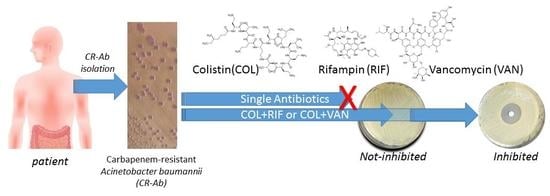
In-Vitro Evaluation of Different Antimicrobial Combinations with and without Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Clinical Data Collection
2.2. Molecular Typing by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Clinical Data Collection
4.2. Antimicrobial Agents
4.3. Molecular Typing by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE)
4.4. Antimicrobial Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maragakis, L.L.; Perl, T.M. Acinetobacter baumannii: Epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, C.M.; Hennon, S.W.; Feldman, M.F. Uncovering the mechanisms of Acinetobacter baumannii virulence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Giuliano, S.; Ceccarelli, G.; Alessandri, F.; Giordano, A.; Brunetti, G.; Venditti, M. Comparison of Septic Shock Due to Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii or Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing K. pneumoniae in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02562-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, J.; Pachon, J. Therapeutic options for Acinetobacter baumannii infections: An update. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 2319–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Alvi, I.A.; Rehman, S.U. Insight into Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, global resistance, mechanisms of resistance, treatment options, and alternative modalities. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Mavroudis, A.D.; Vardakas, K.Z. The antibiotic pipeline for multi-drug resistant gram negative bacteria: What can we expect? Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.J.; McCarthy, M.W. Cefiderocol: A novel siderophore cephalosporin. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertsrisatit, Y.; Santimaleeworagun, W.; Thunyaharn, S.; Traipattanakul, J. In vitro activity of colistin mono- and combination therapy against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, mechanism of resistance, and clinical outcomes of patients infected with colistin-resistant A. baumannii at a Thai university hospital. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, N.C.; Png, K.; Wareham, D.W. Potent synergy and sustained bactericidal activity of a vancomycin-colistin combination versus multidrug-resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5316–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaouakkil, S.; Charra, B.; Hachimi, A.; Nejmi, H.; Benslama, A.; Elmdaghri, N.; Belabbes, H.; Benbachir, M. Colistin and rifampicin in the treatment of nosocomial infections from multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Infect. 2006, 53, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, J.A.; Ambe, L.A.; Casella, L.G.; Townsend, B.M.; Pelletier, M.R.; Ernst, R.K.; Shanks, R.M.; Doi, Y. Activities of vancomycin-containing regimens against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Yahav, D.; Carmeli, Y.; Benattar, Y.D.; Skiada, A.; Andini, R.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Nutman, A.; et al. Colistin alone versus colistin plus meropenem for treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Signoriello, G.; Andini, R.; Mattei, A.; De Cristoforo, M.; Murino, P.; Bassetti, M.; Malacarne, P.; Petrosillo, N.; Galdieri, N.; et al. Colistin and rifampicin compared with colistin alone for the treatment of serious infections due to extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, G.C.; Oliveira, M.S.; Perdigao-Neto, L.V.; Rocha, C.K.; Guimaraes, T.; Rizek, C.; Levin, A.S.; Costa, S.F. Antimicrobial Combinations against Pan-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates with Different Resistance Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Brunel, J.M.; Dubus, J.C.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Rolain, J.M. Colistin: an update on the antibiotic of the 21st century. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horan, T.C.; Andrus, M.; Dudeck, M.A. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am. J. Infect. Control 2008, 36, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villari, P.; Iacuzio, L.; Vozzella, E.A.; Bosco, U. Unusual genetic heterogeneity of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in a university hospital in Italy. Am. J. Infect. Control 1999, 27, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V.; Mickelsen, P.A.; Murray, B.E.; Persing, D.H.; Swaminathan, B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- CLSI. M07-A9; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 9th ed.; Wayne, P.A., Ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Odds, F.C. Synergy, antagonism, and what the chequerboard puts between them. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, S.; Bjelkenbrant, C.; Kahlmeter, G. Validation of EUCAST zone diameter breakpoints against reference broth microdilution. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O353–O360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.; Canton, R.; Dubreuil, L.; Gatermann, S.; Giske, C.; MacGowan, A.