MicroRNA Expression Changes during Interferon-Beta Treatment in the Peripheral Blood of Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study Population
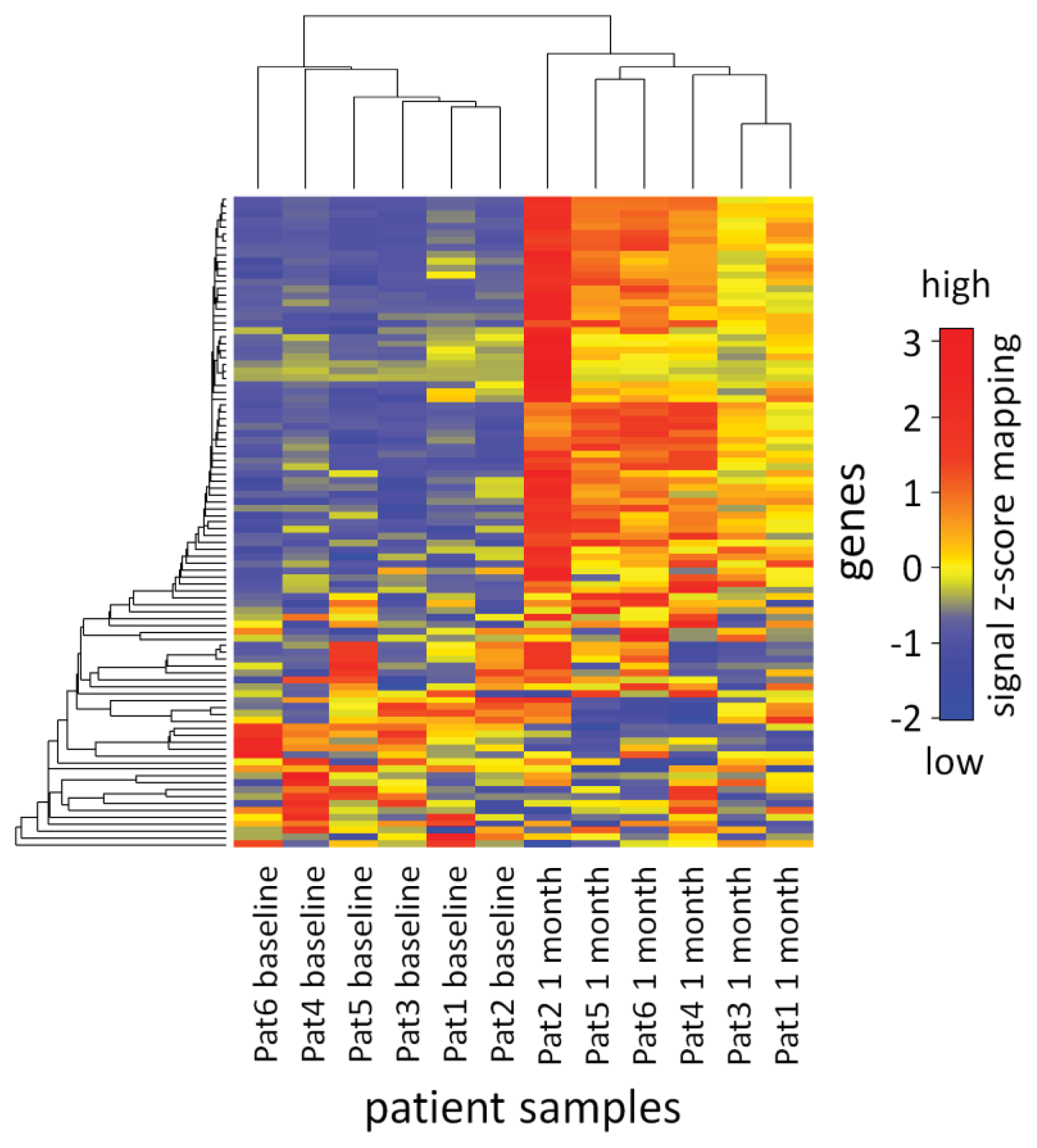
2.2. Parallel Measurement of mRNAs and MicroRNAs in Blood Cells
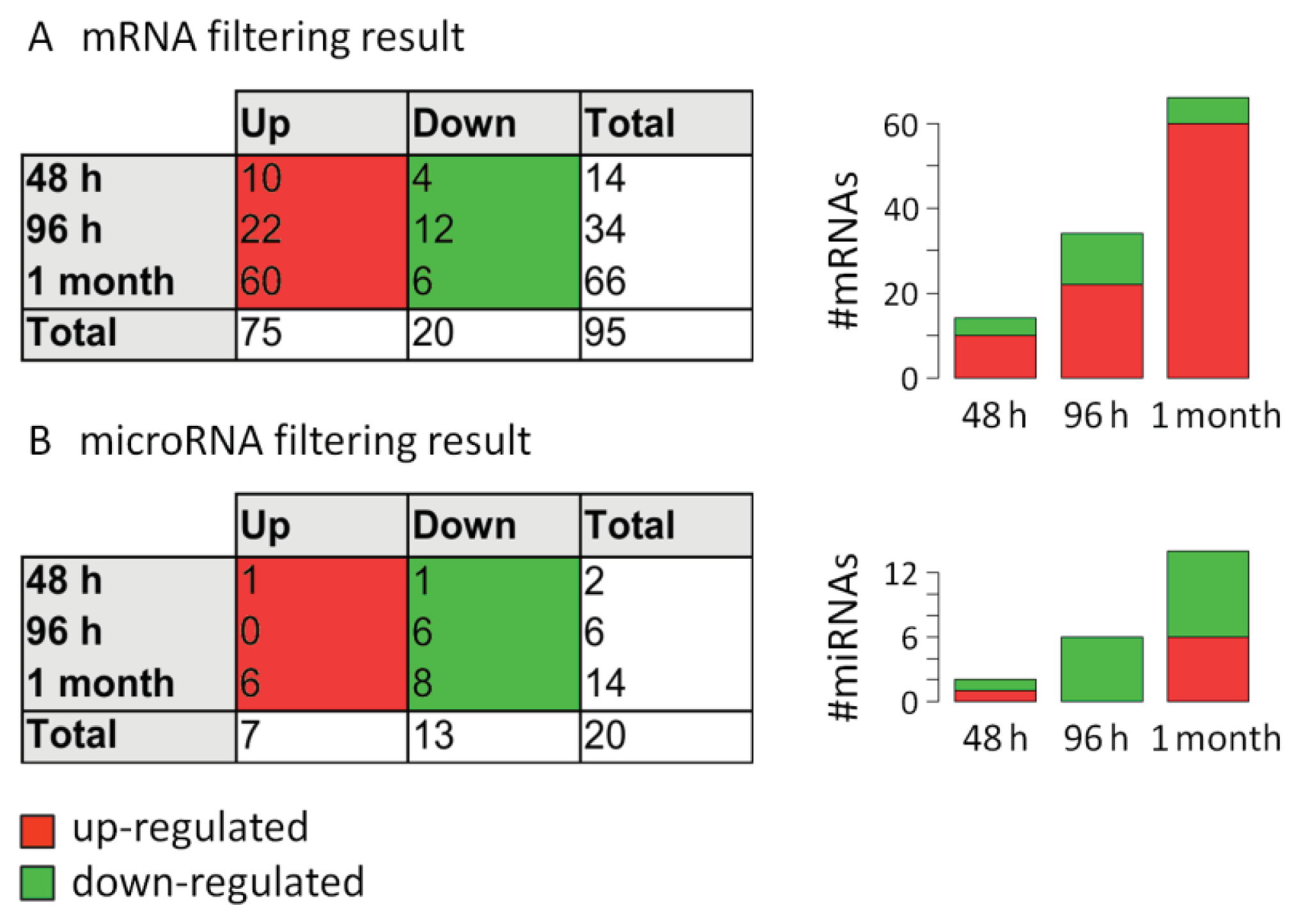
2.3. Analysis of mRNA Expression Dynamics
2.4. Analysis of MicroRNA Expression Dynamics
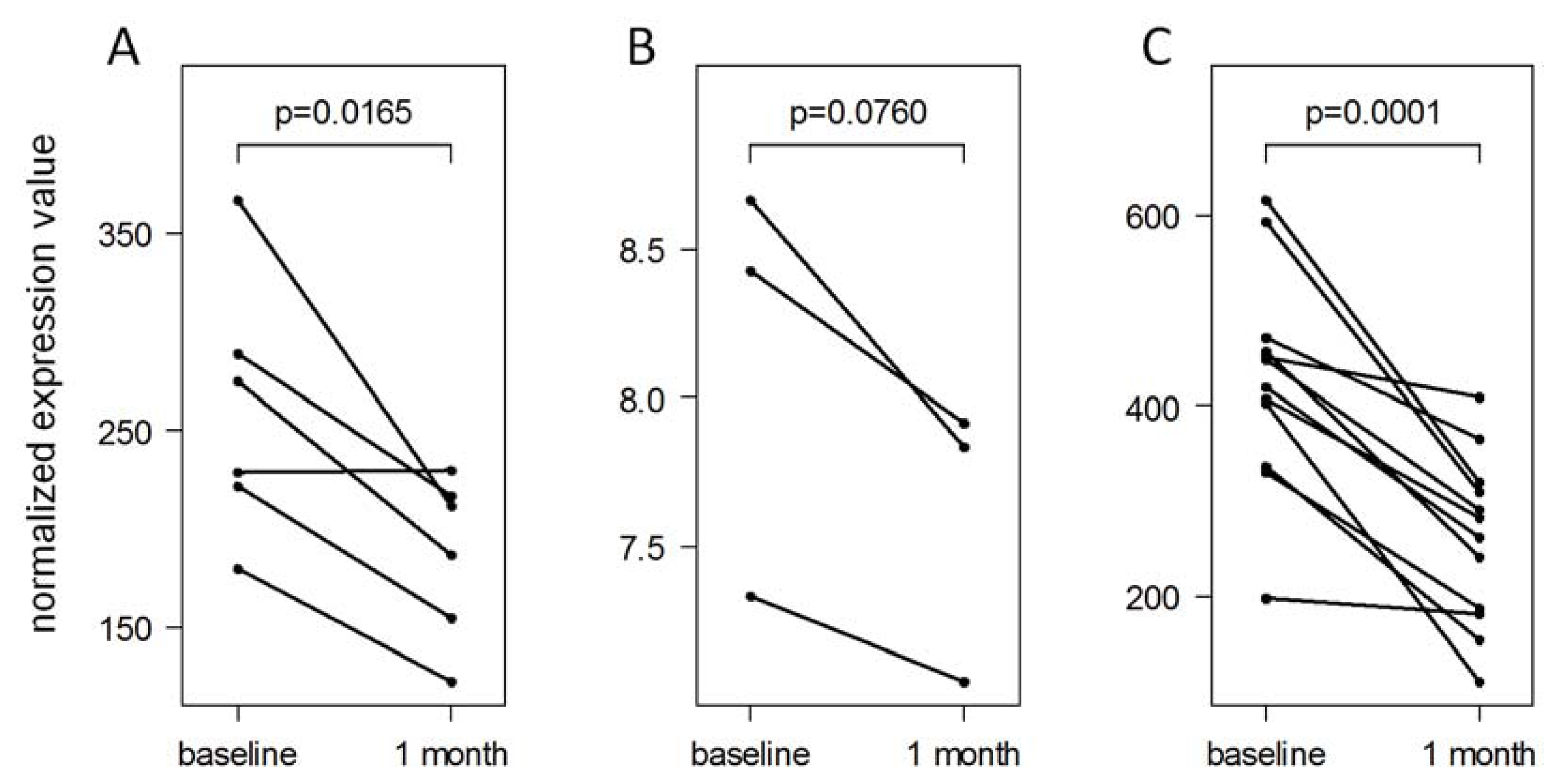
2.5. Validation of IFN-beta-Induced MicroRNA Expression Changes
2.6. Functions of the MicroRNAs in the Context of Multiple Sclerosis
2.7. Interactions between Filtered MicroRNAs and mRNAs
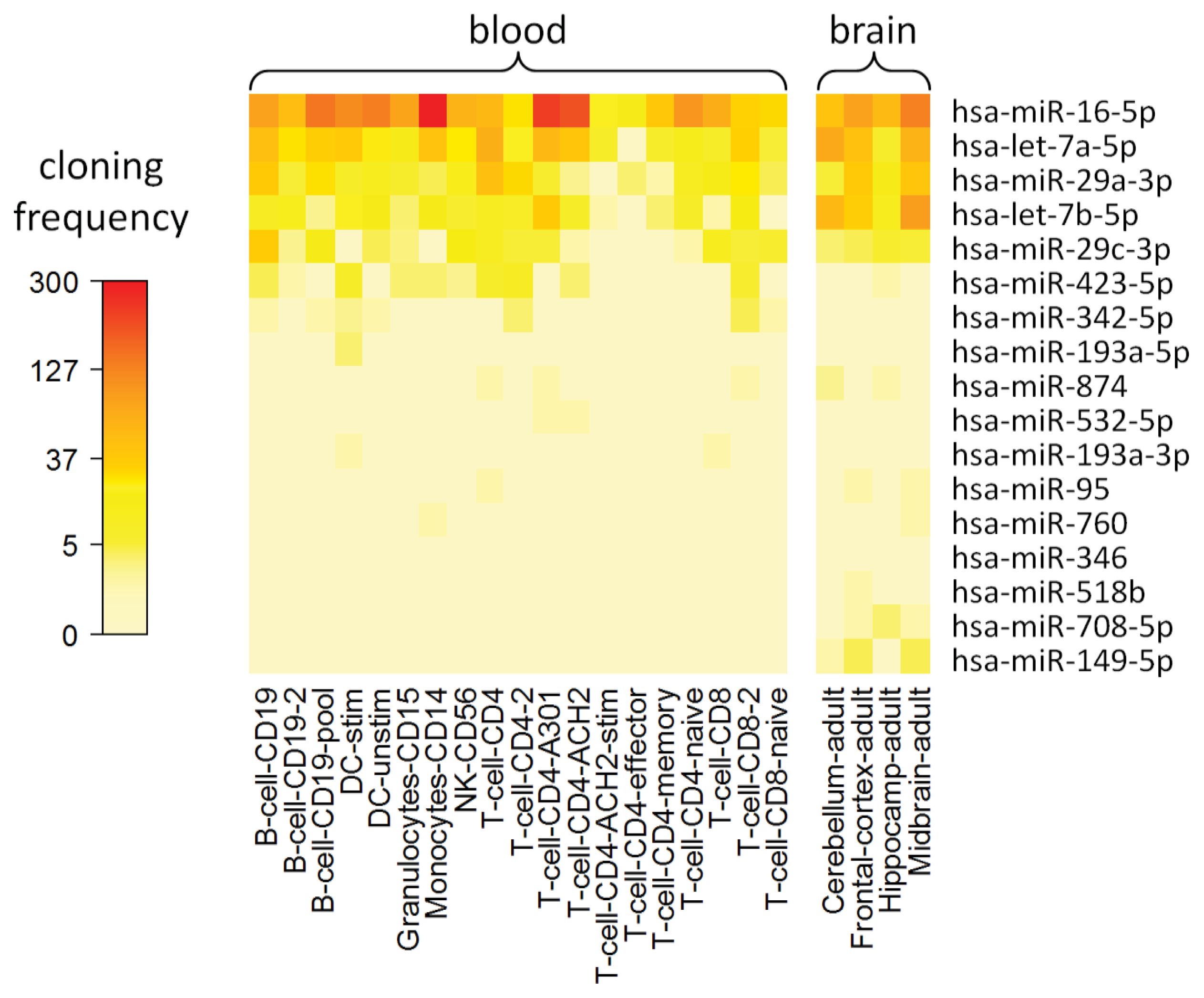
2.8. Cell Type-Specific Expression of IFN-beta-Responsive MicroRNAs
2.9. Final Remarks and Perspectives
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Samples
3.2. Gene Expression Profiling Using Microarrays
3.3. MicroRNA Expression Analysis Using Real-Time PCR
3.4. Validation MicroRNA Analysis Using Microarrays
3.5. Validation MicroRNA Analysis Using Real-Time PCR
3.6. Expression Data Preprocessing
3.7. Filtering of Differentially Expressed mRNAs and MicroRNAs
3.8. Visualization of the mRNA Expression Data
3.9. Evaluation of the MicroRNA Validation Data
3.10. Interaction Network Analysis
3.11. MicroRNA Expression in Different Cell Populations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.H.; Chard, D.T.; Ciccarelli, O. Clinically isolated syndromes. Lancet Neurol 2012, 11, 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar]
- Vosoughi, R.; Freedman, M.S. Therapy of MS. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg 2010, 112, 365–385. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, D.; Hemmer, B. Treatment of multiple sclerosis: Current concepts and future perspectives. J. Neurol 2011, 258, 1747–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Limmroth, V.; Putzki, N.; Kachuck, N.J. The interferon beta therapies for treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: Are they equally efficacious? A comparative review of open-label studies evaluating the efficacy, safety, or dosing of different interferon beta formulations alone or in combination. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord 2011, 4, 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Borden, E.C.; Sen, G.C.; Uze, G.; Silverman, R.H.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Foster, G.R.; Stark, G.R. Interferons at age 50: Past, current and future impact on biomedicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2007, 6, 975–990. [Google Scholar]
- Hecker, M.; Hartmann, C.; Kandulski, O.; Paap, B.K.; Koczan, D.; Thiesen, H.J.; Zettl, U.K. Interferon-beta therapy in multiple sclerosis: The short-term and long-term effects on the patients’ individual gene expression in peripheral blood. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhib-Jalbut, S.; Marks, S. Interferon-beta mechanisms of action in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2010, 74, S17–S24. [Google Scholar]
