New Radioligands for Describing the Molecular Pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
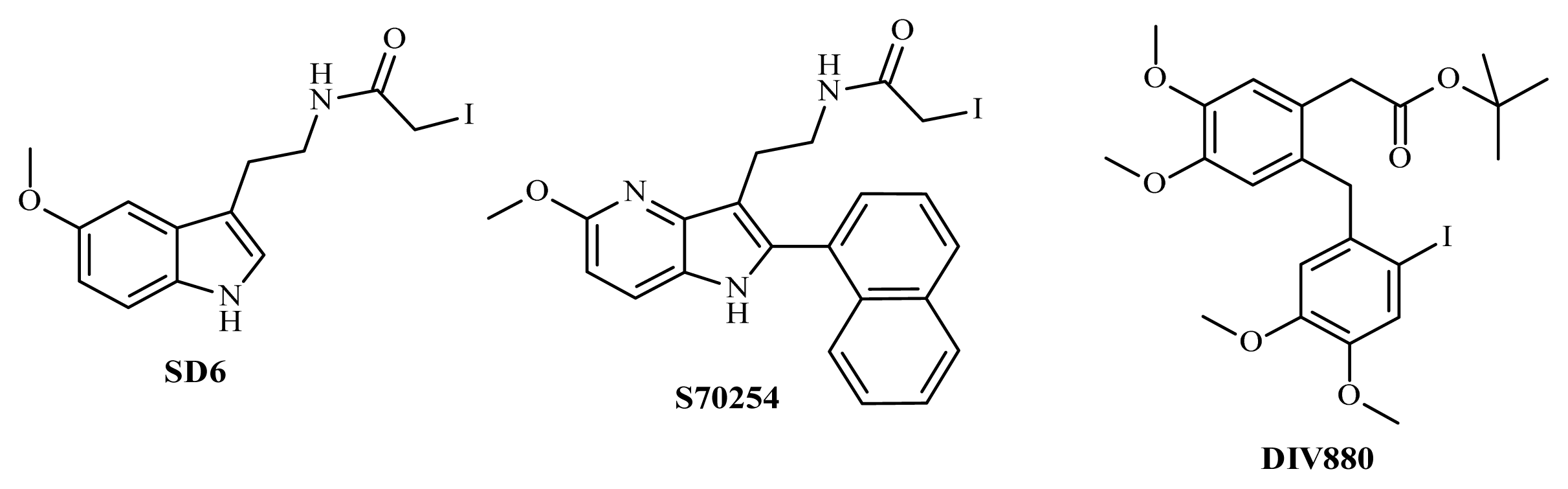
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents and Ligands
3.2. Membrane Preparation
3.3. Membrane Binding Assays
3.3.1. 2-[125I]-iodomelatonin and [35S]-GTPγS Binding Assays
3.3.2. New Ligand Binding Assays
3.4. HTRF cAMP Assay
3.5. Chemistry
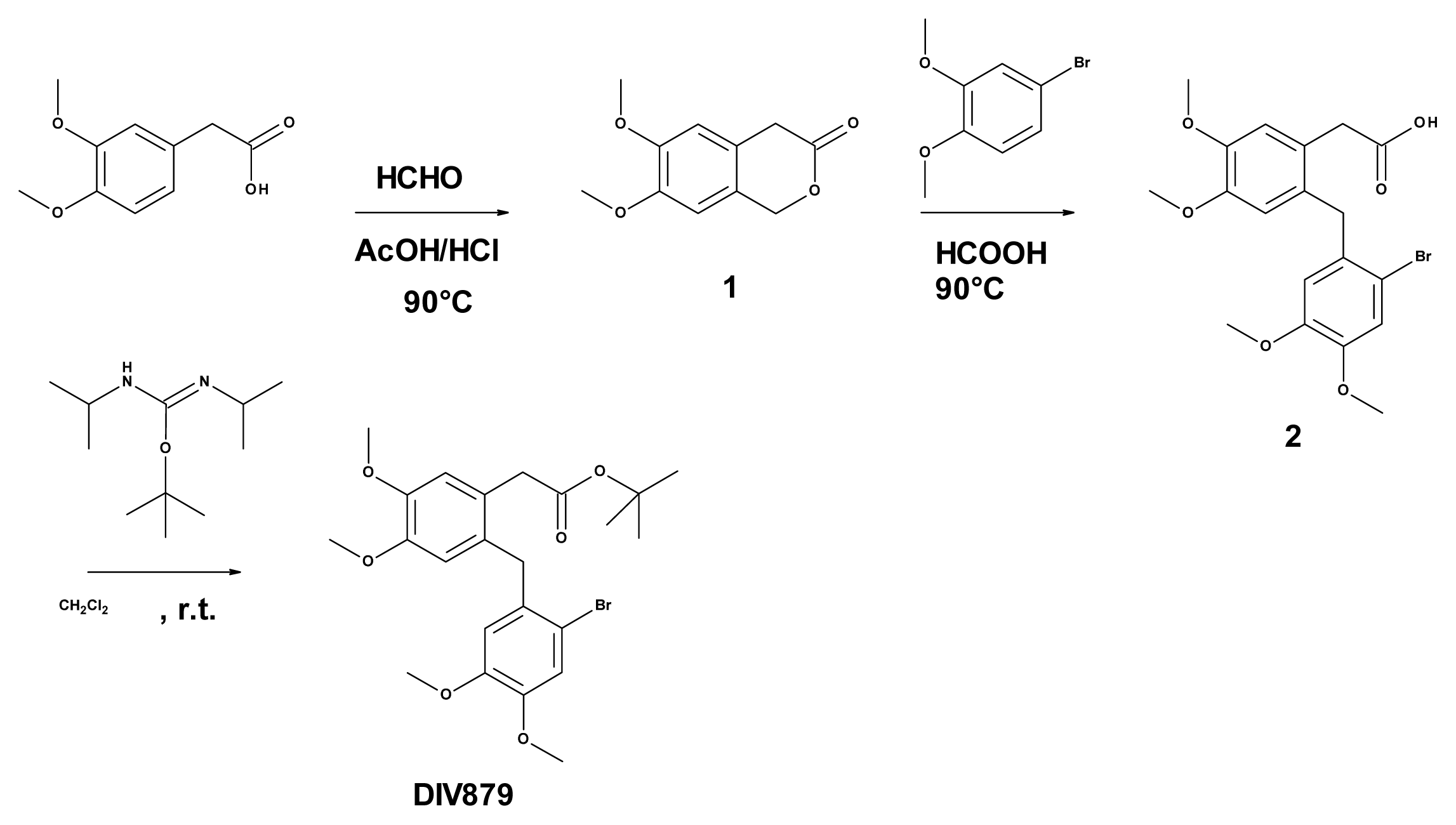
3.6. Synthesis of Tert-butyl 2-(2-[(2-bromo-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4,5-dimethoxy phenyl) Acetate (DIV879)
3.6.1. General Procedures
3.6.2. Synthesis of 6,7-dimethoxy-3-isochromanone (Compound 1, Figure 3)
3.6.3. Synthesis of 2-([(2-bromo-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl) Acetic Acid (Compound 2, Figure 3)
3.6.4. Synthesis of Tert-butyl 2-(2-[(2-bromo-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4,5-dimethoxy phenyl) Acetate (DIV879, Figure 3)
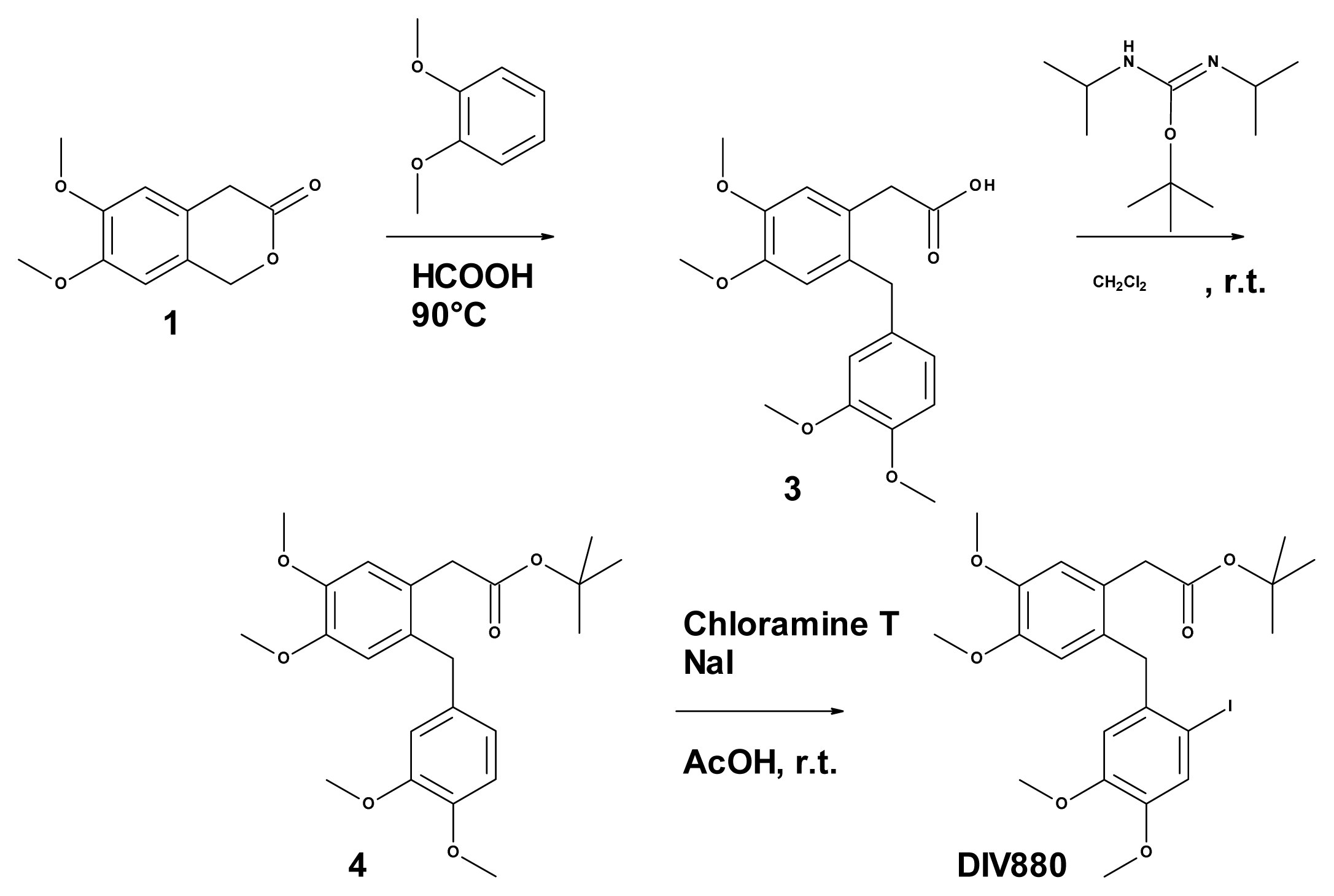
3.7. Synthesis of DIV880
3.7.1. Synthesis of 2-(2-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl) Acetic Acid (Compound 3, Figure 4)
3.7.2. Synthesis of 2-(2-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4,5-dimethoxy phenyl) Acetate (Compound 4, Figure 4)
3.7.3. Synthesis of 2-(2-[(2-iodo-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4,5-dimethoxy phenyl) Acetate (DIV880, Figure 4)
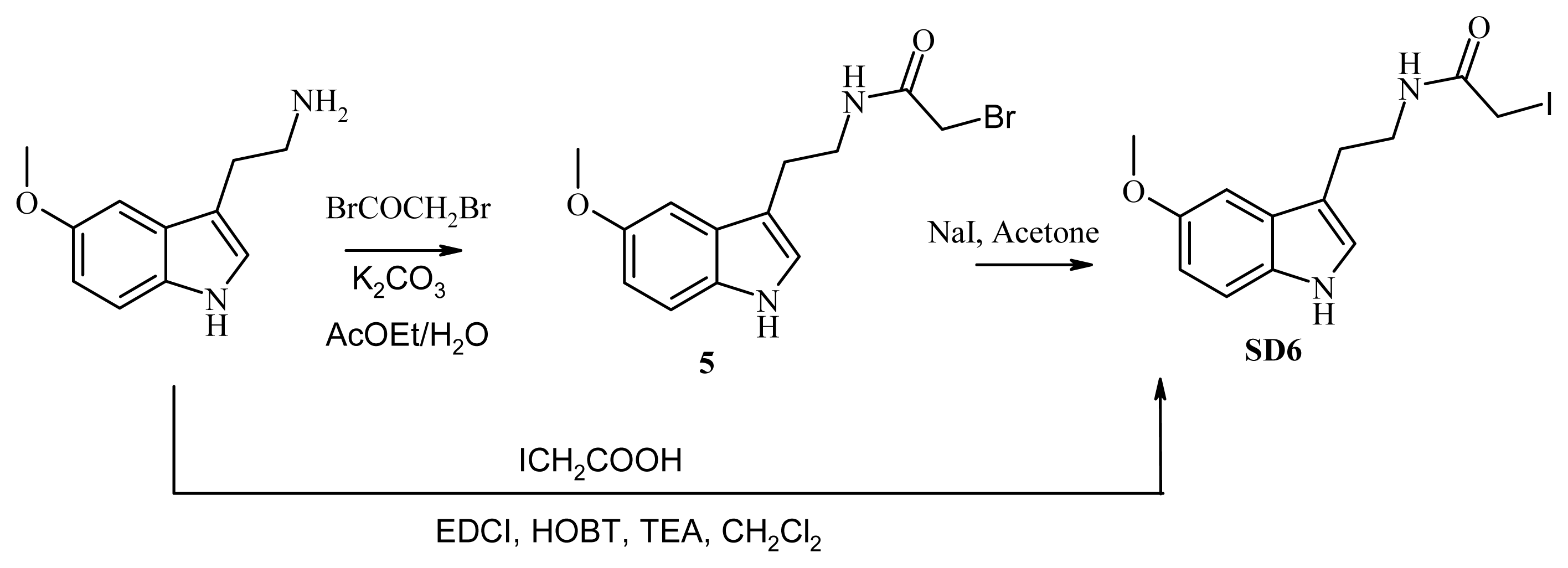
3.8. Synthesis of SD6
3.8.1. Synthesis of N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]iodoacetamide (SD6), Route A
3.8.2. Synthesis of N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]iodoacetamide (compound SD6, Figure 5), Route B
