Mechanisms of Lin28-Mediated miRNA and mRNA Regulation—A Structural and Functional Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
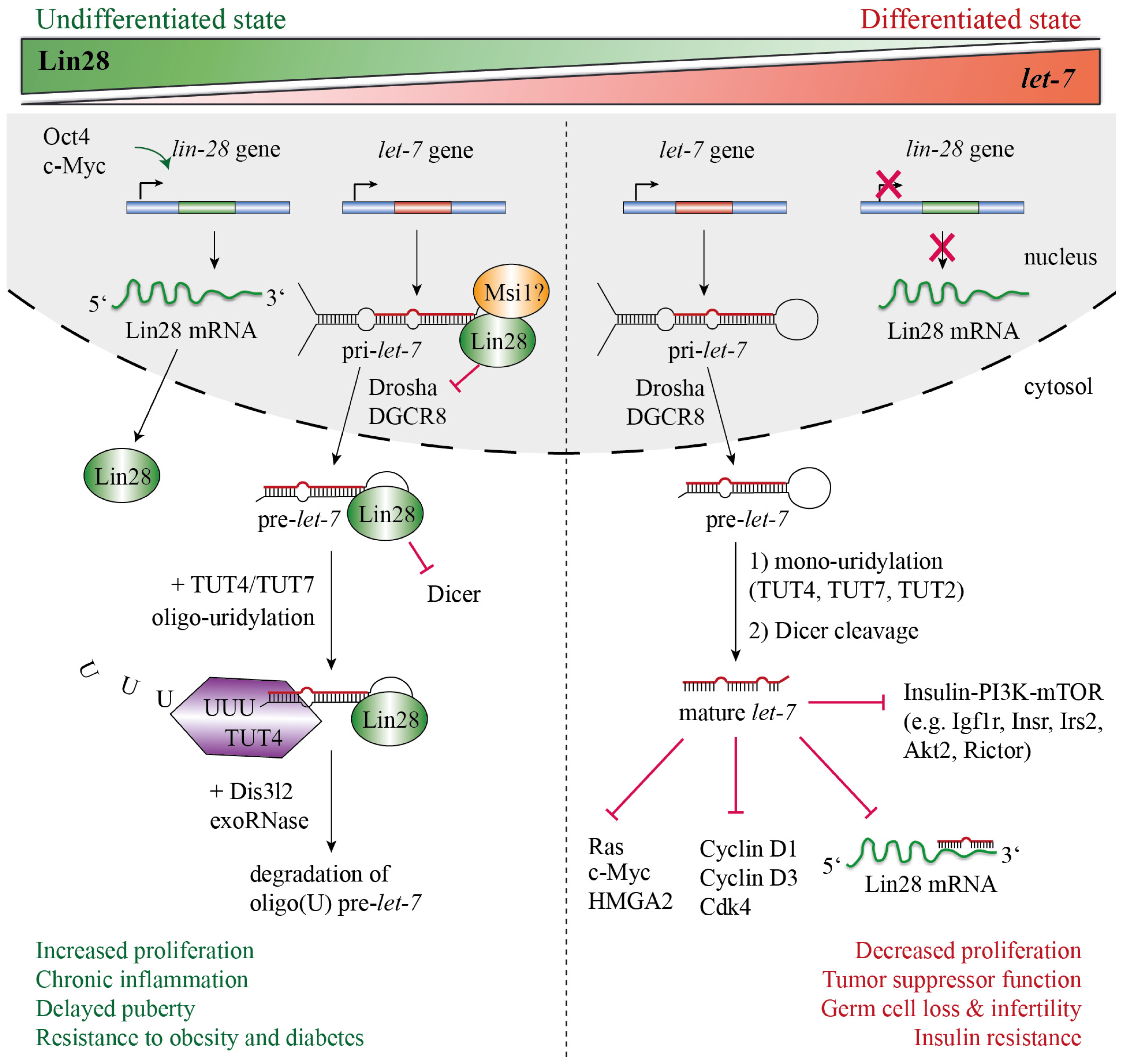
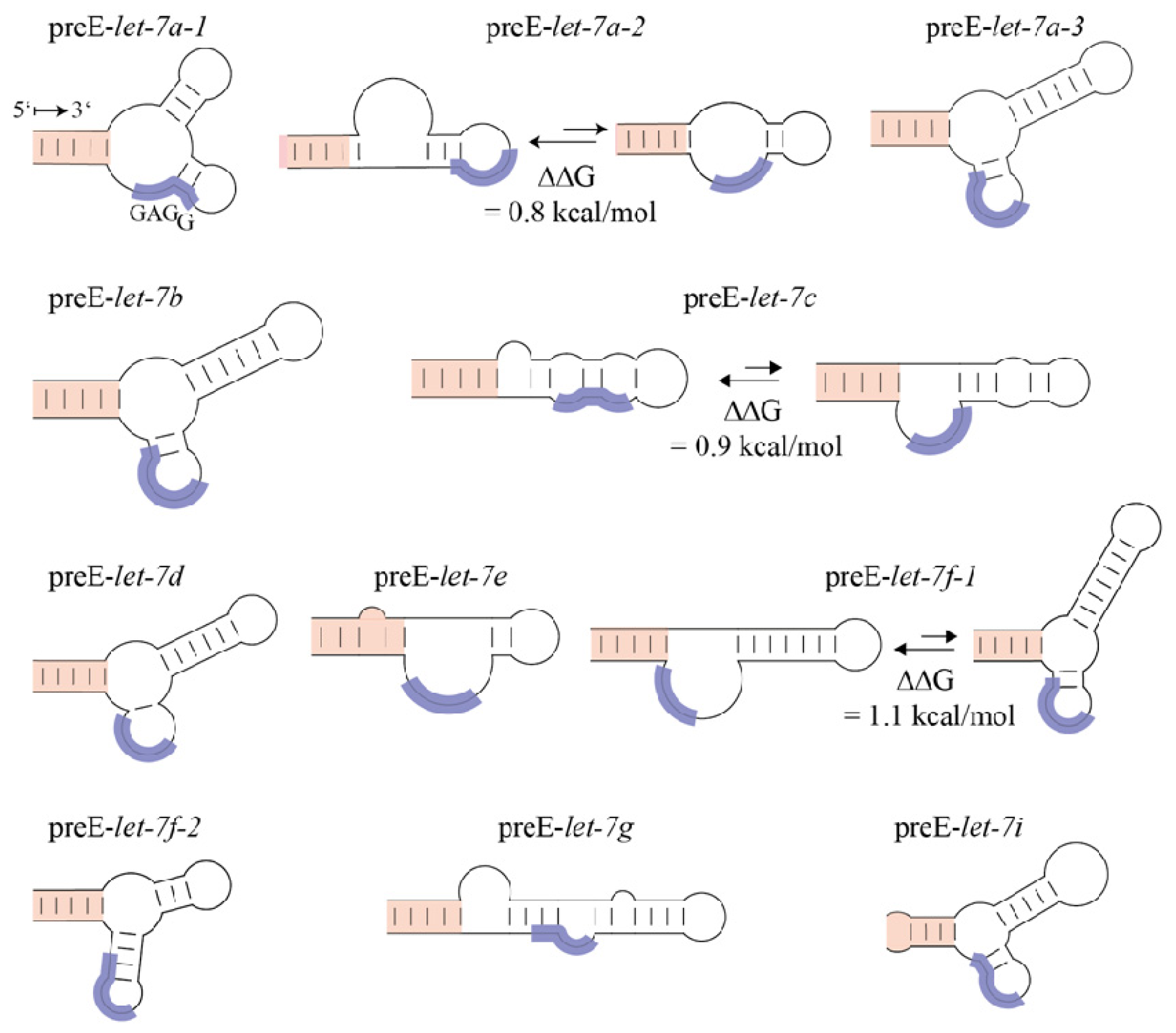
2. Lin28 Blocks let-7 Processing
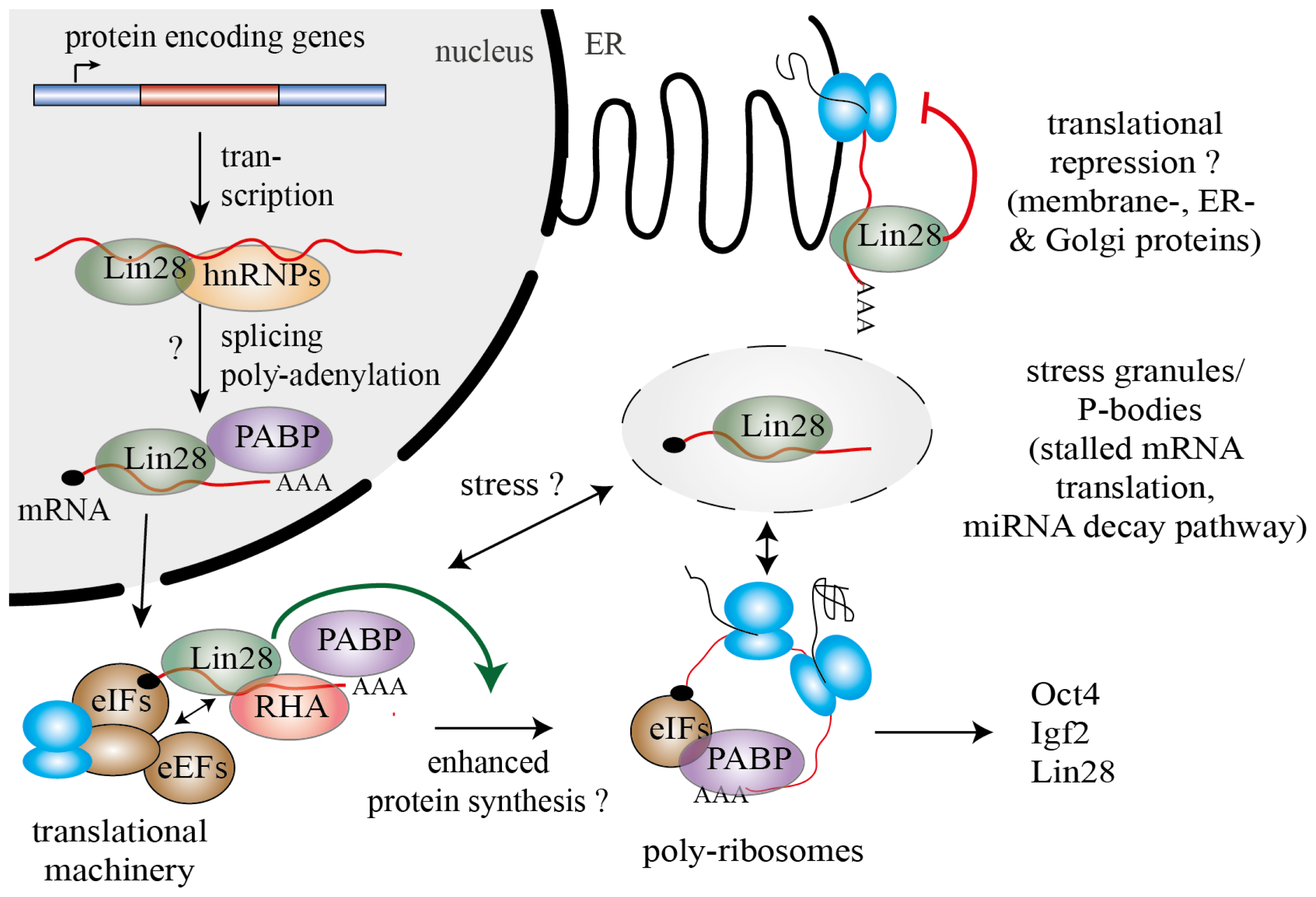
3. Lin28 Influences mRNA Translation
4. Functional Importance of Lin28-Mediated mRNA and miRNA Regulation for Stem Cell Maintenance, Cancer and Development
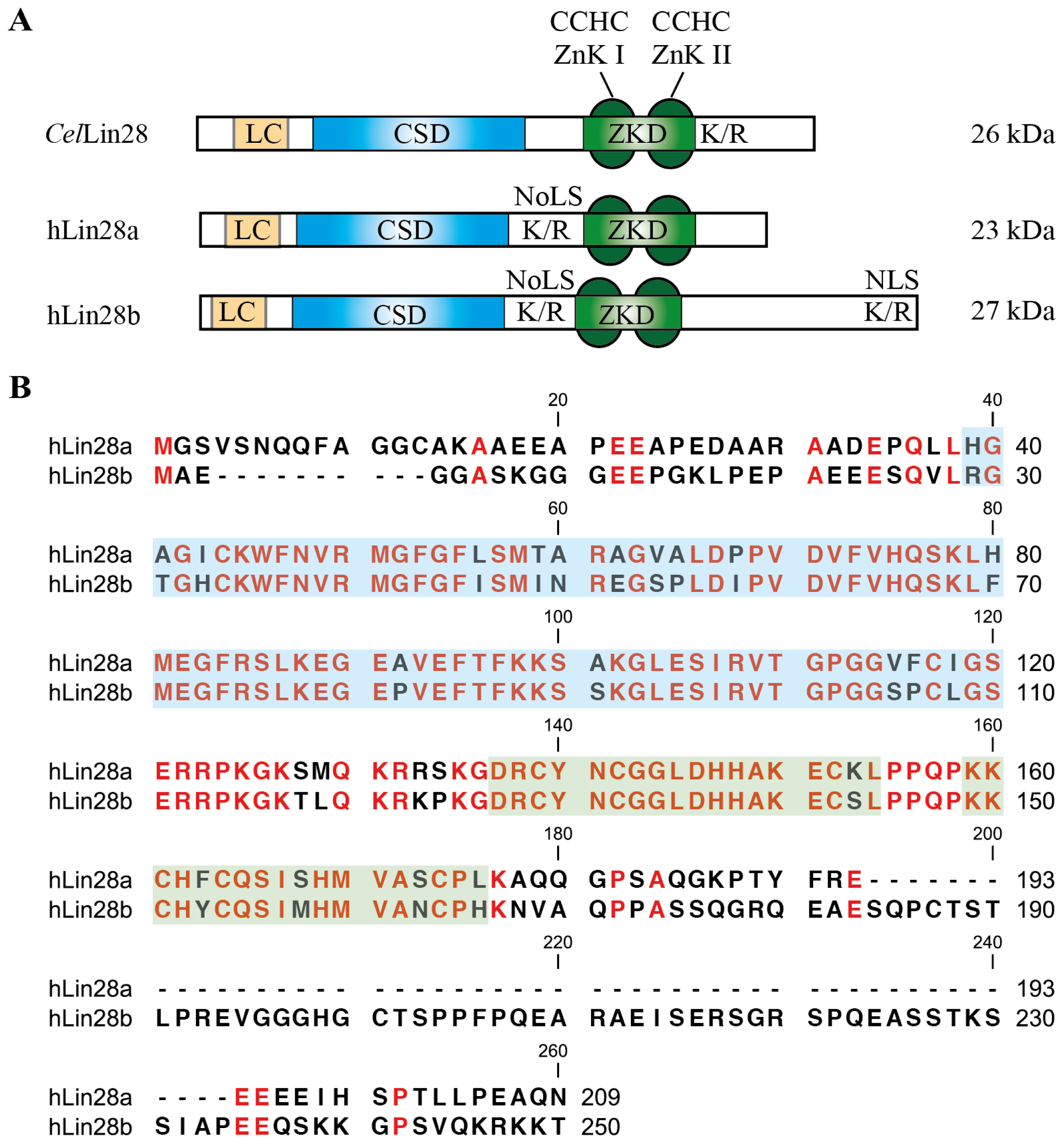
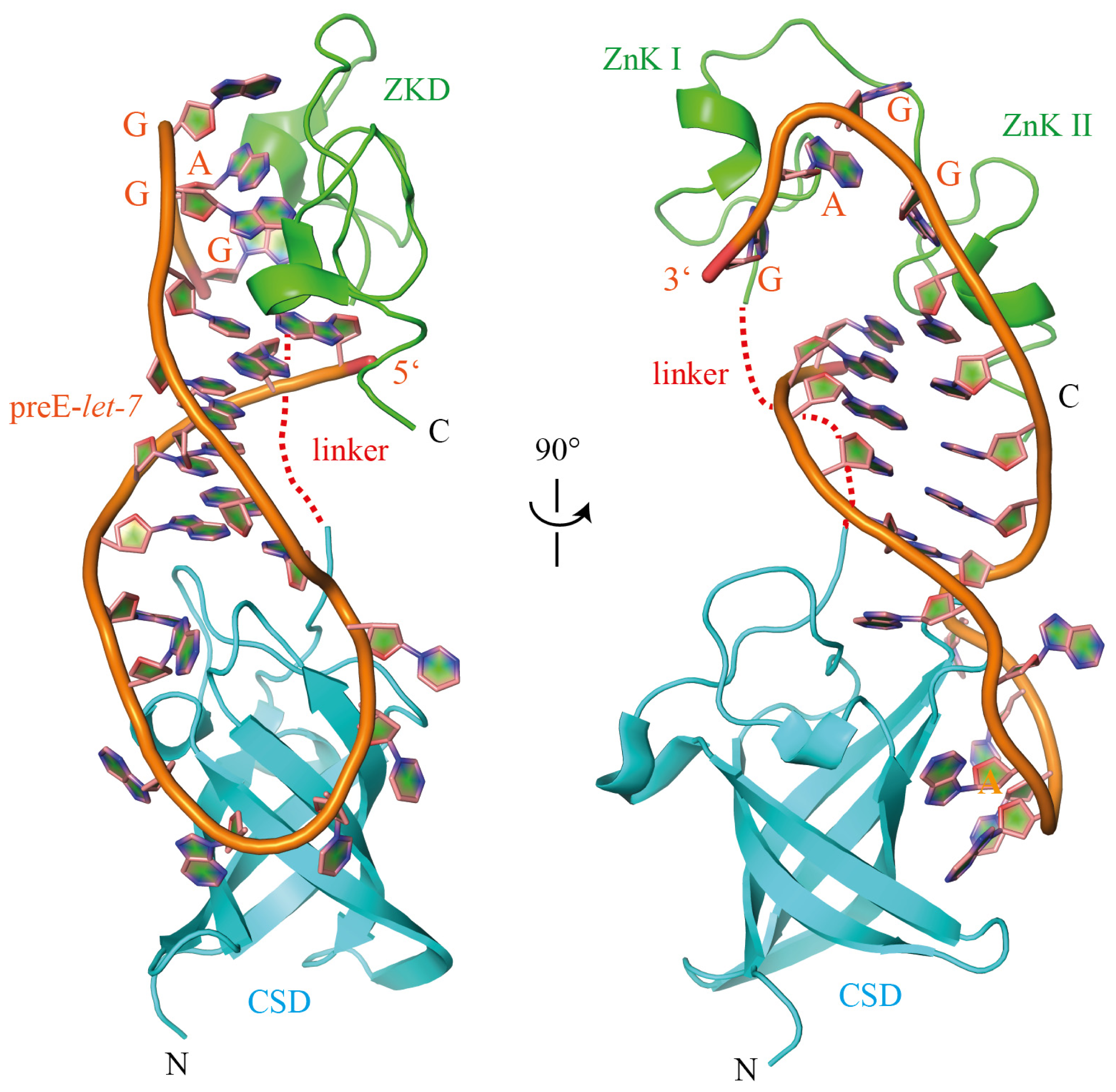
5. Structural Basis for the RNA-Binding Specificity of Lin28
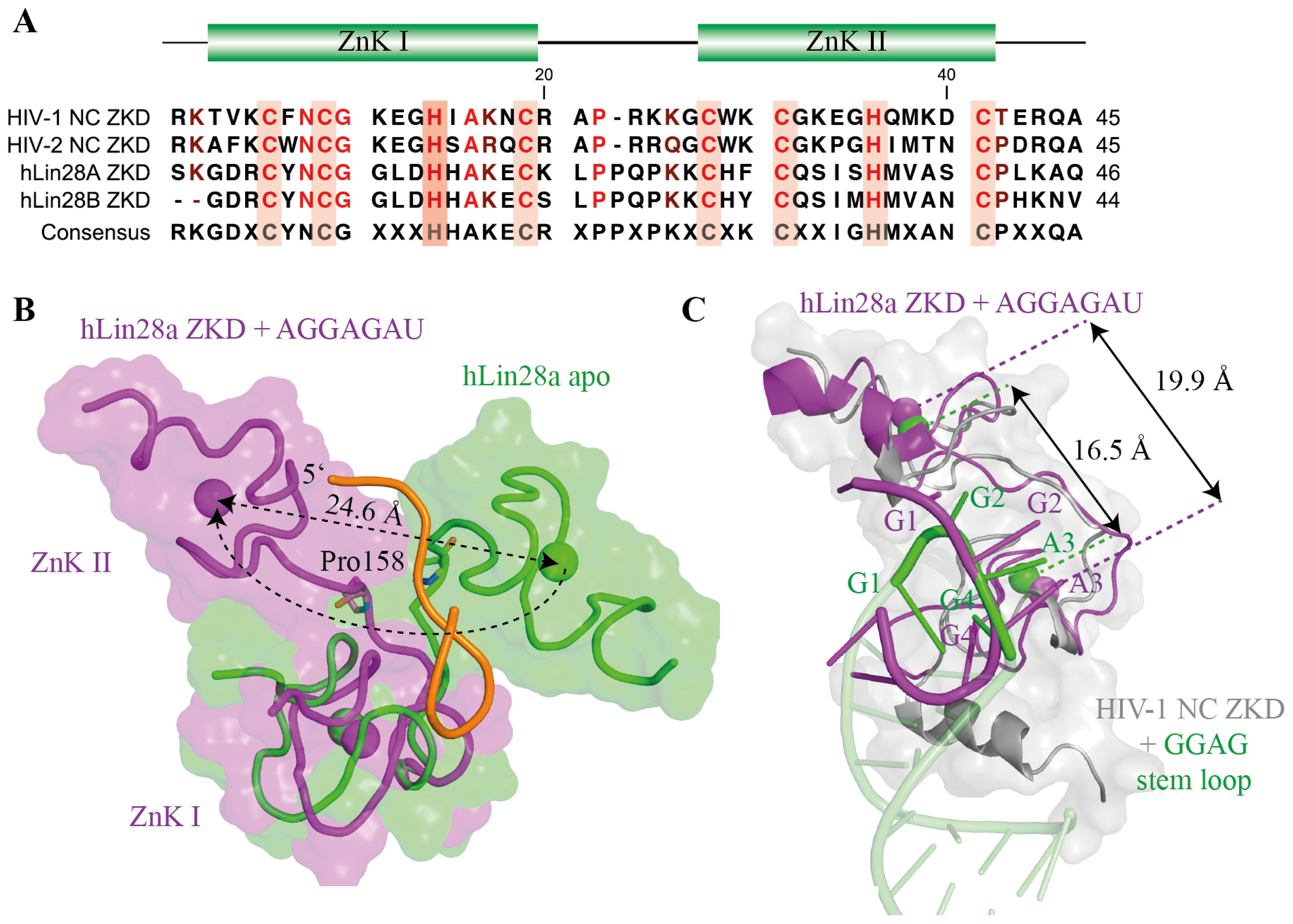
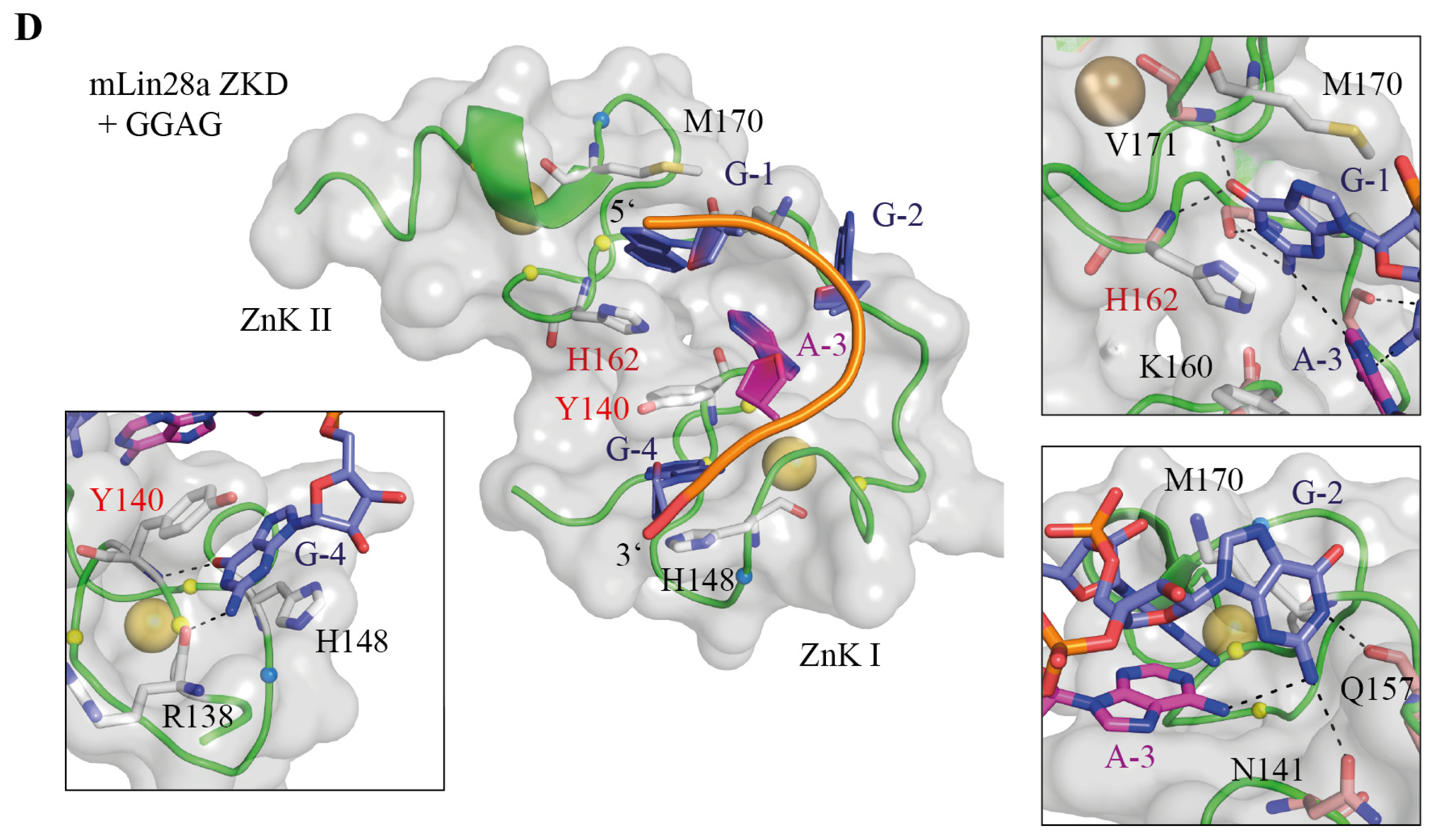
5.1. The Lin28 Zinc-Knuckle Domain Specifically Recognizes GGAG or GGAG-Like Motifs
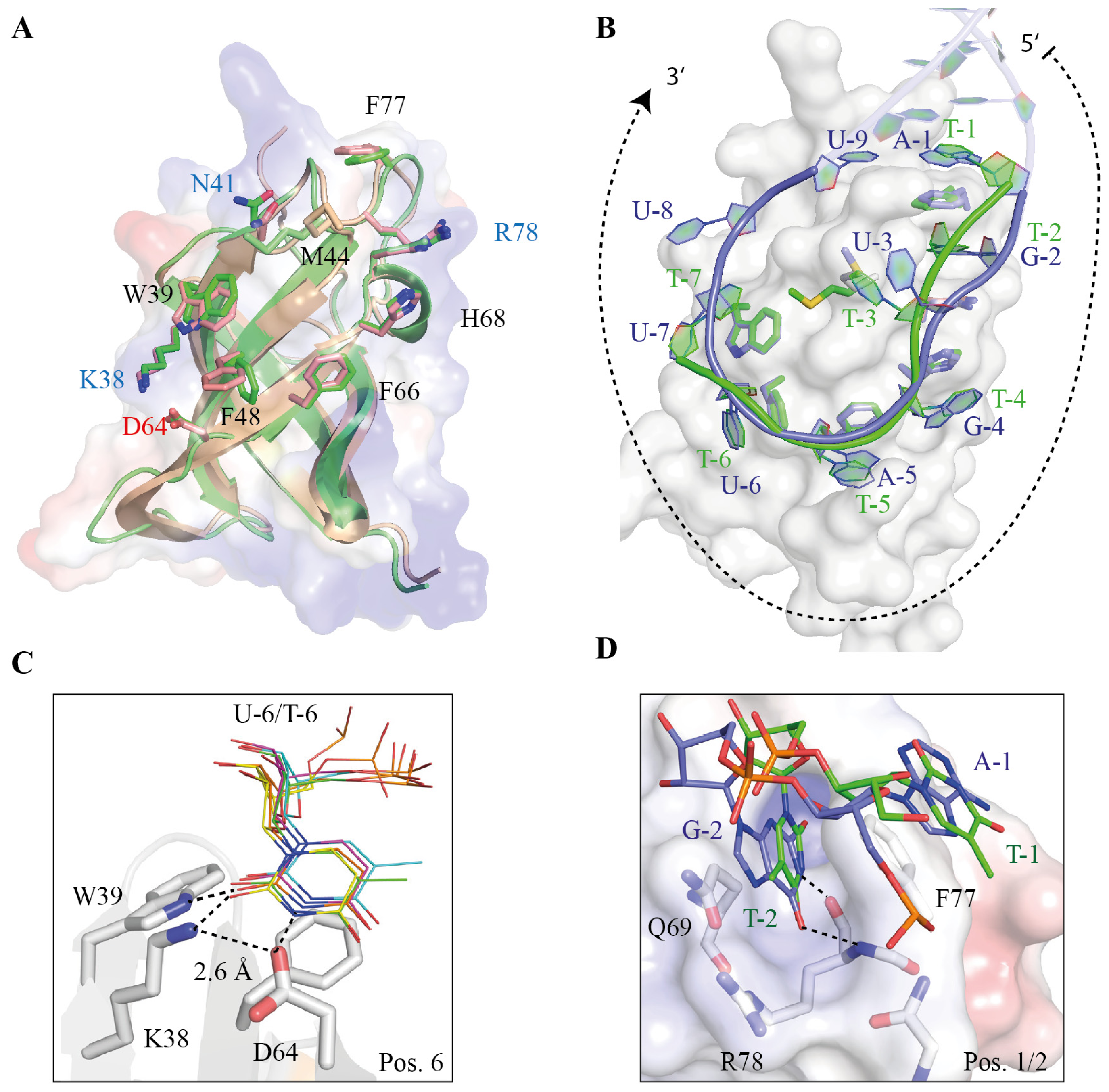
5.2. The Lin28 CSD Has Broad Sequence Specificity and Can Induce Local Structural Changes within RNAs
6. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Ambros, V.; Horvitz, H. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 1984, 226, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, E.G.; Lee, R.C.; Ambros, V. The cold shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C. elegans and is regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell 1997, 88, 637–646. [Google Scholar]
- Seggerson, K.; Tang, L.; Moss, E.G. Two genetic circuits repress the Caenorhabditis elegans heterochronic gene lin-28 after translation initiation. Dev. Biol 2002, 243, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, E.G.; Tang, L. Conservation of the heterochronic regulator Lin-28, its developmental expression and microRNA complementary sites. Dev. Biol 2003, 258, 432–442. [Google Scholar]
- Darr, H.; Benvenisty, N. Genetic analysis of the role of the reprogramming gene LIN-28 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 352–362. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Vodyanik, M.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.; Frane, J.; Tian, S.; Nie, J.; Jonsdottir, G.; Ruotti, V.; Stewart, R.; et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007, 318, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, I.; Joo, C.; Kim, Y.-K.; Ha, M.; Yoon, M.-J.; Cho, J.; Yeom, K.-H.; Han, J.; Kim, V.N. TUT4 in concert with Lin28 suppresses microRNA biogenesis through pre-microRNA uridylation. Cell 2009, 138, 696–708. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ito, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ge, X.; Kodama, T.; Aburatani, H. Identification and characterization of lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene 2006, 384, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- King, C.E.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Castells, A.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Lee, J.-S.; Rustgi, A.K. LIN28B promotes colon cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar]
