97.4 | 1.4 | 96.4 |
| 4 | 4.2 | 102.6 | 2.5 | 102.6 | 3.0 | 101.8 | |
| 12 | 0.0 | 104.8 | 0.5 | 104.9 | 0.3 | 104.7 | |
| PHBA | 8.5 | 1.1 | 99.2 | 1.7 | 99.2 | 1.8 | 96.8 |
| 17 | 2.5 | 103.8 | 2.8 | 103.8 | 2.6 | 99.7 | |
| 51 | 0.5 | 100.8 | 0.9 | 101.1 | 0.6 | 100.9 | |
| Agnuside | 20 | 1.8 | 100.2 | 2.2 | 100.2 | 1.6 | 97.3 |
| 40 | 2.8 | 102.4 | 3.3 | 102.4 | 3.5 | 100.0 | |
| 120 | 0.7 | 103.8 | 0.7 | 104.0 | 0.7 | 104.1 | |
| VA | 1.5 | 1.0 | 98.1 | 1.6 | 98.1 | 2.0 | 98.0 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 103.2 | 0.7 | 103.2 | 0.9 | 103.8 | |
| 9 | 0.1 | 104.7 | 0.2 | 104.6 | 0.2 | 104.6 | |
| Vanillin | 0.5 | 1.4 | 95.8 | 1.3 | 95.8 | 1.4 | 96.3 |
| 1 | 0.3 | 100.4 | 0.7 | 100.4 | 0.5 | 101.1 | |
| 3 | 0.1 | 104.9 | 0.5 | 104.2 | 0.6 | 104.3 | |
| Luteolin | 0.5 | 1.3 | 103.7 | 1.0 | 103.7 | 1.3 | 104.0 |
| 1 | 0.4 | 96.0 | 0.8 | 96.0 | 0.9 | 95.0 | |
| 3 | 0.2 | 99.4 | 0.7 | 98.6 | 0.6 | 98.8 | |
| DHTMF | 1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 1.8 | 100.0 | 1.9 | 97.7 |
| 2 | 0.3 | 98.2 | 0.4 | 98.2 | 0.5 | 98.0 | |
| 6 | 0.3 | 95.7 | 0.7 | 96.6 | 0.8 | 96.5 | |
| Casticin | 7.5 | 0.7 | 99.1 | 1.9 | 99.1 | 1.4 | 96.2 |
| 15 | 2.7 | 100.7 | 2.0 | 100.7 | 2.3 | 99.3 | |
| 45 | 0.7 | 101.7 | 1.1 | 102.9 | 1.0 | 102.5 | |
| Compounds | Unspiked (µg) | Spike (µg) | Spiked (µg) | Average Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 1.49 | 1.36 | 2.78 | 95.0 | 1.46 |
| PHBA | 5.70 | 5.40 | 10.87 | 95.8 | 0.94 |
| Agnuside | 18.75 | 14.16 | 33.06 | 100 | 4.13 |
| VA | 1.41 | 1.00 | 2.44 | 103 | 0.98 |
| Vanillin | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.91 | 103 | 1.57 |
| Luteolin | 0.75 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 101 | 3.22 |
| DHTMF | 1.39 | 0.76 | 2.19 | 105 | 1.10 |
| Casticin | 5.40 | 5.00 | 10.27 | 97.5 | 0.16 |
| Production Region | PCA | PHBA | Agnuside | VA | Vanillin | Luteolin | DHTMF | Casticin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No.1 (Guangxi) | 7.67 ± 0.35 | 35.13 ± 1.38 | 98.93 ± 2.25 | 7.06 ± 0.12 | 2.77 ± 0.11 | 8.70 ± 0.03 | 24.80 ± 1.02 | 100.77 ± 4.19 |
| No. 2 (Guangdong) | 3.51 ± 0.05 | 13.81 ± 0.21 | 47.94 ± 2.33 | 6.91 ± 0.12 | 1.84 ± 0.01 | 3.79 ± 0.18 | - | 30.67 ± 0.55 |
| No. 3 (Hubei) | 10.00 ± 0.11 | 25.12 ± 0.42 | 73.94 ± 1.75 | 6.85 ± 0.82 | 5.83 ± 0.16 | 5.50 ± 0.26 | 13.56 ± 0.24 | 61.36 ± 0.74 |
| No. 4 (Sichuan) | 21.63 ± 0.50 | 53.16 ± 1.00 | 29.33 ± 1.41 | - | 5.88 ± 0.12 | 3.52 ± 0.16 | - | 29.40 ± 0.51 |
| No. 5 (Shandong) | 7.12 ± 0.12 | 22.34 ± 0.63 | 34.21 ± 0.50 | 8.93 ± 0.29 | - | - | 2.72 ± 0.09 | 8.52 ± 0.18 |
| No. 6 (Hebei) | 6.99 ± 0.24 | 27.76 ± 1.22 | 62.66 ± 1.57 | 4.66 ± 0.04 | 2.28 ± 0.11 | 4.60 ± 0.18 | 12.04 ± 0.29 | 48.68 ± 2.40 |
| No. 7 (Anhui) | 16.49 ± 0.37 | 64.06 ± 1.79 | 184.92 ± 6.92 | 12.52 ± 0.18 | 4.28 ± 0.17 | 7.32 ± 0.14 | 14.78 ± 0.51 | 55.88 ± 1.71 |
| No. 7 (Anhui) * | 10.11 ± 0.25 | 56.45 ± 0.41 | 145.72 ± 4.27 | 10.86 ± 0.30 | 4.47 ± 0.03 | 6.22 ± 0.13 | 13.01 ± 0.13 | 47.93 ± 0.48 |