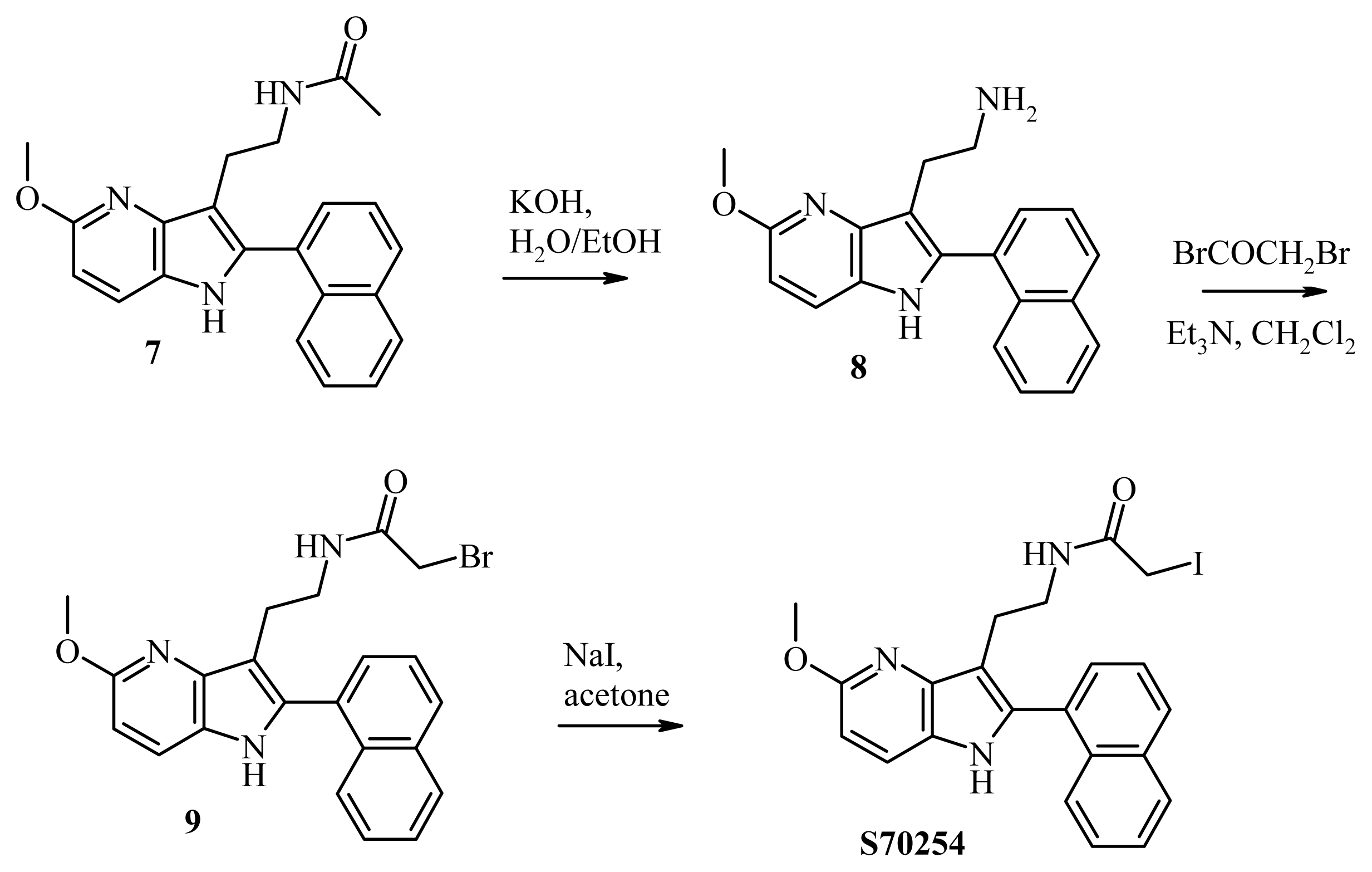
3.9. Synthesis of S70254
3.9.1. Synthesis of 2-[5-methoxy-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridine-3-yl]ethan-1-amine (compound 8, Figure 6)
3.9.2. Synthesis of 2-bromo-N-2-[5-methoxy-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridine-3-yl] Acetamide (Compound 9, Figure 6)
3.9.3. Synthesis of 2-iodo-N-2-[5-methoxy-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridine-3-yl] Acetamide (S70254, Figure 6)
3.10. Radio-Iodination
3.10.1. Radio-Iodination of SD6 and S70254
3.10.2. Radio-Iodination of DIV879
3.11. Selectivity Studies for Melatonin Receptor Ligands
4. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Arendt, J. Melatonin. Clin. Endocrinol 1988, 29, 205–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Skene, D.J.; Arendt, J. Physiology and pharmacology of melatonin in relation to biological rhythms. Pharmacol. Rep 2009, 61, 383–410. [Google Scholar]
- Jockers, R.; Maurice, P.; Boutin, J.A.; Delagrange, P. Melatonin receptors, heterodimerization, signal transduction and binding sites: What’s new? Br. J. Pharmacol 2008, 154, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Vella, F.; Ferry, G.; Delagrange, P.; Boutin, J.A. NRH:Quinone reductase 2: An enzyme of surprises and mysteries. Biochem. Pharmacol 2005, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Reppert, S.M.; Weaver, D.R.; Ebisawa, T. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian melatonin receptor that mediates reproductive and circadian responses. Neuron 1994, 13, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Reppert, S.M.; Godson, C.; Mahle, C.D.; Weaver, D.R.; Slaugenhaupt, S.A.; Gusella, J.F. Molecular characterization of a second melatonin receptor expressed in human retina and brain: The Mel1b melatonin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8734–8738. [Google Scholar]
