Discovery of Novel Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Protocol of Virtual Screening Approach Based on Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore and Molecular Docking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Generation and Validation of Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore
2.2. Parameter Setting and Scoring Function Selection for the Molecular Docking
2.3. Database Screening
3. Computational Methods
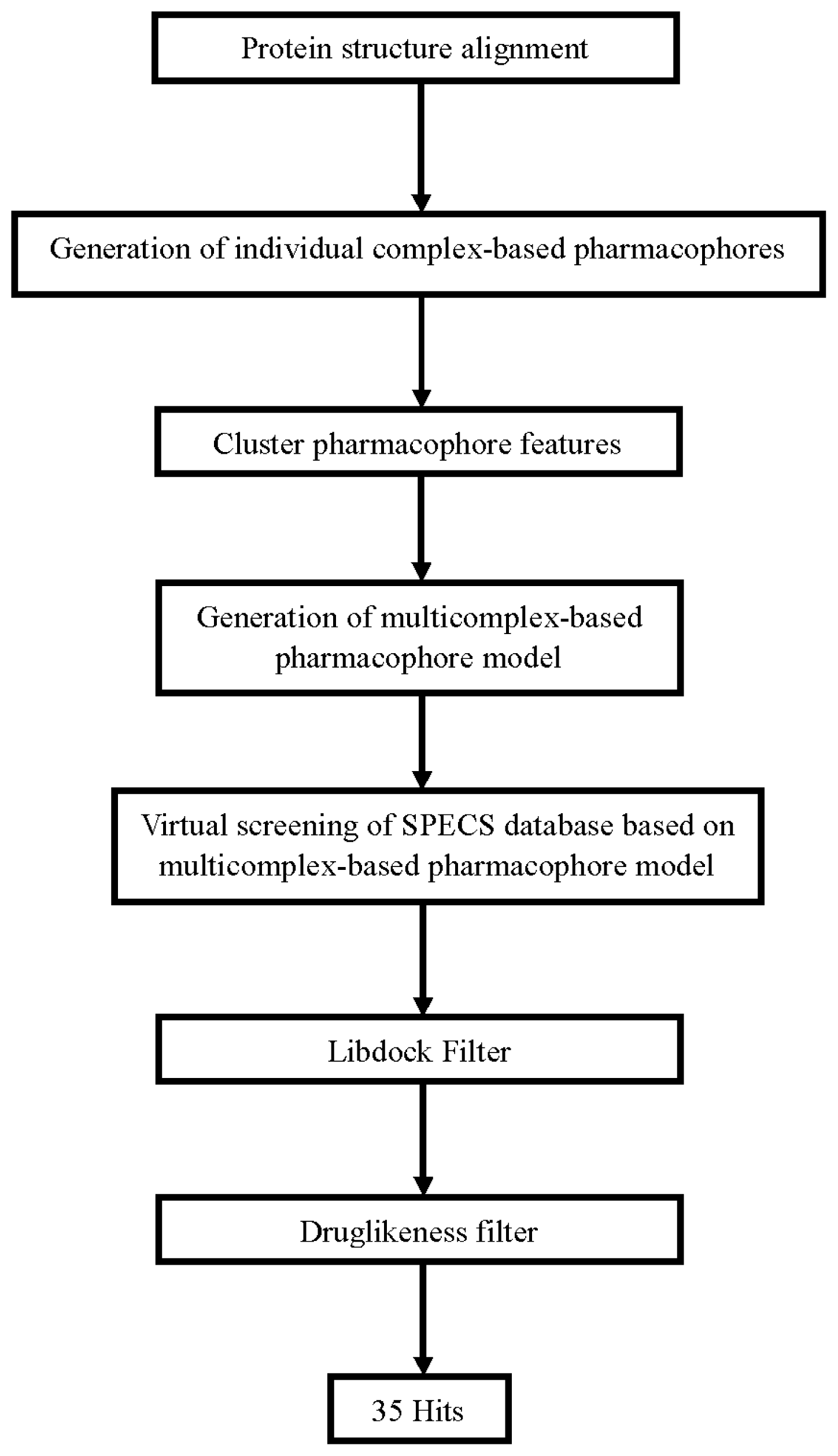
3.1. Generation of Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore Models
3.2. Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening
3.3. Molecular Docking Study
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Kanner, S.B.; Reynolds, A.B.; Vines, R.R.; Parsons, J.T. Monoclonal antibodies to individual tyrosine-phosphorylated protein substrates of oncogene-encoded tyrosine kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3328–3332. [Google Scholar]
- Matkowskyj, K.A.; Keller, K.; Glover, S.; Kornberg, L.; Tran-Son-Tay, R.; Benya, R.V. Expression of GRP and its receptor in well-differentiated colon cancer cell score relates with the presence of focal adhesion kinase phosphorylated at tyrosines 397 and 407. J. Histochem. Cytochem 2003, 51, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.A.; Ginsberg, M.H. Networks and cross-talk: Integrin signaling spreads. Nat. Cell Biol 2002, 4, E65–E68. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hunter, T. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix: Role for the focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase FAK. Cell Struct. Funct 1996, 21, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hauck, C.R.; Sieg, D.J. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol 1999, 71, 435–478. [Google Scholar]
