Structural Basis of Membrane Trafficking by Rab Family Small G Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
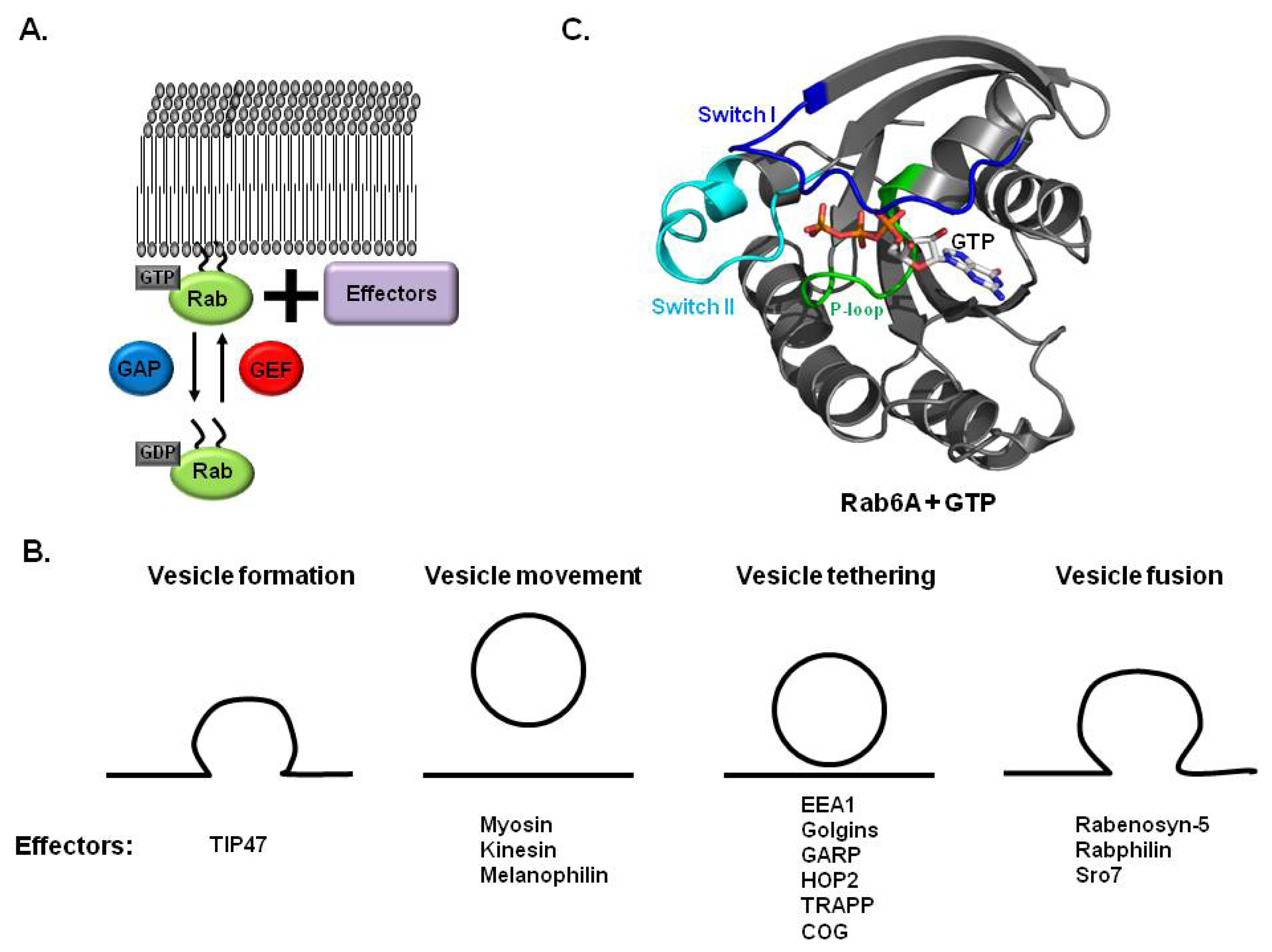
2. Rab and Membrane Trafficking
2.1. Rab GTPases Involved in Membrane Trafficking
2.2. Rab, GEF and GAP in Membrane Trafficking
3. Structures of Rab and Its Effector Complex
3.1. Structure of Rab Subfamily
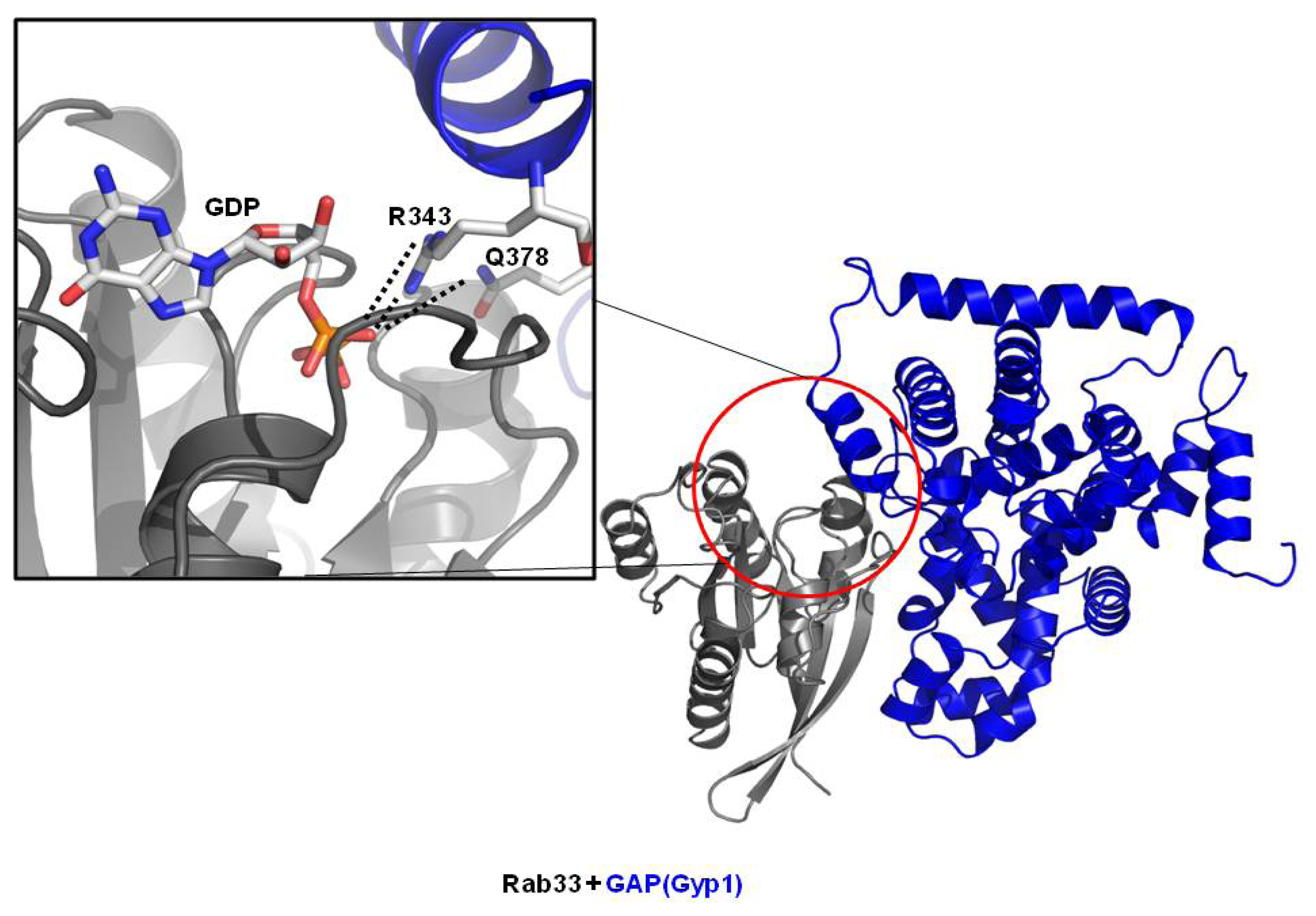
3.2. Structure of Rab/GAP Complex
3.3. Structure of Rab/GEF Complex
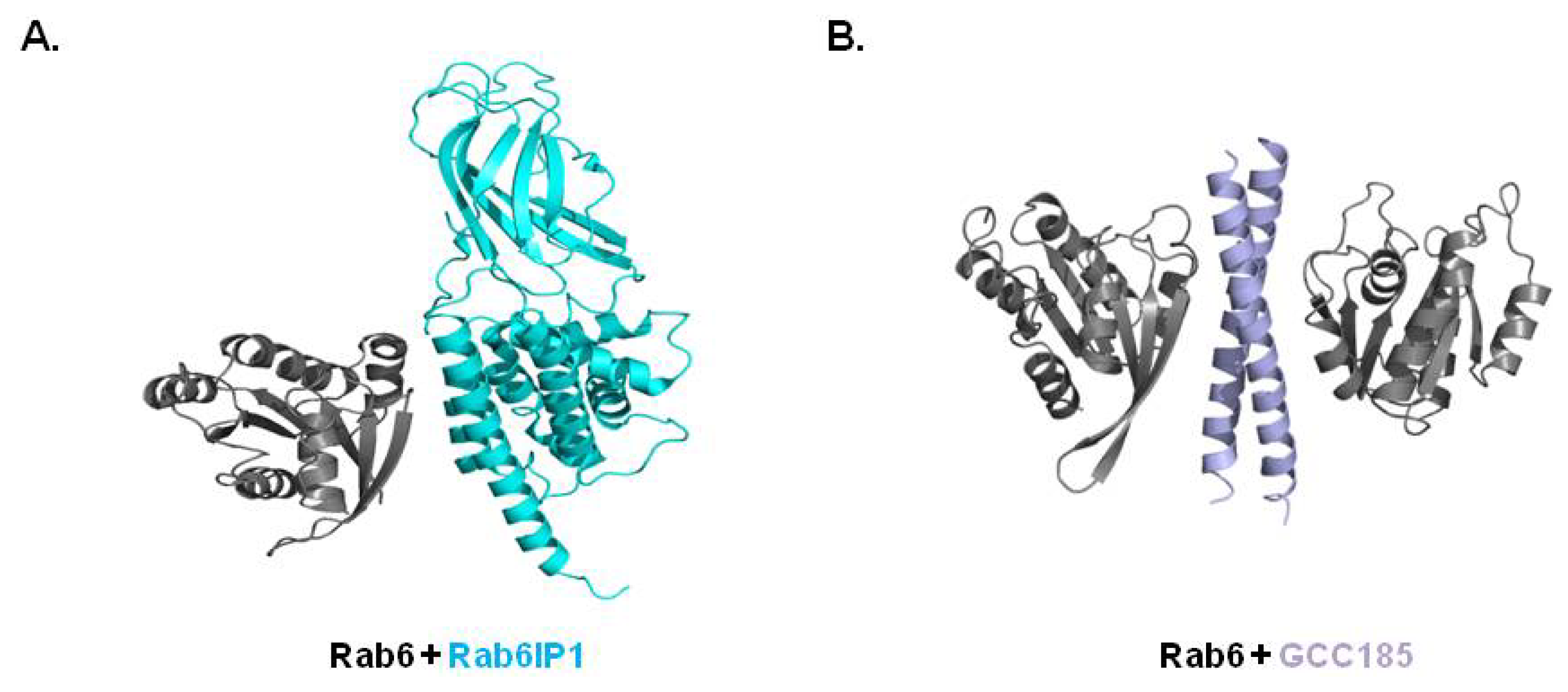
3.4. Structure of Rab/Other Effector Complex
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Goud, B.; Zahraoui, A.; Tavitian, A.; Saraste, J. Small GTP-binding protein associated with Golgi cisternae. Nature 1990, 345, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Grosshans, B.L.; Ortiz, D.; Novick, P. Rabs and their effectors: Achieving specificity in membrane traffic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11821–11827. [Google Scholar]
- Macara, I.G.; Lounsbury, K.M.; Richards, S.A.; McKiernan, C.; Bar-Sagi, D. The ras superfamily of GTPases. FASEB J 1996, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Cherfils, J.; Zeghouf, M. Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol. Rev 2013, 93, 269–309. [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Takai, Y. Small G-protein networks: Their crosstalk and signal cascades. Cell Signal 2000, 12, 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark, H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 10, 513–525. [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark, H.; Olkkonen, V.M. The Rab GTPase family. Genome Biol. 2001, 2. REVIEWS3007. [Google Scholar]
- Gutkowska, M.; Swiezewska, E. Structure, regulation and cellular functions of Rab geranylgeranyl transferase and its cellular partner Rab Escort Protein. Mol. Membr. Biol 2012, 29, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Rab GTPases, membrane trafficking and diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Hutagalung, A.H.; Novick, P.J. Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol. Rev 2011, 91, 119–149. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.; Stauber, T.; del Nery, E.; Vernos, I.; Pepperkok, R.; Nilsson, T. Regulation of microtubule-dependent recycling at the trans-Golgi network by Rab6A and Rab6A′. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 162–177. [Google Scholar]