| No. 7 (Anhui) ** | 16.38 ± 0.52 | 71.01 ± 1.22 | 201.71 ± 3.18 | 15.04 ± 0.29 | 4.65 ± 0.12 | 9.88 ± 0.16 | 14.05 ± 0.46 | 53.60 ± 0.94 |
| No. | Plant | Extracted Compounds | Sample Amounts (g) | Type of Solvent | Solvent Volume (mL) | Extraction Method | Extraction Time (min) | Detection Method | Detection Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vitex negundo and Vitex trifolia | p-hydroxybenzoic acid and agnuside | 50 | Methanol | 1500 | Maceration | 1440 | HPLC-PDA | 18 | [24] |
| 2 | Vitex negundo Linn. | Luteolin | 5 | Methanol | 50 | Reflux | 120 | HPLC | 10 | [25] |
| 3 | Vitex agnus-castus L. Vitex trifolia | Aucubin, homorientin, orientin, agnuside, isovitexin, luteolin-7-O-glucoside and casticin | 500 | Petroleum ether, chloroform and 70%ethanol | - | Maceration | - | LC-MS | 55 | [38] |
| 4 | Vitex trifolia | Casticin | 2 | Petroleum ether and methanol | 50 | Soxhlet | 540 | HPLC | 14 | [30] |
| 5 | Vitex trifolia | Luteolin | 2.5 | MeOH | 35 | UAE | 50 | HPLC | 20 | [27] |
| 6 | PCA, PHBA, agnuside, VA, vanillin, luteolin, DHTMF and casticin | 0.02 | A mixture absolute water/tetrahydrofuran/methanol (3:3:4, v/v/v) | 0.75 | MSPD | 1.25 | HPLC-DAD | 52 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, G.; Li, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, H.; Jin, H.; He, J.; Fang, S.-M.; Chang, Y.-X. A Beta/ZSM-22 Zeolites-Based-Mixed Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Method for the Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Eight Compounds with Different Polarities in Viticis Fructus by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2019, 24, 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193423
He G, Li J, Pang X, Wang H, Jin H, He J, Fang S-M, Chang Y-X. A Beta/ZSM-22 Zeolites-Based-Mixed Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Method for the Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Eight Compounds with Different Polarities in Viticis Fructus by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193423
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Gaogao, Jin Li, Xiaoli Pang, Hui Wang, Hua Jin, Jun He, Shi-Ming Fang, and Yan-Xu Chang. 2019. "A Beta/ZSM-22 Zeolites-Based-Mixed Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Method for the Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Eight Compounds with Different Polarities in Viticis Fructus by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography" Molecules 24, no. 19: 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193423
APA StyleHe, G., Li, J., Pang, X., Wang, H., Jin, H., He, J., Fang, S.-M., & Chang, Y.-X. (2019). A Beta/ZSM-22 Zeolites-Based-Mixed Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Method for the Simultaneous Extraction and Determination of Eight Compounds with Different Polarities in Viticis Fructus by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules, 24(19), 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193423