- Vakkuri, O.; Lamsa, E.; Rahkamaa, E.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Leppaluoto, J. Iodinated melatonin: Preparation and characterization of the molecular structure by mass and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem 1984, 142, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Vakkuri, O.; Rintamaki, H.; Leppaluoto, J. Plasma and tissue concentrations of melatonin after midnight light exposure and pinealectomy in the pigeon. J. Endocrinol 1985, 105, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Browning, C.; Beresford, I.; Fraser, N.; Giles, H. Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin MT(1) and MT(2) receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol 2000, 129, 877–886. [Google Scholar]
- Zlotos, D.P. Recent progress in the development of agonists and antagonists for melatonin receptors. Curr. Med. Chem 2012, 19, 3532–3549. [Google Scholar]
- Boutin, J.A.; Lahaye, C.; Pegurier, C.; Nicolas, J.P.; Fauchere, J.L.; Langlois, M.; Renard, P.; Delagrange, P.; Canet, E. Screening of ligand binding on melatonin receptor using non-peptide combinatorial libraries. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res 2000, 20, 105–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.H.; Su, H.R.; Boutin, J.A.; Renard, M.P.; Wang, M.W. High-throughput screening assay for new ligands at human melatonin receptors. Acta Pharmacol. Sin 2008, 29, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Markl, C.; Clafshenkel, W.P.; Attia, M.I.; Sethi, S.; Witt-Enderby, P.A.; Zlotos, D.P. N-Acetyl-5-arylalkoxytryptamine analogs: Probing the melatonin receptors for MT(1)-selectivity. Arch. Pharm 2011, 344, 666–674. [Google Scholar]
