Defective Autophagosome Formation in p53-Null Colorectal Cancer Reinforces Crocin-Induced Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Crocin Inhibits Proliferation of HCT116 Cell Lines


2.2. Different Method of Cell Cycle Arrest in HCT116 Cells after Crocin Treatment

2.3. Crocin Induces p53-Dependent Apoptosis in HCT116 Cells


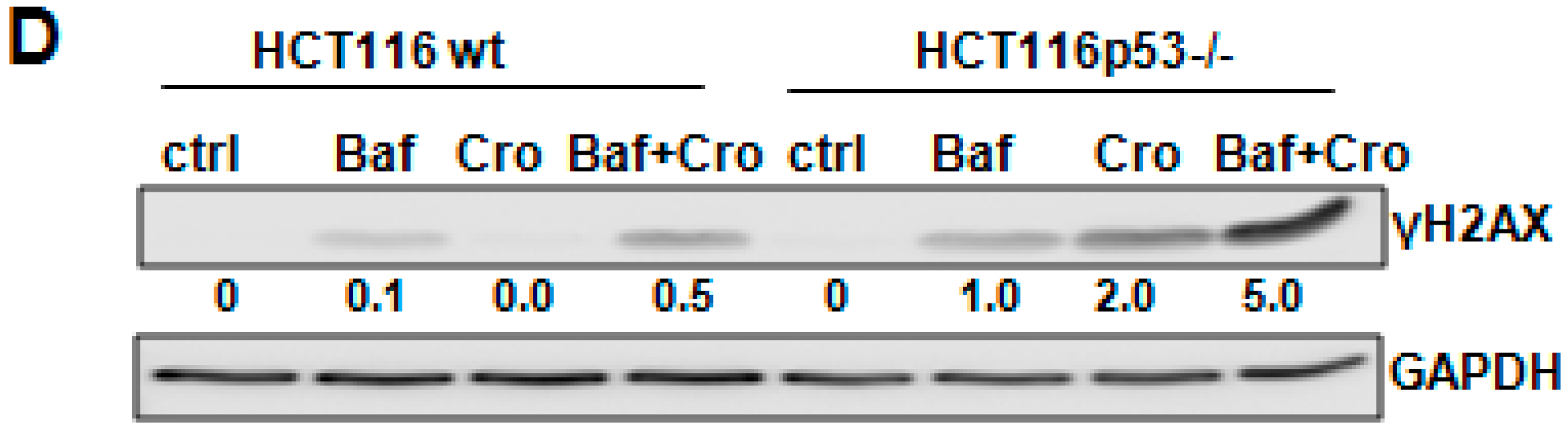
2.4. Crocin Induces Aberrant and Inefficient Autophagy in HCT116 p53−/− Cells