- Goertsches, R.H.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K. Monitoring of multiple sclerosis immunotherapy: From single candidates to biomarker networks. J. Neurol 2008, 255, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Goertsches, R.H.; Zettl, U.K.; Hecker, M. Sieving treatment biomarkers from blood gene-expression profiles: A pharmacogenomic update on two types of multiple sclerosis therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2011, 12, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Reder, A.T.; Velichko, S.; Yamaguchi, K.D.; Hamamcioglu, K.; Ku, K.; Beekman, J.; Wagner, T.C.; Perez, H.D.; Salamon, H.; Croze, E. IFN-beta1b induces transient and variable gene expression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients independent of neutralizing antibodies or changes in IFN receptor RNA expression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res 2008, 28, 317–331. [Google Scholar]
- Gilli, F.; Marnetto, F.; Caldano, M.; Sala, A.; Malucchi, S.; di Sapio, A.; Capobianco, M.; Bertolotto, A. Biological responsiveness to first injections of interferon-beta in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol 2005, 158, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar]
- Bentwich, I.; Avniel, A.; Karov, Y.; Aharonov, R.; Gilad, S.; Barad, O.; Barzilai, A.; Einat, P.; Einav, U.; Meiri, E.; et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat. Genet 2005, 37, 766–770. [Google Scholar]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, D152–D157. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Rajewsky, K. MicroRNA control in the immune system: Basic principles. Cell 2009, 136, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Im, H.I.; Kenny, P.J. MicroRNAs in neuronal function and dysfunction. Trends Neurosci 2012, 35, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Tufekci, K.U.; Oner, M.G.; Genc, S.; Genc, K. MicroRNAs and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune Dis 2010, 2011, 807426. [Google Scholar]
- Guerau-de-Arellano, M.; Alder, H.; Ozer, H.G.; Lovett-Racke, A.; Racke, M.K. miRNA profiling for biomarker discovery in multiple sclerosis: From microarray to deep sequencing. J. Neuroimmunol 2012, 248, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Angerstein, C.; Hecker, M.; Paap, B.K.; Koczan, D.; Thamilarasan, M.; Thiesen, H.J.; Zettl, U.K. Integration of MicroRNA databases to study microRNAs associated with multiple sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol 2012, 45, 520–535. [Google Scholar]
