Molecular Signatures in Urologic Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Prostate Cancer
2.1. TMPRSS2:ETS Gene Fusions
2.2. The Androgen Receptor/Transcription Factor-Derived Molecular Signature
2.3. PTEN Loss
2.4. Spink 1
2.5. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
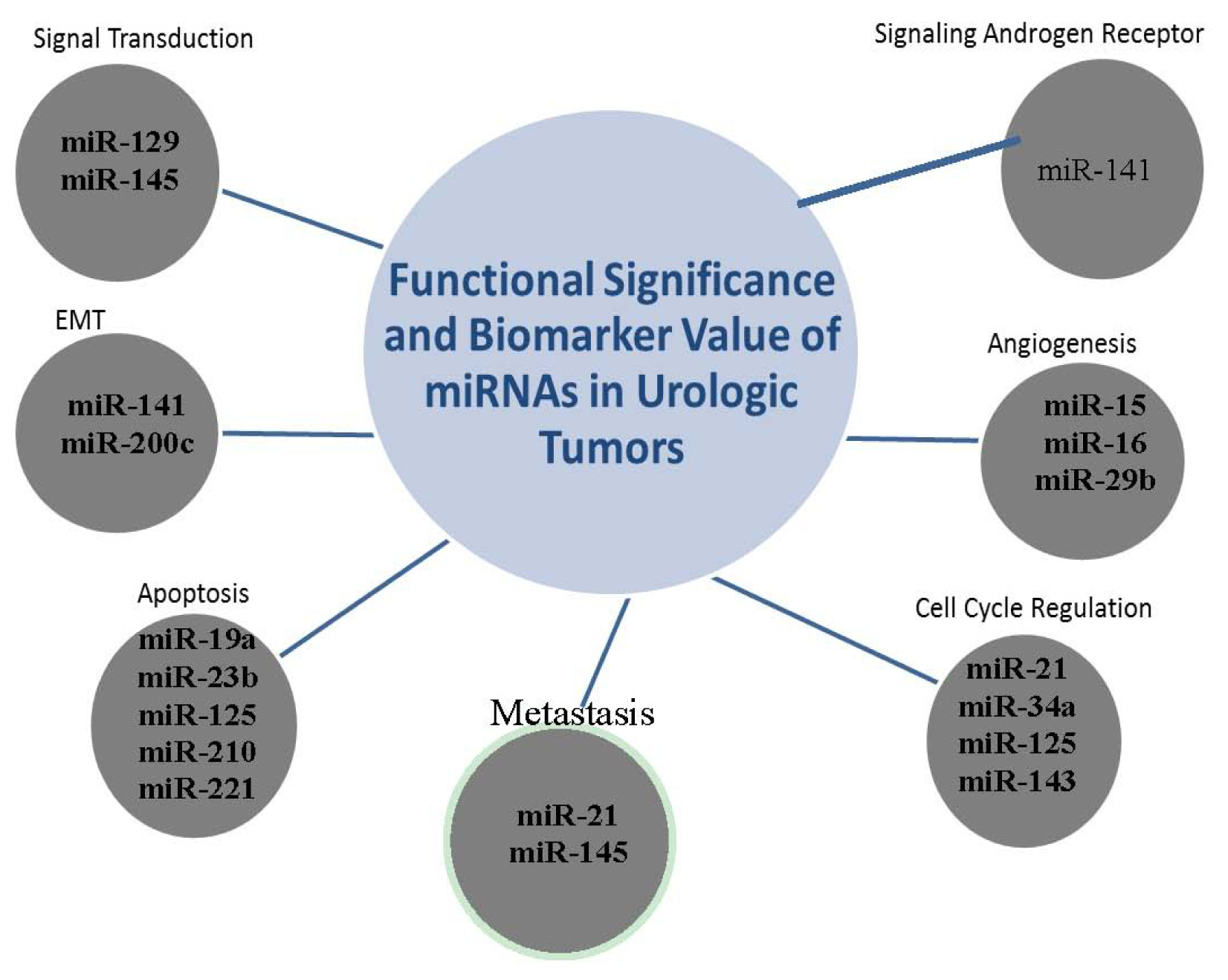
2.6. The Clustering Value of MicroRNAs
2.7. miR-141
3. Bladder Cancer
3.1. Methylation Elevates Genes to Biomarker Status
4. Gene Mutations Shaping Marker Profiles: Really?
4.1. p53
4.2. FGF3R
4.3. Survivin
4.4. The p27 Halt on Cancer Cell Progression
4.5. Integrin-Linked Kinase
4.6. miR-145 and miR-200a
5. Kidney Cancer
5.1. Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) Mutation/Hypoxia Inducing Factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α)
5.2. Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CAIX)
5.3. β-Catenin
5.4. Hypoxia Induced Factor-2 Alpha (HIF-2α)
5.5. miR-34a
6. Optimizing Discovery Platforms
7. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA A Cancer J. Clin 2012, 62, 10–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.F.; Blute, M.L.; Slezak, J.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Zincke, H. The long-term clinical impact of biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer 5 or more years after radical prostatectomy. J. Urol 2003, 170, 1872–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, I.M.; Pauler, D.K.; Goodman, P.J.; Tangen, C.M.; Lucia, M.S.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Ford, L.G.; Lippman, S.M.; Crawford, E.D.; et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level ≤ 4.0 ng per milliliter. N. Engl. J. Med 2004, 350, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, V.A. Screening for prostate cancer: U.S. preventive services task force recommendation statement. Ann. Int. Med 2012, 157, 120–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Rhodes, D.R.; Perner, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Mehra, R.; Sun, X.-W.; Varambally, S.; Cao, X.; Tchinda, J.; Kuefer, R.; et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 2005, 310, 644–648. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.K.; Vaughan, T.B.; Atkinson, T.; Zhu, H.; Kyprianou, N. Emerging biomarkers of prostate cancer (review). Oncol. Rep 2012, 28, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquera, J.-M.; Mehra, R.; Regan, M.M.; Perner, S.; Genega, E.M.; Bueti, G.; Shah, R.B.; Gaston, S.; Tomlins, S.A.; Wei, J.T.; et al. Prevalence of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion prostate cancer among men undergoing prostate biopsy in the United States. Clin. Cancer Res 2009, 15, 4706–4711. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson, A.; Graff, R.E.; Bauer, S.R.; Pitt, M.J.; Lis, R.T.; Stack, E.C.; Martin, N.E.; Kunz, L.; Penney, K.L.; Ligon, A.H.; et al. The TMPRSS2:ERG rearrangement, ERG expression, and prostate cancer outcomes: A cohort study and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev 2012, 21, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ryan, C.J. Castration-resistant prostate cancer: Targeted therapies and individualized treatment. Oncologist 2011, 16, 264–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, C.N. Systemic chemotherapy and new experimental approaches in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, vii91–vii95. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Balk, S.P. Reactivation of androgen receptor-regulated TMPRSS2:ERG gene expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 6027–6032. [Google Scholar]
