The Role of Short-Chain Conjugated Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate (cPHB) in Protein Folding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
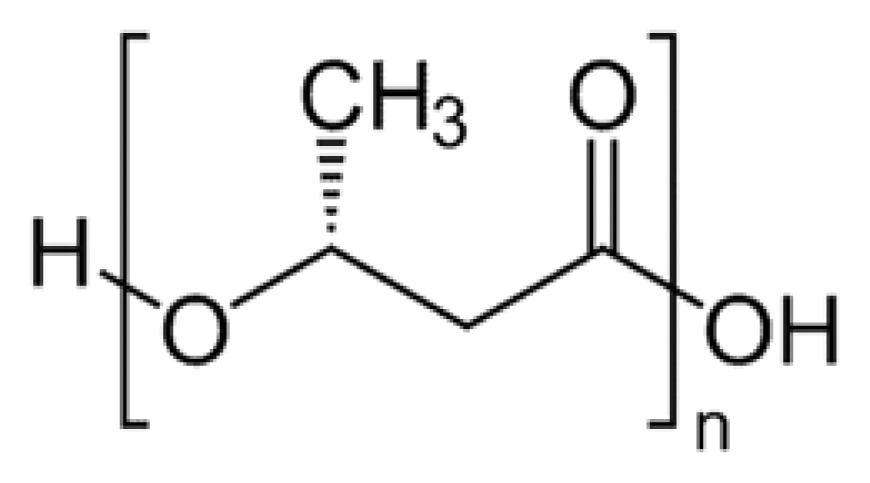
2. Synthesis of PHB
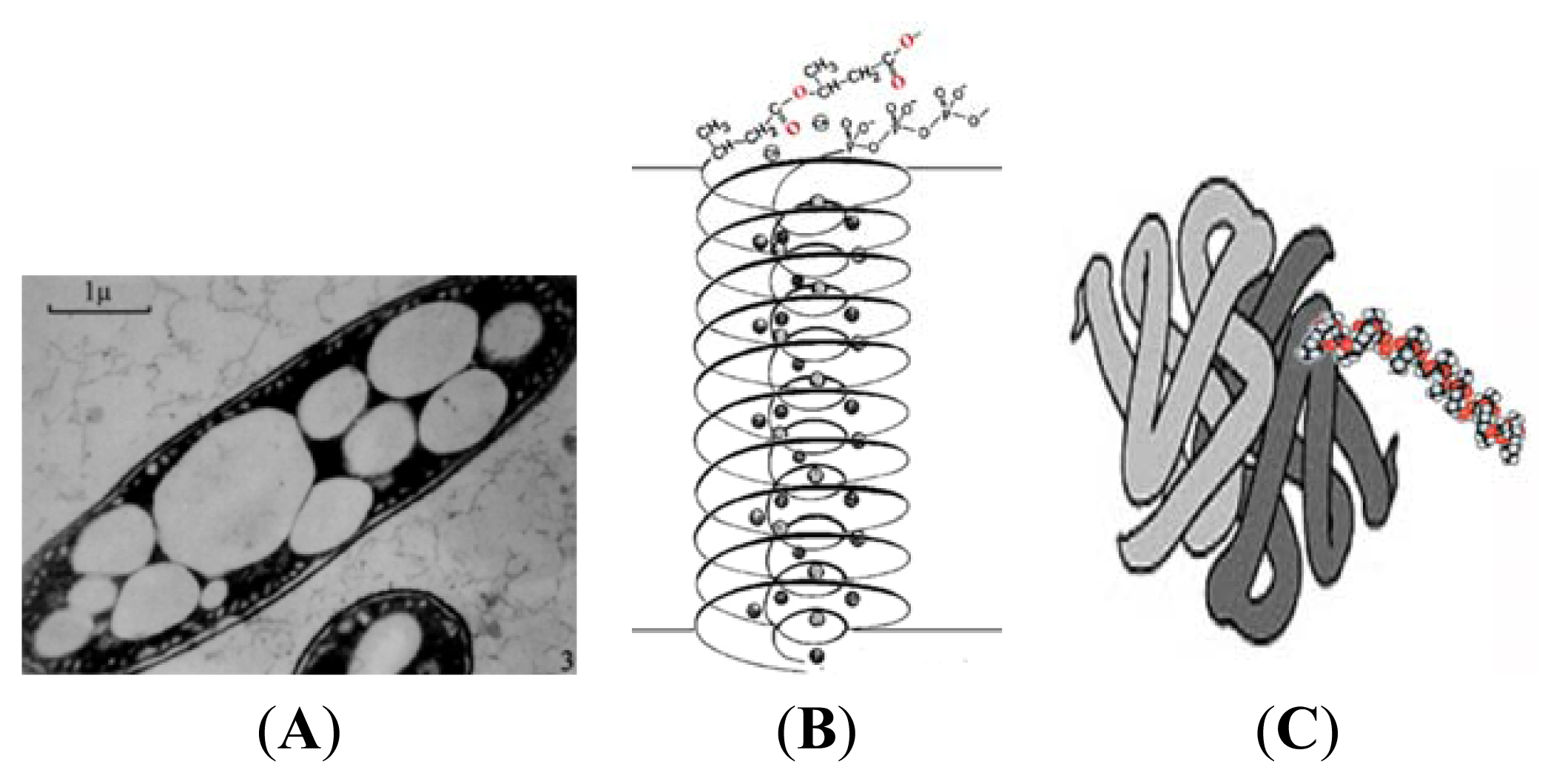
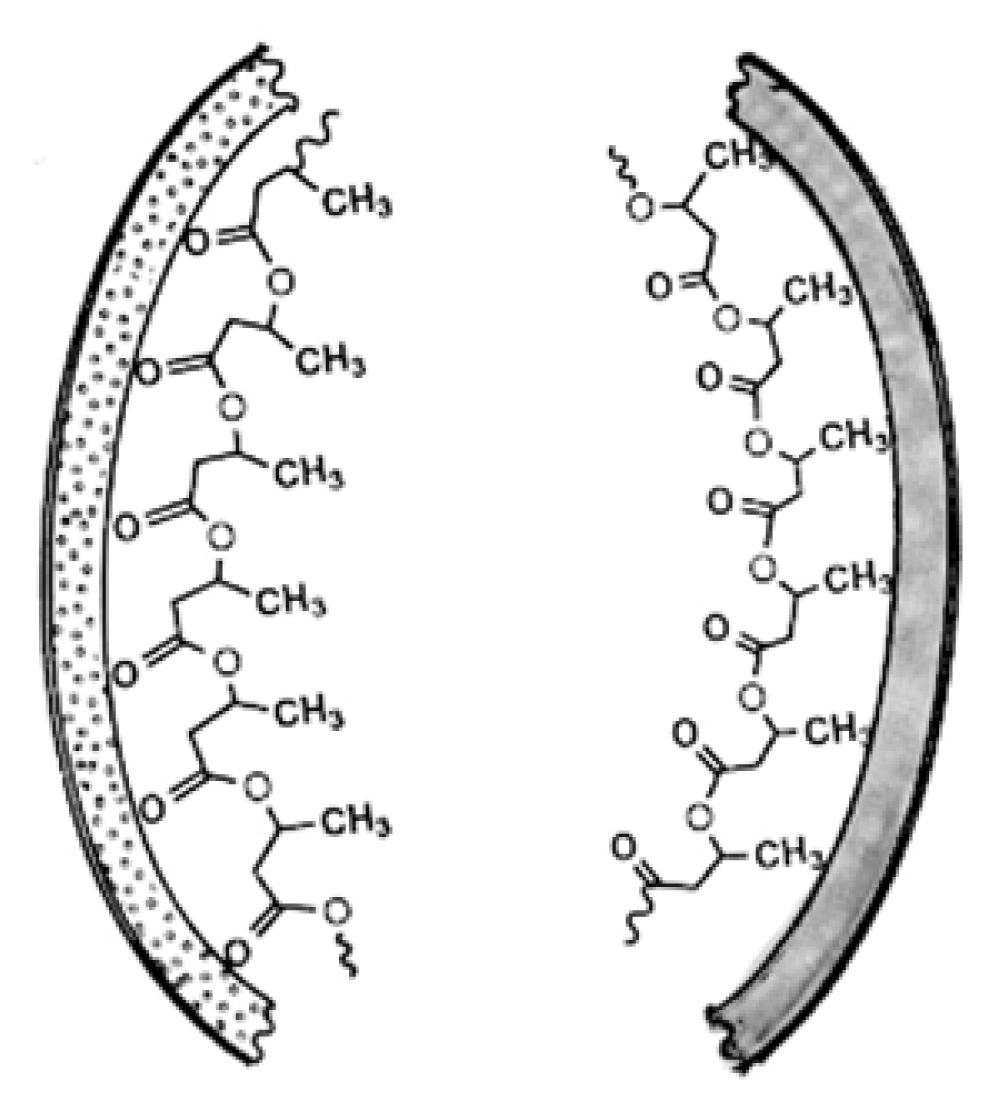
3. Physical Properties of PHB
4. cPHB-Proteins
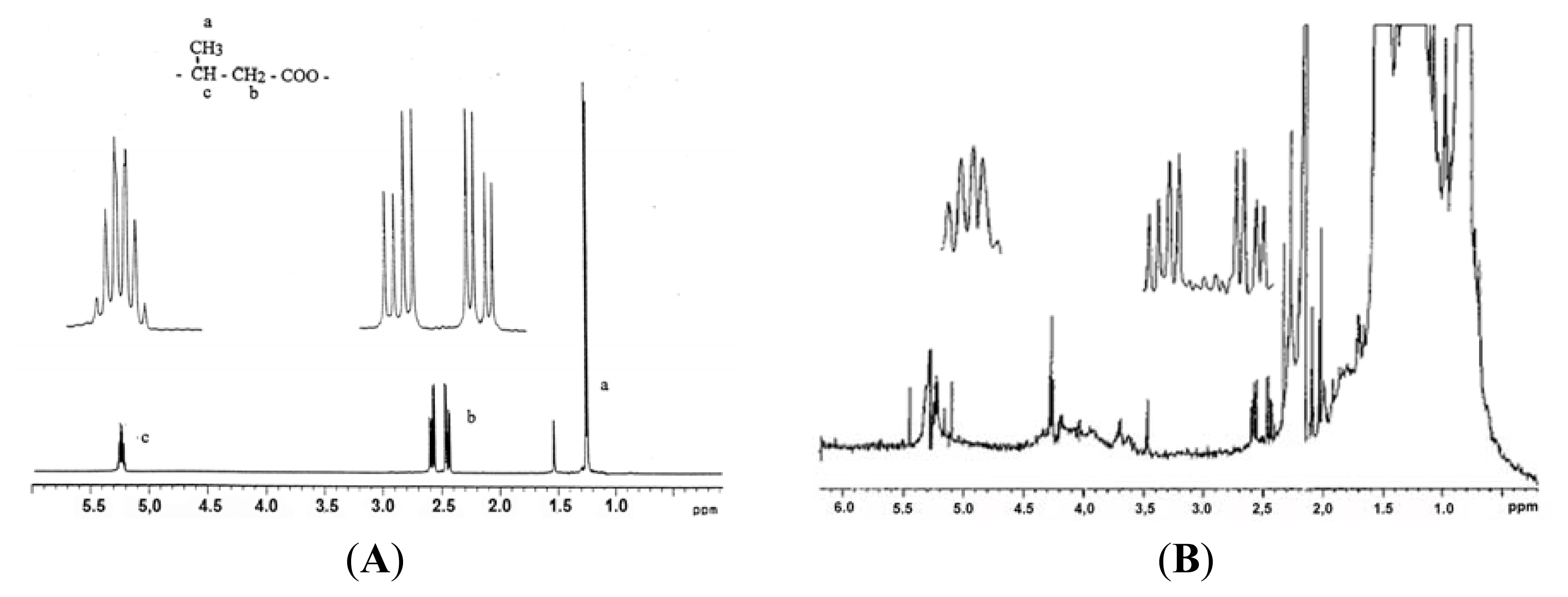
5. Identification of cPHB
6. cPHB-Proteins in Escherichia coli
7. The Role of cPHB in Folding of Outer Membrane Protein A (OmpA) of Escherichia coli
7.1. Structure of OmpA
7.2. Targeting and Folding of OmpA
7.2.1. From the Ribosome to the Cytoplasmic Membrane
7.2.2. Across the Periplasm to the Outer Membrane
8. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lemoigne, M. Produits de Dehydration et de Polymerisation de l’Acide ß-oxobutyrique. Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol 1926, 8, 770–782. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, A.J.; Dawes, E.A. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 54, 450–472. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, A.; Donato, P.; Abbamondi, G.R.; Nicolaus, B. Synthesis, production, and biotechnological applications of exopolysaccharides and polyhydroxyalkanoates by Archaea. Archaea 2011, 2011, e693253. [Google Scholar]
- Nuti, M.P.; de Bertoldi, M.; Lepidi, A.A. Influence of phenylacetic acid on poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) polymerization and cell elongation in Azotobacter chroococcum Beij. Can. J. Microbiol 1972, 18, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Pötter, M.; Steinbüchel, A. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) granule-associated proteins: Impacts on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthesis and degradation. Biomacromolecules 2005, 2, 552–560. [Google Scholar]
- Rehm, B.H. Genetics and biochemistry of polyhydroxyalkanoate granule self-assembly. Biothechnol. Lett 2006, 28, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Jendrossek, D. Polyhydroxyalkanoate granules are complex subcellular organelles (Carbanosomes). J. Bacteriol 2009, 191, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar]
- Elustondo, P.; Zakharian, E.; Pavlov, E. Identification of the polyhydroxybutyrate granules in mammalian cultured cells. Chem. Biodivers 2012, 9, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Sadoff, H.L. d-(−)-Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in membranes of genetically competent bacteria. J. Bacteriol 1983, 156, 778–788. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Hiske, T.W.; Sadoff, H.L. Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate membrane structure and its relationship to genetic transformability in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol 1986, 168, 553–562. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N. Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate/calcium polyphosphate complexes in eukaryotic membranes. Proc. Soc. Exp. Med. Biol 1989, 191, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Sparrow, A.W.; Gardiner, J. Transport of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in human plasma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1123, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N. Biological complexes of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 1992, 103, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Seebach, D.; Brunner, A.; Bürger, H.M.; Schneider, J.; Reusch, R.N. Isolation and 1H-NMR spectroscopic identification of poly(3-hydroxybutanoate) from prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Eur. J. Biochem 1994, 224, 317–328. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N; Sadoff, H.L. Putative structure and functions of a poly-β-hydroxybutyrate/calcium polyphosphate channel in bacterial plasma membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4176–4180. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Huang, R.; Bramble, L.L. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate/polyphosphate complexes form voltage-activated Ca2+ channels in the plasma membranes of Escherichia coli. Biophys. J 1995, 69, 754–766. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Lengweiler, U.D.; Seebach, D.; Reusch, R.N. Proof for a nonproteinaceous calcium-selective channel in Escherichia coli by total synthesis from (R)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid and inorganic polyphosphate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9075–9079. [Google Scholar]
- Castuma, C.E.; Huang, R.; Kornberg, A.; Reusch, R.N. Inorganic polyphosphates in the acquisition of competence in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 12980–12983. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Reusch, R.N. Genetic competence in Escherichia coli requires poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate/calcium polyphosphate membrane complexes and certain divalent cations. J. Bact 1995, 177, 486–490. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N. Transmembrane Ion transport by polyphosphate poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate complexes. Bioch. Moscow 2000, 65, 280–295. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Reusch, R.N. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) is associated with specific proteins in the cytoplasm and membranes of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 22196–22202. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Huang, R.; Kosk-Kosicka, D. Novel components and enzymatic activities of the human erythrocyte plasma membrane calcium pump. FEBS Lett 1997, 412, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Shabalin, O.; Crumbaugh, A.; Wagner, R.; Schröder, O.; Wurm, R. Posttranslational modification of E. coli histone-like protein H-NS and bovine histones by short-chain poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate (cPHB). FEBS Lett 2002, 527, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Bryant, E.M.; Henry, D.N. Increased poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate concentrations in streptozotocin (STZ) diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol 2003, 40, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N. Streptomyces lividans potassium channel contains poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate and inorganic polyphosphate. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 15666–15672. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, M.; Fuerst, M.M.; Shabalin, Y.; Reusch, R.N. Sorting signal of Escherichia coli OmpA is modified by oligo-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian, E.; Reusch, R.N. Haemophilus influenzae outer membrane protein A is associated with inorganic polyphosphate and polyhydroxybutyrate. Biophys. J 2007, 92, 588–593. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, V.; Bresson-Dumont, H.; Gardea, E.; Reusch, R.N.; Gruber, D. Hypothesis: Poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate is a major factor in intraocular pressure. Med. Hypoth 2009, 73, 398–401. [Google Scholar]
