Genotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates from Different Sources in the North-West Province, South Africa, Using Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus PCR Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus (ERIC) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
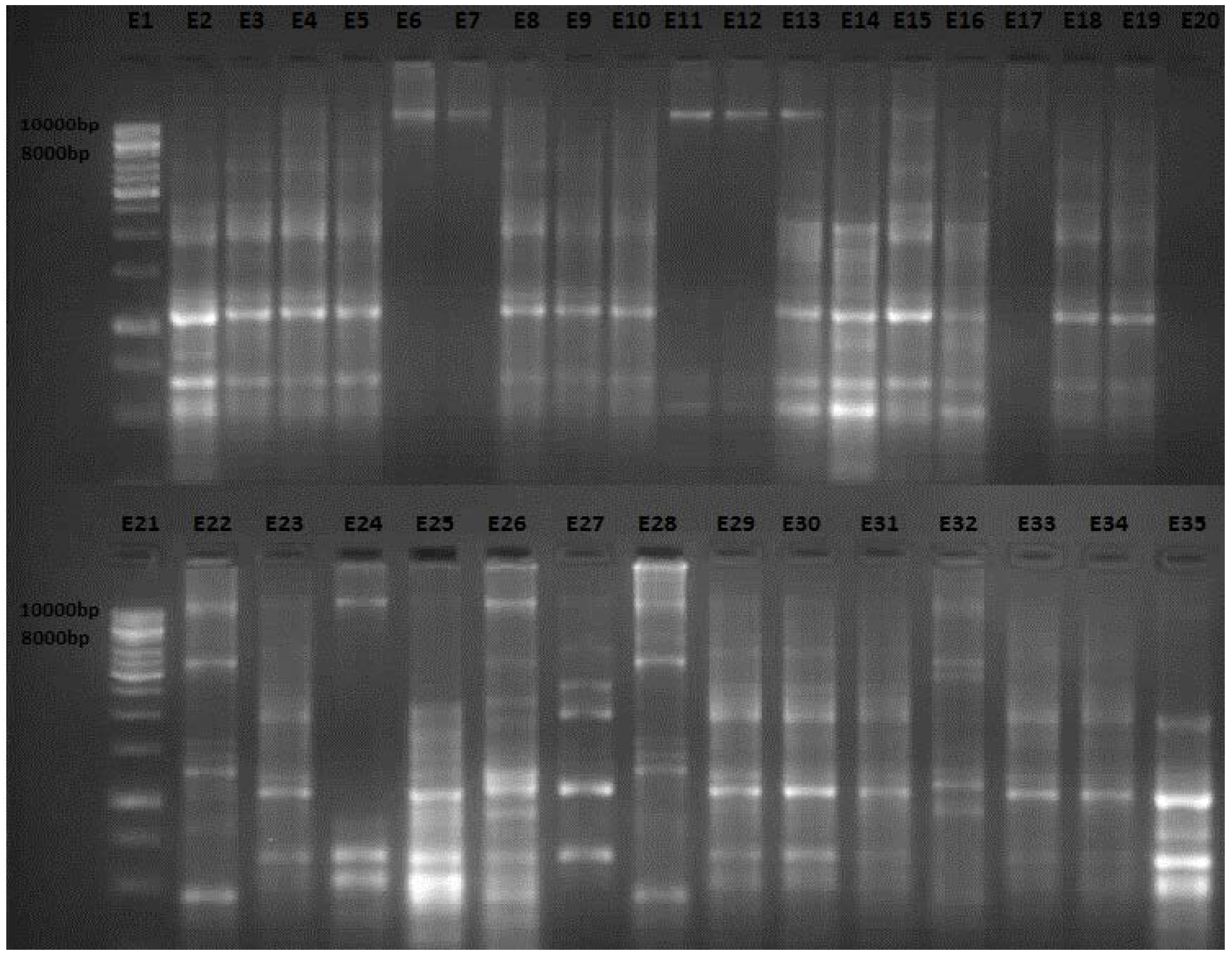
2.2. Discussion

| Specie/Source | Sample Type/Site | Cluster I N = 9 | Cluster II N = 17 | Cluster III N = 2 | Cluster IV N = 6 | Cluster V N = 11 | Cluster VI N = 14 | Cluster VII N = 24 | Cluster VIII N = 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Mafikeng feces | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mafikeng beef | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lichtenburg feces | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Lichtenburg beef | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Koster feces | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Koster beef | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Zeerust feces | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Rustenburg feces | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Rustenburg beef | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pigs | Mafikeng feces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 3 |
| Mafikeng pork | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lichtenburg feces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 4 | |
| Lichtenburg pork | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Koster feces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Koster pork | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Zeerust feces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Zeerust pork | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Rustenburg feces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Rustenburg pork | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |
| Humans | Mafikeng (feces) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Water | Koster (Tap) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Koster (River) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Isolation of E. coli O157:H7
3.2.1. Human Stool and Animal Fecal Samples
| Sample Source | Sampling Area | Nature of Sample | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pigs | Koster | Fecal sample | 8 |
| Lichtenburg | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Mafikeng | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Rustenburg | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Zeerust | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Pigs | Koster | Pork | 8 |
| Lichtenburg | Pork | 8 | |
| Mafikeng | Pork | 8 | |
| Rustenburg | Pork | 8 | |
| Zeerust | Pork | 8 | |
| Bovine | Koster | Fecal sample | 8 |
| Lichtenburg | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Mafikeng | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Rustenburg | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Zeerust | Fecal sample | 8 | |
| Bovine | Koster | Beef | 8 |
| Lichtenburg | Beef | 8 | |
| Mafikeng | Beef | 8 | |
| Rustenburg | Beef | 8 | |
| Zeerust | Beef | 8 | |
| Water | Koster | Water | 8 |
| Lichtenburg | Water | 8 | |
| Mafikeng | Water | 8 | |
| Rustenburg | Water | 8 | |
| Zeerust | Water | 8 | |
| Human | Mafikeng Provincial Hospital | Fecal sample | 20 |
3.2.2. Meat Samples
3.2.3. Water Samples
3.3. E. coli Control Strains
3.4. Extraction of Genomic DNA
3.5. Molecular Identification of E. coli O157:H7 Isolates
| Source | Humans | Pigs | Cattle | Water | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feces | Feces | Pork | Feces | Beef | Taps | River Catchment | ||
| Mafikeng | 1 | 15 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 35 |
| Lichtenburg | NT | 11 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| Koster | NT | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 14 |
| Rustenburg | NT | 10 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| Zeerust | NT | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 1 | 43 | 20 | 16 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 94 |
3.6. ERIC PCR Assays