- Mailliet, F.; Audinot, V.; Malpaux, B.; Bonnaud, A.; Delagrange, P.; Migaud, M.; Barrett, P.; Viaud-Massuard, M.C.; Lesieur, D.; Lefoulon, F.; et al. Molecular pharmacology of the ovine melatonin receptor: Comparison with recombinant human MT1 and MT2 receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol 2004, 67, 667–677. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Audinot, V.; Mailliet, F.; Lahaye-Brasseur, C.; Bonnaud, A.; Le, G.A.; Amosse, C.; Dromaint, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Nagel, N.; Galizzi, J.P.; et al. New selective ligands of human cloned melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol 2003, 367, 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, N.W.; Sugden, D. Antigonadal effects of two novel melatonin analogues in adult Djungarian hamsters. J. Pineal Res 1993, 15, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mazeas, D.; Guillaumet, G.; Viaud, M.C. Synthesis of new melatoninergic ligands including azaindole moiety. Heterocycles 2013, 50, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Viaud, M.C.; Guillaumet, G.; Mazeas, D.; van de Poël, H.; Renard, P.; Pfeiffer, B.; Delagrange, P. Preparation of N-(pyrrolopyridylalkyl)alkanamides and analogs as melatonin receptor ligands. FR Patent 95-4504, 14 April 1995. [Google Scholar]