- Thamilarasan, M.; Koczan, D.; Hecker, M.; Paap, B.; Zettl, U.K. MicroRNAs in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Autoimmun. Rev 2012, 11, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mycko, M.P.; Cichalewska, M.; Machlanska, A.; Cwiklinska, H.; Mariasiewicz, M.; Selmaj, K.W. MicroRNA-301a regulation of a T-helper 17 immune response controls autoimmune demyelination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1248–E1257. [Google Scholar]
- Paap, B.K.; Hecker, M.; Koczan, D.; Zettl, U.K. Molecular biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2013, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waschbisch, A.; Atiya, M.; Linker, R.A.; Potapov, S.; Schwab, S.; Derfuss, T. Glatiramer acetate treatment normalizes deregulated microRNA expression in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 2011, 6, e24604. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Cheng, G.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, I.M.; Cheng, G.; Wieland, S.; Volinia, S.; Croce, C.M.; Chisari, F.V.; David, M. Interferon modulation of cellular microRNAs as an antiviral mechanism. Nature 2007, 449, 919–922. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, U.; Wolkenhauer, O. Web resources for microRNA research. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2013, 774, 225–250. [Google Scholar]
- Dosiou, C.; Lathi, R.B.; Tulac, S.; Huang, S.T.; Giudice, L.C. Interferon-related and other immune genes are downregulated in peripheral blood leukocytes in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 2004, 89, 2501–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Goertsches, R.H.; Hecker, M.; Koczan, D.; Serrano-Fernandez, P.; Moeller, S.; Thiesen, H.J.; Zettl, U.K. Long-term genome-wide blood RNA expression profiles yield novel molecular response candidates for IFN-beta-1b treatment in relapsing remitting MS. Pharmacogenomics 2010, 11, 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hecker, M.; Goertsches, R.H.; Fatum, C.; Koczan, D.; Thiesen, H.J.; Guthke, R.; Zettl, U.K. Network analysis of transcriptional regulation in response to intramuscular interferon-beta-1a multiple sclerosis treatment. Pharmacogenomics J 2012, 12, 134–146. [Google Scholar]
- Peltier, H.J.; Latham, G.J. Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: Identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA 2008, 14, 844–852. [Google Scholar]
- Hecker, M.; Goertsches, R.H.; Engelmann, R.; Thiesen, H.J.; Guthke, R. Integrative modeling of transcriptional regulation in response to antirheumatic therapy. BMC Bioinforma 2009, 10, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Killestein, J.; Polman, C.H. Determinants of interferon beta efficacy in patients with multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2011, 7, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, S.M.; Krüger, C.; Park, B.; Derkow, K.; Rosenberger, K.; Baumgart, J.; Trimbuch, T.; Eom, G.; Hinz, M.; Kaul, D.; et al. An unconventional role for miRNA: Let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci 2012, 15, 827–835. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, S.; Suzuki, K.; Seddiki, N.; Kaplan, W.; Cowley, M.J.; Hood, C.L.; Clancy, J.L.; Murray, D.D.; Méndez, C.; Gelgor, L.; et al. Differential regulation of the Let-7 family of microRNAs in CD4+ T cells alters IL-10 expression. J. Immunol 2012, 188, 6238–6246. [Google Scholar]
- Witwer, K.W.; Sisk, J.M.; Gama, L.; Clements, J.E. MicroRNA regulation of IFN-beta protein expression: Rapid and sensitive modulation of the innate immune response. J. Immunol 2010, 184, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, R.; Healy, B.; Gholipour, T.; Egorova, S.; Musallam, A.; Shuja, M.; Nejad, P.; Patel, B.; Hei, H.; Khoury, S.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for disease staging in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol 2013, 73, 729–740. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzi, J.C.; Brum, D.G.; Zanette, D.L.; de Paula Alves Souza, A.; Barbuzano, F.G.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Barreira, A.A.; da Silva, W.A. miR-15a and 16-1 are downregulated in CD4+ T cells of multiple sclerosis relapsing patients. Int. J. Neurosci 2012, 122, 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, C.; Meira, M.; Hoffmann, F.; Fontoura, P.; Kappos, L.; Lindberg, R.L. Altered microRNA expression in B lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis: Towards a better understanding of treatment effects. Clin. Immunol 2012, 144, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.M.; Guerau-de-Arellano, M.; Costinean, S.; Williams, J.L.; Bottoni, A.; Mavrikis Cox, G.; Satoskar, A.R.; Croce, C.M.; Racke, M.K.; Lovett-Racke, A.E.; et al. miR-29ab1 deficiency identifies a negative feedback loop controlling Th1 bias that is dysregulated in multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol 2012, 189, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Hua, M.; Li, N.; Yao, H.; Cao, X. The microRNA miR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses to intracellular bacterial infection by targeting interferon-gamma. Nat. Immunol 2011, 12, 861–869. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, D.F.; Thomas, M.F.; Hu, J.K.; Yang, Z.; Babiarz, J.E.; Allen, C.D.; Matloubian, M.; Blelloch, R.; Ansel, K.M. MicroRNA-29 regulates T-box transcription factors and interferon-gamma production in helper T cells. Immunity 2011, 35, 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Mott, J.L.; Kurita, S.; Cazanave, S.C.