Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Ultrasonic Degraded Polysaccharide Complex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Viscosity Measurement
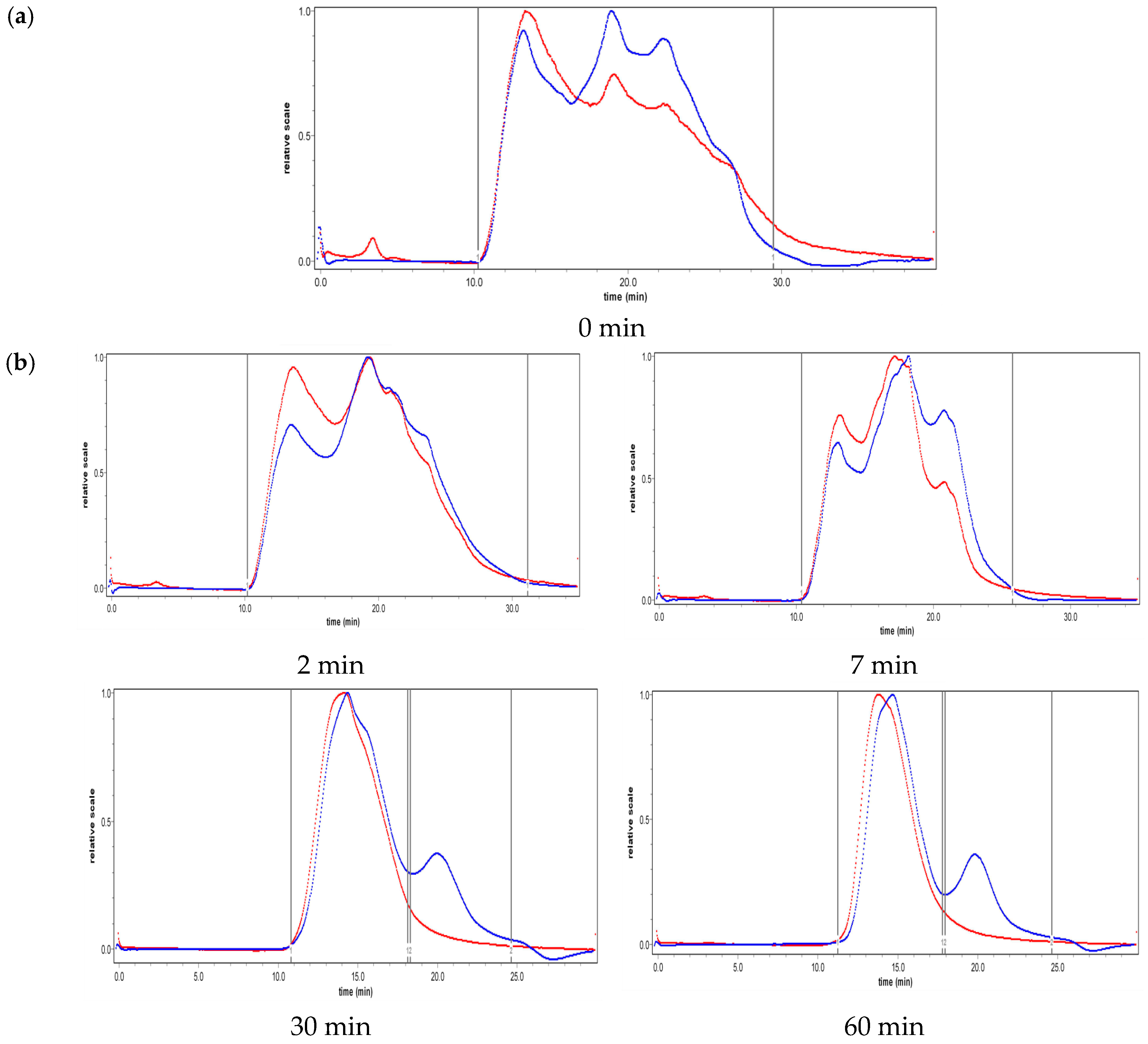
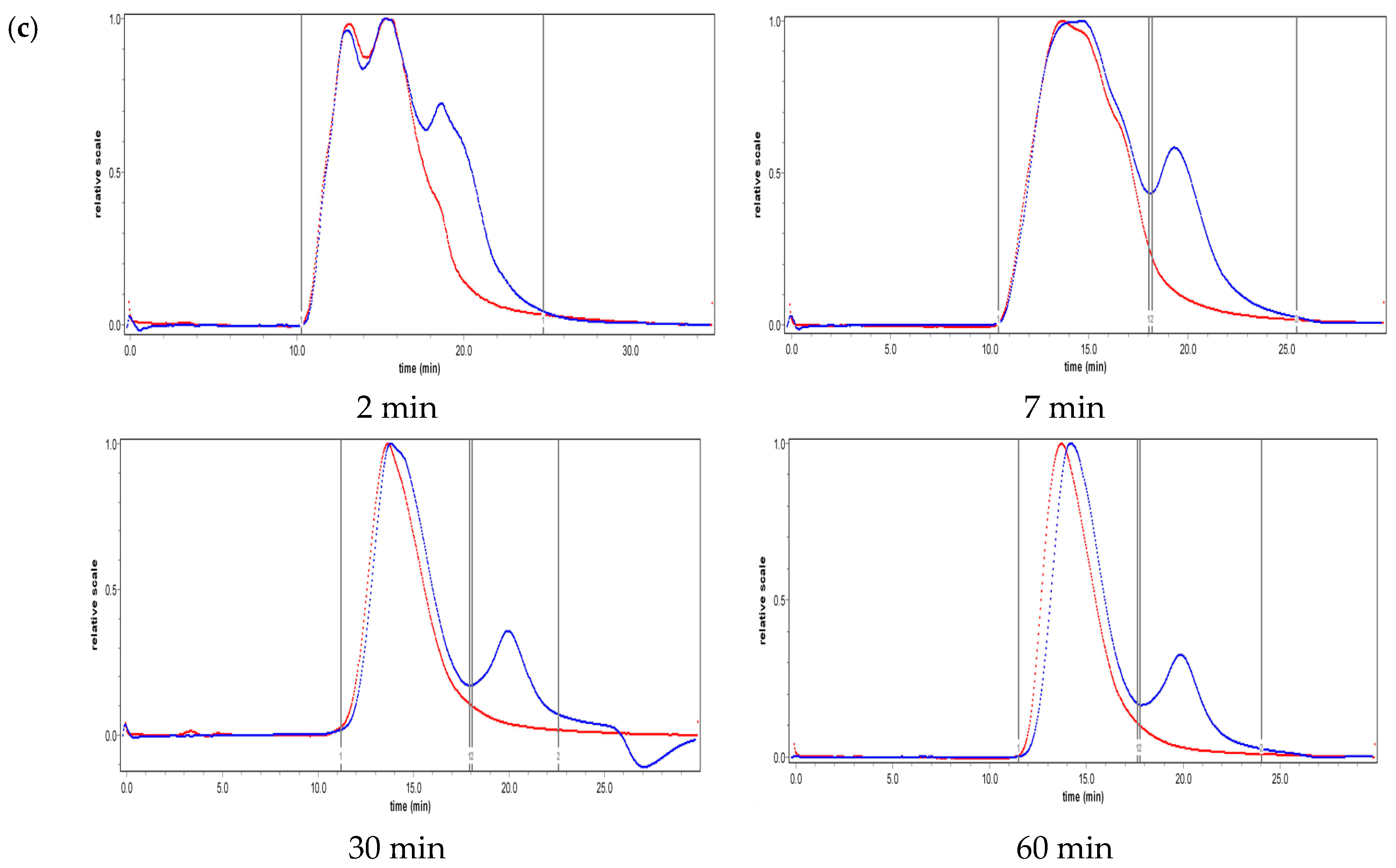
2.2. Effect of Ultrasound on Molecular Weight Distribution
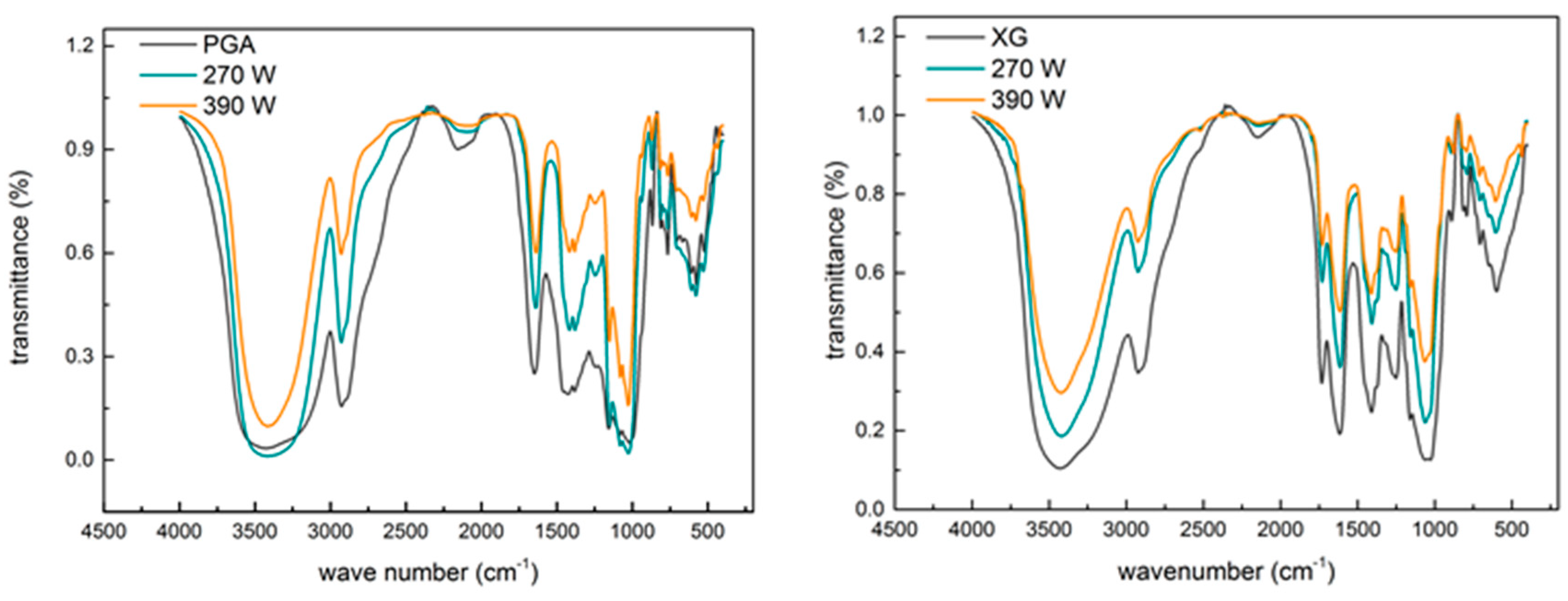
2.3. Effect of Ultrasound on the Primary Structure of Polysaccharides
2.4. Effect of Ultrasound on Interfacial Tension
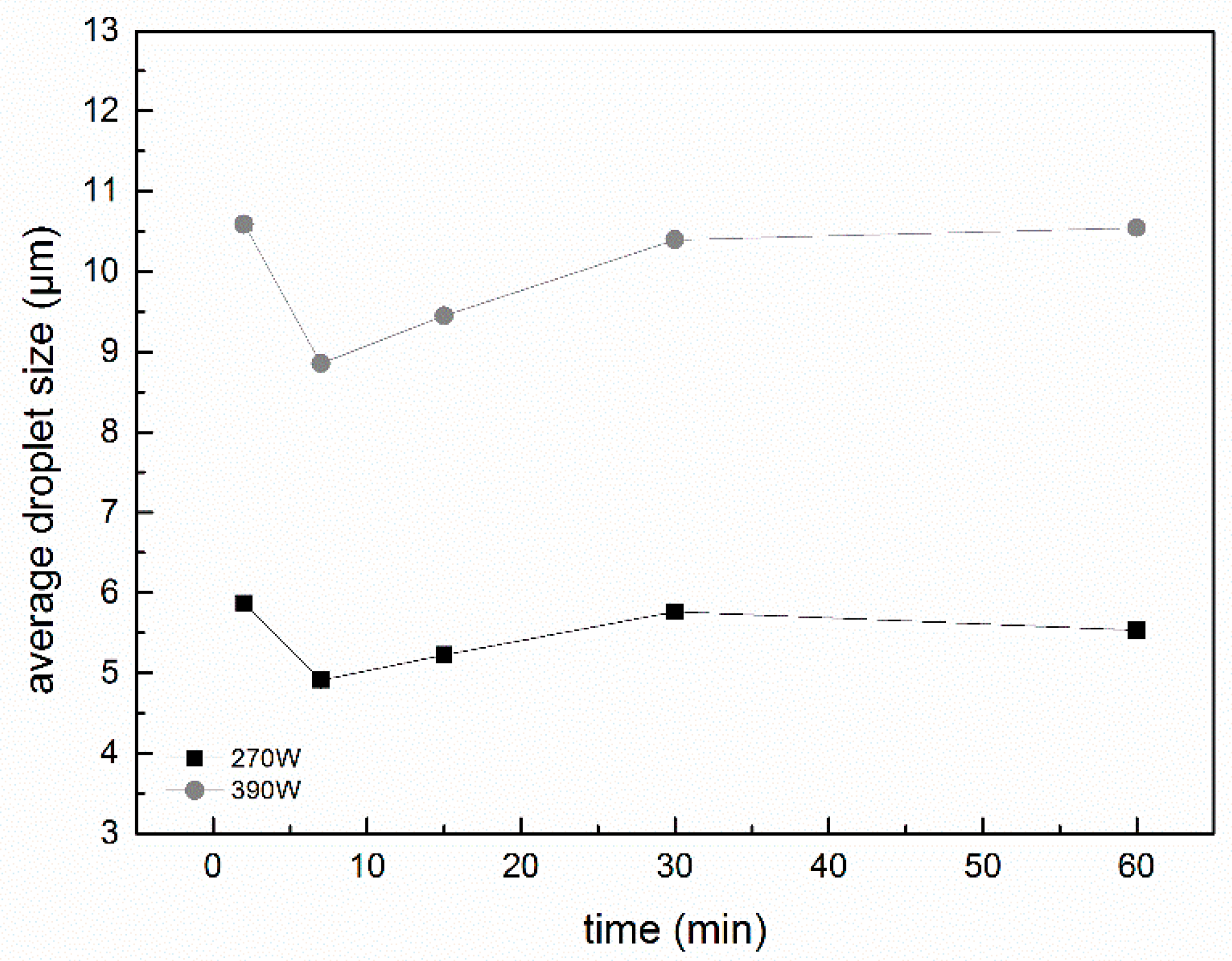
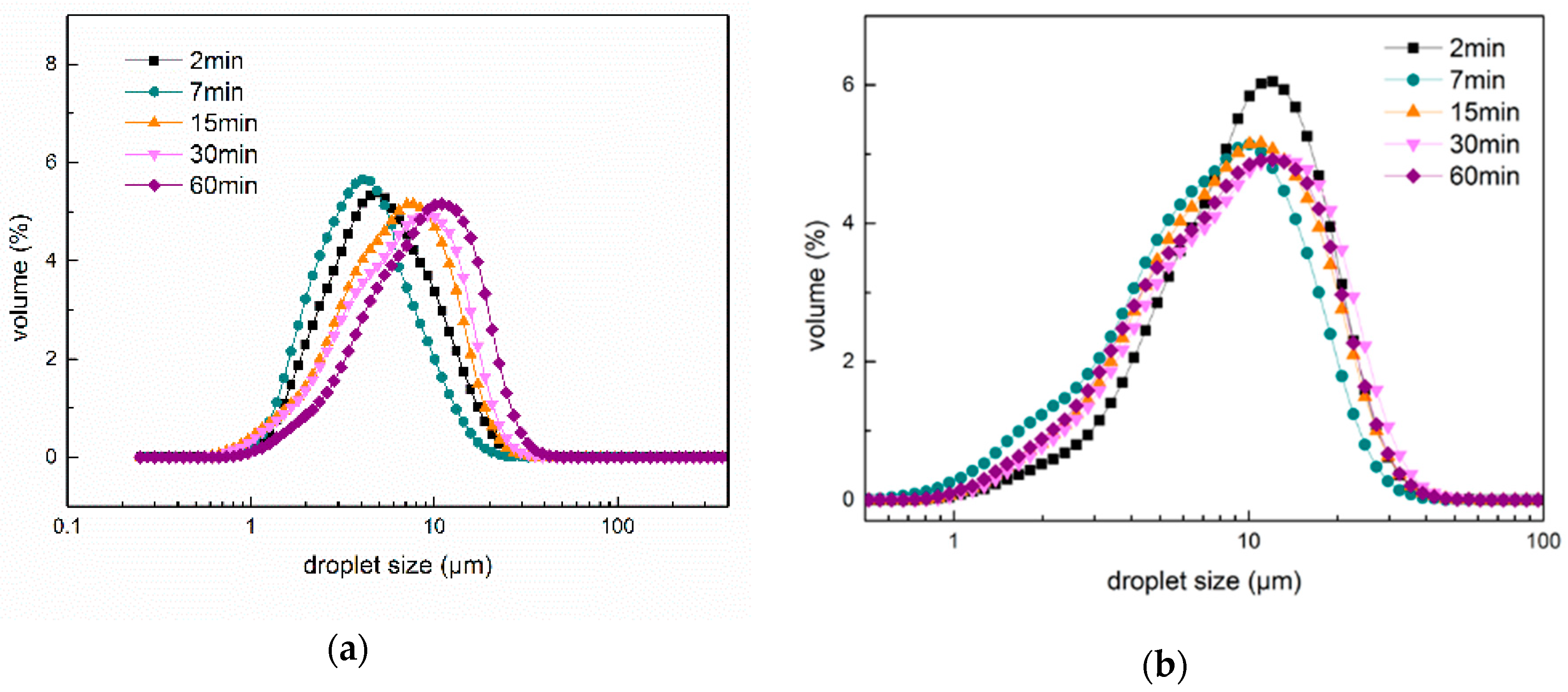
2.5. Particle Size and Size Distribution of Fresh Emulsions
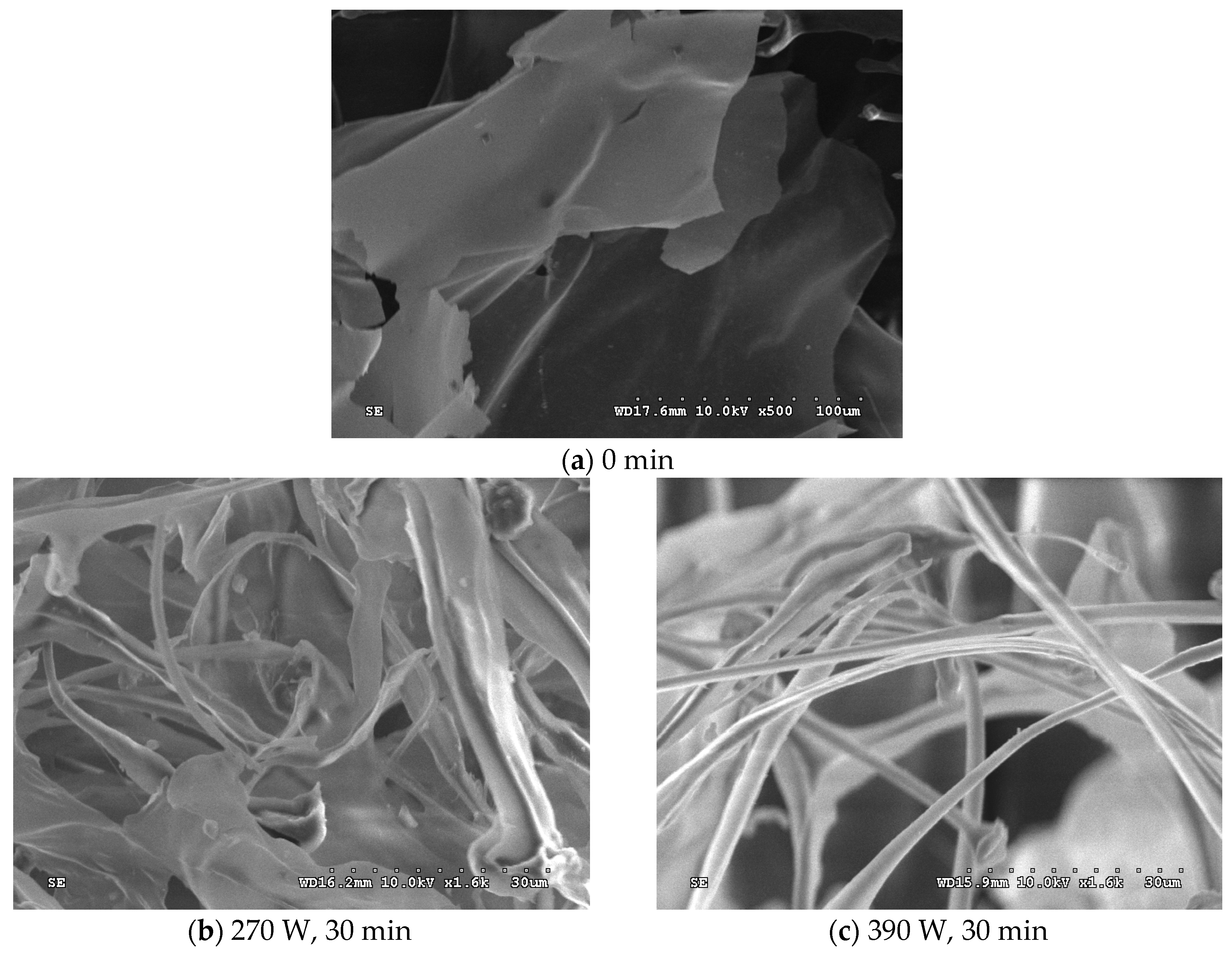
2.6. Microstructure of the Emulsions
2.7. Visual Phase Separation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Polysaccharide Solution Preparation
3.2. Viscosity Measurement
3.3. Preparation of O/W Emulsions
3.4. Determination of Average Molecular Weight and Molecular Weight Distribution
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic Analysis
3.6. Interfacial Characteristics Measurement
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.8. Measurement of Droplet Size