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; Mouton, J.; Skov, R.; Steinbakk, M.; et al. Widespread implementation of EUCAST breakpoints for antibacterial susceptibility testing in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2015, 20, 21008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Oliva, A.; d’Ettorre, G.; D’Abramo, A.; Caresta, E.; Barbara, C.S.; Mascellino, M.T.; Papoff, P.; Moretti, C.; Vullo, V.; et al. The role of vancomycin in addition with colistin and meropenem against colistin-sensitive multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii causing severe infections in a Paediatric Intensive Care Unit. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, R.M.; Ambler, J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Castanheira, M.; Dingle, T.; Hindler, J.A.; Koeth, L.; Sei, K.; Development, C.M.; Standardization Working Group of the Subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. CLSI Methods Development and Standardization Working Group Best Practices for Evaluation of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01934-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.F.; Wootton, M.; Howe, R.A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing breakpoints and methods from BSAC to EUCAST. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Hittle, L.E.; O’Hara, J.A.; Rivera, J.I.; Syed, A.; Shields, R.K.; Pasculle, A.W.; Ernst, R.K.; Doi, Y. Colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Beyond carbapenem resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.; Costantini, S.; De Angelis, M.; Garzoli, S.; Bozovic, M.; Mascellino, M.T.; Vullo, V.; Ragno, R. High Potency of Melaleuca alternifolia Essential Oil against Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2018, 23, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Guan, J.; Wang, X.; Cong, Y. Activity of Colistin in Combination with Meropenem, Tigecycline, Fosfomycin, Fusidic Acid, Rifampin or Sulbactam against Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Murine Thigh-Infection Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornsey, M.; Wareham, D.W. In vivo efficacy of glycopeptide-colistin combination therapies in a Galleria mellonella model of Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3534–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Amaya-Villar, R.; Gutierrez-Pizarraya, A.; Espejo-Gutierrez de Tena, E.; Artero-Gonzalez, M.L.; Corcia-Palomo, Y.; Bautista-Paloma, J. Clinical efficacy and safety of the combination of colistin plus vancomycin for the treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Chemotherapy 2013, 59, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosillo, N.; Giannella, M.; Antonelli, M.; Antonini, M.; Barsic, B.; Belancic, L.; Inkaya, A.C.; De Pascale, G.; Grilli, E.; Tumbarello, M.; et al. Clinical experience of colistin-glycopeptide combination in critically ill patients infected with Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogue, J.M.; Kaye, K.S. Is there really no benefit to combination therapy with colistin? Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.J.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, H.; Yoon, E.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Yong, D.; Lee, K. In vitro antimicrobial synergy of colistin with rifampicin and carbapenems against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 86, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Bergen, P.J.; Bulitta, J.B.; Tsuji, B.; Forrest, A.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Synergistic activity of colistin and rifampin combination against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3738–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tascini, C.; Tagliaferri, E.; Giani, T.; Leonildi, A.; Flammini, S.; Casini, B.; Lewis, R.; Ferranti, S.; Rossolini, G.M.; Menichetti, F. Synergistic activity of colistin plus rifampin against colistin-resistant KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3990–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Li, J. In vitro synergy of colistin combinations against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing OXA-23 carbapenemase. J. Chemother. 2016, 28, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan-Krohn, T.; Pironti, A.; Kirby, J.E. Synergistic Activity of Colistin-Containing Combinations against Colistin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00873-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNair, C.R.; Stokes, J.M.; Carfrae, L.A.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.A.; Coombes, B.K.; Mulvey, M.R.; Brown, E.D. Overcoming mcr-1 mediated colistin resistance with colistin in combination with other antibiotics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaara, M. Agents that increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vidaillac, C.; Benichou, L.; Duval, R.E. In vitro synergy of colistin combinations against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4856–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.; Cipolla, A.; Vullo, V.; Venditti, M.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Falcone, M. Clinical and in vitro efficacy of colistin plus vancomycin and rifampin against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii causing ventilator-associated pneumonia. New Microbiol. 2017, 40, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; He, X.; Li, J. Synergy effect of meropenem-based combinations against Acinetobacter baumannii: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shaer, M.; Nazer, L.H.; Kherallah, M. Rifampicin as adjunct to colistin therapy in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





