Molecular Cloning and Expression of CYP9A61: A Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and Lambda-Cyhalothrin-Inducible Cytochrome P450 cDNA from Cydia pomonella
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Cytochrome P450 Gene (CYP9A61)
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
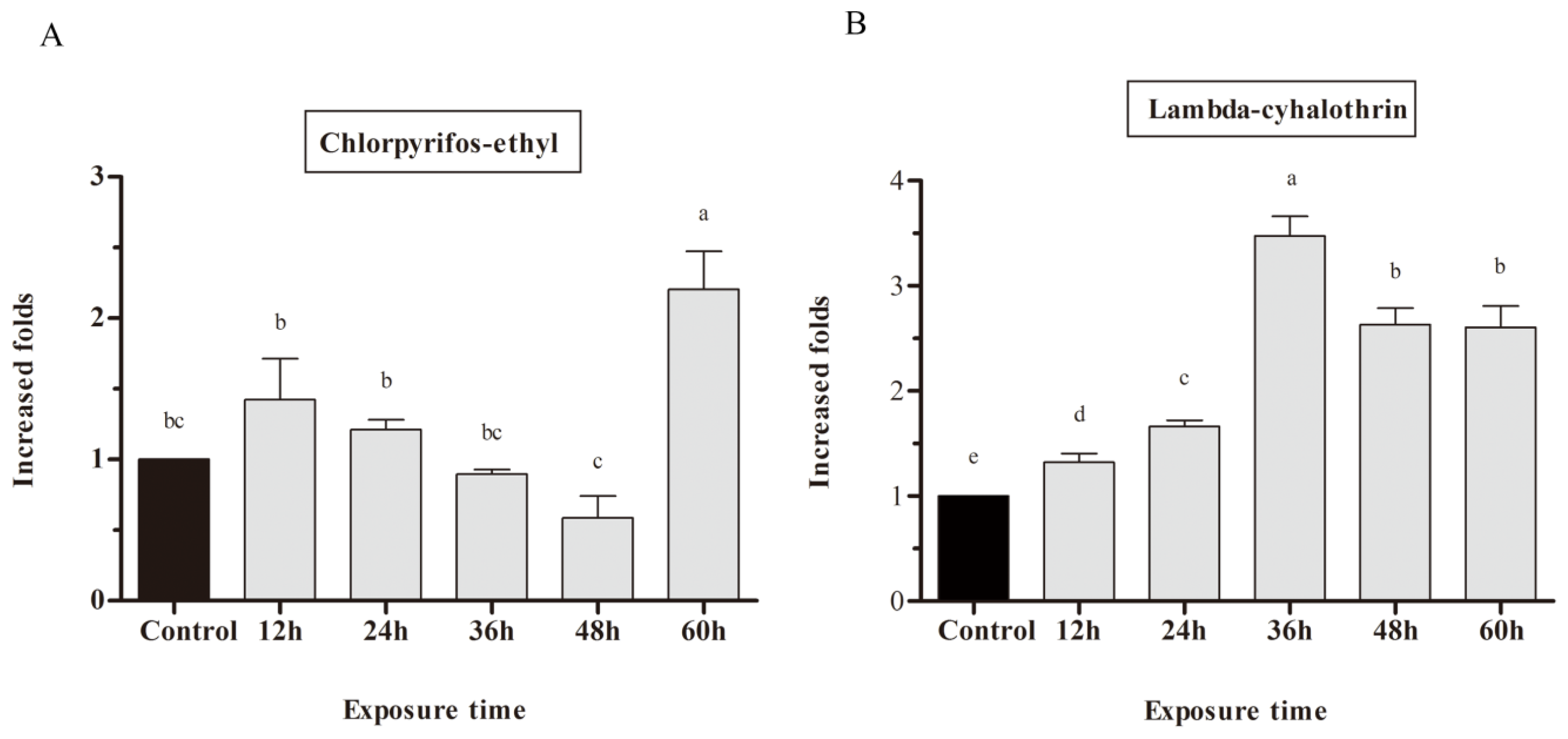
2.3. mRNA Expression of CYP9A in Response to Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and Lambda-Cyhalothrin Exposure
2.4. Developmental Expression Profiles
2.5. Tissue Specific Expression Profiles
2.6. Enzyme Activity
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Insects
4.2. Insecticides and C. pomonella Treatment
4.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis for Molecular Cloning
4.4. Molecular Cloning of CYP9A61 cDNA by 3′ and 5′RACE
4.5. Sequence Analysis
4.6. Real Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.7. Enzyme Activity
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reuveny, H.; Cohen, E. Evaluation of mechanisms of azinphos-methyl resistance in the codling moth Cydia pomonella (L.). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol 2004, 57, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes-Contreras, E.; Reyes, M.; Barros, W.; Sauphanor, B. Evaluation of azinphos-methyl resistance and activity of detoxifying enzymes in codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) from central Chile. J. Econ. Entomol 2007, 100, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, M.; Collange, B.; Rault, M.; Casanelli, S.; Sauphanor, B. Combined detoxification mechanisms and target mutation fail to confer a high level of resistance to organophosphates in Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pestic. Biochem. Phys 2011, 99, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, M.A.; Marques, T.; Bosch, D.; Avilla, J. Assessment of insecticide resistance in eggs and neonate larvae of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pestic. Biochem. Phys 2011, 100, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, C.C.; Sauphanor, B.; Frank, P.; Reyes, M.; Mamuris, Z.; Tsitsipis, J.A.; Vontas, J.; Margaritopoulos, J.T. Insecticide resistance status of the codling moth Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) from Greece. Pestic. Biochem. Phys 2011, 100, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Soleño, J.; Anguiano, O.L.; Cichón, L.B.; Garrido, S.A.; Montagna, C.M. Geographic variability in response to azinphos-methyl in field-collected populations of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) from Argentina. Pest Manag. Sci 2012, 68, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Sauphanor, B.; Bouvier, J.C.; Brosse, V. Spectrum of insecticide resistance in Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in Southeastern France. J. Econ. Entomol 1998, 91, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquier, D.; Charmillot, P.J. Effectiveness of twelve insecticides applied topically to diapausing larvae of the codling moth, Cydia pomonella L. Pest Manag. Sci 2003, 60, 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, M.; Frank, P.; Charmillot, P.J.; Loriatti, C.; Olivares, J.; Pasqualini, E.; Sauphanor, B. Diversity of insecticide resistance mechanisms and spectrum in European populations of codling moth Cydia pomonella. Pest Manag. Sci 2007, 63, 890–902. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, M.A.; Bosch, D.; Sauphanor, B.; Avilla, J. Susceptibility to organophosphate insecticides and activity of detoxifying enzymes in Spanish populations of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J. Econ. Entomol 2010, 103, 482–491. [Google Scholar]