3.9. Fluorescence Microscopy
3.10. Visual Observation of the Phase Separation
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perdih, T.S.; Zupanc, M.; Dular, M. Revision of the mechanisms behind oil-water (O/W) emulsion preparation by ultrasound and cavitation. Ultrason. Soncochem. 2019, 51, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Ye, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, N.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S. Ultrasound effects on the degradation kinetics, structure, and antioxidant activity of sea cucumber fucoidan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Geng, P.; Song, A.X.; Wu, J.Y. Ultrasonic degradation kinetics and rheological profiles of a food polysaccharide (konjac glucomannan) in water. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawitwong, P.; Takigami, S.; Phillips, G.O. Effects of γ-irradiation on molar mass and properties of Konjac mannan. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.L.R.; Gomes, A.; Cunha, R.L. One-step ultrasound producing O/W emulsions stabilized by chitosan particles. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouryieh, H.; Puli, G.; Williams, K.; Aramouni, F. Effects of xanthan-locust bean gum mixtures on the physicochemical properties and oxidative stability of whey protein stabilised oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Sun, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhan, X.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Formation and characterization of zein-propylene glycol alginate-surfactant ternary complexes: Effect of surfactant type. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, M.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Viscoelastic properties, microstructure and stability of high-oleic O/W emulsions stabilised by crayfish protein concentrate and xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronroos, A.; Pentti, P.; Hanna, K. Ultrasonic degradation of aqueous carboxymethylcellulose: Effect of viscosity, molecular mass, and concentration. Ultrason. Soncochem. 2008, 15, 644–648. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Feke, D.L. Rheological and kinetic study of the ultrasonic degradation of xanthan gum in aqueous solutions. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Hsieh, J.F. Propylene glycol alginate-induced coacervation of milk proteins: A proteomics approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, R.; Sanchez, C.C.; Pilosof, A.M.R.; Patino, J.M.R. Interfacial and foaming properties of prolylenglycol alginates: Effect of degree of esterification and molecular weight. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 36, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, K.W.; Mirhosseini, H.; Hamid, N.S.; Osman, A.; Basri, M.; Tan, C.P. Effects of propylene glycol alginate and sucrose esters on the physicochemical properties of modified starch-stabilized beverage emulsions. Molecules 2014, 19, 8691–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Mishra, V.; Singh, P.; Srivastava, A.; Kumar, R. Comparative study of thermal degradation behavior of graft copolymers of polysaccharides and vinyl monomers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 107, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, K.; Jolie, R.P.; Fraeye, I.; van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. Comparative study of the cell wall composition of broccoli, carrot, and tomato: Structural characterization of the extractable pectins and hemicelluloses. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Huan, S.; Gu, J.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of oil-in-water nanoemulsions by dual-channel microfluidization using natural emulsifiers: Saponins, phospholipids, proteins, and polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, Z.B. Ultrasonic effects on the degradation kinetics, preliminary characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus mycelia. Ultrason. Soncochem. 2016, 29, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Ding, T.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D. Ultrasound effects on the degradation kinetics, structure and rheological properties of apple pectin. Ultrason. Soncochem. 2013, 20, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, S. Molecular weight degradation and rheological properties of schizophyllan under ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason. Soncochem. 