Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Magnetite/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Hyperthermia Treatments via a Mechanochemical Route
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
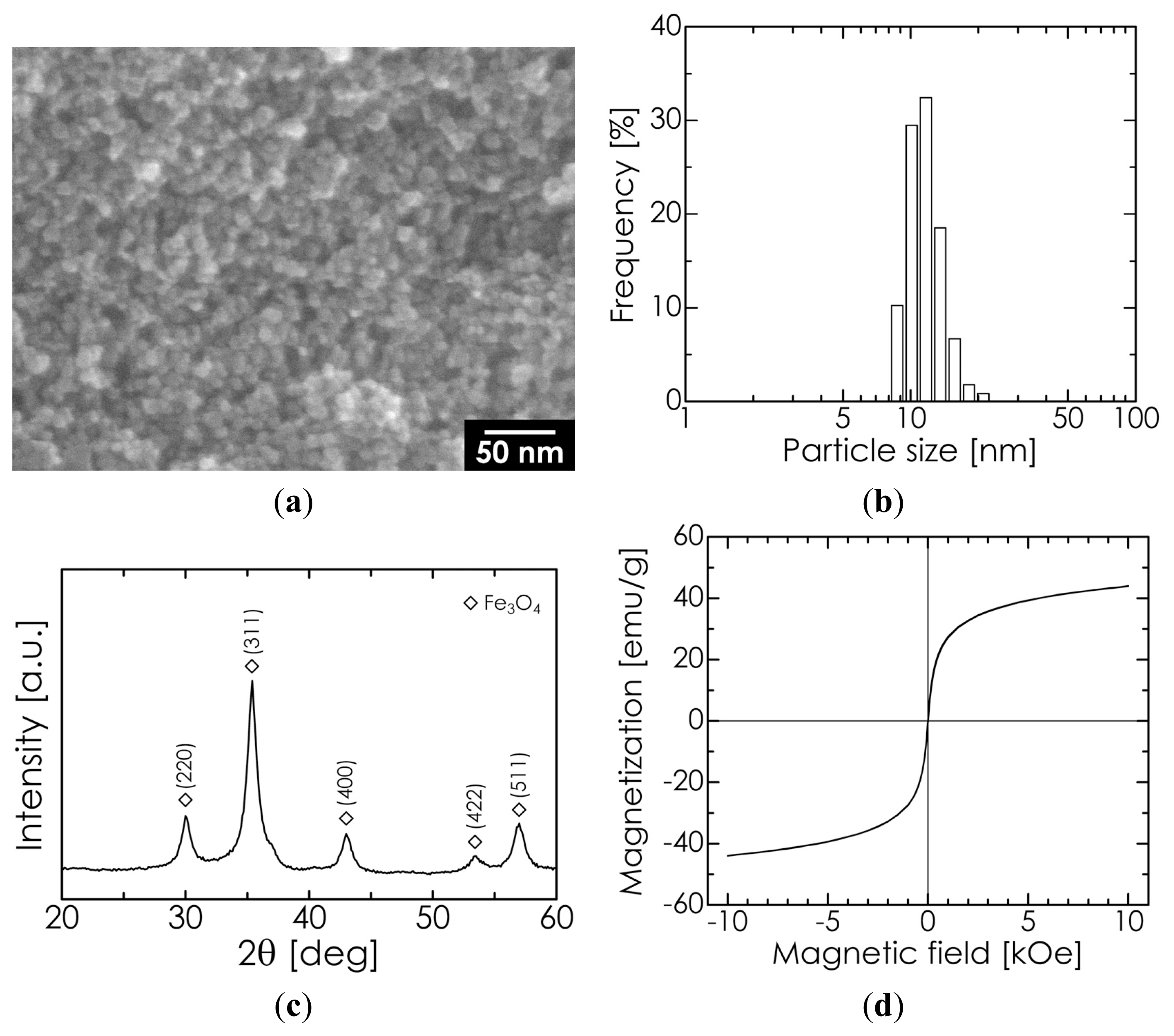
2.1. Properties of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
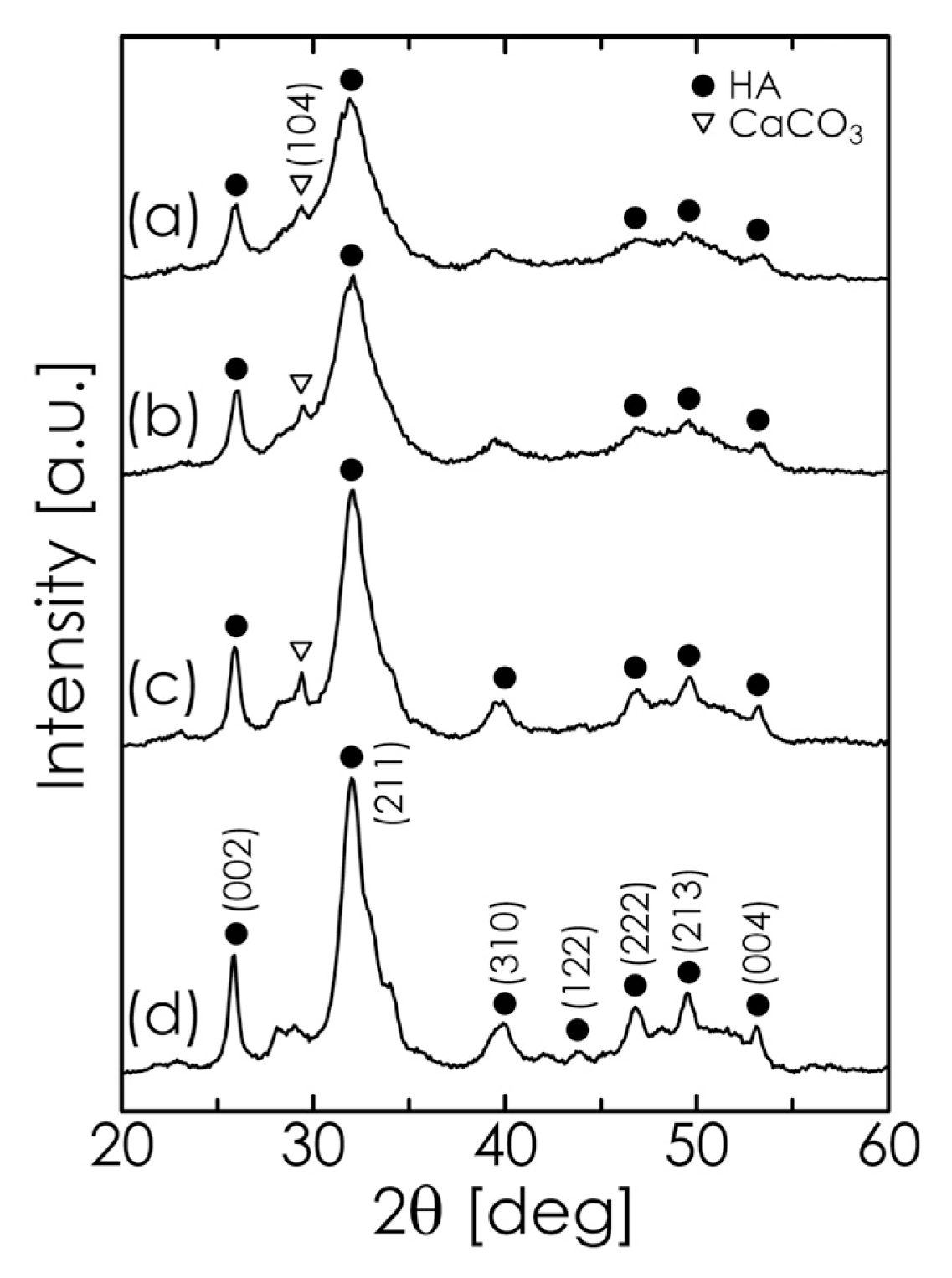
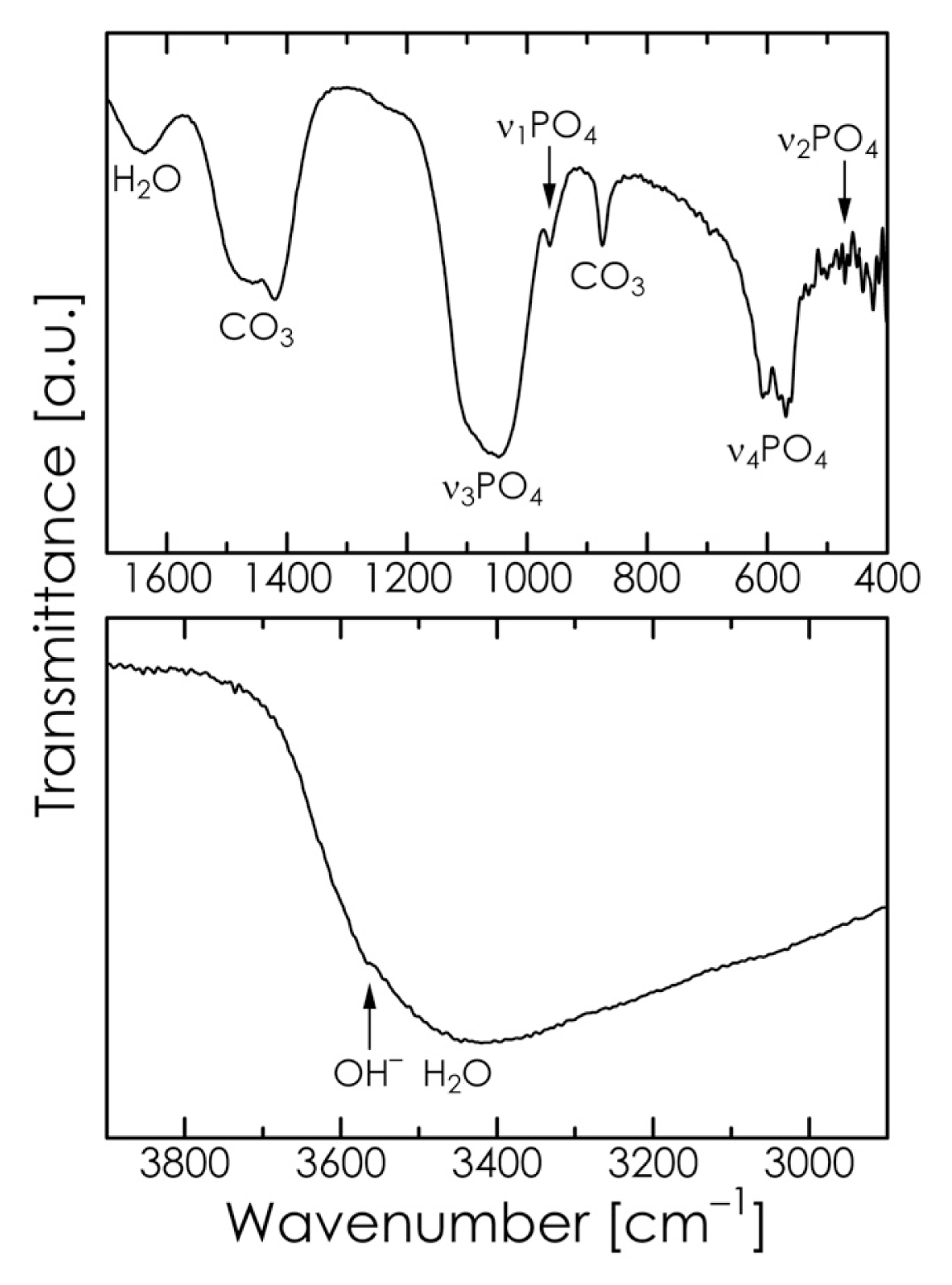
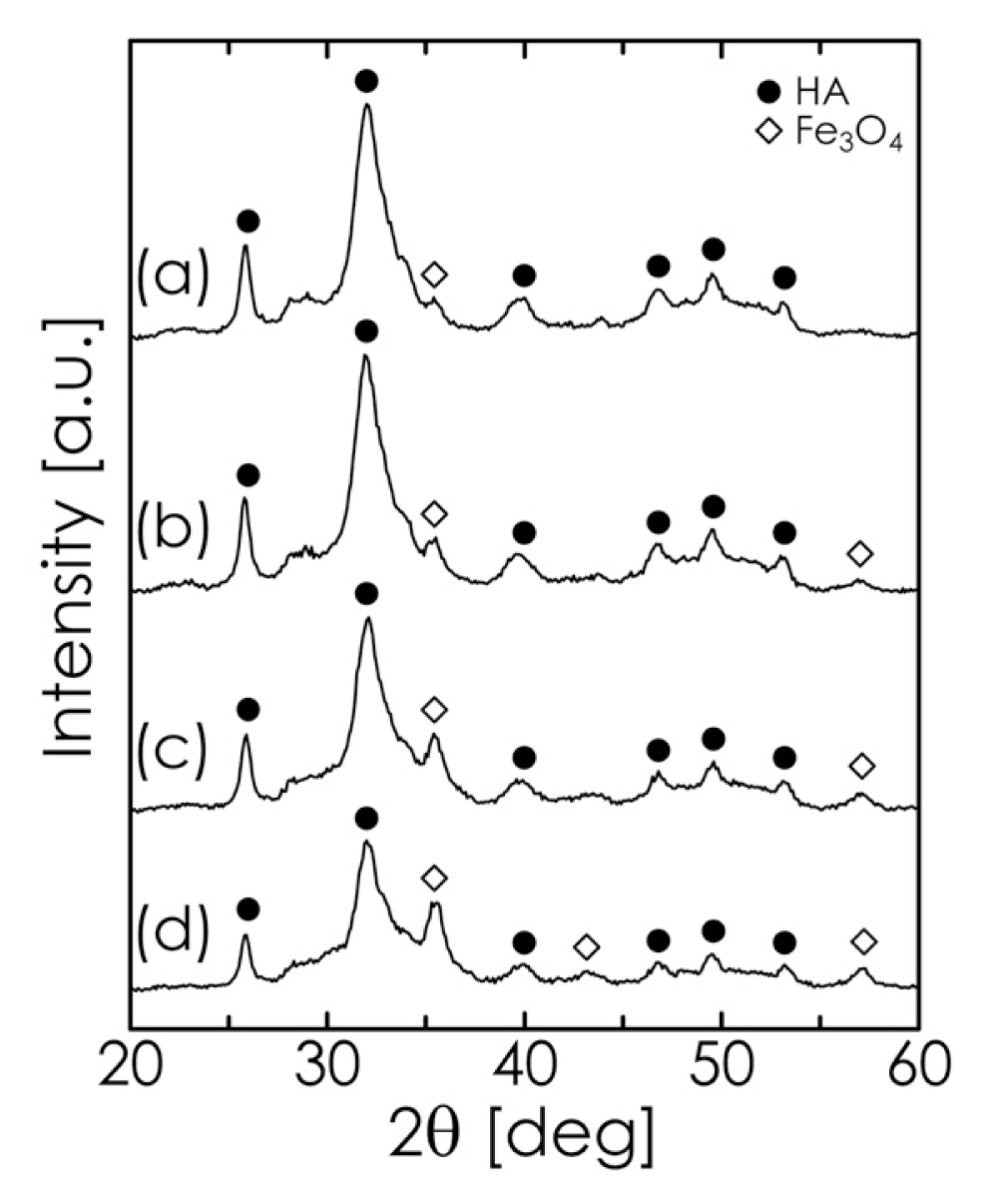
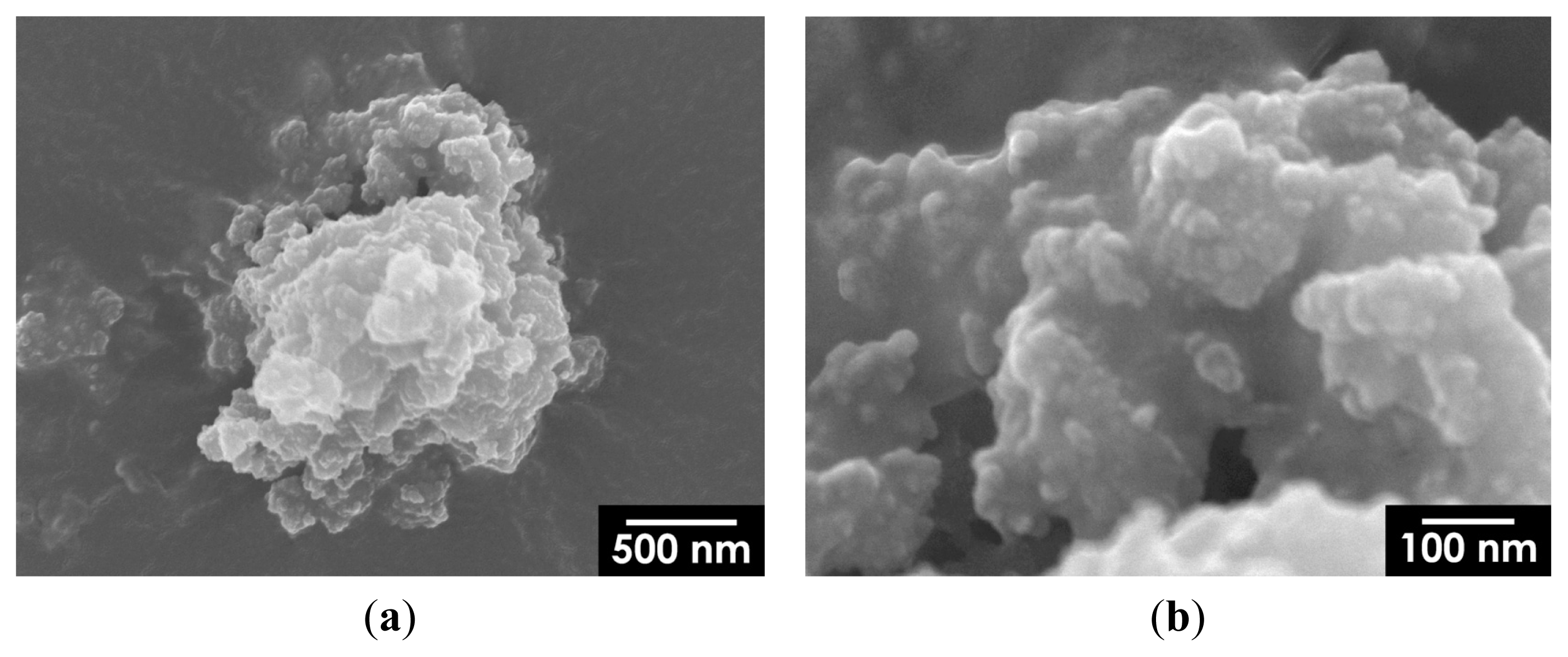
2.2. Mechanochemical Synthesis of HA
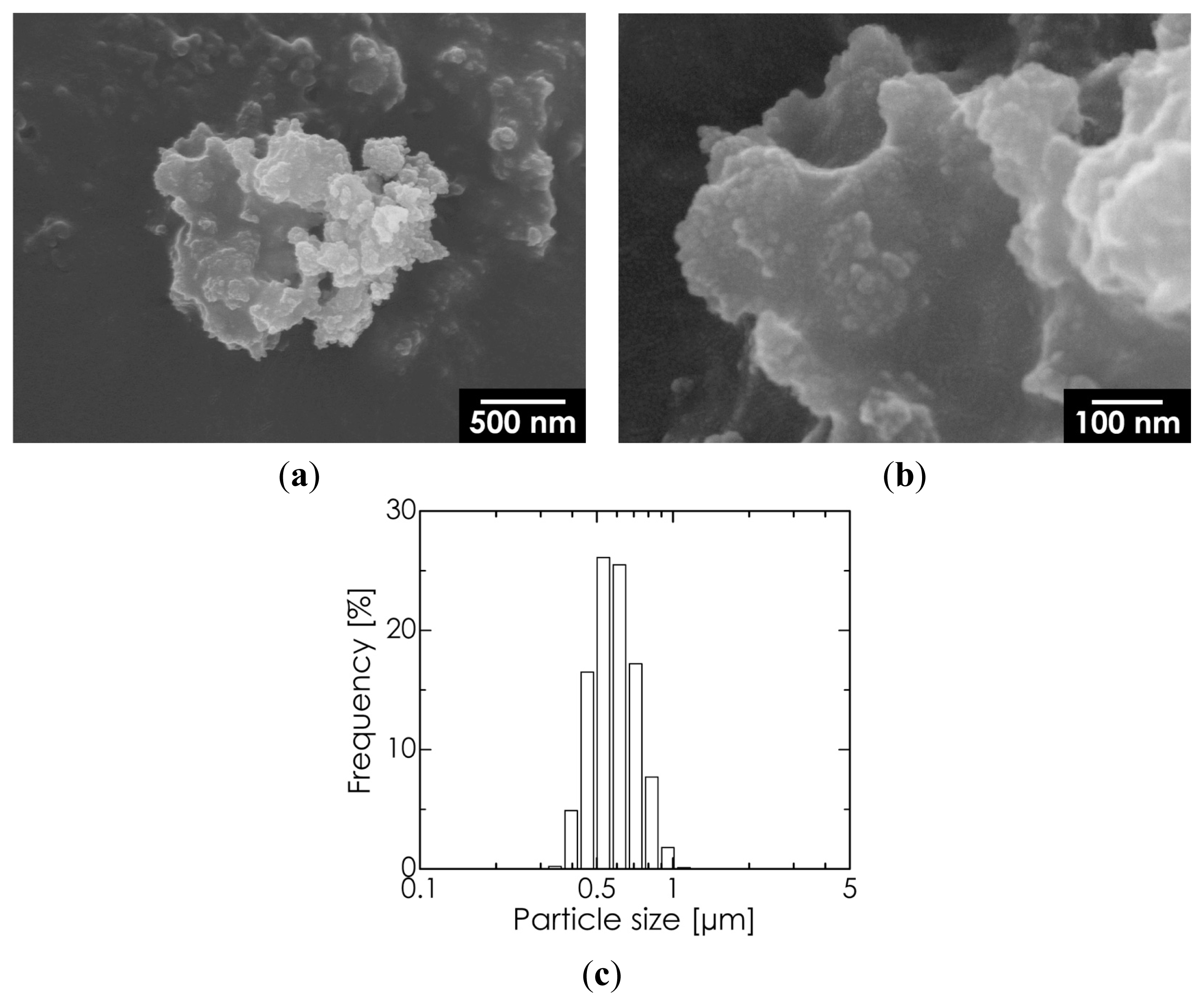
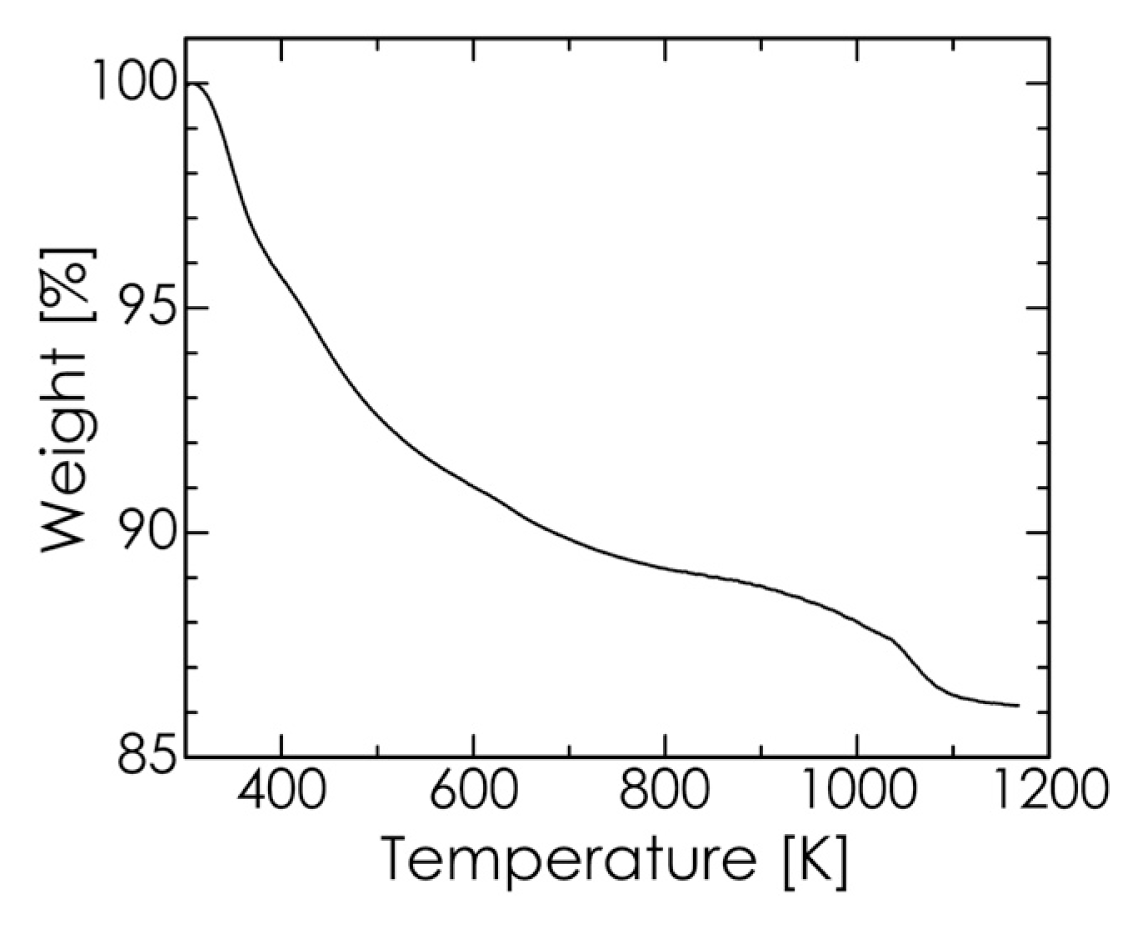
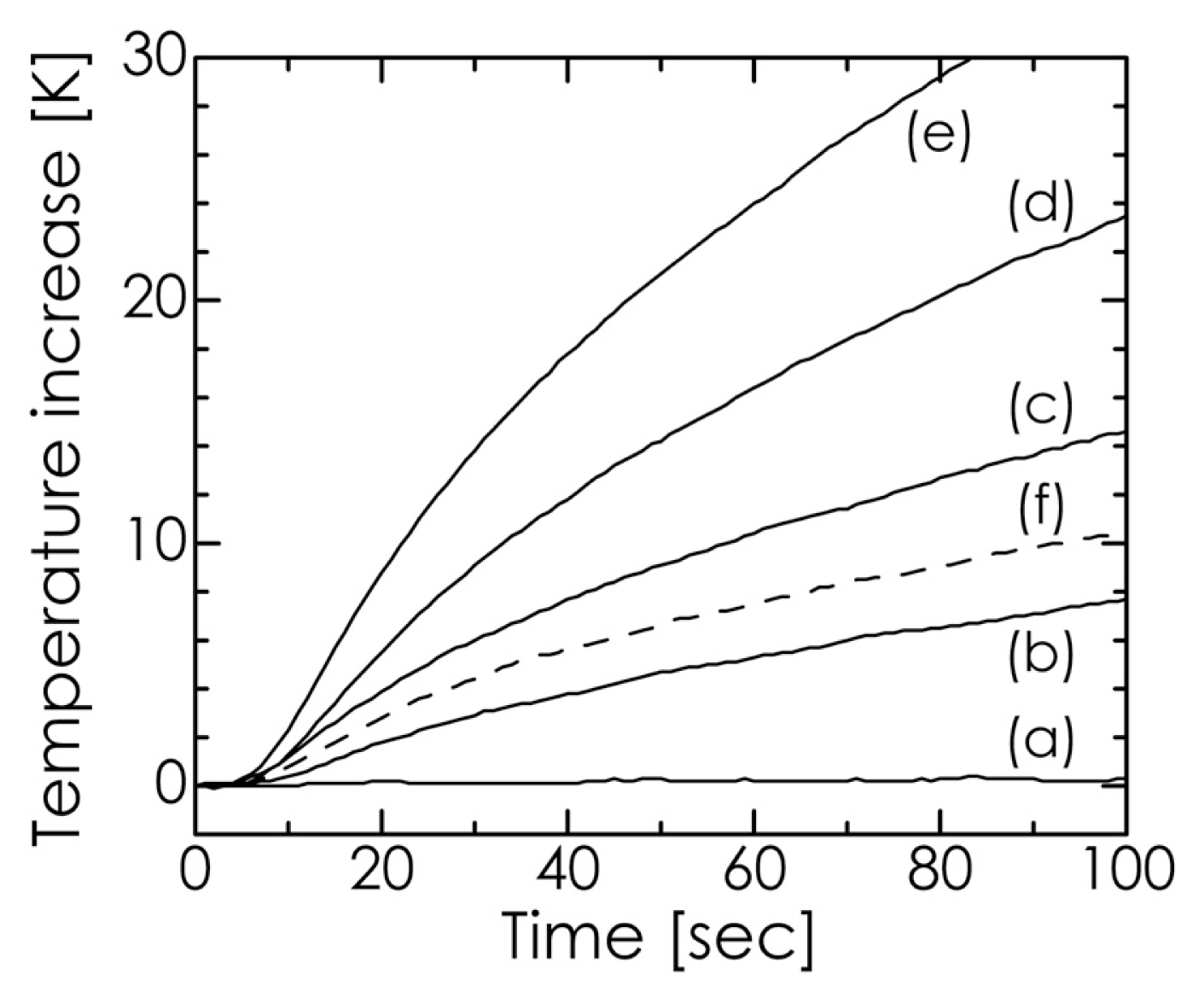
2.3. Hyperthermia-Relevant Properties of Fe3O4/HA Nanocomposites
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Ding, C.C.; Teng, S.H.; Pan, H. In situ generation of chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite microspheres for biomedical application. Mater. Lett 2012, 79, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Nikpour, M.R.; Rabiee, S.M.; Jahanshahi, M. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanocomposite materials for medical engineering applications. Compos. B Eng 2012, 43, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, Q.; Zuo, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J. Novel mesoporous hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite for bone repair. J. Bionic. Eng 2012, 9, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Tien, W.B.; Chen, M.T.; Yao, P.C. Effects of pH and temperature on microstructure and morphology of hydroxyapatite/collagen composites synthesized in vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Lu, J.; Ai, H.; Jiang, B. Novel method for the fabrication of multiscale