- Echard, A.; Jollivet, F.; Martinez, O.; Lacapere, J.J.; Rousselet, A.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Goud, B. Interaction of a Golgi-associated kinesin-like protein with Rab6. Science 1998, 279, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Zerial, M.; McBride, H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2001, 2, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, I.R.; Wittinghofer, A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science 2001, 294, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, M.; Fukui, K.; Sasaki, T.; Imazumi, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Takai, Y. Rab, GAP and GEP make three. Trends Cell Biol 1997, 7, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, J.; de Camilli, P. A novel mammalian guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) specific for rab proteins. Adv. Second. Messenger Phosphoprotein Res 1994, 29, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, H.; Franklin, E.; Recacha, R.; Houdusse, A.; Goud, B.; Khan, A.R. Structural aspects of Rab6-effector complexes. Biochem. Soc. Trans 2009, 37, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Spoerner, M.; Herrmann, C.; Vetter, I.R.; Kalbitzer, H.R.; Wittinghofer, A. Dynamic properties of the Ras switch I region and its importance for binding to effectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4944–4949. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer, S.R. Structural clues to Rab GTPase functional diversity. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 15485–15488. [Google Scholar]
- Shirane, M.; Nakayama, K.I. Protrudin induces neurite formation by directional membrane trafficking. Science 2006, 314, 818–821. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, E.; Pfeffer, S.R. TIP47: A cargo selection device for mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking. Cell 1998, 93, 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, C.M.; Vaerman, J.P.; Goldenring, J.R. Rab11 family interacting protein 2 associates with Myosin Vb and regulates plasma membrane recycling. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 50415–50421. [Google Scholar]
- Short, B.; Haas, A.; Barr, F.A. Golgins and GTPases, giving identity and structure to the Golgi apparatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1744, 383–395. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Reinisch, K.; Ferro-Novick, S. Coats, tethers, Rabs, and SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination of a transport vesicle. Dev. Cell 2007, 12, 671–682. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, W.J.; Tang, B.L. Emerging roles for Rab family GTPases in human cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1795, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser, T. Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: Insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalfo, E.; Gomez-Isla, T.; Rosa, J.L.; Nieto Bodelon, M.; Cuadrado Tejedor, M.; Barrachina, M.; Ambrosio, S.; Ferrer, I. Abnormal alpha-synuclein interactions with Rab proteins in alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 2004, 63, 302–313. [Google Scholar]
- Hattula, K.; Peranen, J. FIP-2, a coiled-coil protein, links Huntingtin to Rab8 and modulates cellular morphogenesis. Curr. Biol 2000, 10, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sapp, E.; Valencia, A.; Kegel, K.B.; Qin, Z.H.; Alexander, J.; Masso, N.; Reeves, P.; Ritch, J.J.; Zeitlin, S.; et al. A function of huntingtin in guanine nucleotide exchange on Rab11. Neuroreport 2008, 19, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sapp, E.; Chase, K.; Comer-Tierney, L.A.; Masso, N.; Alexander, J.; Reeves, P.; Kegel, K.B.; Valencia, A.; Esteves, M.; et al. Disruption of Rab11 activity in a knock-in mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis 2009, 36, 374–383. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno-Yamasaki, E.; Medkova, M.; Coleman, J.; Novick, P. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate controls both membrane recruitment and a regulatory switch of the Rab GEF Sec2p. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 828–840. [Google Scholar]
- Wixler, V.; Wixler, L.; Altenfeld, A.; Ludwig, S.; Goody, R.S.; Itzen, A. Identification and characterisation of novel Mss4-binding Rab GTPases. Biol. Chem 2011, 392, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Itzen, A.; Pylypenko, O.; Goody, R.S.; Alexandrov, K.; Rak, A. Nucleotide exchange via local protein unfolding—Structure of Rab8 in complex with MSS4. EMBO J 2006, 25, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Delprato, A.; Lambright, D.G. Structural basis for Rab GTPase activation by VPS9 domain exchange factors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2007, 14, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.L.; Collins, R.N.; Novick, P.J. Identification of a Sec4p GTPase-activating protein (GAP) as a novel member of a Rab GAP family. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 3253–3256. [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis, S.E.; van Aelst, L. Mind the GAP, Rho, Rab and GDI. Nat. Genet 1998, 19, 106–108. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.D.; Albert, S.; Tcheperegine, S.E.; Burd, C.G.; Gallwitz, D.; Bi, E. The GAP activity of Msb3p and Msb4p for the Rab GTPase Sec4p is required for efficient exocytosis and actin organization. J. Cell Biol 2003, 162, 635–646. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Molina, F.E.; Novick, P.J. A Rab GAP cascade defines the boundary between two Rab GTPases on the secretory pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14408–14413. [Google Scholar]