- King, C.E.; Wang, L.; Winograd, R.; Madison, B.B.; Mongroo, P.S.; Johnstone, C.N.; Rustgi, A.K. LIN28B fosters colon cancer migration, invasion and transformation through let-7-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Maihle, N.J.; Huang, Y. Pluripotency factors Lin28 and Oct4 identify a sub-population of stem cell-like cells in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, S.; Powers, J.; Einhorn, W.; Hoshida, Y.; Ng, T.; Toffanin, S.; O’Sullivan, M.; Lu, J.; Phillips, L.; Lockhart, V.; et al. Lin28 promotes transformation and is associated with advanced human malignancies. Nat. Genet 2009, 41, 843–848. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yuan, R.-H.; Pan, H.-W.; Yang, W.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Jeng, Y.-M. Lin-28B expression promotes transformation and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Shah, S.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Shinoda, G.; Einhorn, W.; Viswanathan, S.; Takeuchi, A.; Grasemann, C.; Rinn, J.; Lopez, M.; et al. Lin28a transgenic mice manifest size and puberty phenotypes identified in human genetic association studies. Nat. Genet 2010, 42, 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Segre, A.V.; Shinoda, G.; Shah, S.P.; Einhorn, W.S.; Takeuchi, A.; Engreitz, J.M.; Hagan, J.P.; Kharas, M.G.; et al. The Lin28/let-7 axis regulates glucose metabolism. Cell 2011, 147, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Jaroszewski, L.; Li, Z.; Cai, X.H.; Weber, C.; Godzik, A. FFAS server: Novel features and applications. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, W38–W44. [Google Scholar]
- Piskounova, E.; Polytarchou, C.; Thornton, J.E.; LaPierre, R.J.; Pothoulakis, C.; Hagan, J.P.; Iliopoulos, D.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28A and Lin28B inhibit let-7 microRNA biogenesis by distinct mechanisms. Cell 2011, 147, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Balzer, E.; Moss, E.G. Localization of the developmental timing regulator Lin28 to mRNP complexes, P-bodies and stress granules. RNA Biol 2007, 4, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, M.; Max, K.E.; Bandaru, P.; Morozov, P.; Gerstberger, S.; Brown, M.; Molina, H.; Tuschl, T. Identification of mRNAs bound and regulated by human LIN28 proteins and molecular requirements for RNA recognition. RNA 2013, 19, 613–626. [Google Scholar]
- Rybak, A.; Fuchs, H.; Smirnova, L.; Brandt, C.; Pohl, E.; Nitsch, R.; Wulczyn, F. A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat. Cell Biol 2008, 10, 987–993. [Google Scholar]