- Gabarra-Niecko, V.; Schaller, M.D.; Unty, J.M. FAK regulates biological processes important for the pathogenesis of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2003, 22, 359–374. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, G.W.; Carragher, N.O.; Avizienyte, E.; Evans, J.; Brunton, V.G.; Frame, M.C. The role of focal adhesion kinase in cancer, new therapeutic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, A.K.; Coffin, J.E.; Schneider, G.B.; DeYoung, B.R.; Gruman, L.M.; Gershenson, D.M.; Schaller, M.D.; Hendrix, M.J.C. Biological significance of focal adhesion kinase in ovarian cancer: role in migration and invasion. Am. J. Pathol 2004, 165, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Cance, W.G.; Harris, J.E.; Iacocca, M.V.; Roche, E.; Yang, X.H.; Chang, J.L.; Simkins, S.; Xu, L.H. Immunohistochemical analyses of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human breast and colon tissues: Correlation with preinvasive and invasive phenotypes. Clin. Cancer Res 2000, 6, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, T.M.; Liu, E.T.; Craven, R.J.; Cance, W.G. Expression of focal adhesion kinase gene and invasive cancer. Lancet 1993, 342, 1024–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.; Machado, J.; Tolnay, M.; Merlo, A. PTEN-independent induction of caspase-mediated cell death and reduced invasion by the focal adhesion targeting domain (FAT) in human astrocytic brain tumors which highly express focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Cancer Res 2001, 61, 5688–5691. [Google