- Pacold, M.E.; Suire, S.; Perisic, O.; Lara-Gonzalez, S.; Davis, C.T.; Walker, E.H.; Hawkins, P.T.; Stephens, L.; Eccleston, J.F.; Williams, R.L. Crystal structure and functional analysis of Ras binding to its effector phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma. Cell 2000, 103, 931–943. [Google Scholar]
- Brunger, A.T.; Milburn, M.V.; Tong, L.; deVos, A.M.; Jancarik, J.; Yamaizumi, Z.; Nishimura, S.; Ohtsuka, E.; Kim, S.H. Crystal structure of an active form of RAS protein, a complex of a GTP analog and the HRAS p21 catalytic domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4849–4853. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Eathiraj, S.; Munson, M.; Lambright, D.G. TBC-domain GAPs for Rab GTPases accelerate GTP hydrolysis by a dual-finger mechanism. Nature 2006, 442, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.; Milburn, M.V.; de Vos, A.M.; Kim, S.H. Structure of ras proteins. Science 1989, 245, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.C.; Yoon, J.H.; Jang, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Do Heo, W.; So, I.; Jeon, J.H.; Park, H.H. Crystal structure of Rab6A′ (Q72L) mutant reveals unexpected GDP/Mg(2)(+) binding with opened GTP-binding domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2012, 424, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bergbrede, T.; Pylypenko, O.; Rak, A.; Alexandrov, K. Structure of the extremely slow GTPase Rab6A in the GTP bound form at 1.8A resolution. J. Struct. Biol 2005, 152, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Eathiraj, S.; Pan, X.; Ritacco, C.; Lambright, D.G. Structural basis of family-wide Rab GTPase recognition by rabenosyn-5. Nature 2005, 436, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Rak, A.; Fedorov, R.; Alexandrov, K.; Albert, S.; Goody, R.S.; Gallwitz, D.; Scheidig, A.J. Crystal structure of the GAP domain of Gyp1p: First insights into interaction with Ypt/Rab proteins. EMBO J 2000, 19, 5105–5113. [Google Scholar]
- Marat, A.L.; Dokainish, H.; McPherson, P.S. DENN domain proteins: Regulators of Rab GTPases. J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 13791–13800. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Bradley, M.J.; Cai, Y.; Kummel, D.; de la Cruz, E.M.; Barr, F.A.; Reinisch, K.M. Insights regarding guanine nucleotide exchange from the structure of a DENN-domain protein complexed with its Rab GTPase substrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18672–18677. [Google Scholar]
