Benzene-Induced Aberrant miRNA Expression Profile in Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Body Weight and Organ Coefficient

| Group | Liver/Body Weight | Spleen/Body Weight | Thymus/Body Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 4.67 ± 0.55 | 0.38 ± 0.10 | 0.15 ± 0.03 |
| Benzene | 5.46 ± 0.26 * | 0.32 ± 0.12 | 0.12 ± 0.02 * |
2.2. Hematological Parameters
| Group | WBC (109/L) | RBC (1012/L) | Hb (g/L) | Plt (109/L) | Neut (109/L) | Lym (109/L) | MCV (fL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8.49 ± 1.25 | 10.11 ± 1.55 | 149.34 ± 20.53 | 715.13 ± 137.46 | 1.35 ± 0.56 | 6.03 ± 1.35 | 51.98 ± 1.15 |
| Benzene | 3.84 ± 1.17 * | 8.97 ± 0.53 * | 136.13 ± 8.24 | 863.72 ± 71.18 * | 0.99 ± 0.39 * | 2.84 ± 0.85 * | 55.9 ± 1.01 * |
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis of HSPCs
| Group | Lin− Cells | Lin−c-Kit+ Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 16026.64 ± 3774.60 | 2465.36 ± 546.65 |
| Benzene | 12339.45 ± 6566.61 | 1307.46 ± 584.37 * |
2.4. Aberrant miRNA Expression Based on Sequencing

| miRNA_ID | Control | Benzene | |log2 (Fold Change)| | p-Value | Significance-Lable | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-17-3p | 83.7974 | 35.1372 | 1.253906 | 0.0114 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-28a-3p | 23.3702 | 8.7843 | 1.411671 | 0.0239 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-29a-3p | 121.5766 | 55.9239 | 1.120329 | 0.0201 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-29c-3p | 1009.316 | 466.1916 | 1.114384 | 0.00865 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-33-5p | 1.6325 | 0 | 13.9948 | 0.0475 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-99a-5p | 624.7338 | 97.3232 | 2.682386 | 0.000487 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-99b-5p | 13.7108 | 3.5659 | 1.942975 | 0.000161 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-100-5p | 2226.083 | 288.6646 | 2.947041 | 0.0000316 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-125a-5p | 61.9113 | 12.6981 | 2.28559 | 0.000129 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-126a-3p | 200.2112 | 77.4933 | 1.369379 | 0.00904 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-126a-5p | 30.3297 | 10.5238 | 1.527075 | 0.0106 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-128-1-5p | 1.4606 | 0 | 13.83427 | 0.000663 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-141-3p | 90.3593 | 26.266 | 1.782477 | 0.000172 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-181a-1-3p | 69.7313 | 20.508 | 1.76562 | 0.00506 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-181d-5p | 1144.295 | 380.4057 | 1.588848 | 0.0000964 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-181a-5p | 5882.768 | 2099.102 | 1.486723 | 0.024 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-181b-1-3p | 28.9987 | 6.5003 | 2.15741 | 0.0188 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-181c-3p | 134.7541 | 46.3262 | 1.540429 | 0.0112 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-188-5p | 0.9368 | 0 | 13.19353 | 0.0147 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-191-5p | 3285.317 | 1517.686 | 1.114159 | 0.0473 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-196b-5p | 34.9694 | 5.3101 | 2.719282 | 0.000407 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-199b-5p | 7.0255 | 3.2044 | 1.132547 | 0.0498 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-203-3p | 125.1852 | 31.8607 | 1.974214 | 0.00191 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-211-5p | 1.117 | 0 | 13.44734 | 0.00186 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-224-5p | 8.4455 | 0 | 16.3659 | 0.000949 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-324-3p | 59.3565 | 28.7012 | 1.048295 | 0.0416 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-342-5p | 11.1361 | 5.3923 | 1.046271 | 0.0338 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-342-3p | 403.5655 | 175.4169 | 1.202015 | 0.00359 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-425-3p | 49.5631 | 20.7827 | 1.253883 | 0.024 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-455-5p | 103.3616 | 26.2759 | 1.975888 | 0.0167 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-455-3p | 14.3486 | 3.2959 | 2.122166 | 0.0034 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-504-5p | 3.5127 | 0 | 15.10029 | 0.000458 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-592-5p | 71.7493 | 5.0445 | 3.830182 | 0.000744 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-671-3p | 8.6863 | 3.0213 | 1.523572 | 0.0323 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-872-5p | 68.65 | 26.0013 | 1.400676 | 0.00157 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-874-3p | 5.8296 | 2.3421 | 1.315594 | 0.00755 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-1291 | 5.1552 | 2.0874 | 1.304321 | 0.00577 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-3060-5p | 1.1071 | 0 | 13.4345 | 0.000621 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-5104 | 2.3198 | 1.0986 | 1.078334 | 0.0317 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-5107-3p | 1.2706 | 0 | 13.63322 | 0.00982 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-5120 | 1.1922 | 0 | 13.54134 | 0.0195 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-6988-3p | 5.0244 | 1.9226 | 1.385893 | 0.00503 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-7043-3p | 22.7206 | 11.078 | 1.036303 | 0.00864 | ** | down |
| mmu-miR-7649-5p | 8.3457 | 2.3483 | 1.829416 | 0.0346 | * | down |
| mmu-let-7i-3p | 1.0463 | 0 | 13.35301 | 0.0185 | * | down |
| mmu-miR-34a-5p | 15.3215 | 83.1308 | 2.439826 | 0.0075 | ** | up |
| mmu-miR-129b-5p | 0 | 3.7399 | 15.19071 | 0.00879 | ** | up |
| mmu-miR-451a | 4681.085 | 14232.5 | 1.604274 | 0.0241 | * | up |
| mmu-miR-144-5p | 46.7118 | 120.2277 | 1.36391 | 0.0251 | * | up |
| mmu-miR-129b-3p | 4.4096 | 18.7862 | 2.090954 | 0.0211 | * | up |
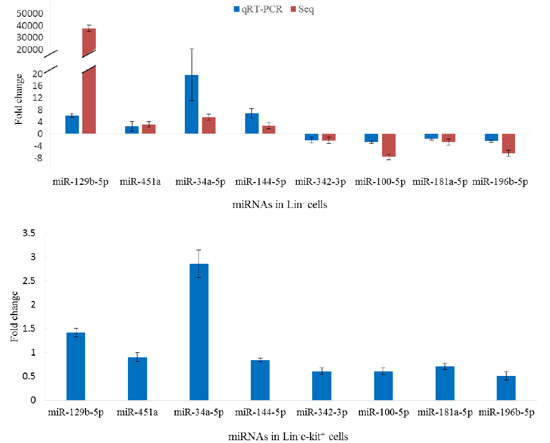
2.5. Validation of miRNA Sequencing