- Heemers, H.V.; Schmidt, L.J.; Sun, Z.; Regan, K.M.; Anderson, S.K.; Duncan, K.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; Ballman, K.V.; Tindall, D.J. Identification of a clinically relevant androgen-dependent gene signature in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.L.; Massie, C.E.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Zecchini, V.; Scott, H.E.; Lamb, A.D.; MacArthur, S.; Stark, R.; Warren, A.Y.; Mills, I.G.; Neal, D.E. The androgen receptor induces a distinct transcriptional program in castration-resistant prostate cancer in man. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, E.; Tarnawski, A. PTEN regulatory functions in tumor suppression and cell biology. Med. Sci. Monit 2004, 10, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Carver, B.S.; Tran, J.; Gopalan, A.; Chen, Z.; Shaikh, S.; Carracedo, A.; Alimonti, A.; Nardella, C.; Varmeh, S.; Scardino, P.T.; et al. Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat. Genet 2009, 41, 619–624. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Joshua, A.M.; Cunha, I.W.; Coudry, R.A.; Fonseca, F.P.; Ludkovski, O.; Zielenska, M.; Soares, F.A.; Squire, J.A. Absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions and PTEN losses in prostate cancer is associated with a favorable outcome. Mod. Pathol 2008, 21, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Krohn, A.; Diedler, T.; Burkhardt, L.; Mayer, P.-S.; de Silva, C.; Meyer-Kornblum, M.; Kötschau, D.; Tennstedt, P.; Huang, J.; Gerhäuser, C.; et al. Genomic deletion of PTEN is associated with tumor progression and early PSA recurrence in ERG fusion-positive and fusion-negative prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol 2012, 181, 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Wu, C.J.; Chu, G.C.; Xiao, Y.; Ho, D.; Zhang, J.; Perry, S.R.; Labrot, E.S.; Wu, X.; Lis, R.; et al. SMAD4-dependent barrier constrains prostate cancer growth and metastatic progression. Nature 2011, 470, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Stenman, U.-H. SPINK1: A new therapeutic target in cancer? Clin. Chem 2011, 57, 1474–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Rhodes, D.R.; Yu, J.; Varambally, S.; Mehra, R.; Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Helgeson, B.E.; Laxman, B.; Morris, D.S.; et al. The role of SPINK1 in ETS rearrangement-negative prostate cancers. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Gerges, N.; Rak, J.; Jabado, N. New technologies for the detection of circulating tumour cells. Br. Med. Bull 2010, 94, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, J.G.; Miller, M.C.; Gross, S.; Allard, W.J.; Gomella, L.G.; Terstappen, L.W. Circulating tumor cells predict survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Urology 2005, 65, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Danila, D.C.; Anand, A.; Sung, C.C.; Heller, G.; Leversha, M.A.; Cao, L.; Lilja, H.; Molina, A.; Sawyers, C.L.; Fleisher, M.; Scher, H.I. TMPRSS2-ERG status in circulating tumor cells as a predictive biomarker of sensitivity in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone acetate. Eur. Urol 2011, 60, 897–904. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, S.; Saini, S.; Dahiya, R. Wnt signaling pathways in urological cancers: Past decades and still growing. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, S.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Yamamura, S.; Hirata, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Deng, G.; Dahiya, R. MicroRNA-205-directed transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 5637–5649. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, I.-S.; Chang, K.-C.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Ke, J.-Y.; Lu, P.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Yeh, S.-D.; Hong, T.-M.; Chen, Y.-L. MicroRNA-320 suppresses the stem cell-like characteristics of prostate cancer cells by downregulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 530–538. [Google Scholar]