- Seebach, D.; Fritz, M.G. Detection, synthesis, structure, and function of oligo(3-hydroxyalkanoates): Contributions by synthetic organic chemists. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 1999, 25, 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger, A.L. Biochemistry; Worth Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1970; p. 427. [Google Scholar]
- Rueping, M.; Dietrich, A.; Buschmann, V.; Fritz, M.G.; Sauer, M.; Seebach, D. On the structure of poly(3-hydroxybutanoic acid) in solution and in phospholipid bilayers circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy with oligo(3-hydroxybutanoic acid) derivatives. Macromolecules 2001, 4, 7042–7048. [Google Scholar]
- Waser, P.; Rueping, M.; Seebach, D. On the solution structure of PHB: Preparation and NMR analysis of isotopically labelled oligo [(R)-3-hydroxybutanoic acids] (OHBs). Helv. Chim. Acta 2001, 84, 1821–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, M.; Seebach, D.; Duchardt, E.; Schwalbe, H. Synthesis and NMR analysis in solution of oligo(3-hydroxyalkanoic acid) derivatives with the side chains of alanine, valine, and leucine (β-depsides): Coming full circle from PHB to β-Peptides to PHB. Helv. Chim. Acta 2002, 85, 633–658. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, P.J.; Hamprecht, F.A.; Schuler, L.D.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Duchardt, E.; Schwalbe, H.; Albert, M.; Seebach, D. A molecular dynamics simulation study of the conformational preferences of oligo-(3-hydroxyalkonoic acids) in chloroform solution. Helv. Chim. Acta 2002, 85, 618–632. [Google Scholar]
- Armand, M.B. Polymer Electrolyte Reviews-1; MacCallum, J.R., Vincent, C.A., Eds.; Elsevier Applied Science: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- MacCallum, J.R.; Vincent, C.A. Polymer Electrolytes Review-1; MacCallum, J.R., Vincent, C.A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 1987; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, F.M. Solid Polymer Electrolytes; VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Seebach, D.; Bürger, H.M.; Plattner, D.A.; Nesper, R.; Fässler, T.F. Complexes of the triolide from (R)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid with sodium, potassium, and barium salts—Crystal structures, ester chelates and ester crowns, crystal packing, bonding, and electron localization functions. Helv. Chim. Acta 1993, 76, 2581–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Bürger, H.M.; Seebach, D. Cation transport across bulk liquid organic membranes with oligomers of (R)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid. Helv. Chim. Acta 1993, 76, 2570–2580. [Google Scholar]
- Seebach, D.; Brunner, A.; Büger, H.M.; Reusch, R.N.; Bramble, L.L. Channel-forming activity of 3-hydroxybutanoic-acid oligomers in planar lipid bilayers. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, M.G.; Walde, P.; Seebach, D. Oligoesters of (R)-3-hydroxybutanoic acid: Transmembrane transport of Ca2+ across lipid bilayers. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 574–580. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian, E.; Thyagarajan, B.; French, R.J.; Pavlov, E.; Rohacs, T. Inorganic polyphosphate modulates TRPM8 channels. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5404. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian, E.; Cao, C.; Rohacs, T. Gating of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channels activated by cold and chemical agonists in planar lipid bilayers. J. Neurosci 2010, 30, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R.N.; Grühn, A.G. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-Conjugated Proteins are Ubiquitous in Both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. In 1996 International Symposium Bacterial Polyhydroxyalkanoates; Eggink, G., Steinbüchel, A., Poirier, Y., Witholt, B., Eds.; NRC Research Press: Ottawa, Canada, 1997; pp. 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Karr, D.B.; Waters, J.K.; Emerich, D.W. Analysis of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids by ion-exclusion high pressure liquid chromatography and UV detection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1983, 46, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Negoda, A.; Negoda, E.; Reusch, R.N. Resolving the native conformation of Escherichia coli. FEBS J 2010, 277, 4427–4437. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.; Reusch, R.N. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate synthase from the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm 2008, 374, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Theodorou, M.C.; Panagiotidis, C.A.; Panagiotidis, C.H.; Pantazaki, A.A.; Kyriakidis, D.A. Involvement of the AtoS-AtoC signal transduction system in poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biopys. Acta 2006, 1760, 896–906. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakidis, D.A.; Theodorou, M.C.; Filippo, P.S.; Kyriakidis, K.D.; Tiligada, E. Effect of histamine on the signal transduction of the AtoS-AtoC two component system and involvement in poly-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Theodorou, M.C.; Kyriakidis, D.A. Calcium channels blockers inhibit the signal transduction through the AtoSC system in Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci 2012, 47, 84–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rychlewski, L.; Zhang, B.; Godzik, A. Functional insights from structural predictions: Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome. Prot. Sci 1999, 8, 614–624. [Google Scholar]
- Saurin, W.; Hofnung, M.; Dassa, E.J. Getting in or out: Early segregation between importers and exporters in the evolution of ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) transporters. Mol. Evol 1999, 48, 22–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, H.A.; Khairudin, A.; Samian, M.R.; Najimudin, N. Sequence analysis and structure prediction of type II Pseudomonas sp. USM 4–55 PHA synthase and an insight into its catalytic mechanism. BMC Struct. Biol 2006, 6, 6–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Kappock, T.J.; Frick, T.; Sinskey, A.J.; Stubbe, J. Lipases provide a new mechanistic model for polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthases: Characterization of the functional residues in Chromatium vinosum PHB synthase. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 3927–3936. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.G.; Mahon, V.; Lambert, M.A.; Fagan, R.P. A molecular Swiss army knife: OmpA structure, function and expression. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2007, 273, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag, I.; Schwarz, H.; Hirota, Y.; Henning, U. Cell envelope and shape of Escherichia coli: Mutants missing the outer membrane lipoprotein and other major outer membrane proteins. J. Bacteriol 1978, 136, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Morona, R.; Klose, M.; Henning, U. Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane protein (OmpA) as a bacteriophage receptor: Analysis of mutant genes expressing altered proteins. J. Bacteriol 1984, 159, 570–578. [Google Scholar]
- Morona, R.; Krämer, C.; Henning, U. Bacteriophage receptor area of outer membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol 1985, 164, 539–564. [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer, M.; Henning, U. Action of major outer cell envelope membrane protein in conjugation of Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol 1977, 129, 1651–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Ried, G.; Henning, U. A unique amino acid substitution in the outer membrane protein OmpA causes conjugation deficiency in Escherichia coli K-12. FEBS Lett 1987, 223, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Belaaouaj, A.; Kim, K.S.; Shapiro, S.D. Degradation of outer membrane protein A in Escherichia coli killing by neutrophil elastase. Science 2000, 289, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Soulas, C.; Baussant, T.; Aubry, J.F.; Delneste, Y.; Barillat, N.; Caron, G.; Renno, T.; Bonnefoy, J.F.; Jeannin, P. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) binds to and activates human macrophages. J. Immunol 2000, 165, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar]
- Godefroy, S.; Corvaia, N.; Schmitt, D.; Aubry, J.P.; Bonnefoy, J.Y.; Jeannin, P.; Staquet, M.J. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) activates human epidermal langerhans cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol 2003, 82, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, K.S. Current concepts on Escherichia coli K1Translocation of the blood-brain barrier. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol 2004, 42, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.; Prasadaroa, N.V. Outer membrane protein A and OprF: Versatile roles in Gram-negative bacterial infections. FEBS J 2012, 279, 919–931. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez Barrios, A.F.; Zuo, R.; Ren, D.; Wood, T.K. Hha, YbaJ, and OmpA regulate Escherichia coli K12 biofilm formation and conjugation plasmids abolish motility. Biotech. Bioeng 2005, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tamm, L.K.; Arora, A.; Kleinschmidt, J.H. Structure and assembly of β-Barrel membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 32399–32402. [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer, M.; Hindennach, I.; Garten, W.; Henning, U. Major proteins of the Escherichia coli outer cell envelope membrane interaction of protein II with lipopolysaccharide. Eur. J. Biochem 1978, 82, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Ried, G.; Koebnik, R.; Hindennach, I.; Mutschler, B.; Henning, U. Membrane topology and assembly of the outer membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli K12. Mol. Gen. Genet 1994, 243, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Koebnik, R. Membrane assembly of the E. coli outer membrane protein OmpA: Exploring sequence constraints on transmembrane β-strands. J. Mol. Biol 1999, 285, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Koebnik, R. Structural and functional roles of the surface exposed loops of the β-barrel membrane protein OmpA from Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol 1999, 181, 3688–3694. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt, J.H.; Tamm, L.K. Secondary and tertiary structure formation of the β-barrel membrane protein OmpA is synchronized and depends on membrane thickness. J. Mol. Biol 2002, 324, 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, H.; Jähnig, F. Models for the structure of outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli derived from raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. J. Mol. Biol 1986, 190, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, A.; Abildgaard, F.; Bushweiler, J.H.; Tamm, L.K. Structure of outer membrane protein A transmembrane domain by NMR spectroscopy. Nat. Struct. Biol 2001, 8, 334–336. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, C.; Hilty, C.; Bonjour, S.; Adeishvili, K.; Pervushin, K.; Wüthrich, K. Solution NMR studies of the integral membrane proteins OmpX and OmpA from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 2001, 504, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Pautsch, A.; Schulz, G.E. Structure of the outer membrane protein A transmembrane domain. Nat. Struct. Biol 1998, 5, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Pautsch, A.; Schulz, G.E. High-resolution structure of the OmpA membrane domain. J. Mol. Biol 2000, 298, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, P.J.; Faraldo-Gomez, J.D.; Sansom, M.S. OmpA: A pore or not a pore? Simulation and modeling studies. Biophys. J 2002, 83, 763–75. [Google Scholar]
- Domene, C.; Bond, P.J.; Sansom, M.S. Membrane protein simulations: Ion channels and bacterial outer membrane proteins. Adv. Prot. Chem 2003, 66, 159–193. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Ji, X.; Qi, J.; Ma, Y.; Mao, X.; Zou, Q. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic studies of the C-terminal domain of outer membrane protein A from enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Acta Crystallog. Sect. F. Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun 2010, 66, 929–931. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.H.; Lee, W.C.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, J.C.; Cheong, C.; Kim, H.Y. Cloning, purification and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the OmpA-like domain of peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein from Acinetobacter Baumannii. Acta Crystllogr. Sect. F. Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun 2012, 68, 1351–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Danoff, E.J.; Fleming, K.G. The soluble, periplasmic domain of OmpA folds as an independent unit and displays chaperone activity by reducing the self-association propensity of the unfolded OmpA transmembrane β-barrel. Biophys. Chem 2011, 159, 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Rawling, E.G.; Martin, N.L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Epitope mapping of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa major outer membrane porin protein OprF. Infect. Immun 1995, 63, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.P.; Williams, Y.U.; Miller, S.; Nikaido, H. The C-terminal domain of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium OmpA is an immunodominant antigen in mice but appears to be only partially exposed on the bacterial cell surface. Infect. Immun 2003, 71, 3937–3946. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanteur, D.; Lakey, J.H.; Pattus, F. Bacterial Cell Wall; Ghuysen, J.M., Hakenbeck, R., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer, T.; Cowan, S.W. Prediction of membrane-spanning β-strands and its application to maltoporin. Protein Sci 1993, 2, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci, T. From sequence alignment to structure prediction: The case of the OmpF porin family. Mol. Microbiol 1994, 14, 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos, C. An alternative topological model for Escherichia coli OmpA. Prot. Sci 1996, 5, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, E.; Nikaido, H. Pore-forming activity of OmpA protein of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem 1992, 267, 2507–2511. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, E.; Nikaido, H. OmpA protein of Escherichia coli outer membrane occurs in open and closed channel forms. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 17981–17987. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, A.; Rinehart, D.; Szabo, G.; Tamm, L.K. Refolded outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli forms ion channels with two conductive states in planar lipid bilayers. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian, E.; Reusch, R.N. Outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli forms temperature-sensitive channels in planar lipid bilayers. FEBS Lett 2003, 555, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharian, E.; Reusch, R.N. Kinetics of folding of Escherichia coli OmpA from narrow to large pore conformation in a planar bilayer. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 6701–6707. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, R. Insights into the structure and assembly of Escherichia coli outer membrane A. FEBS J 2012, 279, 894–909. [Google Scholar]
- Bremer, E.; Cole, S.T.; Hindemach, I.; Henning, U.; Beck, E.; Kurz, C.; Schaller, H. Export of a protein into the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12. Stable incorporation of the OmpA protein requires less than 193 amino-terminal amino-acid residues. Eur. J. Biochem 1982, 122, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Klose, M.; Schwarz, H.; MacIntyre, S.; Freudl, R.; Eschbach, M.; Henning, U. Internal deletions in the gene for an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein define an area possibly important for recognition of the outer membrane by this polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem 1988, 263, 13291–13296. [Google Scholar]
- Klose, M.; MacIntyre, S.; Schwarz, H.; Henning, U. The influence of amino substitutions within the mature part of an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein ompa on assembly of the polypeptide into its membrane. J. Biol. Chem 1988, 263, 13297–13302. [Google Scholar]
- Freudl, R.; Klose, M.; Henning, U. Export and sorting of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protein OmpA. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr 1990, 22, 441–449. [Google Scholar]
- Klose, M.; Storiko, A.; Stierhof, Y.-D.; Hindennach, I.; Mustschler, B.; Henning, U. Membrane assembly of outer membrane protein OmpA of E. coli. J. Biol. Chem 1993, 268, 25664–25670. [Google Scholar]