- Gaytan, F.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Manfredi-Lozano, M.; Garcia-Galiano, D.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Romero-Ruiz, A.; Leon, S.; Morales, C.; Cordido, F.; Pinilla, L.; Tena-Sempere, M. Distinct expression patterns predict differential roles of the miRNA-binding proteins, Lin28 and Lin28b, in the mouse testis: Studies during postnatal development and in a model of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.A.; Thomson, J.M.; Hammond, S.M. Lin-28 interaction with the Let-7 precursor loop mediates regulated microRNA processing. RNA 2008, 14, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, S.R.; Daley, G.Q.; Gregory, R.I. Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science 2008, 320, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Jing, W.; Lei, X.-X.; Feng, C.; Peng, S.; Boris-Lawrie, K.; Huang, Y. Evidence that Lin28 stimulates translation by recruiting RNA helicase A to polysomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, 3724–3734. [Google Scholar]
- Polesskaya, A.; Cuvellier, S.; Naguibneva, I.; Duquet, A.; Moss, E.; Harel-Bellan, A. Lin-28 binds IGF-2 mRNA and participates in skeletal myogenesis by increasing translation efficiency. Genes Dev 2007, 21, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.; Martindale, M.Q.; Kuroda, M.I.; Maller, B.; Hayward, D.C.; Ball, E.E.; Degnan, B.; Müller, P.; et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000, 408, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart, B.; Slack, F.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.; Bettinger, J.; Rougvie, A.; Horvitz, H.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wynsberghe, P.; Kai, Z.; Massirer, K.; Burton, V.; Yeo, G.; Pasquinelli, A. LIN-28 co-transcriptionally binds primary let-7 to regulate miRNA maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2011, 18, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mondol, V.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Let’s make it happen: The role of let-7 microRNA in development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol 2012, 99, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.M.; Newman, M.; Parker, J.S.; Morin-Kensicki, E.M.; Wright, T.; Hammond, S.M. Extensive post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications for cancer. Genes Dev 2006, 20, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Wulczyn, F.; Smirnova, L.; Rybak, A.; Brandt, C.; Kwidzinski, E.; Ninnemann, O.; Strehle, M.; Seiler, A.; Schumacher, S.; Nitsch, R. Post-transcriptional regulation of the let-7 microRNA during neural cell specification. FASEB J 2007, 21, 415–426. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.H.; Moss, E.G. Temporally regulated expression of Lin-28 in diverse tissues of the developing mouse. Gene Expr. Patterns 2003, 3, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Piskounova, E.; Viswanathan, S.R.; Janas, M.; LaPierre, R.J.; Daley, G.Q.; Sliz, P.; Gregory, R.I. Determinants of microRNA processing inhibition by the developmentally regulated RNA-binding protein Lin28. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 21310–21314. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, F.; Schutz, A.; Doge, N.; Heinemann, U. The Lin28 cold-shock domain remodels pre-let-7 microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 7492–7506. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, Y.; Chen, C.; Gregory, R.I.; Chou, J.J.; Sliz, P. Molecular basis for interaction of let-7 microRNAs with Lin28. Cell 2011, 147, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, H.L.; Bugaut, A.; Armisen, J.; Lehrbach, N.J.; Miska, E.A.; Balasubramanian, S. A LIN28-dependent structural change in pre-let-7g directly inhibits dicer processing. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 7514–7521. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, I.; Joo, C.; Cho, J.; Ha, M.; Han, J.; Kim, V.N. Lin28 mediates the terminal uridylation of let-7 precursor MicroRNA. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- Mullen, T.E.; Marzluff, W.F. Degradation of histone mRNA requires oligouridylation followed by decapping and simultaneous degradation of the mRNA both 5′ to 3′ and 3′ to 5′. Genes Dev 2008, 22, 50–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Goodman, H.M. Uridine addition after microRNA-directed cleavage. Science 2004, 306, 997. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.M.; Triboulet, R.; Thornton, J.E.; Gregory, R.I. A role for the Perlman syndrome exonuclease Dis3l2 in the Lin28-let-7 pathway. Nature 2013, 497, 244–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hagan, J.P.; Piskounova, E.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28 recruits the TUTase Zcchc11 to inhibit let-7 maturation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2009, 16, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, J.E.; Chang, H.M.; Piskounova, E.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28-mediated control of let-7 microRNA expression by alternative TUTases Zcchc11 (TUT4) and Zcchc6 (TUT7). RNA 2012, 18, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, I.; Ha, M.; Lim, J.; Yoon, M.J.; Park, J.E.; Kwon, S.C.; Chang, H.; Kim, V.N. Mono-uridylation of pre-microRNA as a key step in the biogenesis of group II let-7 microRNAs. Cell 2012, 151, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Lehrbach, N.J.; Armisen, J.; Lightfoot, H.L.; Murfitt, K.J.; Bugaut, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Miska, E.A. LIN-28 and the poly(U) polymerase PUP-2 regulate let-7 microRNA processing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2009, 16, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, H.; Okada, Y.; Imai, T.; Iwanami, A.; Mischel, P.S.; Okano, H. Musashi1 cooperates in abnormal cell lineage protein 28 (Lin28)-mediated let-7 family microRNA biogenesis in early neural differentiation. J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 16121–16130. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.X.; Xu, J.; Ma, W.; Qiao, C.; Newman, M.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Huang, Y. Determinants of mRNA recognition and translation regulation by Lin28. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 3574–3584. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Huang, Y. Histone H2a mRNA interacts with Lin28 and contains a Lin28-dependent posttranscriptional regulatory element. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 4256–4263. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, K.; Huang, Y. Lin28 modulates cell growth and associates with a subset of cell cycle regulator mRNAs in mouse embryonic stem cells. RNA 2009, 15, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Chang, H.; Kwon, S.C.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.; Choe, J.; Ha, M.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, V.N. LIN28A is a suppressor of ER-associated translation in embryonic stem cells. Cell 2012, 151, 765–777. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Huang, Y. Lin28-mediated post-transcriptional regulation of Oct4 expression in human embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Chen, L.-L.; Lei, X.-X.; Yang, L.; Lin, H.; Carmichael, G.G.; Huang, Y. Genome-wide studies reveal that Lin28 enhances the translation of genes important for growth and survival of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 496–504. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, R.; Munschauer, M.; Mastrobuoni, G.; Mayr, F.; Heinemann, U.; Kempa, F.; Rajewski, N.; Landthaler, M. Identification of LIN28-bound mRNAs reveals features of target recognition and regulation. RNA Biol 2013, 10, 1146–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbert, M.L.; Huelga, S.C.; Kapeli, K.; Stark, T.J.; Liang, T.Y.; Chen, S.X.; Yan, B.Y.; Nathanson, J.L.; Hutt, K.R.; Lovci, M.T.; et al. LIN28 binds messenger RNAs at GGAGA motifs and regulates splicing factor abundance. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, J.; Mallanna, S.; Luo, X.; Rizzino, A. Sox2 uses multiple domains to associate with proteins present in Sox2-protein complexes. PLoS One 2010, 5, e15486. [Google Scholar]
- Marson, A.; Levine, S.S.; Cole, M.F.; Frampton, G.M.; Brambrink, T.; Johnstone, S.; Guenther, M.G.; Johnston, W.K.; Wernig, M.; Newman, J.; et al. Connecting microRNA genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Cell 2008, 134, 521–533. [Google Scholar]
- Melton, C.; Judson, R.L.; Blelloch, R. Opposing microRNA families regulate self-renewal in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature 2010, 463, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, J.; Saha, K.; Pando, B.; van Zon, J.; Lengner, C.J.; Creyghton, M.P.; van Oudenaarden, A.; Jaenisch, R. Direct cell reprogramming is a stochastic process amenable to acceleration. Nature 2009, 462, 595–601. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhong, X.; Lin, X.; Guo, J.; Zou, L.; Tanyi, J.L.; Shao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, L.P.; Hwang, W.T.; et al. Lin-28 homologue A (LIN28A) promotes cell cycle progression via regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), cyclin D1 (CCND1), and cell division cycle 25 homolog A (CDC25A) expression in cancer. J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 17386–17397. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.C.; Zeitels, L.R.; Hwang, H.W.; Chivukula, R.R.; Wentzel, E.A.; Dews, M.; Jung, J.; Gao, P.; Dang, C.V.; Beer, M.A.; et al. Lin-28B transactivation is necessary for Myc-mediated let-7 repression and proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3384–3389. [Google Scholar]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Struhl, K. An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 2009, 139, 693–706. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lin, X.; Zhong, X.; Kaur, S.; Li, N.; Liang, S.; Lassus, H.; Wang, L.; Katsaros, D.; Montone, K.; et al. Double-negative feedback loop between reprogramming factor LIN28 and microRNA let-7 regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 9463–9472. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhanovsky, V.; Lowe, S.W. Stem cells: The promises and perils of p53. Nature 2009, 460, 1085–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Lettre, G.; Jackson, A.U.; Gieger, C.; Schumacher, F.R.; Berndt, S.I.; Sanna, S.; Eyheramendy, S.; Voight, B.F.; Butler, J.L.; et al. Identification of ten loci associated with height highlights new biological pathways in human growth. Nat. Genet 2008, 40, 584–591. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, K.K.; Elks, C.E.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.H.; Luan, J.; Andersen, L.B.; Bingham, S.A.; Brage, S.; Smith, G.D.; Ekelund, U.; et al. Genetic variation in LIN28B is associated with the timing of puberty. Nat. Genet 2009, 41, 729–733. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, J.R.; Stolk, L.; Franceschini, N.; Lunetta, K.L.; Zhai, G.; McArdle, P.F.; Smith, A.V.; Aspelund, T.; Bandinelli, S.; Boerwinkle, E.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies two loci influencing age at menarche. Nat. Genet 2009, 41, 648–650. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.J.; Olson, E.N. Control of glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by the Let-7 family of microRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21075–21080. [Google Scholar]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; de Guzman, R.N.; Turner, R.B.; Chancellor, K.J.; Wu, Z.R.; Summers, M.F. NMR structure of the HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein bound to stem-loop SL2 of the psi-RNA packaging signal. Implications for genome recognition. J. Mol. Biol 2000, 301, 491–511. [Google Scholar]