Scholar]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Cance, W.G. Focal Adhesion Kinase and p53 Signaling in Cancer Cells. Int. Rev. Cytol 2007, 263, 103–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Naomoto, Y.; Bao, X.; Watanabe, N.; Sakurama, K.; Noma, K.; Motoki, T.; Tomono, Y.; Fukazawa, T.; Shirakawa, Y.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase as potential target for cancer therapy. Onco. Rep 2009, 22, 973–979. [Google Scholar]
- Slack-Davis, J.K.; Martin, K.H.; Tilghman, R.W.; Iwanicki, M.; Ung, E.J.; Autry, C.; Luzzio, M.J.; Cooper, B.; Kath, J.C.; Roberts, W.G.; et al. Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 14845–14852. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Keir, S.T.; Song, L.; Wickman, S.; Jackson, D.; Ohmori, O.; Bigner, D.D.; Friedman, H.S.; Rich, J.N. A novel low-molecular weight inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, TAE226, inhibits glioma growth. Mol. Carcinog 2007, 46, 488–496. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nimwegen, M.J.; van de Water, B. Focal adhesion kinase: A potential target in cancer therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol 2007, 73, 597–609. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.T.; Chen, X.L.; Lim, Y.; Hanson, D.A.; Vo, T.T.; Howerton, K.; Larocque, N.; Fisher, S.J.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Ilic, D. Nuclear FAK promotes cell proliferation and survival through FERM-enhanced p53 degradation. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Marti-Renom, M.A.; Stuart, A.C.; Fiser, A.; Sanchez, R.; Melo, F.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 2000, 29, 291–325. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.Y.; Chen, Y.D.; You, Q.D. 3D-QSAR studies of arylcarboxamides with inhibitory activity on InhA using pharmacophore-based alignment. Chem. Biol. Drug Des 2010, 75, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhaery, S.S.; Roy, K.K.; Saxena, A.K. Consensus Superiority of the Pharmacophore-Based Alignment, Over Maximum Common Substructure (MCS): 3D-QSAR Studies on Carbamates as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2009, 49, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Qiu, M.H.; Li, R.; Ouyang, L.; Wu, F.B.; Song, X.R.; Cheng, L.; Xiang, M.L.; Yu, L.T. Multicomplex-based pharmacophore-guided 3D-QSAR studies of N-substituted 2′-(amino-aryl-) benzothiazoles as Aurora-A inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des 2012, 79, 960–971. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; He, G.; Huang, W.; Song, X.R.; Wu, F.B.; Xiang, M.L. Combined Structure-Based Pharmacophore and 3D-QSAR Studies on Phenylalanine Series Compounds as TPH1 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 5348–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucl. Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Courcy, B.; Piquemal, J.P.; Garbay, C.; Gresh, N. Polarizable Water Molecules in Ligand-Macromolecule Recognition. Impact on the Relative Affinities of Competing Pyrrolopyrimidine Inhibitors for FAK Kinase. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar]
- Discovery Studio, version 3.5; Accelrys Inc: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012.