- McConahey, P.J.; Dixon, F.J. Radioiodination of proteins by the use of the chloramine-T method. Methods Enzymol 1980, 70, 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Coge, F.; Guenin, S.P.; Fery, I.; Migaud, M.; Devavry, S.; Slugocki, C.; Legros, C.; Ouvry, C.; Cohen, W.; Renault, N.; et al. The end of a myth: Cloning and characterization of the ovine melatonin MT(2) receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol 2009, 158, 1248–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Devavry, S.; Legros, C.; Brasseur, C.; Cohen, W.; Guenin, S.P.; Delagrange, P.; Malpaux, B.; Ouvry, C.; Coge, F.; Nosjean, O.; et al. Molecular pharmacology of the mouse melatonin receptors MT(1) and MT(2). Eur. J. Pharmacol 2012, 677, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.Q.; Takaki, K.; Chen, J.; Bertenshaw, S.; Iben, L.; Mahle, C.D.; Ryan, E.; Wu, D.; Gao, Q.; Xu, C. (R)-2-(4-Phenylbutyl)dihydrobenzofuran derivatives as melatoninergic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2005, 15, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Rivara, S.; Pala, D.; Lodola, A.; Mor, M.; Lucini, V.; Dugnani, S.; Scaglione, F.; Bedini, A.; Lucarini, S.; Tarzia, G.; et al. MT(1)-selective melatonin receptor ligands: Synthesis, pharmacological evaluation, and molecular dynamics investigation of N-{[(3-O-substituted) anilino]alkyl}amides. Chem. Med. Chem 2012, 7, 1954–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Descamps-Francois, C.; Yous, S.; Chavatte, P.; Audinot, V.; Bonnaud, A.; Boutin, J.A.; Delagrange, P.; Bennejean, C.; Renard, P.; Lesieur, D. Design and synthesis of naphthalenic dimers as selective MT1 melatoninergic ligands. J. Med. Chem 2003, 46, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Larraya, C.; Guillard, J.; Renard, P.; Audinot, V.; Boutin, J.A.; Delagrange, P.; Bennejean, C.; Viaud-Massuard, M.C. Preparation of 4-azaindole and 7-azaindole dimers with a bisalkoxyalkyl spacer in order to preferentially target melatonin MT1 receptors over melatonin MT2 receptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2004, 39, 515–526. [Google Scholar]