- Short, B.; Preisinger, C.; Schaletzky, J.; Kopajtich, R.; Barr, F.A. The Rab6 GTPase regulates recruitment of the dynactin complex to Golgi membranes. Curr. Biol 2002, 12, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar]
- Monier, S.; Jollivet, F.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Johannes, L.; Goud, B. Characterization of novel Rab6-interacting proteins involved in endosome-to-TGN transport. Traffic 2002, 3, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Fridmann-Sirkis, Y.; Siniossoglou, S.; Pelham, H.R. TMF is a golgin that binds Rab6 and influences Golgi morphology. BMC Cell Biol 2004, 5, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Bergbrede, T.; Chuky, N.; Schoebel, S.; Blankenfeldt, W.; Geyer, M.; Fuchs, E.; Goody, R.S.; Barr, F.; Alexandrov, K. Biophysical analysis of the interaction of Rab6a GTPase with its effector domains. J. Biol. Chem 2009, 284, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermeier, C.; Brunger, A.T. Structural basis of Rab effector specificity: Crystal structure of the small G protein Rab3A complexed with the effector domain of rabphilin-3A. Cell 1999, 96, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Recacha, R.; Boulet, A.; Jollivet, F.; Monier, S.; Houdusse, A.; Goud, B.; Khan, A.R. Structural basis for recruitment of Rab6-interacting protein 1 to Golgi via a RUN domain. Structure 2009, 17, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Del Nery, E.; Miserey-Lenkei, S.; Falguieres, T.; Nizak, C.; Johannes, L.; Perez, F.; Goud, B. Rab6A and Rab6A′ GTPases play non-overlapping roles in membrane trafficking. Traffic 2006, 7, 394–407. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev, I.; Splinter, D.; Keijzer, N.; Wulf, P.S.; Demmers, J.; Ohtsuka, T.; Modesti, M.; Maly, I.V.; Grosveld, F.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Akhmanova, A. Rab6 regulates transport and targeting of exocytotic carriers. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Miserey-Lenkei, S.; Waharte, F.; Boulet, A.; Cuif, M.H.; Tenza, D.; El Marjou, A.; Raposo, G.; Salamero, J.; Heliot, L.; Goud, B.; et al. Rab6-interacting protein 1 links Rab6 and Rab11 function. Traffic 2007, 8, 1385–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Burguete, A.S.; Fenn, T.D.; Brunger, A.T.; Pfeffer, S.R. Rab and Arl GTPase family members cooperate in the localization of the golgin GCC185. Cell 2008, 132, 286–298. [Google Scholar]
