Changes in Ultrastructure and Cytoskeletal Aspects of Human Normal and Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Exposed to Interleukin-1β and Cyclical Hydrostatic Pressure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
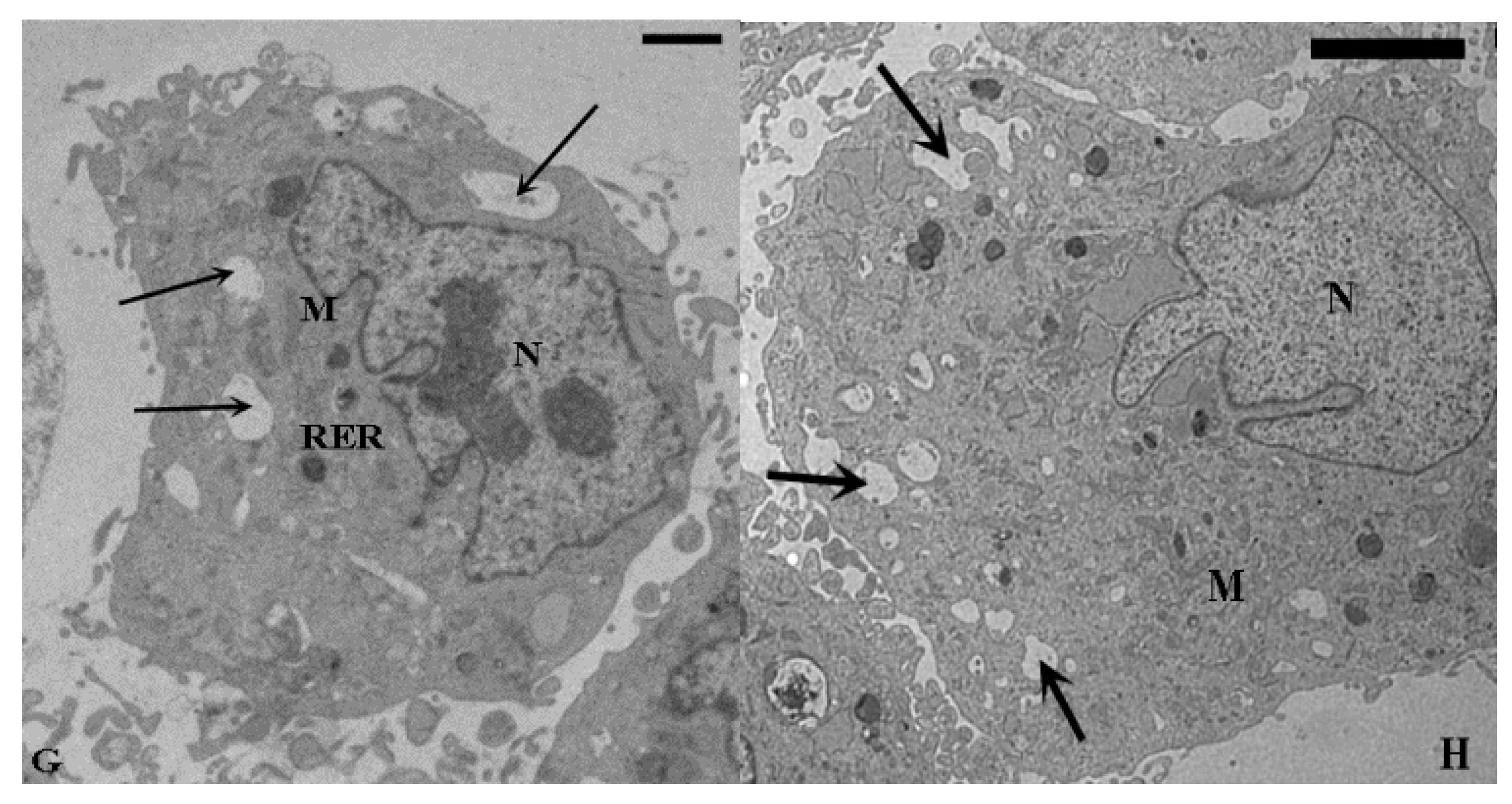
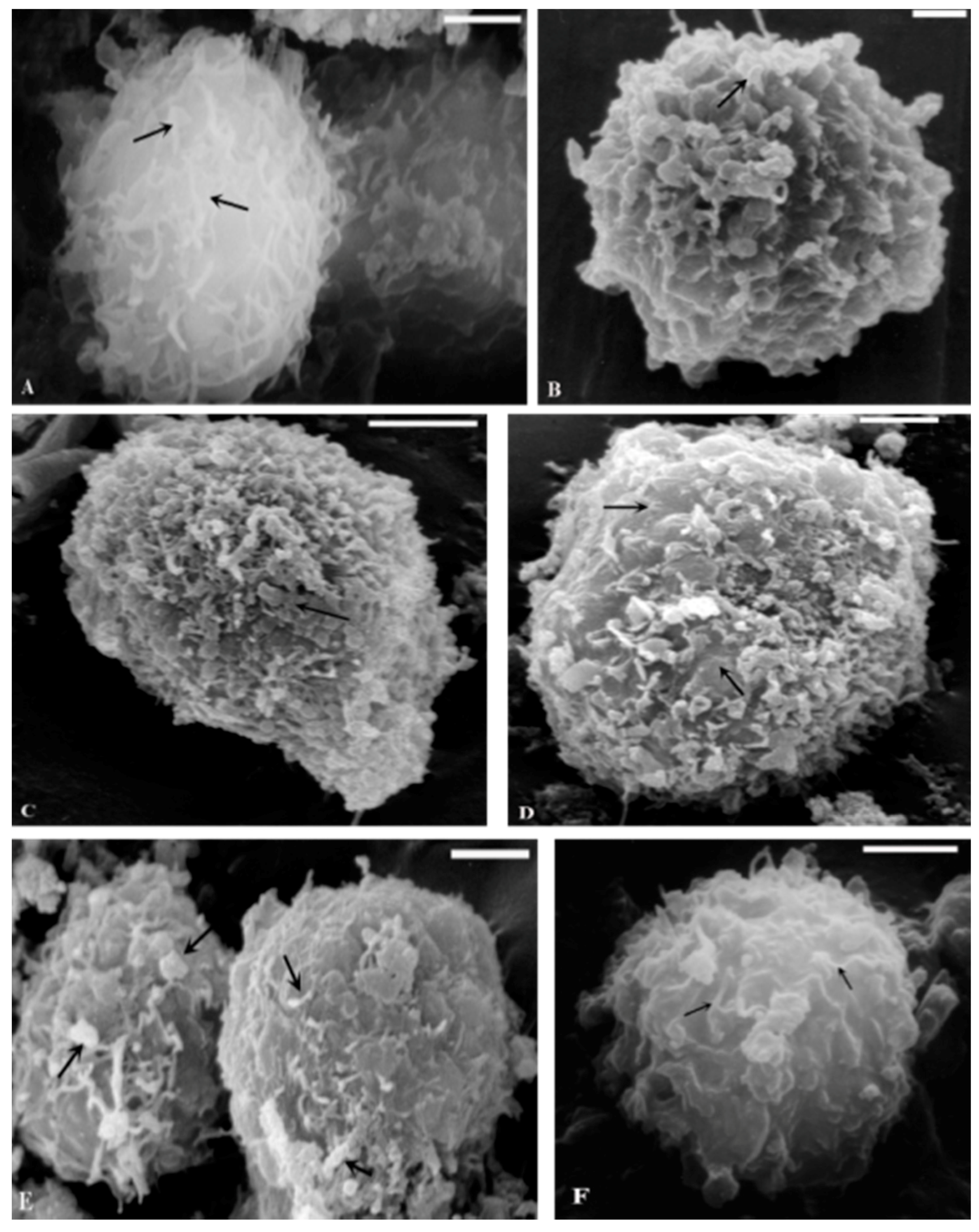
2.1. TEM and SEM Analysis

| Characteristics | Basal | IL-1β | Cyclical HP | Cyclical HP + IL-1β | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | OA | N | OA | N | OA | N | OA | |
| Mitochondria (number per cell) | 7.1 ± 2.5 | 3.3 ± 1.8 ** | 5.3 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 0.9 | 7.7 ± 2.7 | 6.6 ± 2.2 ** | 6 ± 1.4 | 4.1 ± 2.5 * |
| Golgi bodies (number per cell) | 2.7 ± 1.2 | 1.7 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 0.8 ± 2.4 | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 2.7 ± 1.5 | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 2.1 * |
| Vacuolization (>5) (cells %) | 4.9 ± 1.2 | 13 ± 1.2 ** | 11 ± 1.1 | 32.6 ± 1.4 ** | 4.2 ± 0.10 | 9 ± 1.3 | 9 ± 1.2 | 20 ± 1.3 * |
| Marginated Chromatin (cells %) | 5 ± 2.1 | 12 ± 1.7 ** | 10 ± 2.4 | 30 ± 2.7 ** | 5 ± 2.5 | 10 ± 1.9 | 7 ± 2.2 | 18 ± 1.8 * |

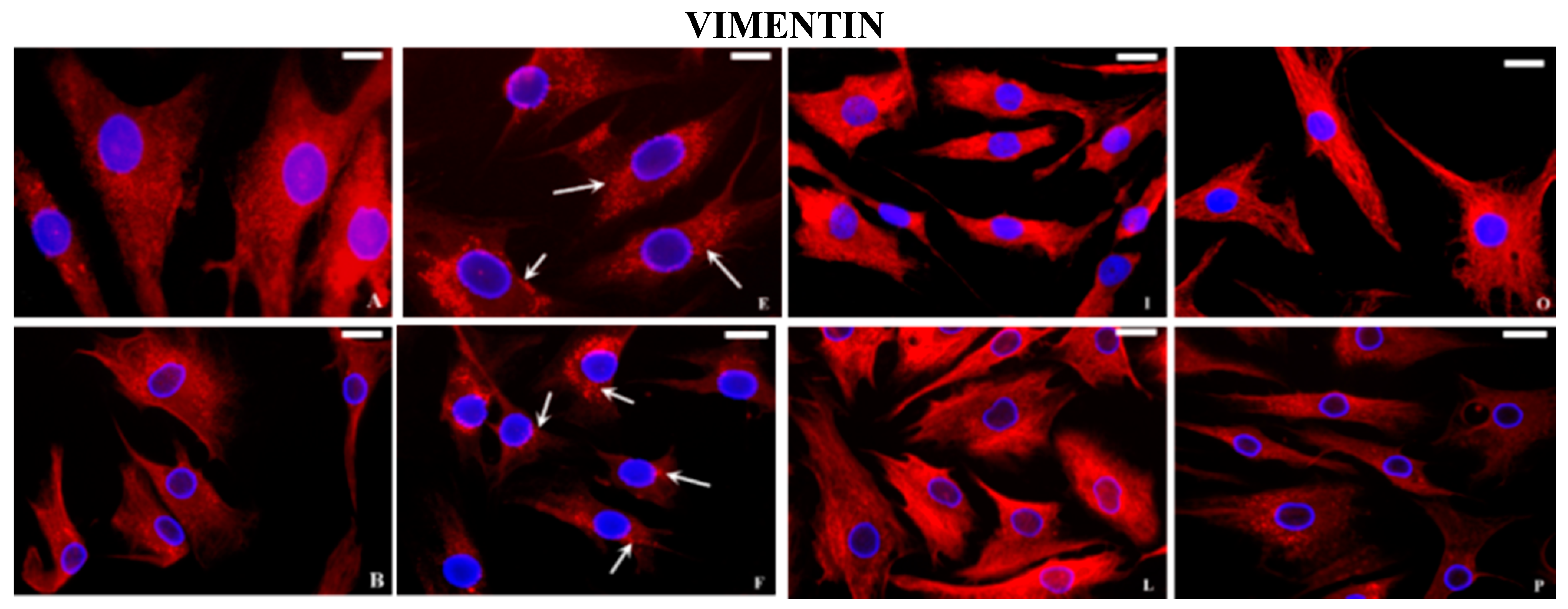
2.2. Immunocytochemical Examination


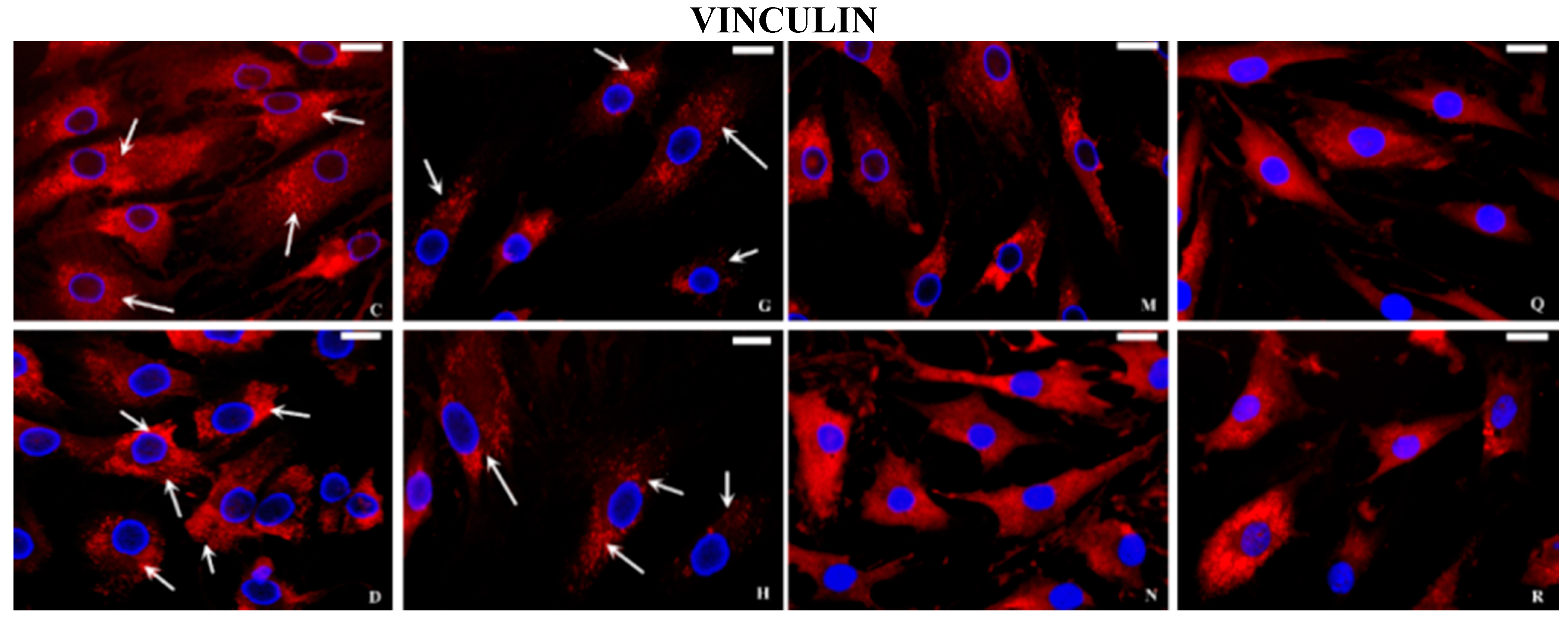
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Pressurization System
4.4. Morphological Analysis
4.5. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
4.6. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.7. Morphometric and Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martel-Pelletier, J.M. Pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2004, 12, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malemud, C.J. Biologic basis of osteoarthritis: State of the evidence. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. The role of cytokines in cartilage matrix degeneration in osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 427, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daheshia, M.; Yao, J.Q. The Interleukin 1β pathway in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Lajeunesse, D.; Pelletier, J.P.; Fahmi, H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, T.; McKenna, L.; Zien, A.; Fan, Z.; Gebhard, P.M.; Zimmer, R. Gene expression profiling of serum- and interleukin-1 β-stimulated primary human adult articular chondrocytes a molecular analysis based on chondrocytes isolated from one donor. Cytokine 2005, 31, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grodzinsky, A.J.; Levenston, M.E.; Jin, M.; Frank, E.H. Cartilage tissue remodeling in response to mechanical forces. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 691–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.B. Mechanical loading, cartilage degradation, and arthritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1211, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkkinen, J.J.; Ikonen, J.; Lammi, M.J.; Laakkonen, J.; Tammi, M.; Helminen, H.J. Effects of cyclic hydrostatic pressure on proteoglycan synthesis in cultured chondrocytes and articular cartilage explants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 300, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, T.; Seedhom, B.B.; Yao, J.Q.; Kirkham, J.; Brookes, S.; Bonass, W.A. Hydrostatic pressure modulates proteoglycan metabolism in chondrocytes seeded in agarose. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, A.; Collodel, G.; Petraglia, A.; Nerucci, F.; Moretti, E.; Galeazzi, M. Effect of hydrostatic pressure of various magnitudes on osteoarthritic chondrocytes exposed to IL-1β. Ind. J. Med. Res. 2010, 132, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Nerucci, F.; Fioravanti, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Collodel, G.; Marcolongo, R. Effects of chondroitin sulfate and interleukin-1beta on human chondrocyte cultures exposed to pressurization: A biochemical and morphological study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2000, 8, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blain, E.J. Involvement of the cytoskeletal elements in articular cartilage homeostasis and pathology. Int. J. Exp. Path. 2009, 90, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trickey, W.R.; Vail, T.P.; Guilak, F. The role of the cytoskeleton in the viscoelastic properties of human articular chondrocytes. J. Orthop. Res. 2004, 22, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capin-Gutierrez, N.; Talamas-Rohana, P.; Gonzalez-Robles, A.; Lavalle-Montalvo, C.; Kouri, J.B. Cytoskeleton disruption in chondrocytes from a rat osteoarthrosic (OA)-induced model: Its potential role in OA pathogenesis. Histol. Histopathol. 2004, 19, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, M.; Archer, C.W.; Ralphs, J.R. Cytoskeleton of cartilage cells. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1994, 28, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langelier, E.; Suetterlin, R.; Hoemann, C.D.; Aebi, U.; Buschmann, M.D. The chondrocyte cytoskeleton in mature articular cartilage: Structure and distribution of actin, tubulin, and vimentin filaments. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshimizu, T.; Kawai, M.; Kondou, H.; Tachikawa, K.; Sakai, N.; Ozono, K.; Michigami, T. Vinculin functions as a regulator of chondrogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15760–15775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, W.H.; Liddington, R.C.; Critchley, D.R. The structure and regulation of vinculin. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, A.; Nerucci, F.; Annefeld, M.; Collodel, G.; Marcolongo, R. Morphological and cytoskeletal aspects of cultivated normal and osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes after cyclical pressure: A pilot study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2003, 21, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hodge, W.A.; Fijan, R.S.; Carlson, K.L.; Burgess, R.G.; Harris, W.H.; Mann, R.W. Contact pressures in the human hip joint measured in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2879–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, A.; Benetti, D.; Coppola, G.; Collodel, G. Effect of continuous high hydrostatic pressure on the morphology and cytoskeleton of normal and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes cultivated in alginate gels. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parkkinen, J.J.; Lammi, M.J.; Pelttari, A.; Helminen, H.J.; Tammi, M.; Virtanen, I. Altered Golgi apparatus in hydrostatically loaded articular cartilage chondrocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1993, 52, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccetti, B.; Collodel, G.; Piomboni, P. Apoptosis in human ejaculated sperm cells. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 1996, 28, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Battistelli, M.; Salucci, S.; Olivotto, E.; Facchini, A.; Minguzzi, M.; Guidotti, S.; Pagani, S.; Flamigni, F.; Borzì, R.M.; Facchini, A.; et al. Cell death in human articular chondrocyte: A morpho-functional study in micromass model. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamli, Z.; Sharif, M. Chondrocyte apoptosis: A cause or consequence of osteoarthritis? Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 14, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotz, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Kühn, K. Mechanisms of chondrocyte apoptosis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 1999, 7, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.A.; Lee, Y.J.; Seong, S.C.; Choe, K.W.; Song, Y.W. Apoptotic chondrocyte death in human osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Héraud, F.; Héraud, A.; Harmand, M.F. Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, N.; Haqqi, T.M.; Jepsen, K.J.; Kraay, M.; Welter, J.F.; Goldberg, V.M.; Malemud, C.J. Hydrostatic pressure induces apoptosis in human chondrocytes from osteoarthritic cartilage through up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α, inducible nitric oxide synthase, p53, c-myc, and bax-α, and suppression of bcl-2. J. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 87, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Arai, Y.; Takahashi, K.A.; Terauchi, R.; Ohashi, S.; Mazda, O.; Imanishi, J.; Inoue, A.; Tonomura, H.; Kubo, T. Hydrostatic pressure induces apoptosis of chondrocytes cultured in alginate beads. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfort, J.; Garcia-Giralt, N.; López-Armada, M.J.; Monllau, J.C.; Bonilla, A.; Benito, P.; Blanco, F.J. Decreased metalloproteinase production as a response to mechanical pressure in human cartilage: A mechanism for homeostatic regulation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jortikka, M.O.; Parkkinen, J.J.; Inkinen, R.I.; Kärner, J.; Järveläinen, H.T.; Nelimarkka, L.O.; Tammi, M.I.; Lammi, M.J. The role of microtubules in the regulation of proteoglycan synthesis in chondrocytes under hydrostatic pressure. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 374, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, L.A.; Archer, C.W.; Benjamin, M.; Ralphs, J.R. Organisation of the chondrocyte cytoskeleton and its response to changing mechanical conditions in organ culture. J. Anat. 1999, 194, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, R. Nitric oxide alters chondrocyte function by disrupting cytoskeletal signaling complexes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 1999, 7, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, S.R.; Clancy, R.M.; Ricci, J.L.; di Cesare, P.E.; Rediske, J.J.; Abramson, S.B. Effects of nitric oxide on chondrocyte migration, adhesion, and cytoskeletal assembly. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckes, B.; Dogic, D.; Colucci-Guyon, E.; Wang, N.; Maniotis, A.; Ingber, D.; Merckling, A.; Langa, F.; Aumailley, M.; Delouvée, A.; et al. Impaired mechanical stability, migration and contractile capacity in vimentin-deficient fibroblasts. J. Cell. Sci. 1998, 111, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holloway, I.; Kayser, M.; Lee, D.A.; Bader, D.L.; Bentley, G.; Knight, M.M. Increased presence of cells with multiple elongated processes in osteoarthritic femoral head cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2004, 12, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, S.; Verbruggen, G.; Verdonk, P.C.; Elewaut, D.; Deforce, D. Differential proteome analysis of normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes reveals distortion of vimentin network in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudenschild, D.R.; Chen, J.; Pang, N.; Steklov, N.; Grogan, S.P.; Lotz, M.K.; D’Lima, D.D. Vimentin contributes to changes in chondrocyte stiffness in osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, H.; Albrecht, W.; Laufer, S.; Reichel, H.; Brenner, R.E. IL-1beta regulates FHL2 and other cytoskeleton-related genes in human chondrocytes. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, S.; Guilak, F. Effects of interleukin-1 on calcium signaling and the increase of filamentous actin in isolated and in situ articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, M.M.; Toyoda, T.; Lee, D.A.; Bader, D.L. Mechanical compression and hydrostatic pressure induce reversible changes in actin cytoskeletal organisation in chondrocytes in agarose. J. Biochem. 2006, 39, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriega, S.; Hasanova, G.; Subramanian, A. The effect of ultrasound stimulation on the cytoskeletal organization of chondrocytes seeded in three-dimensional matrices. Cells Tissues Organs 2013, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkkinen, J.J.; Lammi, M.J.; Inkinen, R.; Jortikka, M.; Tammi, M.; Virtanen, I.; Helminen, H.J. Influence of short-term hydrostatic pressure on organisation of stress fibres in cultured chondrocytes. J. Orthop. Res. 1995, 13, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, G.R.; Northrup, D.L.; Guilak, F. Hypo-osmotic stress induces calcium-dependent actin reorganization in articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, P.H.; West, A.C.; Hung, C.T. Chondrocyte intracellular calcium, cytoskeletal organization, and gene expression responses to dynamic osmotic loading. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, L.; Nuki, G.; Salter, D.M. Signalling cascades in mechanotransduction: Cell-matrix interactions and mechanical loading. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.R.; Kinight, M.M.; Lee, D.A.; Bader, D.L. Mechanical compression influences intracellular Ca2+ signaling in chondrocytes seeded in agarose constructs. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elder, B.D.; Athanasiou, K.A. Hydrostatic pressure in articular cartilage tissue engneering: From chondrocytes to tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2009, 15, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.B.; Jin, M.; Dean, D.; Wood, D.J.; Zheng, M.H.; Grodzinsky, A.J. Mechanical compression of cartilage explants induce multiple time-dependent gene expression patterns and involves intracellular calcium and cyclic AMP. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19502–19511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafeber, F.; Veldhuijzen, J.P.; Vanroy, J.L.; Huber-Bruning, O.; Bijlsma, J.W. Intermittent hydrostatic compressive force stimulates exclusively the proteoglycan synthesis of ostearthritic human cartilage. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 31, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward, A.J.; Wagner, D.R.; Kelly, D.J. The pericellular environment regulates cytoskeletal development and the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and determines their response to hydrostatic pressure. Eur. Cells Mater. 2013, 25, 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, R.; Alarcon, G.; Appelrouth, D.; Bloch, D.; Borestein, D.; Brandt, K.; Brown, C.; Cooke, T.D.; Daniel, W.; Feldman, D.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankin, H.J.; Dorfman, H.; Lippiello, L.; Zarins, A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteoarthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1971, 53A, 523–537. [Google Scholar]