- Brase, J.C.; Johannes, M.; Schlomm, T.; Fälth, M.; Haese, A.; Steuber, T.; Beissbarth, T.; Kuner, R.; Sültmann, H. Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Lodes, M.J.; Caraballo, M.; Suciu, D.; Munro, S.; Kumar, A.; Anderson, B. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microaray. PLoS One 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catto, J.W.F.; Alcaraz, A.; Bjartell, A.S.; de Vere White, R.; Evans, C.P.; Fussel, S.; Hamdy, F.C.; Kallioniemi, O.; Mengual, L.; Schlomm, T.; Visakorpi, T. MicroRNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer: A systematic review. Eur. Urol 2011, 59, 671–681. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, O.; Ahmad, A.; Sethi, S.; Sarkar, F. Recent updates on the role of microRNAs in prostate cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol 2012, 5, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Felici, A.; Pino, M.S.; Carlini, P. A changing landscape in castration resistant prostate cancer treatment. Front. Endocrinol 2012, 3, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Avritscher, E.B.C.; Cooksley, C.D.; Grossman, H.B.; Sabichi, A.L.; Hamblin, L.; Dinney, C.P.; Elting, L.S. Clinical model of lifetime cost of treating bladder cancer and associated complications. Urology 2006, 68, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, K.; Enokida, H.; Tachiwada, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Seki, N.; Nakagawa, M. Increased SKP2 and CKS1 gene expression contributes to the progression of human urothelial carcinoma. J. Urol 2007, 178, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, M.J.; Grau, L.; Franco, N.; Orenes, E.; Alvarez, M.; Blanca, A.; Heredero, O.; Palacios, A.; Urrutia, M.; Fernández, J.M.; et al. Multiplexed methylation profiles of tumor suppressor genes in bladder cancer. J. Mol. Diagn 2011, 13, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, M.W.Y.; Chan, L.W.; Tang, N.L.S.; Tong, J.H.M.; Lo, K.W.; Lee, T.L.; Cheung, H.Y.; Wong, W.S.; Chan, P.S.F.; Lai, F.M.M.; To, K.F. Hypermethylation of multiple genes in tumor tissues and voided urine in urinary bladder cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res 2002, 8, 464–470. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, M.; Esteller, M. DNA methylation: A profile of methods and applications. DNA methylation: A profile of methods and applications. Biotechniques 2002, 33, 632, ,634,636–649.. [Google Scholar]
- Reinert, T. Methylation markers for urine-based detection of bladder cancer: The next generation of urinary markers for diagnosis and surveillance of bladder cancer. Adv. Urol 2012, 2012, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchet, B.P.; de Fromentel, C.C.; Puisieux, A.; Galmarini, C.M. p53 as a target for anti-cancer drug development. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol 2006, 58, 190–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Yu, T.-J.; Wu, W.-J.; Yang, M.-C.; Lung, F.-W. p53 codon 72 polymorphism as a progression index for bladder cancer. Oncol. Rep 2011, 27, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Kamat, A.M.A.M.; Mathew, P.P. Bladder cancer: Imperatives for personalized medicine. Oncology 2011, 25, 951–958, ,960.. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, N.; Elzagheid, A.; El-Hashmi, H.; Syrjanen, K.; Alhakim, S. The potential value of EGFR and P53 immunostaining in tumors of the urinary bladder. Libyan J. Med 2009, 4, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Iyer, G.; Janakiraman, M.; Lin, O.; Heguy, A.; Tickoo, S.K.; Fine, S.W.; Gopalan, A.; Chen, Y.-B.; Balar, A.; et al. Somatic mutation of fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 (FGFR3) defines a distinct morphological subtype of high-grade urothelial carcinoma. J. Pathol 2011, 224, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, S.; MacLennan, G.T.; Williamson, S.R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Montironi, R. Bladder cancer: Translating molecular genetic insights into clinical practice. Hum. Pathol 2011, 42, 455–481. [Google Scholar]