- Jagoe, W.N.; Lindsay, A.J.; Read, R.J.; McCoy, A.J.; McCaffrey, M.W.; Khan, A.R. Crystal structure of rab11 in complex with rab11 family interacting protein 2. Structure 2006, 14, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Aligianis, I.A.; Morgan, N.V.; Mione, M.; Johnson, C.A.; Rosser, E.; Hennekam, R.C.; Adams, G.; Trembath, R.C.; Pilz, D.T.; Stoodley, N.; et al. Mutation in Rab3 GTPase-activating protein (RAB3GAP) noncatalytic subunit in a kindred with Martsolf syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2006, 78, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Aligianis, I.A.; Johnson, C.A.; Gissen, P.; Chen, D.; Hampshire, D.; Hoffmann, K.; Maina, E.N.; Morgan, N.V.; Tee, L.; Morton, J.; et al. Mutations of the catalytic subunit of RAB3GAP cause Warburg Micro syndrome. Nat Genet 2005, 37, 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hennies, H.C.; Kornak, U.; Zhang, H.; Egerer, J.; Zhang, X.; Seifert, W.; Kuhnisch, J.; Budde, B.; Natebus, M.; Brancati, F.; et al. Gerodermia osteodysplastica is caused by mutations in SCYL1BP1, a Rab-6 interacting golgin. Nat. Genet 2008, 40, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, K.; de Jonghe, P.; Coen, K.; Verpoorten, N.; Auer-Grumbach, M.; Kwon, J.M.; FitzPatrick, D.; Schmedding, E.; de Vriendt, E.; Jacobs, A.; et al. Mutations in the small GTP-ase late endosomal protein RAB7 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2B neuropathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2003, 72, 722–727. [Google Scholar]
- Nachury, M.V.; Loktev, A.V.; Zhang, Q.; Westlake, C.J.; Peranen, J.; Merdes, A.; Slusarski, D.C.; Scheller, R.H.; Bazan, J.F.; Sheffield, V.C.; et al. A core complex of BBS proteins cooperates with the GTPase Rab8 to promote ciliary membrane biogenesis. Cell 2007, 129, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Standley, C.; Sapp, E.; Valencia, A.; Qin, Z.H.; Kegel, K.B.; Yoder, J.; Comer-Tierney, L.A.; Esteves, M.; Chase, K.; et al. Mutant huntingtin impairs vesicle formation from recycling endosomes by interfering with Rab11 activity. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 29, 6106–6116. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, D.; Seelow, D.; Jehee, F.S.; Perlyn, C.A.; Alonso, L.G.; Bueno, D.F.; Donnai, D.; Josifova, D.; Mathijssen, I.M.; Morton, J.E.; et al. RAB23 mutations in Carpenter syndrome imply an unexpected role for hedgehog signaling in cranial-suture development and obesity. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2007, 80, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.W.; Lahad, J.P.; Kuo, W.L.; Lapuk, A.; Yamada, K.; Auersperg, N.; Liu, J.; Smith-McCune, K.; Lu, K.H.; Fishman, D.; et al. The RAB25 small GTPase determines aggressiveness of ovarian and breast cancers. Nat. Med 2004, 10, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Barral, D.C.; Ramalho, J.S.; Anders, R.; Hume, A.N.; Knapton, H.J.; Tolmachova, T.; Collinson, L.M.; Goulding, D.; Authi, K.S.; Seabra, M.C. Functional redundancy of Rab27 proteins and the pathogenesis of Griscelli syndrome. J. Clin. Invest 2002, 110, 247–257. [Google Scholar]

| GEF | GAP | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of GEF | Target Rab | Name of GAP | Target Rab |
| RABIF | Rab3A, Rab8 | TBC1D2 | Rab7 |
| RAB3IP | Rab3A | TBC1D3C | Rab5 |
| RABGEF1 | Rab5, Rab22 | TBC1D13 | Rab35 |
| RIN1 | Rab5 | RUTBC1 | Rab 9A |
| ANKRD27 | Rab32, Rab38 | RAB3GAP | Rab3 |
| Rab family | Membrane traffic pathway | Associated diseases | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rab3 | Exocytosis, neurotransmitter release | Warburg micro syndrome (Rab3GAP mutation), Martsolf syndrome (Rab3GAP mutation) | [60,61] |
| Rab6 | Golgi mediated vesicle transport | Gerodermia osteodysplastica (Rab6 effector Golgin mutation) | [62] |
| Rab7 | Late endosome to lysosome | Charcot-Marie-Tooth | [63] |
| Rab8 | Exocytosis, TGN to plasma membrane | Bardet-Biedel syndrome, Huntington’s disease | [64] |
| Rab11 | TGN to plasma membrane | Huntington’s disease | [30,65] |
| Rab23 | Protein transport to plasma membrane | Carpenter syndrome | [66] |
| Rab25 | RE to Plasma membrane | Epithelial cancers | [67] |
| Rab27 | Exocytosis | Griscelli syndrome | [68] |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.H. Structural Basis of Membrane Trafficking by Rab Family Small G Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8912-8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058912
Park HH. Structural Basis of Membrane Trafficking by Rab Family Small G Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):8912-8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058912
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyun Ho. 2013. "Structural Basis of Membrane Trafficking by Rab Family Small G Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 8912-8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058912
APA StylePark, H. H. (2013). Structural Basis of Membrane Trafficking by Rab Family Small G Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 8912-8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058912