3.7. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cowden, J.M.; Ahmed, S.; Donaghy, M.; Riley, A. Epidemiological investigation of the central Scotland outbreak of Escherichia coli O157 infection, November to December 1996. Epidemiol. Infect. 2001, 126, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dundas, S.; Todd, W.T.; Stewart, A.I.; Murdoch, P.S.; Chaudhuri, A.K.; Hutchinson, S.J. The central Scotland Escherichia coli O157: H7 outbreak: Risk factors for the haemolytic uremic syndrome and death among hospitalized patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, A.E.; Caprioli, A.; Minelli, F.; Gianviti, A.; de Petris, L.; Edefonti, A.; Montini, G.; Ferretti, A.; de Palo, T.; Gaido, M.; et al. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections associated with haemolytic uremic syndrome, Italy, 1988–2000. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutin, L.; Krause, G.; Zimmermann, S.; Kaulfuss, S.; Gleier, K. Characterisation of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli strains isolated from human patients in Germany over a 3-year period. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1099–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.G.; Tserenpuntsag, B.; Kacica, M.; Smith, P.F.; Morse, D.L. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome incidence in New York. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, R.M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Taylor, C.M.; Adak, G.K.; Chart, H.; Cheasty, T.; Coia, J.E.; Gillespie, I.A.; Locking, M.E.; Reilly, W.J.; et al. Childhood haemolytic uraemic syndrome, United Kingdom and Ireland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, E.E.; Ehlers, M.M.; Grabow, W.O.K. The occurrence of E. coli O157:H7 in Southern African water sources intended for direct and indirect human consumption. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3085–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.J.; Miller, G.; Breuer, T.; Kennedy, M.; Higgins, C.; Walford, J.; McKee, G.; Fox, K.; Bibb, W.; Mead, P. A waterborne outbreak of Escherichia coli O157 infections and haemolytic uraemic syndrome: Implications for rural water systems. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Inatomi, J.; Wake, A.; Takamizawa, M.; Katayama, H.; Iwata, T. Failure of pre-diarrheal antibiotics to prevent haemolytic uraemic syndrome in serologically proven Escherichia coli O157:H7 gastrointestinal infection. J. Paediat. 1999, 135, 768–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhitil, S.; Jakšic, S.; Petrak, T.; Botka-Petrak, K. Presence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef and ground baby beef meat. Food Protect. 2004, 64, 862–864. [Google Scholar]
- Law, D. Virulence factors of Escherichia coli O157 and other Shiga toxin-producing. E. coli. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, A.W.; Paton, C.J. Direct detection and characterisation of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli by multiplex PCR for stx1, stx2, eae, ehxA and saa. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierard, D.; Muyldermans, G.; Moriau, L.; Stevens, D.; Lauwers, S. Identification of new verocytotoxin type 2 variant B-subunit genes in human and animal Escherichia coli isolates. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.; Scheef, J.; Morabito, S.; Caprioli, A.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H. A new Shiga toxin 2 variant (Stx2f) from Escherichia coli isolated from pigeons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, M.T.; Garrett, V.; Mohle-Boetani, J.C.; Barros, M.; Farrar, J.A.; Rios, R.; Abbott, S.; Sowadsky, R.; Komatsu, K.; Mandrell, R.; et al. A multistate outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection linked to consumption of beef tacos at a fast-food restaurant chain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, E.S.; Scheftel, J.M.; Boxrud, D.J.; Vought, K.J.; Danila, R.N.; Elfering, K.M. Outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections associated with no intact blade-tenderized frozen steaks sold by door-to-door vendors. Food Protect. 2005, 68, 1198–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Magwira, C.A.; Gashe, B.A.; Collison, E.K. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance profiles of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in beef products from retail outlets in Gaborone, Botswana. Food Protect. 2005, 68, 403–406. [Google Scholar]