- Thangapandian, S.; John, S.; Sakkiah, S.; Lee, K.W. Potential virtual lead identification in the discovery of renin inhibitors: application of ligand and structure-based pharmacophore modeling approaches. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2011, 46, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, J.J.; Sterling, T.; Mysinger, M.M.; Bolstad, E.S.; Coleman, R.G. ZINC: A Free Tool to Discover Chemistry for Biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2012, 52, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar]
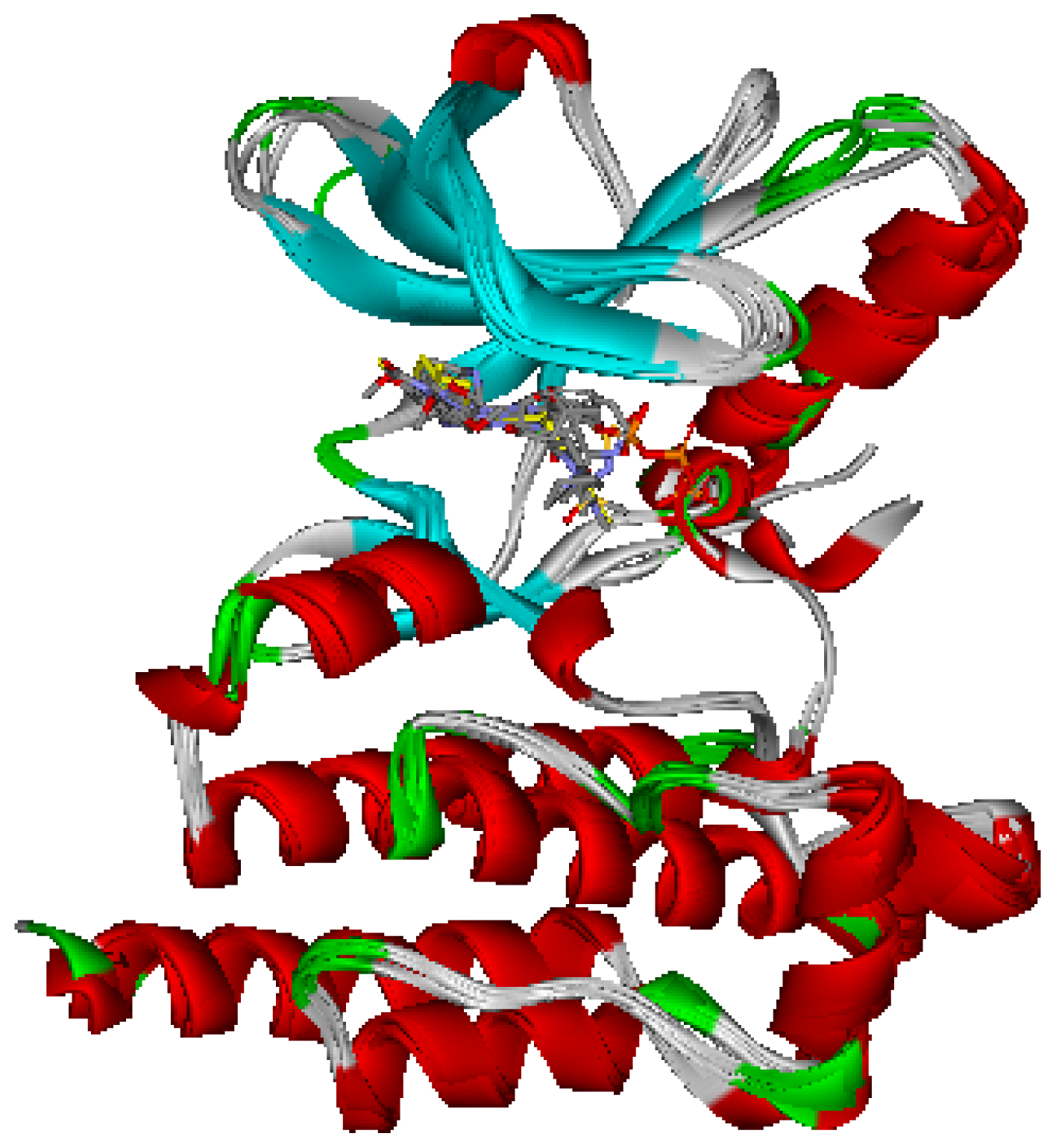
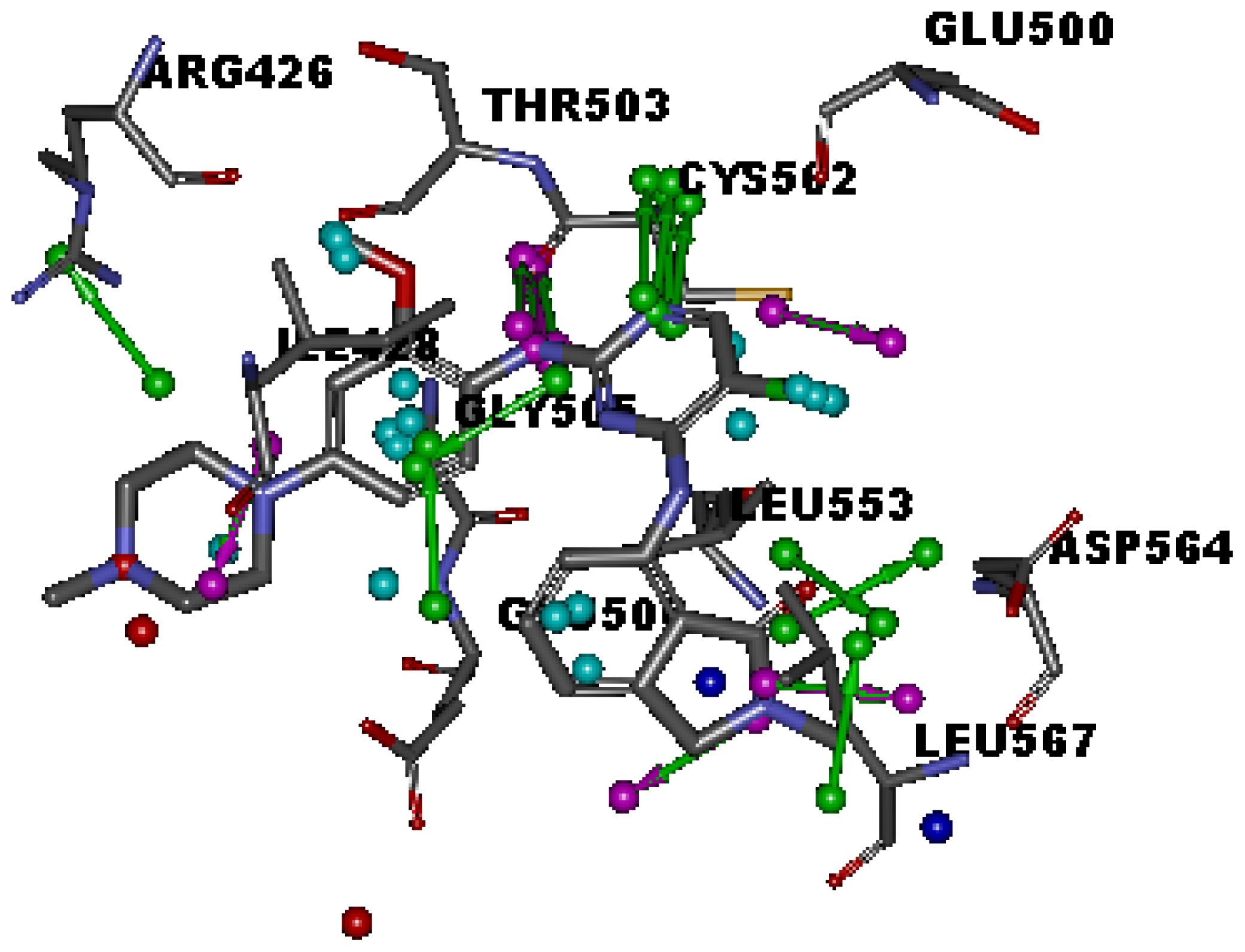

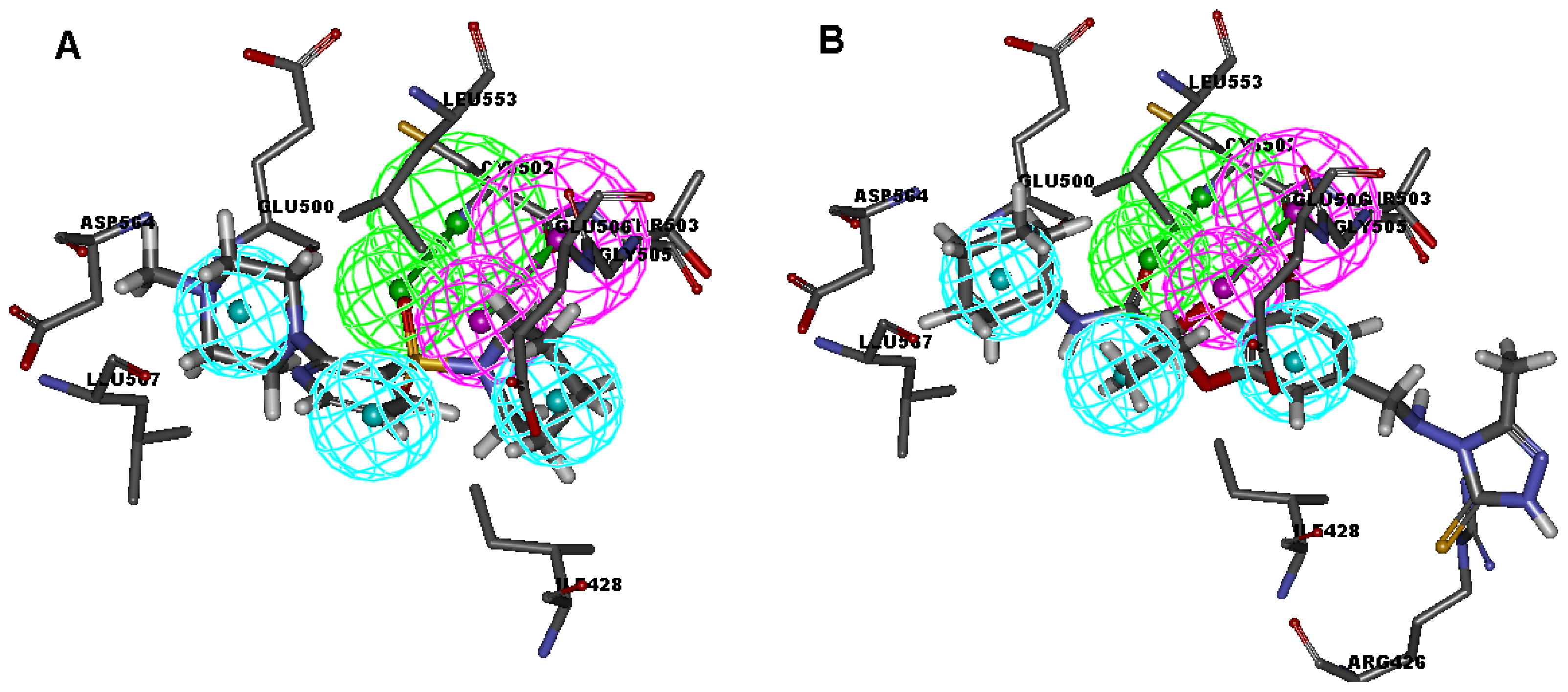
| No. | Feature Name | ID | Count | Statistical frequency (%) | Structure-based Pharmacophore model | Related amino acid residues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HBA-F 1 | A1 | 4 | 57 | √ | Cys 502 |
| 2 | HBA-F 2 | A2 | 2 | 28 | ||
| 3 | HBA-F 3 | A3 | 2 | 28 | ||
| 4 | HBA-F 4 | A4 | 1 | 14 | ||
| 5 | HBD 1 | D1 | 4 | 57 | √ | Thr 503 |
| 6 | HBD 2 | D2 | 2 | 28 | ||
| 7 | HBD 3 | D3 | 1 | 14 | ||
| 8 | HBD 4 | D4 | 1 | 14 | ||
| 9 | Hydrophobic 1 | H1 | 4 | 57 | √ | Ile 428, Gly 505 |
| 10 | Hydrophobic 2 | H2 | 4 | 57 | √ | Met 499, Leu 553 |
| 11 | Hydrophobic 3 | H3 | 3 | 43 | √ | Leu567 |
| 12 | Hydrophobic 4 | H4 | 2 | 28 | ||
| 13 | Hydrophobic 5 | H5 | 1 | 14 | ||
| 14 | Negative Ionizable | Neg | 1 | 14 | ||
| 15 | Positive Ionizable | Pos | 1 | 5 |
| No. | PDB | Resolution | Ligand | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2ETM | 2.30 | 7PY | 2006-10-10 |
| 2 | 2IJM | 2.19 | ATP | 2007-8-14 |
| 3 | 2JKK | 2.00 | BI9 | 2008-9-9 |
| 4 | 2JKM | 2.31 | BII | 2008-9-9 |
| 5 | 2JKO | 1.65 | BIJ | 2008-9-9 |
| 6 | 2JKQ | 2.60 | VG8 | 2008-9-9 |
| 7 | 3BZ3 | 2.20 | YAM | 2008-4-1 |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, F.; Xu, T.; He, G.; Ouyang, L.; Han, B.; Peng, C.; Song, X.; Xiang, M. Discovery of Novel Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Protocol of Virtual Screening Approach Based on Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore and Molecular Docking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15668-15678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215668
Wu F, Xu T, He G, Ouyang L, Han B, Peng C, Song X, Xiang M. Discovery of Novel Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Protocol of Virtual Screening Approach Based on Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore and Molecular Docking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(12):15668-15678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215668
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Fengbo, Ting Xu, Gu He, Liang Ouyang, Bo Han, Cheng Peng, Xiangrong Song, and Mingli Xiang. 2012. "Discovery of Novel Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Protocol of Virtual Screening Approach Based on Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore and Molecular Docking" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 12: 15668-15678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215668
APA StyleWu, F., Xu, T., He, G., Ouyang, L., Han, B., Peng, C., Song, X., & Xiang, M. (2012). Discovery of Novel Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors Using a Hybrid Protocol of Virtual Screening Approach Based on Multicomplex-Based Pharmacophore and Molecular Docking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(12), 15668-15678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215668