- Jendrossek, D.; Hendrick, R. Microbial degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 2002, 56, 403–422. [Google Scholar]
- Negoda, A.; Negoda, E.; Reusch, R.N. Oligo-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate modification of sorting signal enables pore formation by Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1798, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Bulieris, P.V.; Behrens, S.; Holst, O.; Kleinschmidt, J.H. Folding and insertion of the outer membrane protein OmpA is assisted by the chaperone skp and by lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 9092–9099. [Google Scholar]
- Tamm, L.K.; Hong, H.; Liang, B. Folding and assembly of beta-barrel membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1666, 250–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen, J.E.; Otzen, D.E. Interactions between folding factors and bacterial outer membrane proteins. Mol. Microbiol 2005, 57, 326–346. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, N.; Kahne, D.; Silhavy, T.J. Advances in understanding bacterial outermembrane biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2006, 4, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Collet, J.-F.; Bardwell, J.C.A. Oxidative protein folding in bacteria. Mol. Microbiol 2002, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Inaba, K. The disulfide bond formation dsb system. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2008, 18, 450–458. [Google Scholar]

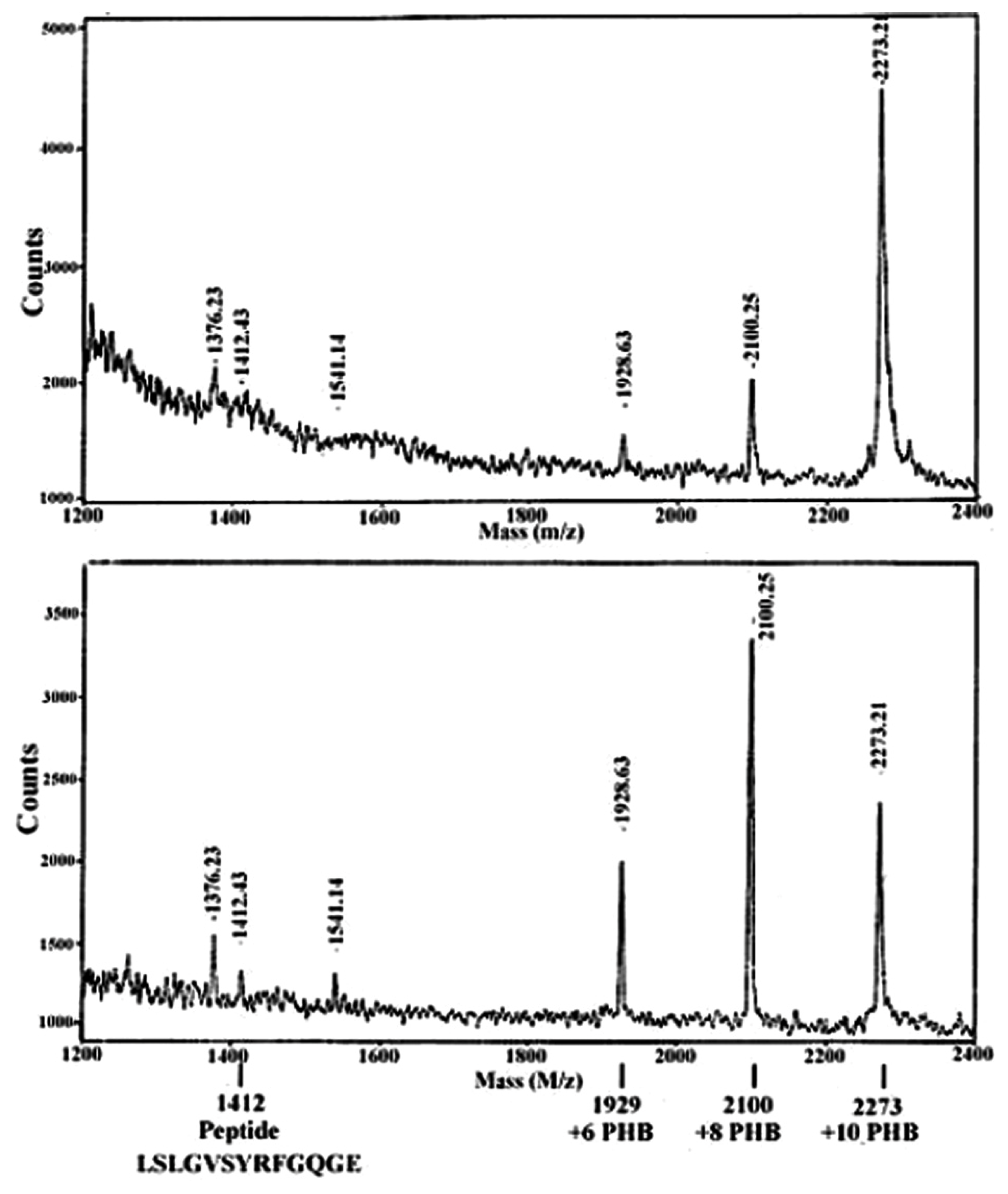
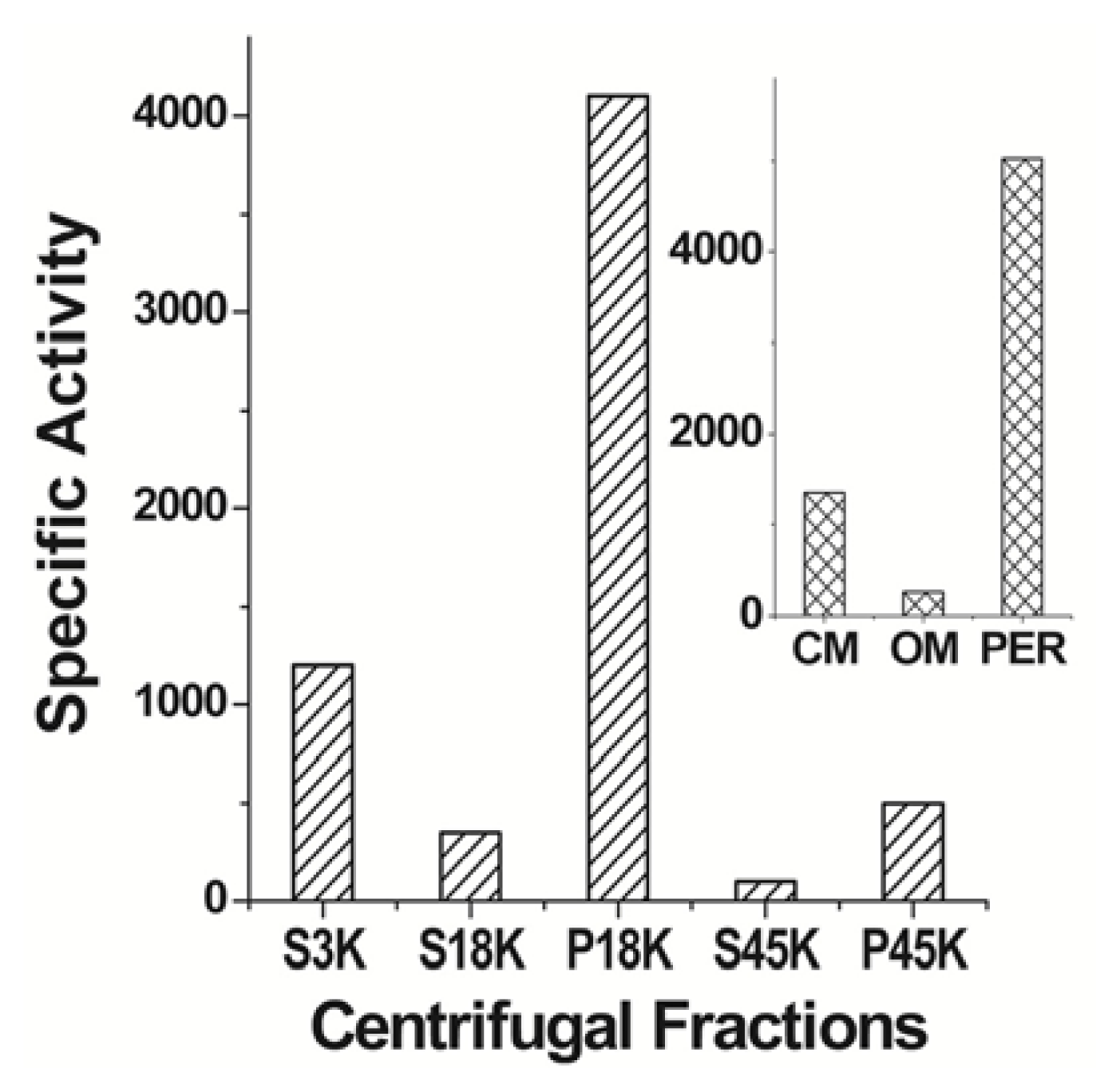
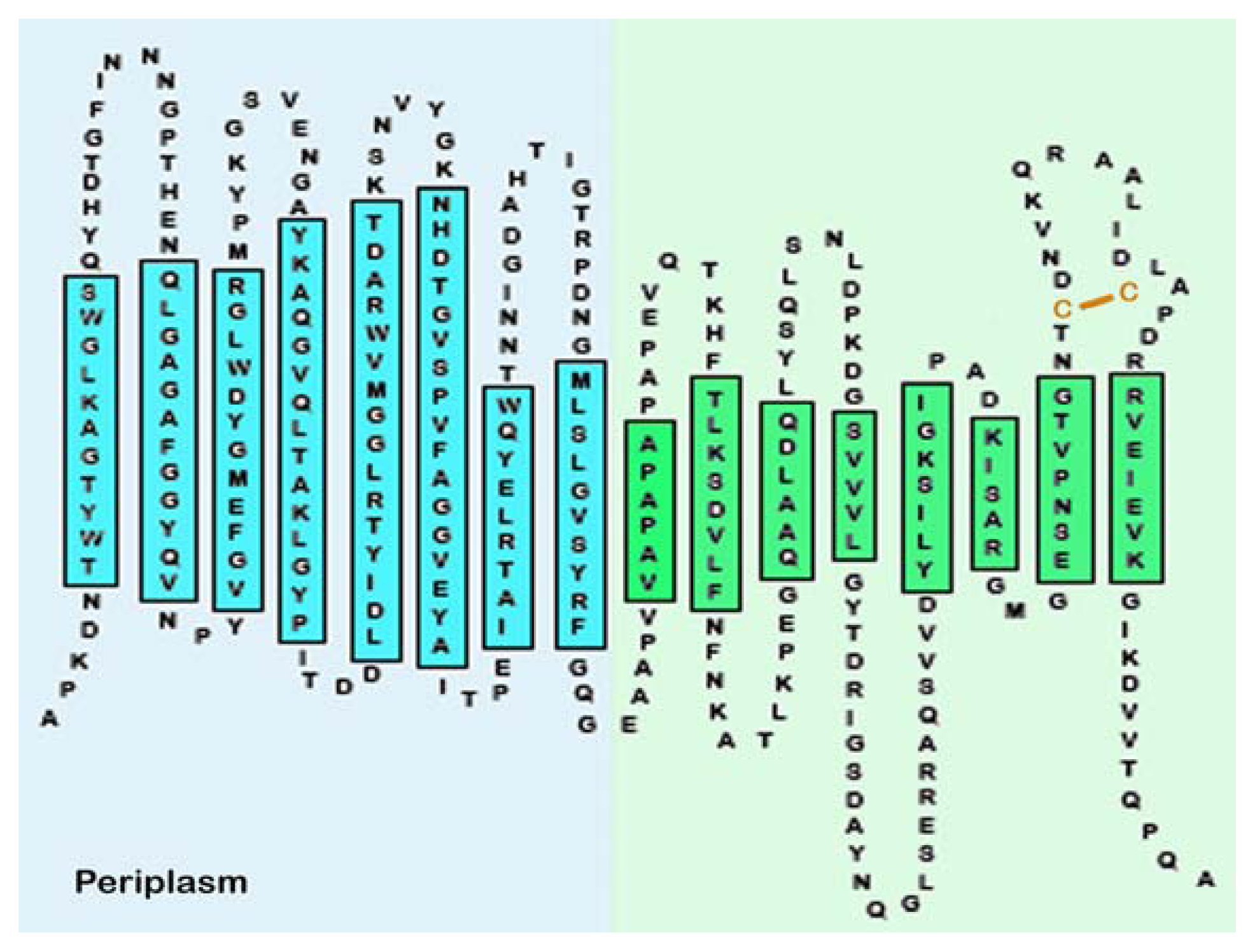

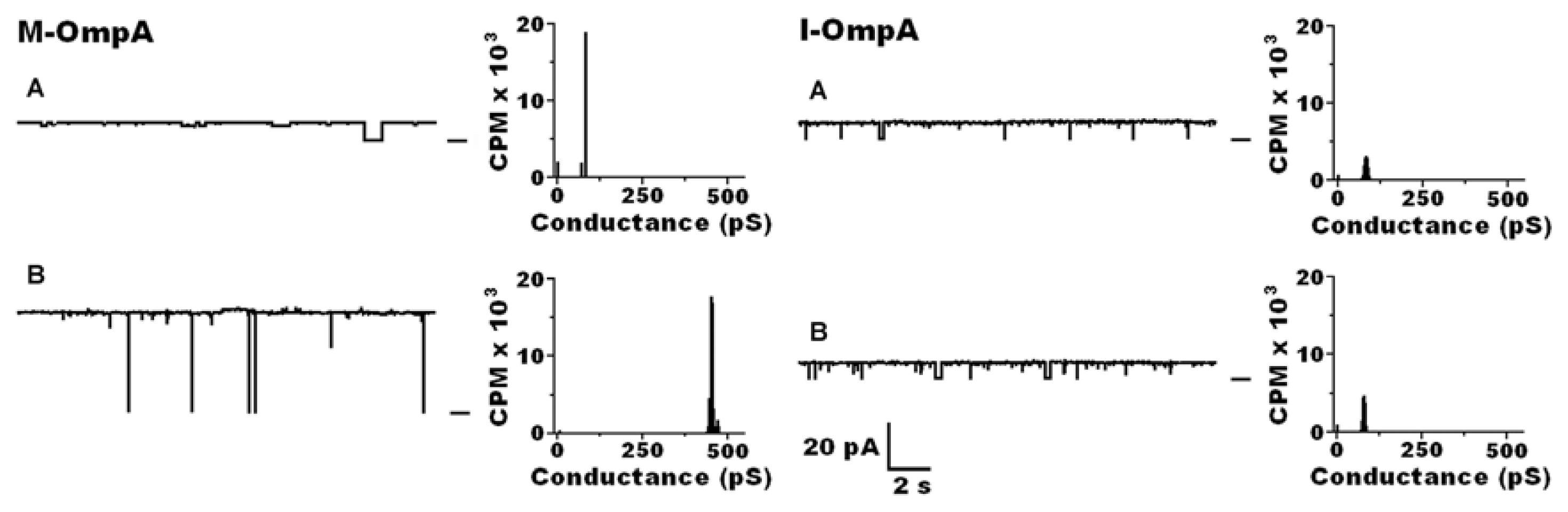
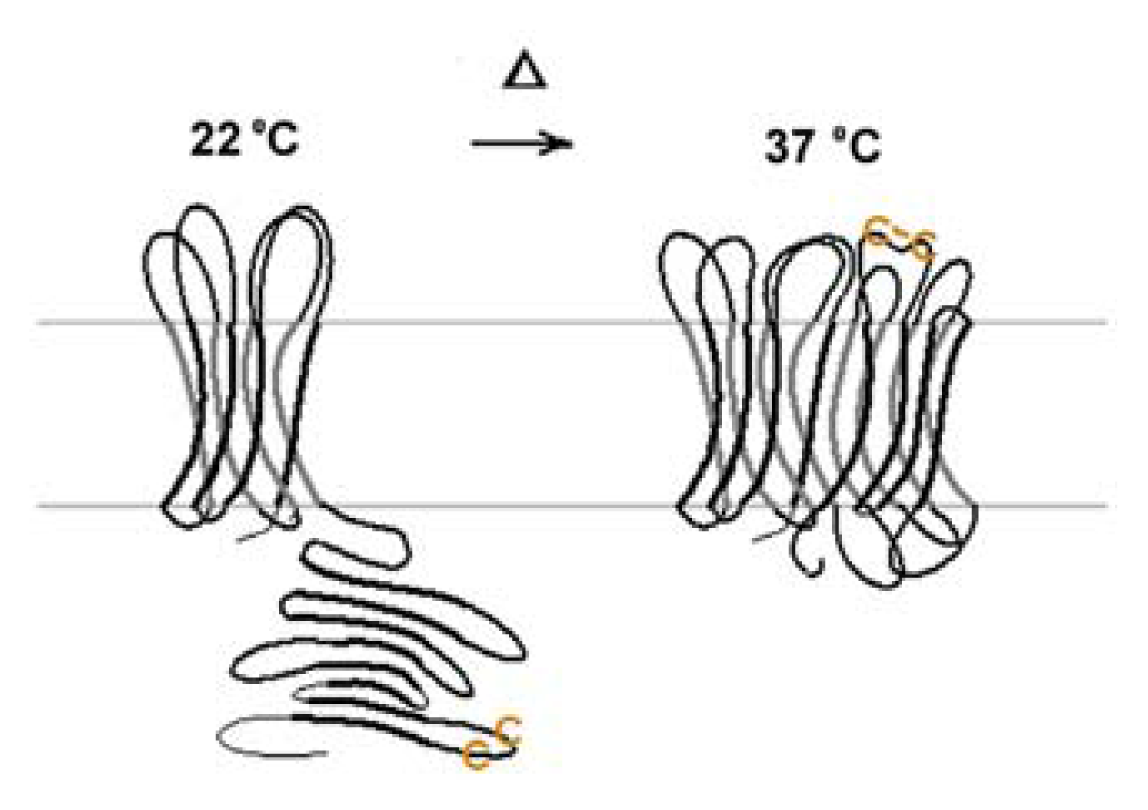
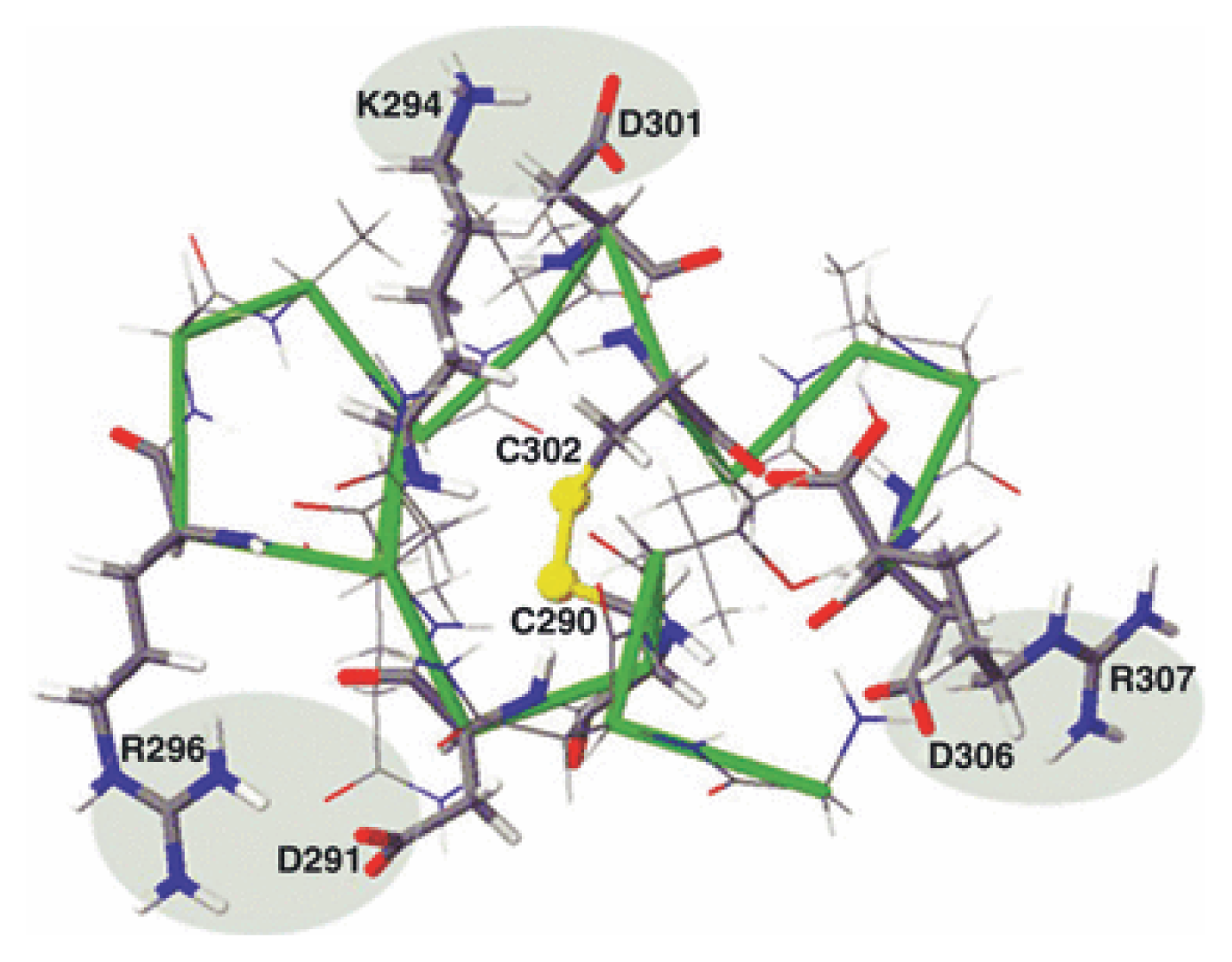
| Protein | MW kDa | Gene | Cellular location |
|---|---|---|---|
| OmpA | 37.2 | ompA | OM |
| OmpF | 39.3 | ompF | OM |
| OmpC | 40.3 | ompC | OM |
| OmpW | 22.9 | yciD | OM |
| Braun’s Lipoprotein | 7.2 | lpp | OM |
| ATP synthase, β subunit | 50.3 | atpD | CM |
| GroEL | 57.1 | mopA | CM |
| EF-Tu | 43.2 | tufA, tufB | CM |
| EF-TS | 30.2 | tsf | Cytoplasm |
| DNAK | 69.0 | dnaK | Cytoplasm |
| L7/L12 | 12.2 | rplL | Cytoplasm |
| S1 | 61.1 | rpsA | Cytoplasm |
| H-NS | 15.4 | hns | Cytoplasm |
| RNA polymerase, α subunit | 150.6 | rpoA | Cytoplasm |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Reusch, R.N. The Role of Short-Chain Conjugated Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate (cPHB) in Protein Folding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10727-10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140610727
Reusch RN. The Role of Short-Chain Conjugated Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate (cPHB) in Protein Folding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(6):10727-10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140610727
Chicago/Turabian StyleReusch, Rosetta N. 2013. "The Role of Short-Chain Conjugated Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate (cPHB) in Protein Folding" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 6: 10727-10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140610727
APA StyleReusch, R. N. (2013). The Role of Short-Chain Conjugated Poly-(R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate (cPHB) in Protein Folding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(6), 10727-10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140610727