2015, 23, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Ding, T.; Ye, X. Effect of degradation methods on the structural properties of citrus pectin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T. Ultrasound-mediated nettle oil nanoemulsions stabilized by purified jujube polysaccharide: Process optimization, microbial evaluation and physicochemical storage stability. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 234, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivero, P.; Gohtani, S.; Yoshii, H.; Nakamura, A. Physical properties of oil-in-water emulsions as a function of oil and soy soluble polysaccharide types. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juttulapa, M.; Piriyaprasarth, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Sriamornsak, P. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on stability of emulsions containing zein and pectin. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.; Razavi, S.H.; Mousavi, S.M. Ultrasound-assisted formation of the canthaxanthin emulsions stabilized by arabic and xanthan gums. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Cayado, L.A.; Alfaro, M.C.; Munoz, J.; Raymundo, A.; Sousa, I. Development and rheological properties of ecological emulsions formulated with a biosolvent and two microbial polysaccharides. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Xiang, D.; Wang, B.; Gong, X. Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Ultrasonic Degraded Polysaccharide Complex. Molecules 2019, 24, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061097
Li Y, Xiang D, Wang B, Gong X. Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Ultrasonic Degraded Polysaccharide Complex. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061097
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yujie, Dong Xiang, Bo Wang, and Xiaoyue Gong. 2019. "Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Ultrasonic Degraded Polysaccharide Complex" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061097
APA StyleLi, Y., Xiang, D., Wang, B., & Gong, X. (2019). Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by Ultrasonic Degraded Polysaccharide Complex. Molecules, 24(6), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061097