structure collagen/hydroxyapatite-microsphere composites based on CaCO3 microparticle templates. Mater. Lett 2012, 80, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kochi, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Shirosaki, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A. Preparation of injectable hydroxyapatite/collagen nanocomposite artificial bone. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 493–494, 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.P.; Chang, F.N. Preparation and characterization of hydroxyapatite/gelatin composite membranes for immunoisolation. Appl. Surf. Sci 2012, 262, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kailasanathan, C.; Selvakumar, N.; Naidu, V. Structure and properties of titania reinforced nano-hydroxyapatite/gelatin bio-composites for bone graft materials. Ceram. Int 2012, 38, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri, D.; Ghosh, S.; Agarwal, A. Carbon nanotube reinforced hydroxyapatite composite for orthopedic application: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1727–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Watari, F.; Liao, S.; Yokoyama, A.; Omori, M.; Ai, H.; Cui, F. Carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites fabricated by spark plasma sintering for bonegraft applications. Appl. Surf. Sci 2012, 262, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.Y.; Zhang, N.Y.; Wei, L.; Wei, J.W.; Deng, Q.Y.; Lu, X.; Duan, K.; Weng, J. Fabrication of carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites via an in situ process. Appl. Surf. Sci 2012, 262, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Nathanael, A.J.; Lee, J.H.; Mangalaraj, D.; Hong, S.I.; Rhee, Y.H. Multifunctional properties of hydroxyapatite/titania bio-nano-composites: Bioactivity and antimicrobial studies. Powder Technol 2012, 228, 410–415. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakopoulou, T.; Todorova, N.; Romanos, G.; Vaimakis, T.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.; Trapalis, C. Composite hydroxyapatite/TiO2 materials for photocatalytic oxidation of NOx. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Enayati-Jazi, M.; Solati-Hashjin, M.; Nemati, A.; Bakhshi, F. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite/titania nanocomposites using in situ precipitation technique. Superlattice Microst 2012, 51, 877–885. [Google Scholar]
- Pujiyanto, E.; Tontowi, A.E.; Wildan, M.W.; Siswomihardjo, W. Porous hydroxyapatite-zirconia composites prepared by powder deposition and pressureless sintering. Adv. Mater. Res 2012, 445, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, H.C.; Barreto, M.C. Tailoring the microstructure of sol-gel derived hydroxyapatite/zirconia nanocrystalline composites. Nanoscale Res. Lett 2011, 6, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, J. Removal of lead from aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite/magnetite composite adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J 2010, 165, 827–834. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Preparation of magnetic hydroxyapatite and their use as recyclable adsorbent for phenol in wastewater. Clean 2011, 39, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, C.; Wu, D.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, Z.; Lan, Y. Kinetic and thermodynamic sorption study of radiocobalt by magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem 2012, 291, 637–647. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, C. Temperature dependence of magnetic property and photocatalytic activity of Fe3O4/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull 2010, 45, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.P.; Gong, X.Y.; Zhang, C.J. Recyclable Fe3O4/hydroxyapatite composite nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications. Chem. Eng. J 2010, 165, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, S.; Hosono, T.; Jeyadevan, B.; Kamitakahara, M.; Ioku, K. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite/hydroxyapatite composite material for hyperthermia therapy for bone cancer. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn 2008, 116, 950–954. [Google Scholar]
- Andronescu, E.; Ficai, M.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, D.; Maganu, M.; Ficai, A. Synthesis and characterization of collagen/hydroxyapatite: Magnetite composite material for bone cancer treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med 2010, 21, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar]
- Inukai, A.; Sakamoto, N.; Aono, H.; Sakurai, O.; Shinozaki, K.; Suzuki, H.; Wakiya, N. Synthesis and hyperthermia property of hydroxyapatite-ferrite hybrid particles by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2011, 323, 965–969. [Google Scholar]
- Panseri, S.; Cunha, C.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Russo, A.; Giavaresi, G.; Marcacci, M.; Hung, C.T.; Tampieri, A. Magnetic hydroxyapatite bone substitutes to enhance tissue regeneration: Evaluation in vitro using osteoblast-like cells and in vivo in a bone defect. PLoS One 2012, 7, e38710. [Google Scholar]