- Sauphanor, B.; Cuany, A.; Bouvier, J.C.; Brosse, V.; Amichot, M.; Bergé, J.B. Mechanism of resistance to deltamethrin in Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pestic. Biochem. Phys 1997, 58, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier, J.C.; Bués, R.; Boivin, T.; Boudinhon, L.; Beslay, D.; Sauphanor, B. Deltamethrin resistance in the codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): Inheritance and number of genes involved. Heredity 2001, 87, 456–462. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, D.M.; Wise, J.C.; Poppen, R.V.; Gut, L.J.; Hollingworth, R.M. Resistance of codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), larvae in Michigan to insecticides with different modes of action and the impact on field residual activity. Pest Manag. Sci 2008, 64, 881–890. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.G. Cytochromes P450 and insecticide resistance. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 1999, 29, 757–777. [Google Scholar]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect Cytochrome P450. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science; Gilber, L.I., Iatrou, K., Gill, S., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: London, UK, 2005; Volume 4, pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.C.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Molecular mechanisms of metabolic resistance to synthetic and natural xenobiotics. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2007, 52, 231–253. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.F.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. CYP9Q–mediated detoxification of acaricides in the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12657–12662. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, M.A. P450s in plant-insect interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, G.R.; Zhou, Q. Molecular characterization of cytochrome P450 CYP6B47 cDNAs and 5′-flanking sequence from Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Its response to lead stress. J. Insect Physiol 2012, 58, 726–736. [Google Scholar]
- Nebert, D.W.; Gonzalez, F.J. P450 genes: Structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1987, 56, 945–993. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, R.L.; Goh, D.; Thompson, D.M.; Verma, K.D.; Heckel, D.G.; Gahan, L.J.; Roe, R.M.; Hodgson, E. Cytochrome P450 (CYP)9A1 in Heliothis virescens: The first member of a new CYP family. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 1997, 27, 605–615. [Google Scholar]
- Poupardin, R.; Reynaud, S.; Strode, C.; Ranson, H.; Vontas, J.; David, J.P. Cross-induction of detoxification genes by environmental xenobiotics and insecticides in the mosquito Aedes aegypti: Impact on larval tolerance to chemical insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 2008, 38, 540–551. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.D.; Mamidala, P.; Rajarapu, S.P.; Jones, S.C.; Mittapalli, O. Transcriptomics of the Bed Bug (Cimex lectularius). PLoS One 2011, 6, e16336. [Google Scholar]
- Komagata, O.; Kasai, S.; Tomita, T. Overexpression of cytochrome P450 genes in pyrethroid-resistant Culex quinquefasciatus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 2010, 40, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hasemann, C.A.; Kurumbail, R.G.; Boddupalli, S.S.; Peterson, J.A.; Deisenhofer, J. Structure and function of cytochromes P450: A comparative analysis of three crystal structures. Structure 1995, 3, 41–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.J.; Ma, C.X.; Li, M.; Sheng, C.F.; Liu, H.X.; Qiu, X.H. CYP9A12 and CYP9A17 in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera: Sequence similarity, expression profile and xenobiotic response. Pest Manag. Sci 2010, 66, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Bisgaard, H.C.; Forbes, V.E. Identification and expression of two novel cytochrome P450 genes, belonging to CYP4 and a new CYP331 family, in the polychaete Capitella capitata sp.I. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2004, 325, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, J.L.; Snyder, M.J.; Koener, J.F.; Feyereisen, R. Inducible P450s of the CYP9 family from larval Manduca sexta midgut. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 2000, 30, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Q.; Tang, T.; Liu, J.Q.; Feng, X.Y.; Qiu, L.H. Identification and expression analysis of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase gene in the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. Gene 2012, 511, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Goff, G.L.; Hilliou, F.; Siegfried, B.D.; Boundy, S.; Wajnberg, E.; Sofer, L.; Audant, P.; French-Constant, R.H.; Feyereisen, R. Xenobiotic response in Drosophila melanogaster: Sex dependence of P450 and GST gene induction. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 2006, 36, 674–682. [Google Scholar]