- Maruzumi, M.; Morita, M.; Matsouka, Y.; Uekawa, A.; Nakamura, T.; Fugi, K. Mass food poisoning caused by beef offal contaminated by Escherichia coli O157. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 58, 397. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, P.A.; Siddons, C.A.; Wright, D.J.; Norman, P.; Fox, J.; Crick, E. Cattle as a possible source of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 in man. Epidemiol. Infect. 1993, 111, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, G.; Wasteson, Y.; Heir, E.; Berget, O.I.; Herikstad, H. Escherichia coli O157:H7 in faeces from cattle, sheep and pigs in the southwest part of Norway during 1998 and 1999. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 65, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateba, C.N.; Mbewe, M.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. The prevalence of Escherichia coli O157 strains in cattle, pigs and humans in the North-West Province, South Africa. SAJS 2008, 104, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fegan, N.; Vanderlinde, P.; Higgs, G.; Desmarchelier, P. The prevalence and concentration of Escherichia coli O157 in faeces of cattle from different production systems at slaughter. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versalovic, J.; Schneider, M.; de Bruijn, F.J.; Lupski, J.R. Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria with repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Methods Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 5, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, B.R.; Broersma, K.; Mazumder, A. Comparison of five Rep-PCR genomic fingerprinting methods for differentiation of faecal Escherichia coli from humans, poultry and wild birds. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateba, C.N.; Mbewe, M. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 virulence genes in isolates from beef, pork, water, human and animal species in the North-West Province, South Africa: Public health implications. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutton, S.; Baldwin, T.; Williams, H.; McNeish, A.S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: Basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Omisakin, F.; Macrae, M.; Ogden, I.D.; Strachan, N.J. Concentration and prevalence of Escherichia coli O157 in faeces at slaughter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2444–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateba, C.N.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Characterisation of Escherichia coli O157 strains from humans, cattle and pigs in the North-West Province, South Africa. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 128, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panangala, V.S.; van Santen, V.L.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Klesius, P.H. Analysis of 16S–23S intergenic spacer regions of the rRNA operons in Edwardsiella ictaluri and Edwardsiella tarda isolates from fish. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.M.; Scheutz, F. Characterization of Escherichia coli O157 isolates from Danish cattle and human patients by genotyping and presence and variants of virulence genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 88, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meichtri, L.; Miliwebsky, E.; Gioffré, A.; Chinen, I.; Baschkier, A.; Chillemi, G.; Guth, B.E.; Masana, M.O.; Cataldi, A.; Rodríguez, H.R.; et al. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in healthy young beef steers from Argentina: Prevalence and virulence properties. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 96, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ateba, C.N.; Mbewe, M. Genotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates from Different Sources in the North-West Province, South Africa, Using Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus PCR Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9735-9747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069735
Ateba CN, Mbewe M. Genotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates from Different Sources in the North-West Province, South Africa, Using Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus PCR Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(6):9735-9747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069735
Chicago/Turabian StyleAteba, Collins Njie, and Moses Mbewe. 2014. "Genotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates from Different Sources in the North-West Province, South Africa, Using Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus PCR Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 6: 9735-9747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069735
APA StyleAteba, C. N., & Mbewe, M. (2014). Genotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates from Different Sources in the North-West Province, South Africa, Using Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus PCR Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(6), 9735-9747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069735