- Tamm, I.; Wang, Y.; Sausville, E.; Scudiero, D.A.; Vigna, N.; Oltersdorf, T.; Reed, J.C. IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by fas (CD95), bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res 1998, 58, 5315–5320. [Google Scholar]
- Berrada, N.; Amzazi, S.; Ameziane El Hassani, R.; Benbacer, L.; El Mzibri, M.; Khyatti, M.; Chafiki, J.; Abbar, M.; Al Bouzidi, A.; Ameur, A.; Attaleb, M. Epigenetic alterations of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), retinoic acid receptor beta (RARbeta) and survivin genes in tumor tissues and voided urine of bladder cancer patients. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 58, OL1744–OL1751. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, J.H.; Godoy, G.; Amiel, G.E.; Lerner, S.P. Urine survivin as a diagnostic biomarker for bladder cancer: A systematic review. BJU Int 2012, 110, 630–636. [Google Scholar]
- Shariat, S.F.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Godoy, G.; Karam, J.A.; Ashfaq, R.; Fradet, Y.; Isbarn, H.; Montorsi, F.; Jeldres, C.; Bastian, P.J.; et al. Survivin as a prognostic marker for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: A multicenter external validation study. Clin. Cancer Res 2009, 15, 7012–7019. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pizzo, J.J.; Borkowski, A.; Jacobs, S.C.; Kyprianou, N. Loss of cell cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder correlates with tumor grade and patient survival. Am. J. Pathol 1999, 155, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Elazeez, T.A.; El-Balshy, A.E.-L.M.; Khalil, M.M.; El-Tabye, M.M.; Abdul-Halim, H. Prognostic significance of P27 (Kip 1) and MUC1 in papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Urol. Ann. 2011, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Galea, C.A.; Nourse, A.; Wang, Y.; Sivakolundu, S.G.; Heller, W.T.; Kriwacki, R.W. Role of intrinsic flexibility in signal transduction mediated by the cell cycle regulator, p27Kip1. J. Mol. Biol 2008, 376, 827–838. [Google Scholar]
- Hannigan, G.; Troussard, A.A.; Dedhar, S. Integrin-linked kinase: A cancer therapeutic target unique among its ILK. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, Y.; Assi, K.; Ogawa, O.; Raven, P.A.; Dedhar, S.; Gleave, M.E.; Salh, B.; So, A.I. The importance of integrin-linked kinase in the regulation of bladder cancer invasion. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 521–531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Downregulation of integrin-linked kinase inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in bladder cancer cells. Cell. Signal 2012, 24, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.J.; Jeong, P.; Kim, W.-T.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Song, P.H. Cell-free microRNAs in urine as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol 2012, 41, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Posadas, E.M.; Figlin, R.A. Systemic therapy in renal cell carcinoma: Advancing paradigms. Oncology 2012, 26, 290–301. [Google Scholar]
- Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; Bukowski, R.M.; Curti, B.D.; George, D.J.; Hudes, G.R.; Redman, B.G.; Margolin, K.A.; Merchan, J.R.; Wilding, G. Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA 2006, 295, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar]