- De Guzman, R.N.; Wu, Z.R.; Stalling, C.C.; Pappalardo, L.; Borer, P.N.; Summers, M.F. Structure of the HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein bound to the SL3 psi-RNA recognition element. Science 1998, 279, 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Pappalardo, L.; Kerwood, D.J.; Pelczer, I.; Borer, P.N. Three-dimensional folding of an RNA hairpin required for packaging HIV-1. J. Mol. Biol 1998, 282, 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins, A.; Yang, A.; Bouvette, J.; Omichinski, J.G.; Legault, P. Importance of the NCp7-like domain in the recognition of pre-let-7g by the pluripotency factor Lin28. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Loughlin, F.E.; Gebert, L.F.; Towbin, H.; Brunschweiger, A.; Hall, J.; Allain, F.H. Structural basis of pre-let-7 miRNA recognition by the zinc knuckles of pluripotency factor Lin28. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2012, 19, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrerio, A.L.; Berg, J.M. Design of single-stranded nucleic acid binding peptides based on nucleocapsid CCHC-box zinc-binding domains. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 9638–9643. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, F. Structural and Functional Analysis of Lin28-mediated Inhibition of let-7 miRNA Biogenesis; Freie Universität Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mihailovich, M.; Militti, C.; Gabaldón, T.; Gebauer, F. Eukaryotic cold shock domain proteins: Highly versatile regulators of gene expression. Bioessays 2010, 32, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, M.M.; Makhatadze, G.I. Major cold shock proteins, CspA from Escherichia coli and CspB from Bacillus subtilis, interact differently with single-stranded DNA templates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1479, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, M.M.; Yutani, K.; Makhatadze, G.I. Interactions of the cold shock protein CspB from Bacillus subtilis with single-stranded DNA. Importance of the T base content and position within the template. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 15511–15518. [Google Scholar]
- Max, K.E.A.; Zeeb, M.; Bienert, R.; Balbach, J.; Heinemann, U. T-rich DNA single strands bind to a preformed site on the bacterial cold shock protein Bs-CspB. J. Mol. Biol 2006, 360, 702–714. [Google Scholar]
- Max, K.E.A.; Zeeb, M.; Bienert, R.; Balbach, J.; Heinemann, U. Common mode of DNA binding to cold shock domains. Crystal structure of hexathymidine bound to the domain-swapped form of a major cold shock protein from Bacillus caldolyticus. FEBS J 2007, 274, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H.P.; Estibeiro, P.; Wear, M.A.; Max, K.E.A.; Heinemann, U.; Cubeddu, L.; Gallagher, M.P.; Sadler, P.J.; Walkinshaw, M.D. Sequence specificity of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins: A novel DNA microarray approach. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, e75. [Google Scholar]
- Zeeb, M.; Max, K.E.A.; Weininger, U.; Löw, C.; Sticht, H.; Balbach, J. Recognition of T-rich single-stranded DNA by the cold shock protein Bs-CspB in solution. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, 4561–4571. [Google Scholar]
- Phadtare, S. Unwinding activity of cold shock proteins and RNA metabolism. RNA Biol 2011, 8, 394–397. [Google Scholar]