- Nikou, D.; Ranson, H.; Hemingway, J. An adult-specific CYP6 P450 gene is overexpressed in a pyrethroid-resistant strain of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Gene 2003, 318, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, M.J.; Stevens, J.L.; Andersen, J.F.; Feyereisen, R. Expression of cytochrome P450 genes of the CYP4 family in midgut and fat body of the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1995, 321, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.; Sztal, T.; Pasricha, S.; Sridhar, M.; Batterham, P.; Daborn, P.J. Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster cytochrome P450 genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.C.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Jasmonate and salicylate induce expression of herbivore cytochrome P450 genes. Nature 2002, 419, 712–715. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.N.; Li, T.; Reid, W.R.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L. Multiple cytochrome P450 genes: Their constitutive overexpression and permethrin induction in insecticide resistant mosquitoes Culex quinquefasciatus. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23403. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier, J.C.; Boivin, T.; Beslay, D.; Sauphanor, B. Age- dependent response to insecticides and enzymatic variation in susceptible and resistant codling moth larvae. Arch. Insect Biochem 2002, 51, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, T.L.; Zangerl, A.R.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Developmental variation in cytochrome P450 expression in Papilio polyxenes in response to xanthotoxin, a hostplant allelochemical. Arch. Insect Biochem 2011, 48, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Strode, C.; Wondji, C.S.; David, J.P.; Hawkes, N.J.; Lumjuan, N.; Nelson, D.R.; Drane, D.R.; Karunaratne, S.H.P.P.; Hemingway, J.; Black, W.C.I.V.; et al. Genomic analysis of detoxification genes in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol.Biol 2008, 38, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- González, I.F.; Quiñones, M.L.; Lenhart, A.; Brogdon, W.G. Insecticide resistance status of Aedes aegypti (L.) from Colombia. Pest Manag. Sci 2011, 67, 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yue, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y. Functional expression of Helicoverpa armigera CYP9A12 and CYP9A14 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Pestic. Biochem. Phys 2008, 92, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Denison, M.S.; Whitlock, J.P. Xenobiotic-inducible transcription of cytochrome P450 genes. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 18175–18178. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.G. Insect Cytochrome P450s: Thinking beyond Detoxification. In Toxicology and Molecular Biology; Liu, N.N., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2008; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Serikawa, K.A.; Xu, X.L.; Mackay, V.L.; Law, G.L.; Zong, Q.; Zhao, L.P.; Bumgarner, R.; Morris, D.R. The transcriptome and its translation during recovery from cell cycle arrest in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2003, 2, 191–204. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, J.; Marguerat, S.; Bähler, J. Post-transcriptional control of gene expression: A genome-wide perspective. Trends Biochem. Sci 2005, 30, 506–514. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, T.M.; Henikoff, J.G.; Henikoff, S. CODEHOP (Consensus-Degenerate Hybrid Oligonucleotide Primer) PCR primer design. Nucleic Acids Res 2003, 31, 3763–3766. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallance, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin, L.J.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 404–405. [Google Scholar]