- Mesangeau, C.; Peres, B.; Descamps-Francois, C.; Chavatte, P.; Audinot, V.; Coumailleau, S.; Boutin, J.A.; Delagrange, P.; Bennejean, C.; Renard, P.; et al. Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel naphthalenic derivatives as selective MT(1) melatoninergic ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2010, 18, 3426–3436. [Google Scholar]

| A—hMT1 | Affinity | [35S]-GTPγS | TR-FRET-cAMP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKi | pEC50 | Emax (%) | pEC50 | Emax (%) | |
| 2IMLT | 10.44 ± 0.08 | 9.79 ± 0.11 | 108 ± 3 | 10.09 ± 0.01 | 90 ± 5 |
| SD6 | 9.94 ± 0.01 | 9.79 ± 0.17 | 115 ± 10 | 8.58 ± 0.14 | 103 ± 10 |
| S70254 | 6.18 ± 0.10 | 7.10 ± 0.04 | 15 ± 2 | 5.84 ± 0.14 | 78 ± 12 |
| DIV879 | 6.25 ± 0.03 | <5 | ND | ND | ND |
| DIV880 | 6.08 ± 0.01 | 5.9 ± 0.02 | 10 ± 1 | <5 | ND |
| B—hMT2 | Affinity | [35S]-GTPγS | TR-FRET-cAMP | ||
| pKi | pEC50 | Emax (%) | pEC50 | Emax (%) | |
| 2IMLT | 9.80 ± 0.05 | 9.80 ± 0.12 | 121 ± 13 | 10.15 ± 0.002 | 99 ± 2 |
| SD6 | 9.89 ± 0.22 | 9.97 ± 0.05 | 114 ± 16 | 9.16 ± 0.02 | 103 ± 1 |
| S70254 | 8.73 ± 0.23 | 8.69 ± 0.30 | 43 ± 1 | 7.47 ± 0.21 | 76.5 ± 1 |
| DIV879 | 8.14 ± 0.04 | 7.91 ± 0.161 | 58 ± 2 | ND | ND |
| DIV880 | 8.02 ± 0.02 | 7.97 ± 0.18 | 67 ± 8 | 7.79 ± 0.09 | 97 ± 1 |
| [125I]-2IMLT | [125I]-SD6 | [125I]-S70254 | [125I]-DIV880 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKd | Bmax fmol/mg of protein | pKd | Bmax fmol/mg of protein | pKd | Bmax fmol/mg of protein | pKd | Bmax fmol/mg of protein | |