- Phadtare, S.; Severinov, K. Nucleic acid melting by Escherichia coli CspE. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 5583–5590. [Google Scholar]
- Phadtare, S.; Tyagi, S.; Inouye, M.; Severinov, K. Three amino acids in Escherichia coli CspE surface-exposed aromatic patch are critical for nucleic acid melting activity leading to transcription antitermination and cold acclimation of cells. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 46706–46711. [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk, K.; Feng, W.; Jiang, W.; Tejero, R.; Emerson, S.D.; Inouye, M.; Montelione, G.T. Solution NMR structure of the major cold shock protein (CspA) from Escherichia coli: Identification of a binding epitope for DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5114–5118. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, H.; Herrler, M.; Willimsky, G.; Marahiel, M.A.; Heinemann, U. Overproduction, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the major cold shock protein from Bacillus subtilis, CspB. Proteins 1992, 14, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, H.; Jiang, W.; Inouye, M.; Heinemann, U. Crystal structure of CspA, the major cold shock protein of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5119–5123. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, H.; Marahiel, M.A.; Heinemann, U. Universal nucleic acid-binding domain revealed by crystal structure of the B. subtilis major cold-shock protein. Nature 1993, 364, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Schnuchel, A.; Wiltscheck, R.; Czisch, M.; Herrler, M.; Willimsky, G.; Graumann, P.; Marahiel, M.A.; Holak, T.A. Structure in solution of the major cold-shock protein from Bacillus subtilis. Nature 1993, 364, 169–171. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, R.; Max, K.E.; Heinemann, U.; Balbach, J. RNA single strands bind to a conserved surface of the major cold shock protein in crystals and solution. RNA 2012, 18, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Phadtare, S.; Inouye, M.; Severinov, K. The mechanism of nucleic acid melting by a CspA family protein. J. Mol. Biol 2004, 337, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayr, F.; Heinemann, U. Mechanisms of Lin28-Mediated miRNA and mRNA Regulation—A Structural and Functional Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 16532-16553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816532
Mayr F, Heinemann U. Mechanisms of Lin28-Mediated miRNA and mRNA Regulation—A Structural and Functional Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(8):16532-16553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816532
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayr, Florian, and Udo Heinemann. 2013. "Mechanisms of Lin28-Mediated miRNA and mRNA Regulation—A Structural and Functional Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 8: 16532-16553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140816532