- Rini, B.I.; Small, E.J. Small, biology and clinical development of vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol 2005, 23, 1028–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Pouyssegur, J.; Dayan, F.; Mazure, N.M. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature 2006, 441, 437, –443... [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G. Hypoxia, clonal selection, and the role of HIF-1 in tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol 2000, 35, 71–103. [Google Scholar]
- Staller, P.; Sulitkova, J.; Lisztwan, J.; Moch, H.; Oakeley, E.J.; Krek, W. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 downregulated by von hippel-lindau tumour suppressor pVHL. Nature 2003, 425, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich, B.C.; Sheinin, Y.; Lohse, C.M.; Thompson, R.H.; Cheville, J.C.; Zavada, J.; Kwon, E.D. Carbonic anhydrase IX is not an independent predictor of outcome for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol 2007, 25, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Beasley, N.J.P.; Watson, P.H.; Turner, K.J.; Pastorek, J.; Sibtain, A.; Wilson, G.D.; Turley, H.; Talks, K.L.; Maxwell, P.H.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible expression of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res 2000, 60, 7075–7083. [Google Scholar]
- Švastová, E.; Hulíková, A.; Rafajová, M.; Zat’ovičová, M.; Gibadulinová, A.; Casini, A.; Cecchi, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Pastorek, J.R.; Pastoreková, S. Hypoxia activates the capacity of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX to acidify extracellular pH. FEBS Lett 2004, 577, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Nusse, R. Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res 2005, 15, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Peruzzi, B.; Athauda, G.; Bottaro, D.P. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene product represses oncogenic β-catenin signaling in renal carcinoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14531–14536. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Kim, W.Y. Two sides to every story: The HIF-dependent and HIF-independent functions of pVHL. J. Cell. Mol. Med 2011, 15, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Koukourakis, M.I.; Bentzen, S.M.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Wilson, G.D.; Daley, F.M.; Saunders, M.I.; Dische, S.; Sivridis, E.; Harris, A.L. Endogenous markers of two separate hypoxia response pathways (hypoxia inducible factor 2 alpha and carbonic anhydrase 9) are associated with radiotherapy failure in head and neck cancer patients recruited in the CHART randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol 2006, 24, 727–735. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, K.K.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, Y.-T.; Yamada, T.; Akatsuka, S.; Hu, Q.; Yoshihara, M.; Ohara, H.; Takehashi, M.; Shinohara, T.; et al. Association of microRNA-34a overexpression with proliferation is cell type-dependent. Cancer Sci 2007, 98, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Larkin, S.; Kyprianou, N. Molecular Signatures in Urologic Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18421-18436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140918421
Larkin S, Kyprianou N. Molecular Signatures in Urologic Tumors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(9):18421-18436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140918421
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarkin, Spencer, and Natasha Kyprianou. 2013. "Molecular Signatures in Urologic Tumors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 9: 18421-18436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140918421
APA StyleLarkin, S., & Kyprianou, N. (2013). Molecular Signatures in Urologic Tumors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(9), 18421-18436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140918421