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Transcriptional suppression of mir-29b-1/mir-29a promoter by c-Myc, hedgehog, and NF-kappaB. J. Cell Biochem 2010, 110, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Verrier, J.D.; Lau, P.; Hudson, L.; Murashov, A.K.; Renne, R.; Notterpek, L. Peripheral myelin protein 22 is regulated post-transcriptionally by miRNA-29a. Glia 2009, 57, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli-Boneschi, F.; Fenoglio, C.; Brambilla, P.; Sorosina, M.; Giacalone, G.; Esposito, F.; Serpente, M.; Cantoni, C.; Ridolfi, E.; Rodegher, M.; et al. MicroRNA and mRNA expression profile screening in multiple sclerosis patients to unravel novel pathogenic steps and identify potential biomarkers. Neurosci. Lett 2012, 508, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Junker, A.; Krumbholz, M.; Eisele, S.; Mohan, H.; Augstein, F.; Bittner, R.; Lassmann, H.; Wekerle, H.; Hohlfeld, R.; Meinl, E. MicroRNA profiling of multiple sclerosis lesions identifies modulators of the regulatory protein CD47. Brain 2009, 132, 3342–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Haghikia, A.; Haghikia, A.; Hellwig, K.; Baraniskin, A.; Holzmann, A.; Décard, B.F.; Thum, T.; Gold, R. Regulated microRNAs in the CSF of patients with multiple sclerosis: A case-control study. Neurology 2012, 79, 2166–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, R.L.; Hoffmann, F.; Mehling, M.; Kuhle, J.; Kappos, L. Altered expression of miR-17-5p in CD4+ lymphocytes of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. Eur. J. Immunol 2010, 40, 888–898. [Google Scholar]
- Otaegui, D.; Baranzini, S.E.; Armañanzas, R.; Calvo, B.; Muñoz-Culla, M.; Khankhanian, P.; Inza, I.; Lozano, J.A.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Asensio, A.; et al. Differential micro RNA expression in PBMC from multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6309. [Google Scholar]
- Ovcharenko, D.; Kelnar, K.; Johnson, C.; Leng, N.; Brown, D. Genome-scale microRNA and small interfering RNA screens identify small RNA modulators of TRAIL-induced apoptosis pathway. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 10782–10788. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, A.; Leidinger, P.; Lange, J.; Borries, A.; Schroers, H.; Scheffler, M.; Lenhof, H.P.; Ruprecht, K.; Meese, E. Multiple sclerosis: MicroRNA expression profiles accurately differentiate patients with relapsing-remitting disease from healthy controls. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7440. [Google Scholar]
- Ridolfi, E.; Fenoglio, C.; Cantoni, C.; Calvi, A.; de Riz, M.; Pietroboni, A.; Villa, C.; Serpente, M.; Bonsi, R.; Vercellino, M.; et al. Expression and genetic analysis of microRNAs involved in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2013, 14, 4375–4384. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Morgan, M.J.; Choksi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Liu, Z.G. MicroRNAs modulate the noncanonical transcription factor NF-kappaB pathway by regulating expression of the kinase IKKalpha during macrophage differentiation. Nat. Immunol 2010, 11, 799–805. [Google Scholar]