| Patient | Type of Infection | Therapy | Duration of Therapy (days) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BSI | C + M + V | 14 | Cured |
| 2 | HAP | C + M + V | 13 | Cured |
| 3 | SSI | C + T + V | 30 | Cured |
| 4 | SSI | C + R | 14 | Cured |
| 5 | BSI | C + M | 30 | Cured |
| 6 | HAP | C + V + R | 14 | Cured |
| 7 | BSI | C + M + V | 6 | Died* |
| 8 | HAP | C + M | 17 | Cured |
| 9 | HAP | C + M | 14 | Cured |
| 10 | HAP | C + M | 14 | Cured |
| 11 | HAP | C + M | 14 | Cured |
| 12 | HAP | C + T | 14 | Cured |
| 13 | HAP | C + M | 10 | Died* |
| 14 | HAP | C + M + V | 14 | Cured |
| Antibiotic | MEM | COL | VAN | RIF | GEN | TIG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MBD | MBD | E-Test | MBD | MBD | MBD | E-Test | MBD | |
| Patients/Clinical Isolates | 1 | 128 | 1.000 | 0.750 | 256 | 8 | 4 | 2.00 | 0.50 |
| 2 | 256 | 0.250 | 0.300 | 32 | 4 | >512 | 1.50 | 1.00 | |
| 3 | 256 | 0.060 | 0.380 | 64 | >512 | 2 | 0.75 | 1.00 | |
| 4 | 128 | 0.032 | 0.075 | 128 | >512 | >512 | 2.00 | 0.50 | |
| 5 | 32 | 0.125 | 0.380 | 64 | 4 | >512 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 6 | 128 | 4.000 | 4.00 | 64 | 4 | 512 | 3.00 | 0.50 | |
| 7 | 512 | 0.015 | 0.750 | 128 | >512 | >512 | 2.00 | 1.00 | |
| 8 | 256 | 0.030 | 0.380 | 128 | 4 | 32 | 1.50 | 0.25 | |
| 9 | 256 | 0.250 | 0.500 | 128 | 4 | >512 | 2.00 | 0.50 | |
| 10 | 32 | 2.000 | 1.000 | 128 | 2 | >512 | 1.50 | 0.50 | |
| 11 | 128 | 0.500 | 1.500 | 64 | 16 | 64 | 0.75 | 0.75 | |
| 12 | 8 | 256.0 | 128.0 | 32 | >512 | 2 | 1.00 | 0.25 | |
| 13 | 64 | 0.125 | 0.500 | 32 | 4 | >512 | 1.50 | 0.25 | |
| 14 | 32 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 64 | 4 | 256 | 2.00 | 0.50 | |
| Strains | PFGE Pattern | COL + MEM | COL + RIF | COL + VAN | COL + TIG | MEM + TIG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FICI° | Syn | FICI | Syn | FICI | Syn | FICI | Syn | FICI | Syn | ||
| 1 | B | 0.375 | S | 0.375 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.375 | S | 1.000 | I |
| 2 | B1 | 0.625 | I | 0.375 | S | 0.625 | I | 1.000 | I | 0.500 | S |
| 3 | B | 0.625 | I | 0.625 | I | 0.750 | I | 0.625 | I | 0.375 | S |
| 4 | A | 0.750 | I | 0.625 | I | 0.625 | I | 1.000 | I | 0.750 | I |
| 5 | D | 0.625 | I | 0.500 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.625 | I |
| 6 * | C | 0.250 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.250 ° | S | 0.250 | S | 0.375 | S |
| 7 | A1 | 1.000 | I | 1.000 | I | 1.000 | I | 2.000 | I | 0.625 | I |
| 8 | E1 | 0.625 | I | 0.750 | I | 0.375 | S | 2.000 | I | 1.000 | I |
| 9 | B2 | 0.750 | I | 0.750 | I | 0.625 | I | 2.000 | I | 0.250 | S |
| 10 | E | 0.250 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.250 | S | 0.625 | I |
| 11 | - | 1.000 | I | 0.250 | S | 0.375 | S | 0.375 | S | 0.375 | S |
| 12 ** | D2 | 0.750 | I | 0.250 | S | 0.625 § | I | 2.000 | I | 1.000 | I |
| 13 | D1 | 2.000 | I | 0.625 | I | 0.625 | I | 2.000 | I | 0.625 | I |
| 14 | E1 | 0.625 | I | 0.250 | S | 0.625 | I | 0.750 | I | 0.625 | I |
| Total n | 3/14 | 8/14 | 6/14 | 5/14 | 5/14 | ||||||
| Total (%) | 21.4 | 57.1 | 42.8 | 35.7 | 35.7 | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliva, A.; Garzoli, S.; De Angelis, M.; Marzuillo, C.; Vullo, V.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Ragno, R. In-Vitro Evaluation of Different Antimicrobial Combinations with and without Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Molecules 2019, 24, 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050886
Oliva A, Garzoli S, De Angelis M, Marzuillo C, Vullo V, Mastroianni CM, Ragno R. In-Vitro Evaluation of Different Antimicrobial Combinations with and without Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):886. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050886
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliva, Alessandra, Stefania Garzoli, Massimiliano De Angelis, Carolina Marzuillo, Vincenzo Vullo, Claudio M. Mastroianni, and Rino Ragno. 2019. "In-Vitro Evaluation of Different Antimicrobial Combinations with and without Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii" Molecules 24, no. 5: 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050886
APA StyleOliva, A., Garzoli, S., De Angelis, M., Marzuillo, C., Vullo, V., Mastroianni, C. M., & Ragno, R. (2019). In-Vitro Evaluation of Different Antimicrobial Combinations with and without Colistin Against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Molecules, 24(5), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050886