- Panseri, S.; Russo, A.; Giavaresi, G.; Sartori, M.; Veronesi, F.; Fini, M.; Salter, D.M.; Ortolani, A.; Strazzari, A.; Visani, A.; et al. Innovative magnetic scaffolds for orthopedic tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100A, 2278–2286. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.B.; Hu, H.; Xie, L.Q.; Lan, F.; Jiang, W.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z.W. Magnetic responsive hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds construction for bone defect reparation. Int. J. Nanomed 2012, 7, 3365–3378. [Google Scholar]
- Bañobre-López, M.; Piñeiro-Redondo, Y.; de Santis, R.; Gloria, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Tampieri, A.; Dediu, V.; Rivas, J. Poly(caprolactone) based magnetic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Appl. Phys 2011, 109, 07, B313.. [Google Scholar]
- Tampieri, A.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Sprio, S.; Landi, E.; Bertinetti, L.; Panseri, S.; Pepponi, G.; Goettlicher, J.; Bañobre-López, M.; Rivas, J. Intrinsic magnetism and hyperthermia in bioactive Fe-doped hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater 2012, 8, 843–851. [Google Scholar]
- Gloria, A.; Russo, T.; D’Amora, U.; Zeppetelli, S.; D’Alessandro, T.; Sandri, M.; Bañobre-López, M.; Piñeiro-Redondo, Y.; Uhlarz, M.; Tampieri, A.; et al. Magnetic poly(ɛ-caprolactone)/iron-doped hydroxyapatite nanocomposite substrates for advanced bone tissue engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120833. [Google Scholar]
- Ansar, E.B.; Ajeesh, M.; Yokogawa, Y.; Wunderlich, W.; Varma, H. Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide embedded hydroxyapatite bioceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc 2012, 95, 2695–2699. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, T.; Mizutani, N.; Watano, S.; Yanagida, T.; Kawai, T. Size control of magnetite nanoparticles by organic solvent-free chemical coprecipitation at room temperature. J. Exp. Nanosci 2010, 5, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, T.; Yabuuchi, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Watano, S. Scale-up methodology for tumbling ball mill based on impact energy of grinding balls using discrete element analysis. Adv. Powder Technol 2010, 21, 623–629. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Isobe, T.; Senna, M. Magnetic properties of ultrafine magnetite particles and their slurries prepared via in situ precipitation. Colloids Surf. A 1996, 109, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.C.; Pinheiro, A.G.; Miranda, M.A.R.; Góes, J.C.; Sombra, A.S.B. Structural properties of hydroxyapatite obtained by mechanosynthesis. Solid State Sci 2003, 5, 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiri-Tabrizi, B.; Shokuhfar, A.; Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi, R. Synthesis and structural evaluation of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite obtained by mechanochemical treatment in polyamide6 vials. J. Nano Res 2009, 7, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.C.; Hsu, H.C.; Wu, Y.N.; Ho, W.F. Hydroxyapatite synthesized from oyster shell powders by ball milling and heat treatment. Mater. Charact 2011, 62, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Bayraktar, D.; Tas, A.C. Chemical preparation of carbonated calcium hydroxyapatite powders at 37 °C in urea-containing synthetic body fluids. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc 1999, 19, 2573–2579. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.W.; Oakes, C.S.; Byrappa, K.; Riman, R.E.; Brown, K.; TenHuisen, K.S.; Janas, V.F. Synthesis, characterization, and dispersion properties of hydroxyapatite prepared by mechanochemical-hydrothermal methods. J. Mater. Chem 2004, 14, 2425–2432. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, C.; Yanwei, W.; Hong, L.; Zhengzheng, P.; Kangde, Y. Synthesis of carbonated hydroxyapatite nanofibers by mechanochemical methods. Ceram. Int 2005, 31, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Orthophosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Regnier, P.; Lasaga, A.C.; Berner, R.A.; Han, O.H.; Zilm, K.W. Mechanism of CO32− substitution in carbonate-fluorapatite: Evidence from FTIR spectroscopy, 13C NMR, and quantum mechanical calculations. Am. Miner 1994, 79, 809–818. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, K.; Matsuya, S.; Lin, X.; Lei, Z.; Yuasa, T.; Miyamoto, Y. Fabrication of low crystalline B-type carbonate apatite block from low crystalline calcite block. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn 2010, 118, 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Suchanek, W.L.; Shuk, P.; Byrappa, K.; Riman, R.E.; TenHuisen, K.S.; Janas, V.F. Mechanochemical-hydrothermal synthesis of carbonated apatite powders at room temperature. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 699–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.G.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, Z.H. Mechanochemical-hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of fluoridated hydroxyapatite. Mater. Res. Bull 2005, 40, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Murase, K.; Oonoki, J.; Takata, H.; Song, R.; Angraini, A.; Ausanai, P.; Matsushita, T. Simulation and experimental studies on magnetic hyperthermia with use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Radiol. Phys. Technol 2011, 4, 194–202. [Google Scholar]


© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwasaki, T.; Nakatsuka, R.; Murase, K.; Takata, H.; Nakamura, H.; Watano, S. Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Magnetite/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Hyperthermia Treatments via a Mechanochemical Route. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9365-9378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059365
Iwasaki T, Nakatsuka R, Murase K, Takata H, Nakamura H, Watano S. Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Magnetite/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Hyperthermia Treatments via a Mechanochemical Route. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):9365-9378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059365
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwasaki, Tomohiro, Ryo Nakatsuka, Kenya Murase, Hiroshige Takata, Hideya Nakamura, and Satoru Watano. 2013. "Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Magnetite/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Hyperthermia Treatments via a Mechanochemical Route" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 9365-9378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059365
APA StyleIwasaki, T., Nakatsuka, R., Murase, K., Takata, H., Nakamura, H., & Watano, S. (2013). Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Magnetite/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Hyperthermia Treatments via a Mechanochemical Route. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 9365-9378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059365