- Nerucci, F.; Fioravanti, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Spinelli, G.; Marcolongo, R. Preparation of a pressurization system to study the effect of hydrostatic pressure on chondrocyte cultures. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1998, 34, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.K. A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell. Biol. 1965, 27, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Annefeld, M. A new test method for the standardized evaluation of changes in the ultrastructure of chondrocytes. Int. J. Tissue React. 1985, 7, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collodel, G.; Fioravanti, A.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Lamboglia, A.; Fontani, V.; Maioli, M.; Santaniello, S.; Pigliaru, G.; Castagna, A.; Moretti, E.; et al. Effects of regenerative radioelectric asymmetric conveyer treatment on human normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes exposed to IL-1β. A biochemical and morphological study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pascarelli, N.A.; Collodel, G.; Moretti, E.; Cheleschi, S.; Fioravanti, A. Changes in Ultrastructure and Cytoskeletal Aspects of Human Normal and Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Exposed to Interleukin-1β and Cyclical Hydrostatic Pressure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26019-26034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125936
Pascarelli NA, Collodel G, Moretti E, Cheleschi S, Fioravanti A. Changes in Ultrastructure and Cytoskeletal Aspects of Human Normal and Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Exposed to Interleukin-1β and Cyclical Hydrostatic Pressure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(11):26019-26034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125936
Chicago/Turabian StylePascarelli, Nicola Antonio, Giulia Collodel, Elena Moretti, Sara Cheleschi, and Antonella Fioravanti. 2015. "Changes in Ultrastructure and Cytoskeletal Aspects of Human Normal and Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Exposed to Interleukin-1β and Cyclical Hydrostatic Pressure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 11: 26019-26034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125936
APA StylePascarelli, N. A., Collodel, G., Moretti, E., Cheleschi, S., & Fioravanti, A. (2015). Changes in Ultrastructure and Cytoskeletal Aspects of Human Normal and Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Exposed to Interleukin-1β and Cyclical Hydrostatic Pressure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(11), 26019-26034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125936