- Dweep, H.; Sticht, C.; Pandey, P.; Gretz, N. miRWalk—Database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by “walking” the genes of three genomes. J. Biomed. Inform 2011, 44, 839–847. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.D.; Lin, F.M.; Wu, W.Y.; Liang, C.; Huang, W.C.; Chan, W.L.; Tsai, W.T.; Chen, G.Z.; Lee, C.J.; Chiu, C.M.; et al. miRTarBase: A database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, D163–D169. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Pichlmair, A.; Górna, M.W.; Superti-Furga, G.; Nagar, B. Structural basis for viral 5′-PPP-RNA recognition by human IFIT proteins. Nature 2013, 494, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Katibah, G.E.; Lee, H.J.; Huizar, J.P.; Vogan, J.M.; Alber, T.; Collins, K. tRNA binding, structure, and localization of the human interferon-induced protein IFIT5. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Schmitz, U.; Gupta, S.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Kunz, M.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Vera, J. Computational analysis of target hub gene repression regulated by multiple and cooperative miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 8818–8834. [Google Scholar]
- Leaman, D.W.; Chawla-Sarkar, M.; Vyas, K.; Reheman, M.; Tamai, K.; Toji, S.; Borden, E.C. Identification of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor-1 as an interferon-stimulated gene that augments TRAIL Apo2L-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 28504–28511. [Google Scholar]
- Elefant, N.; Berger, A.; Shein, H.; Hofree, M.; Margalit, H.; Altuvia, Y. RepTar: A database of predicted cellular targets of host and viral miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, D188–D194. [Google Scholar]
- Hundeshagen, A.; Hecker, M.; Paap, B.K.; Angerstein, C.; Kandulski, O.; Fatum, C.; Hartmann, C.; Koczan, D.; Thiesen, H.J.; Zettl, U.K. Elevated type I interferon-like activity in a subset of multiple sclerosis patients: Molecular basis and clinical relevance. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Hausser, J.; Berninger, P.; Rodak, C.; Jantscher, Y.; Wirth, S.; Zavolan, M. MirZ: An integrated microRNA expression atlas and target prediction resource. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, W266–W272. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Alexiou, P.; Vergoulis, T.; Gleditzsch, M.; Prekas, G.; Dalamagas, T.; Megraw, M.; Grosse, I.; Sellis, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. miRGen 2.0: A database of microRNA genomic information and regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, D137–D141. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, Z.S.; Pasquinelli, A.E. MicroRNA assassins: Factors that regulate the disappearance of miRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2010, 17, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hentze, M.W.; Preiss, T. Circular RNAs: Splicing’s enigma variations. EMBO J 2013, 32, 923–925. [Google Scholar]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, F.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Coppe, A.; Sirota, A.; Safran, M.; Shmoish, M.; Ferrari, S.; Lancet, D.; Danieli, G.A.; Bicciato, S. Novel definition files for human GeneChips based on GeneAnnot. BMC Bioinf 2007, 8, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, M.; Valdivia, H. Modelling the limit of detection in real-time quantitative PCR. Eur. Food Res. Technol 2008, 226, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar]

| Patient | Type | Age | Disease duration | EDSS (baseline) | EDSS (1 year) | Relapses (1 year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pat1 | CIS | 28 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0 |
| Pat2 | RRMS | 38 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0 |
| Pat3 | RRMS | 22 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0 |
| Pat4 | RRMS | 50 | 12 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Pat5 | CIS | 60 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Pat6 | RRMS | 27 | 2 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2 |
| Patient | Baseline | ~48 h | ~96 h | 1 month |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pat1 | 380 | 374 | 364 | 373 |
| Pat2 | 375 | 407 | 392 | 362 |
| Pat3 | 427 | 400 | 408 | 407 |
| Pat4 | 390 | 387 | 388 | 389 |
| Pat5 | 285 | 258 | 266 | 262 |
| Pat6 | 431 | 451 | 446 | 391 |
| Mature miRNA | Sequence | Expression change | Family | pre-miRNA | pri-miRNA | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7a-5p | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUAGUU | up-regulated | let-7 | MIRLET7A1 | chr9 (q22.32) | |
| MIRLET7A2 | MIR100HG | chr11 (q24.1) | ||||
| MIRLET7A3 | MIRLET7BHG | chr22 (q13.31) | ||||
| hsa-let-7b-5p | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUGUGGUU | up-regulated | let-7 | MIRLET7B | MIRLET7BHG | chr22 (q13.31) |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | UAGCAGCACGUAAAUAUUGGCG | up-regulated | mir-15 | MIR16-1 | DLEU2 | chr13 (q14.2) |
| MIR16-2 | SMC4 | chr3 (q25.33) | ||||
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | AGGGCUUAGCUGCUUGUGAGCA | down-regulated | mir-27 | MIR27A | chr19 (p13.13) | |
| hsa-miR-29a-3p | UAGCACCAUCUGAAAUCGGUUA | down-regulated | mir-29 | MIR29A | chr7 (q32.3) | |
| hsa-miR-29b-1-5p | GCUGGUUUCAUAUGGUGGUUUAGA | down-regulated | mir-29 | MIR29B1 | chr7 (q32.3) | |
| hsa-miR-29c-3p | UAGCACCAUUUGAAAUCGGUUA | down-regulated | mir-29 | MIR29C | chr1 (q32.2) | |
