Biological Screening of Newly Synthesized BIAN N-Heterocyclic Gold Carbene Complexes in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BIAN N-Heterocyclic Carbene Gold Complexes Induce Lethality and Malformations in Zebrafish Embryos

| Concentration (µM) | [IPr(BIAN)AuCl] | [IPr(BIAN)AuOAc] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Embryos Used * | % Mortality | Number of Embryos Used * | % Mortality | |
| Control (1% DMSO v/v treated embryos) | 54.00 ± 0.57 | 0.0 ± 0.00 | 50.00 ± 0.57 | 0.0 ± 0.00 |
| 1 | 51.00 ± 0.59 | 0.0 ± 0.00 | 51.00 ± 0.57 | 0.0 ± 0.00 |
| 10 | 50.00 ± 1.15 | 1.0 ± 1.00 | 50.00 ± 1.00 | 3.0 ± 0.5 |
| 15 | 50.00 ± 1.15 | 3.0 ± 1.00 | 50.00 ± 1.52 | 5.0 ± 0.50 |
| 30 | 51.00 ± 1.15 | 5.0 ± 0.57 | 51.00 ± 1.52 | 10.0 ± 1.14 |
| 50 | 52.00 ± 1.15 | 25.0 ± 1.52 | 52.00 ± 1.15 | 60.0 ± 2.00 |
| 100 | 50.00 ± 1.00 | 80.0 ± 0.57 | 50.00 ± 1.16 | 100 ± 0.00 |
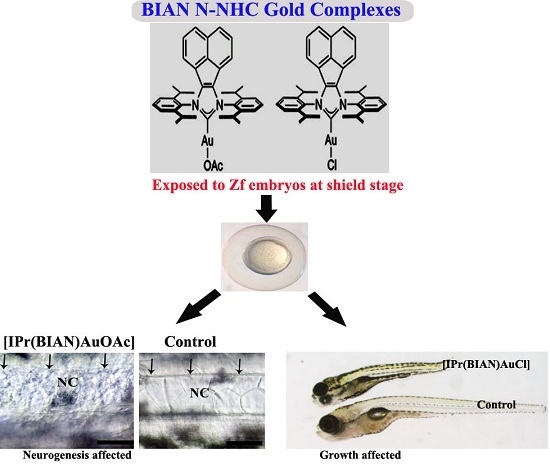
2.2. The Gold Acetate Complex [IPr(BIAN)AuOAc] Induces Neurotoxicity by Hindering Brain Formation and Degeneration of the Notochord in Exposed Embryos


2.3. The BIAN NHC Gold Chloride Complex [IPr(BIAN)AuCl] Exposure Induced Delay in Development, Stunted Growth and Organ Malformation in Zebrafish Embryos


3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Biological Screening
4.1.1. Animals
4.1.2. Embryo Treatment
4.1.3. Microscopy and Photography
4.1.4. Measurement of Glutathione (GSH) Level in Zebrafish Embryos
4.2. Chemistry
Syntheses of BIAN NHC Gold Complexes
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrmann, W.A.; Köcher, C. N-Heterocyclic carbenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 2162–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, D.S.; Cavell, K.J.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Zerovalent palladium and nickel complexes of heterocyclic carbenes: Oxidative addition of organic halides, carbon-carbon coupling processes, and the heck reaction. Organometallics 1999, 18, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, M.N.; Richter, C.; Schedler, M.; Glorius, F. An overview of N-heterocyclic carbenes. Nature 2014, 510, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aher, S.B.; Muskawar, P.N.; Thenmozhi, K.; Bhagat, P.R. Recent developments of metal N-heterocyclic carbenes as anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Deng, L. Metal-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as anti-tumor agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.K.; Gust, R. Metal N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as potential antitumor metallodrugs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 755–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, A.; Cisnetti, F. Advances in metal-carbene complexes as potent anti-cancer agents. Metallomics 2012, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindi, K.M.; Panzner, M.J.; Tessier, C.A.; Cannon, C.L.; Youngs, W.J. The medicinal applications of imidazolium carbene-metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3859–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teyssot, M.L.; Jarrousse, A.S.; Manin, M.; Chevry, A.; Roche, S.; Norre, F.; Beaudoin, C.; Morel, L.; Boyer, D.; Mahiou, R.; et al. Metal-NHC complexes: A survey of anti-cancer properties. Dalton Trans. 2009, 6894–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raubenheimer, H.G.; Cronje, S. Carbene complexes of gold: Preparation, medical application and bonding. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1998–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbiani, R.; Can, S.; Kitanovic, I.; Alborzinia, H.; Stefanopoulou, M.; Kokoschka, M.; Mönchgesang, S.; Sheldrick, W.S.; Wölfl, S.; Ott, I. Comparative in vitro evaluation of N-heterocyclic carbene gold(I) complexes of the benzimidazolylidene type. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8646–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Oehninger, L.; Geldmacher, Y.; Alborzinia, H.; Wolfl, S.; Sheldrick, W.S.; Ott, I. Gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes with naphthalimide ligands as combined thioredoxin reductase inhibitors and DNA intercalators. Chem. Med. Chem. 2014, 9, 1794–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.V.; Barnard, P.J.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Brayshaw, S.K.; Hickey, J.L.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Cationic, linear Au(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, structure and anti-mitochondrial activity. Dalton Trans. 2006, 3708–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.J.; Teraoka, H.; Heideman, W.; Peterson, R.E. Zebrafish as a model vertebrate for investigating chemical toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parng, C.; Seng, W.L.; Semino, C.; McGrath, P. Zebrafish: A preclinical model for drug screening. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2002, 1, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, R.T.; Link, B.A.; Dowling, J.E.; Schreiber, S.L. Small molecule developmental screens reveal the logic and timing of vertebrate development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12965–12969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elzatahry, A.A.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Elsayed, E.A.; Butorac, R.R.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Wadaan, M.A.; Cowley, A.H. Nanofiber composites containing N-heterocyclic carbene complexes with antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2829–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Butorac, R.R.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Cowley, A.H. Antimicrobial properties of some bis(imino)acenaphthene (BIAN)-supported N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of silver and gold. Molecules 2011, 16, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berners-Price, S.J. Activating platinum anticancer complexes with visible light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardon, C.; Boscutti, G.; Fregona, D. Beyond platinums: Gold complexes as anticancer agents. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melaiye, A.; Simons, R.S.; Milsted, A.; Pingitore, F.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Tessier, C.A.; Youngs, W.J. Formation of water-soluble pincer silver(I)-carbene complexes: A novel antimicrobial agent. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, J.L.; Ruhayel, R.A.; Barnard, P.J.; Baker, M.V.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Filipovska, A. Mitochondria-targeted chemotherapeutics: The rational design of gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes that are selectively toxic to cancer cells and target protein selenols in preference to thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12570–12571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, I.; Temelli, N.; Gunal, S.; Demir, S. Gold(I) complexes of N-heterocyclic carbene ligands containing benzimidazole: Synthesis and antimicrobial activity. Molecules 2010, 15, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenzner, J.K.; Biersack, B.; Kalie, H.; Andronache, I.C.; Kaps, L.; Schuppan, D.; Sasse, F.; Schobert, R. Gold(I) biscarbene complexes derived from vascular-disrupting combretastatin A-4 address different targets and show antimetastatic potential. Chem. Med. Chem. 2014, 9, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftci, O.; Beytur, A.; Vardi, N.; Ozdemir, I. Evaluation of reproductive toxicity in male rats treated with novel synthesized ruthenium(II) and gold(I)-NHC complexes. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, O.; Ozdemir, I.; Cakir, O.; Demir, S. The determination of oxidative damage in heart tissue of rats caused by ruthenium(II) and gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2011, 27, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, J.M.; Prades, A.; del Carmen Ramos, M.; Peris, E.; Ripoll-Gomez, J.; Poyatos, M.; Burgos, J.S. Biomedical properties of a series of ruthenium-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes based on oxidant activity in vitro and assessment in vivo of biosafety in zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish 2010, 7, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehninger, L.; Stefanopoulou, M.; Alborzinia, H.; Schur, J.; Ludewig, S.; Namikawa, K.; Munoz-Castro, A.; Koster, R.W.; Baumann, K.; Wolfl, S.; et al. Evaluation of arene ruthenium(II) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as organometallics interacting with thiol and selenol containing biomolecules. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Bai, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, R.; Zhu, J.H.; Huang, C. Developmental lead acetate exposure induces embryonic toxicity and memory deficit in adult zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012, 34, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strmac, M.; Braunbeck, T. Effects of triphenyltin acetate on survival, hatching success, and liver ultrastructure of early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 44, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, C.; Skutella, T.; Lezoualch, F.; Post, A.; Widmann, M.; Newton, C.J.; Holsboer, F. Neuroprotection against oxidative stress by estrogens: Structure-activity relationship. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: Where are we now? J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1634–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.; Abramov, A.Y. Mechanism of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, S.C.; Mead, R.J.; Shaw, P.J. Oxidative stress in ALS: A mechanism of neurodegeneration and a therapeutic target. BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2006, 1762, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, P.H. Free radicals in brain metabolism and pathology. Br. Med. Bull. 1993, 49, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutowicz, M. The influence of reactive oxygen species on the central nervous system. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2011, 65, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bironaite, D.; Ollinger, K. The hepatotoxicity of rhein involves impairment of mitochondrial functions. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1997, 103, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K.; Nakaki, T. Glutathione in cellular redox homeostasis: Association with the excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). Molecules 2015, 20, 8742–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, J.S.; Shaw, C.A. Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: The role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res. Rev. 1997, 25, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Maher, P.; Schubert, D. A role for 12-lipoxygenase in nerve cell death caused by glutathione depletion. Neuron 1997, 19, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, A.; Dey, S.K.; Das, S.; Munda, R.N.; Dinda, J.; Das Saha, K. Gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complex inhibits mouse melanoma growth by p53 upregulation. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbiani, R.; Kitanovic, I.; Alborzinia, H.; Can, S.; Kitanovic, A.; Onambele, L.A.; Stefanopoulou, M.; Geldmacher, Y.; Sheldrick, W.S.; Wolber, G.; et al. Benzimidazol-2-ylidene gold(I) complexes are thioredoxin reductase inhibitors with multiple antitumor properties. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8608–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Ilan, O.; Chuang, C.C.; Schwahn, D.J.; Yang, S.; Joshi, S.; Pedersen, J.A.; Hamers, R.J.; Peterson, R.E.; Heideman, W. TiO2 nanoparticle exposure and illumination during zebrafish development: Mortality at parts per billion concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4726–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Qin, H. The relationship between early embryo development and tumourigenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2697–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, M.; Holding, C. Human embryonic genes re-expressed in cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 8085–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kho, A.T.; Zhao, Q.; Cai, Z.; Butte, A.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Rowitch, D.H.; Kohane, I.S. Conserved mechanisms across development and tumorigenesis revealed by a mouse development perspective of human cancers. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.K.; Nael, A.T.; Butorac, R.; Evans, D.A.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Wadaan, M.A.M.; Cowley, A.H. BIAN N-heterocyclic gold carbene complexes induced cytotoxicity in human cancer cells via upregulating oxidative stres. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Strahle, U.; Scholz, S.; Geisler, R.; Greiner, P.; Hollert, H.; Rastegar, S.; Schumacher, A.; Selderslaghs, I.; Weiss, C.; Witters, H.; et al. Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—A commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, K.V.; Butorac, R.R.; Abernethy, C.D.; Cowley, A.H. Synthesis and coordination compounds of a bis(imino)acenaphthene (BIAN)-supported N-heterocyclic carbene. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 7401–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farooq, M.; Taha, N.A.; Butorac, R.R.; Evans, D.A.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Elsayed, E.A.; Wadaan, M.A.M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Cowley, A.H. Biological Screening of Newly Synthesized BIAN N-Heterocyclic Gold Carbene Complexes in Zebrafish Embryos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24718-24731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024718
Farooq M, Taha NA, Butorac RR, Evans DA, Elzatahry AA, Elsayed EA, Wadaan MAM, Al-Deyab SS, Cowley AH. Biological Screening of Newly Synthesized BIAN N-Heterocyclic Gold Carbene Complexes in Zebrafish Embryos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(10):24718-24731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024718
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarooq, Muhammad, Nael Abu Taha, Rachel R. Butorac, Daniel Anthony Evans, Ahmed A. Elzatahry, Elsayed Ahmed Elsayed, Mohammad A. M. Wadaan, Salem S. Al-Deyab, and Alan H. Cowley. 2015. "Biological Screening of Newly Synthesized BIAN N-Heterocyclic Gold Carbene Complexes in Zebrafish Embryos" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 10: 24718-24731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024718
APA StyleFarooq, M., Taha, N. A., Butorac, R. R., Evans, D. A., Elzatahry, A. A., Elsayed, E. A., Wadaan, M. A. M., Al-Deyab, S. S., & Cowley, A. H. (2015). Biological Screening of Newly Synthesized BIAN N-Heterocyclic Gold Carbene Complexes in Zebrafish Embryos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(10), 24718-24731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024718