- Hulo, N.; Bairoch, A.; Bulliard, V.; Cerutti, L.; Castro, E.D.; Langendijk-Genevaux, P.S.; Pagni, M.; Sigrist, C.J.A. The PROSITE database. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, D227–D230. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, J.; Milpetz, F.; Bork, P.; Ponting, C.P. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: Identification of signaling domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 95, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.L. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and mRNA expression stability detection of β-actin gene in codling moth Cydia pomonella (L.). J. Northwest A&F Univ.: Nat. Sci. Ed 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.D.; Chen, S.; Devine, G.J.; Denholmb, I.; Jewess, P.; Moores, G.D. The involvement of microsomal oxidases in pyrethroid resistance in Helicoverpa armigera from Asia. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol 2004, 34, 763–773. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar]






| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Primer used |
|---|---|---|
| P9-3F1 | GGTCAAGCAGATCACCGTGaarganttyga | 3′RACE |
| P9-3F2 | GGCCTTCCTGTTCTTCTTCgsnggntwyga | 3′RACE |
| oligod(T) | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTAC(T)18VN | 3′RACE |
| 10 × UPM | Long: CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | 3′RACE |
| Short: CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC | 3′RACE | |
| P9-5R1 | CCGCTCGGGGTCGaayttnthngg | 5′RACE |
| P9-5R2 | GGCGCAGGTGGCGatnacrtcrtt | 5′RACE |
| Outer Primer | TACCGTCGTTCCACTAGTGATTT | 5′RACE |
| Inner Primer | CGCGGATCCTCCACTAGTGATTTCACTATAGG | 5′RACE |
| P9ORF-F | ATGGTCTTCATTTACCTCCT | ORF cloning |
| P9ORF-R | TCAATTCTTGCGTGGCCTAAAC | ORF cloning |
| P9F | GAAAAGTTTACATCCAACCCGAC | Full-length cloning |
| P9R | GACGTTATAATATAACGTTTATTTCAG | Full-length cloning |
| QCYP9F | AAATACCGCTCTGGGCATAC | qPCR |
| QCYP9R | GATACGCCATCACCTTTACTT | qPCR |
| QActinF | CGGCATCCACGAAACCACCT | qPCR |
| QActinR | TGGAAGGAGCCAGTGCGG | qPCR |
| Source | d.f.a | Mean square | F | pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorpyrifos | ||||
| Insecticide exposure | 1 | 10.694 | 22.775 | 0.000 |
| Exposure time | 7 | 44.106 | 99.932 | 0.000 |
| Insecticide exposure × exposure time | 7 | 9.781 | 20.831 | 0.000 |
| Error | 80 | 0.470 | ||
| Lambda-cyhalothrin | ||||
| Insecticide exposure | 1 | 288.956 | 745.795 | 0.000 |
| Exposure time | 7 | 138.226 | 150.066 | 0.000 |
| Insecticide exposure × exposure time | 7 | 44.372 | 47.087 | 0.000 |
| Error | 80 | 0.921 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Molecular Cloning and Expression of CYP9A61: A Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and Lambda-Cyhalothrin-Inducible Cytochrome P450 cDNA from Cydia pomonella. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24211-24229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224211
Yang X, Li X, Zhang Y. Molecular Cloning and Expression of CYP9A61: A Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and Lambda-Cyhalothrin-Inducible Cytochrome P450 cDNA from Cydia pomonella. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(12):24211-24229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224211
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xueqing, Xianchun Li, and Yalin Zhang. 2013. "Molecular Cloning and Expression of CYP9A61: A Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and Lambda-Cyhalothrin-Inducible Cytochrome P450 cDNA from Cydia pomonella" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 12: 24211-24229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224211
APA StyleYang, X., Li, X., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Molecular Cloning and Expression of CYP9A61: A Chlorpyrifos-Ethyl and Lambda-Cyhalothrin-Inducible Cytochrome P450 cDNA from Cydia pomonella. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(12), 24211-24229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224211