2.5. Crocin Modulation of HCT116 Cells’ Fate Was p53-Dependent

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. In Vitro Analysis
4.2. MTT Cell Proliferation Assay
4.3. Crystal Violet Assay
4.4. Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis of DNA Contents
4.5. Apoptotic Assessment Using Annexin V-PI Staining
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Immunofluorescence Labeling
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyle, P.; Langman, J.S. ABC of colorectal cancer: Epidemiology. Br. Med. J. 2000, 321, 805–808. [Google Scholar]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.; Ward, E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, E.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Fuhler, G.M. The role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.L.D.; Chen, H.Y.; Cho, W.C.S.; Meng, X.M.; Tong, Y. The efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine as an adjunctive therapy for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2012, 20, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.M.; Chan, W.Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, C.H.K. Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakkol-Afshari, J.; Brook, A.; Mousavi, S.H. Study of cytotoxic and apoptogenic properties of saffron extract in human cancer cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Hamza, A.; Bajbouj, K.; Ashraf, S.S.; Daoud, S. Saffron: A potential candidate for a novel anti-cancer drug against hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 857–867. [Google Scholar]
- Bajbouj, K.; Schulze-Luehrmann, J.; Diermeier, S.; Amin, A.; Schneider-Stock, R. The anticancer effect of saffron in two p53 isogenic colorectal cancer cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullaev, F.I. Cancer chemopreventive and tumoricidal properties of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 227, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Melnyk, J.P.; Wang, S.; Marcone, M.F. Chemical and biological properties of the world’s most expensive spice: Saffron. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Kim, S.O.; Li, Y.; Han, J. Autophagy contributes to caspase-independent macrophage cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 19179–19187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, I.P.; Oliveira, L.; Tucci, P.; Alvarez-Valín, F.; A Coudry, R.; Marín, M. Different mutation profiles associated to p53 accumulation in colorectal cancer. Gene 2012, 499, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. p53, The cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacopetta, B. TP53 mutation in colorectal cancer. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyiraneza, C.; Jouret-Mourin, A.; Kartheuser, A.; Camby, P.; Plomteux, O.; Detry, R.; Dahan, K.; Sempoux, C. Distinctive patterns of p53 protein expression and microsatellite instability in human colorectal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2011, 42, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaravadi, R.K.; Yu, D.; Lum, J.J.; Bui, T.; Christophorou, M.A.; Evan, G.I.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Thompson, C.B. Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, B. Cell biology: Autophagy and cancer. Nature 2007, 446, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, K.N.; Tekedereli, I.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Ozpolat, B. Targeting the prodeath and prosurvival functions of autophagy as novel therapeutic strategies in cancer. Autophagy 2010, 6, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Cho, T.J.; Woo, B.H.; Choi, K.U.; Lee, C.H.; Ryu, M.H.; Park, H.R. Curcumin-induced autophagy contributes to the decreased survival of oral cancer cells. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzawa, T.; Kondo, Y.; Ito, H.; Kondo, S.; Germano, I. Induction of autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells by arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Kanzawa, T.; Germano, I.M.; Komata, T.; Ito, H.; Kondo, Y.; Kondo, S. Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Lim, M.H.; Kim, K.M.; Jeon, B.H.; Song, W.O.; Kim, T.W. Cordycepin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells are independent of the estrogen receptor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2011, 257, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, H.H.; Wang, C.Z.; Ni, M.; Fishbein, A.; Mehendale, S.R.; Xie, J.T.; Shoyama, C.Y.; Yuan, C.S. Crocin from Crocus sativus possesses significant anti-proliferation effects on human colorectal cancer cells. Exp. Oncol. 2007, 29, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Waldman, T.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. p21 is necessary for the p53-mediated G1 arrest in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5187–5190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giaccio, M. Crocetin from saffron: An active component of an ancient spice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Tagawa, Y.; Yoshimori, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Masaki, R.; Tashiro, Y. Bafilomycin A1 prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H4IIE cells. Cell Struct. Funct. 1998, 23, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abeliovich, H.; Agostinis, P.; Agrawal, D.K.; Aliev, G.; Askew, D.S.; Baba, M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Bahr, B.A.; Ballabio, A.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy 2008, 4, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.C.; Hsiao, J.R.; Lian, Y.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, B.M. The apoptotic effect of cordycepin on human OEC-M1 oral cancer cell line. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 60, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartel, A.L.; Radhakrishnan, S.K. Lost in transcription: p21 Repression, mechanisms, and consequences. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3980–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.H.; Shih, R.S.; Schoene, N.W.; Lei, K.Y. Zinc-induced G2/M blockage is p53 and p21 dependent in normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C1342–C1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, P.G.; Normand, G.; Gillissen, B.; Wendt, J.; Dörken, B.; Daniel, P.T. Cooperative effect of p21Cip1/WAF-1 and 14-3-3σ on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction by p14ARF. Oncogenes 2008, 27, 6707–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjetovic, K.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L.; Misirkic-Marjanovic, M.; Vucicevic, L.; Stevanovic, D.; Zogovic, N.; Sumarac-Dumanovic, M.; Micic, D.; Trajkovic, V. In vitro and in vivo anti-melanoma action of metformin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, L.; Platini, F.; Scardino, A.; Alabiso, O.; Vasapollo, G.; Tessitore, L. Autophagy inhibition enhances anthocyanin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2476–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Shao, S.H.; Xu, Z.X.; Hennessy, B.; Ding, Z.; Larrea, M.; Kondo, S.; Dumont, D.J.; Gutterman, J.U.; Walker, C.L.; et al. The energy sensing LKB1–AMPK pathway regulates p27kip1 phosphorylation mediating the decision to enter autophagy or apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.W. Autophagy inhibition enhances ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in PC3 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelio, I.; Melino, G.; Knight, R.A. Cell death pathology: Cross-talk with autophagy and its clinical implications. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.M. p53 and autophagy in cancer: Guardian of the genome meets guardian of the proteome. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Y.; Yu, Q.J.; Zhang, R.D.; Liu, B. Core signaling pathways of survival/death in autophagy-related cancer networks. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Gestwicki, J.E.; Murphy, L.O.; Klionsky, D.J. Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Cuervo, A.M.; Seglen, P.O. Methods for monitoring autophagy from yeast to human. Autophagy 2007, 3, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Cuervo, A.M.; Ravikumar, B.; Sarkar, S.; Korolchuk, V.; Kaushik, S.; Klionsky, D.J. In search of an “autophagomometer”. Autophagy 2009, 5, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Ma, S.; Liang, B.; Yi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, R.; Cui, L.; Jia, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. The different regulatory effects of p53 status on multidrug resistance are determined by autophagy in ovarian cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2012, 66, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goussetis, D.J.; Altman, J.K.; Glaser, H.; McNeer, J.L.; Tallman, M.S.; Platanias, L.C. Autophagy is a critical mechanism for the induction of the antileukemic effects of arsenic trioxide. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29989–29997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, B.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 2008, 132, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Kanzawa, T.; Sawaya, R.; Kondo, S. The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman-Antosiewicz, A.; Johnson, D.E.; Singh, S.V. Sulforaphane causes autophagy to inhibit release of cytochrome C and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5828–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Rocha, H.; Garcia-Garcia, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Franco, R. DNA damage and autophagy. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, A.; Bajbouj, K.; Koch, A.; Gandesiri, M.; Schneider-Stock, R. Defective Autophagosome Formation in p53-Null Colorectal Cancer Reinforces Crocin-Induced Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1544-1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011544
Amin A, Bajbouj K, Koch A, Gandesiri M, Schneider-Stock R. Defective Autophagosome Formation in p53-Null Colorectal Cancer Reinforces Crocin-Induced Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(1):1544-1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011544
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Amr, Khuloud Bajbouj, Adrian Koch, Muktheshwar Gandesiri, and Regine Schneider-Stock. 2015. "Defective Autophagosome Formation in p53-Null Colorectal Cancer Reinforces Crocin-Induced Apoptosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 1: 1544-1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011544
APA StyleAmin, A., Bajbouj, K., Koch, A., Gandesiri, M., & Schneider-Stock, R. (2015). Defective Autophagosome Formation in p53-Null Colorectal Cancer Reinforces Crocin-Induced Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(1), 1544-1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011544