| hMT1 | 10.69 ± 0.07 | 688 ± 153 | 10.85 ± 0.01 | 276 ± 50 | - | - | - | - |
| hMT2 | 10.16 ± 0.03 | 1,998 ± 318 | 10.18 ± 0.11 | 1,929 ± 308 | 9.61 ± 0.14 | 1,778 ± 87 | 9.65 ± 0.07 | 2,308 ± 0.07 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Legros, C.; Matthey, U.; Grelak, T.; Pedragona-Moreau, S.; Hassler, W.; Yous, S.; Thomas, E.; Suzenet, F.; Folleas, B.; Lefoulon, F.; et al. New Radioligands for Describing the Molecular Pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8948-8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058948
Legros C, Matthey U, Grelak T, Pedragona-Moreau S, Hassler W, Yous S, Thomas E, Suzenet F, Folleas B, Lefoulon F, et al. New Radioligands for Describing the Molecular Pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):8948-8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058948
Chicago/Turabian StyleLegros, Céline, Ulrich Matthey, Teresa Grelak, Sandrine Pedragona-Moreau, Werner Hassler, Saïd Yous, Emmanuel Thomas, Franck Suzenet, Benoît Folleas, François Lefoulon, and et al. 2013. "New Radioligands for Describing the Molecular Pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 8948-8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058948
APA StyleLegros, C., Matthey, U., Grelak, T., Pedragona-Moreau, S., Hassler, W., Yous, S., Thomas, E., Suzenet, F., Folleas, B., Lefoulon, F., Berthelot, P., Caignard, D.-H., Guillaumet, G., Delagrange, P., Brayer, J.-L., Nosjean, O., & Boutin, J. A. (2013). New Radioligands for Describing the Molecular Pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 8948-8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14058948