| hsa-miR-95 | UUCAACGGGUAUUUAUUGAGCA | down-regulated | mir-95 | MIR95 | ABLIM2 | chr4 (p16.1) |
| hsa-miR-149-5p | UCUGGCUCCGUGUCUUCACUCCC | down-regulated | mir-149 | MIR149 | GPC1 | chr2 (q37.3) |
| hsa-miR-181c-3p | AACCAUCGACCGUUGAGUGGAC | down-regulated | mir-181 | MIR181C | chr19 (p13.13) | |
| hsa-miR-193a-3p | AACUGGCCUACAAAGUCCCAGU | down-regulated | mir-193 | MIR193A | chr17 (q11.2) | |
| hsa-miR-193a-5p | UGGGUCUUUGCGGGCGAGAUGA | down-regulated | mir-193 | MIR193A | chr17 (q11.2) | |
| hsa-miR-342-5p | AGGGGUGCUAUCUGUGAUUGA | up-regulated | mir-342 | MIR342 | EVL | chr14 (q32.2) |
| hsa-miR-346 | UGUCUGCCCGCAUGCCUGCCUCU | up-regulated | mir-346 | MIR346 | GRID1 | chr10 (q23.2) |
| hsa-miR-423-5p | UGAGGGGCAGAGAGCGAGACUUU | down-regulated | mir-423 | MIR423 | NSRP1 | chr17 (q11.2) |
| hsa-miR-518b | CAAAGCGCUCCCCUUUAGAGGU | up-regulated | mir-515 | MIR518B | chr19 (q13.42) | |
| hsa-miR-532-5p | CAUGCCUUGAGUGUAGGACCGU | down-regulated | mir-188 | MIR532 | CLCN5 | chrX (p11.23) |
| hsa-miR-708-5p | AAGGAGCUUACAAUCUAGCUGGG | down-regulated | mir-708 | MIR708 | TENM4 | chr11 (q14.1) |
| hsa-miR-760 | CGGCUCUGGGUCUGUGGGGA | up-regulated | mir-760 | MIR760 | chr1 (p22.1) | |
| hsa-miR-874 | CUGCCCUGGCCCGAGGGACCGA | down-regulated | mir-874 | MIR874 | KLHL3 | chr5 (q31.2) |
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hecker, M.; Thamilarasan, M.; Koczan, D.; Schröder, I.; Flechtner, K.; Freiesleben, S.; Füllen, G.; Thiesen, H.-J.; Zettl, U.K. MicroRNA Expression Changes during Interferon-Beta Treatment in the Peripheral Blood of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 16087-16110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816087
Hecker M, Thamilarasan M, Koczan D, Schröder I, Flechtner K, Freiesleben S, Füllen G, Thiesen H-J, Zettl UK. MicroRNA Expression Changes during Interferon-Beta Treatment in the Peripheral Blood of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(8):16087-16110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816087
Chicago/Turabian StyleHecker, Michael, Madhan Thamilarasan, Dirk Koczan, Ina Schröder, Kristin Flechtner, Sherry Freiesleben, Georg Füllen, Hans-Jürgen Thiesen, and Uwe Klaus Zettl. 2013. "MicroRNA Expression Changes during Interferon-Beta Treatment in the Peripheral Blood of Multiple Sclerosis Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 8: 16087-16110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816087
APA StyleHecker, M., Thamilarasan, M., Koczan, D., Schröder, I., Flechtner, K., Freiesleben, S., Füllen, G., Thiesen, H.-J., & Zettl, U. K. (2013). MicroRNA Expression Changes during Interferon-Beta Treatment in the Peripheral Blood of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(8), 16087-16110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816087