2.6. Aberrant Expression of miRNAs in Lin−c-Kit+ Cells of Mice Exposed to Benzene

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Benzene Exposure
4.3. Organ Coefficient and Hematological Parameters
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis

4.5. Sorting of HSPCs through Flow Cytometry and Total RNA Extraction
4.6. Illumina Sequencing of miRNAs
4.7. Verification of Sequencing through qRT-PCR Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.H.; Ye, L.L.; Wang, J.W.; Ren, J.C.; Xu, X.W.; Feng, N.N.; Zhou, L.F.; Ru, J.G.; Hao, Y.H.; Tian, W.; et al. Effect of polymorphic metabolizing genes on micronucleus frequencies among benzene-exposed shoe workers in China. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, F.; Alves, G.; Otero, U.B.; Tabalipa, M.M.; Scherrer, L.R.; Kosyakova, N.; Ornellas, M.H.; Liehr, T. Monitoring of gas station attendants exposure to benzene, toluene, xylene (BTX) using three-color chromosome painting. Mol. Cytogenet. 2014, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protano, C.; Andreoli, R.; Manini, P.; Guidotti, M.; Vitali, M. A tobacco-related carcinogen: assessing the impact of smoking behaviours of cohabitants on benzene exposure in children. Tob. Control. 2012, 21, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protano, C.; Andreoli, R.; Manini, P.; Vitali, M. Urinary trans, trans-muconic acid and S-phenylmercapturic acid are indicative of exposure to urban benzene pollution during childhood. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, N.O.F.; Kassem, N.O.; Jackson, S.R.; Liles, S.; Daffa, R.M.; Zarth, A.T.; Younis, M.A.; Carmella, S.G.; Hofstetter, C.R.; Chatfield, D.A.; et al. Benzene Uptake in Hookah Smokers and Non-smokers Attending Hookah Social Events: Regulatory Implications. Cancer Epidemol. Biomark. 2014, 23, 2793–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protano, C.; Guidotti, M.; Manini, P.; Petyx, M.; la Torre, G.; Vitali, M. Benzene exposure in childhood: Role of living environments and assessment of available tools. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Han, Q.L.; Wang, J.; Suriguga; Li, Y.; Yu, C.H.; Li, Y.R.; Yi, Z.C. Phenolic Metabolites of Benzene Induced Caspase-Dependent Cytotoxicities to K562 Cells Accompanied with Decrease in Cell Surface Sialic Acids. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Lai, Y.M.; Hu, K.Q.; Wei, Q.Z.; Liu, Y.G. Human CYP2E1-dependent and human sulfotransferase 1A1-modulated induction of micronuclei by benzene and its hydroxylated metabolites in Chinese hamster V79-derived cells. Mutat. Res. 2014, 770, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, L.P.; Lee, K.M.; Vermeulen, R.; Hosgood, H.D.; Li, G.L.; Yin, S.N.; Rothman, N.; Chanock, S.; Smith, M.T.; et al. Polymorphisms in genes involved in innate immunity and susceptibility to benzene-induced hematotoxicity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Niu, Y.Z.; Liu, S.C.; Yu, W.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.W.; Chen, S.H.; Yang, L.J.; Li, Y.Q. A change in CD3γ, CD3δ, CD3ε, and CD3ζ gene expression in T-lymphocytes from benzene-exposed and benzene-poisoned workers. J. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 9, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Zheng, T.; Lan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Q.; Bi, X.; Kim, C.; Holford, T.; Leaderer, B.; Boyle, P.; et al. Occupational solvent exposure, genetic variation of DNA repair genes, and the risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 21, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnatter, A.R.; Glass, D.C.; Tang, G.; Irons, R.D.; Rushton, L. Myelodysplastic syndrome and benzene exposure among petroleum workers: an international pooled analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaanderen, J.; Lan, Q.; Kromhout, H.; Rothman, N.; Vermeulen, R. Occupational benzene exposure and the risk of chronic myeloid leukemia: a meta-analysis of cohort studies incorporating study quality dimensions. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2012, 55, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.C.; Weiler, J.; Grosshans, H. Regulating the regulators: mechanisms controlling the maturation of microRNAs. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.P.; Lau, N.C.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Grimson, A.; Schelter, J.M.; Castle, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Linsley, P.S.; Johnson, J.M. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 2005, 433, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.J.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Bettinger, J.C.; Rougvie, A.E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Ferracin, M.; Cimmino, A.; di Leva, G.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Iorio, M.V.; Visone, R.; Sever, N.I.; Fabbri, M.; et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.M.; Byrom, M.W.; Shelton, J.; Ford, L.P. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saal, S.; Harvey, S.J. MicroRNAs and the kidney: coming of age. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Ridzon, D.; Wong, L.; Chen, C. Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, S.; Ruohola-Baker, H. microRNA and stem cell function. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 331, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapetrou, E.P.; Korkola, J.E.; Sadelain, M. A genetic strategy for single and combinatorial analysis of miRNA function in mammalian hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Lou, G.; Chen, M.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S. MicroRNAs play a role in the development of human hematopoietic stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Gopalan, V.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K. miR-126 in human cancers: clinical roles and current perspectives. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 96, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asslaber, D.; Pinon, J.D.; Seyfried, I.; Desch, P.; Stocher, M.; Tinhofer, I.; Egle, A.; Merkel, O.; Greil, R. microRNA-34a expression correlates with MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism and treatment-free survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 4191–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X. RDX induces aberrant expression of microRNAs in mouse brain and liver. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. Expression profiling and pathway analysis of microRNA expression in the lungs of mice exposed to long-term, low-dose benzo(a)pyrene. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Niu, P.; Tian, L.; Gao, A. Aberrant miRNA profiles associated with chronic benzene poisoning. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 96, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Tsujimura, N.; Yoshino, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Otsuka, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Nakasono, S. Assessment of benzene-induced hematotoxicity using a human-like hematopoietic lineage in NOD/Shi-scid/IL-2Rgammanull mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.K.; Faiola, B.; Abernethy, D.J.; Marchan, R.; Pluta, L.J.; Wong, V.A.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Butterworth, B.E.; Borghoff, S.J.; Everitt, J.I.; et al. Male mice deficient in microsomal epoxide hydrolase are not susceptible to benzene-induced toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 72, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiola, B.; Bauer, A.K.; Fuller, E.S.; Wong, V.A.; Pluta, L.J.; Abernethy, D.J.; Mangum, J.B.; Everitt, J.I.; Recio, L. Variations in Prkdc and susceptibility to benzene-induced toxicity in mice. Toxicol. Sci 2003, 75, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Hirabayashi, Y. Hematopoietic neoplastic diseases develop in C3H/He and C57BL/6 mice after benzene exposure: strain differences in bone marrow tissue responses observed using microarrays. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Kanno, J.; Kodama, Y.; Matsushima, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Saitoh, M.; Sekita, K.; Uchida, O.; et al. Benzene-induced hematopoietic neoplasms including myeloid leukemia in Trp53-deficient C57BL/6 and C3H/He mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.S.; Zhao, M.D.; Shi, J.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, B.; Fan, W.; Zhou, Y.L. Expression of multidrug resistance 1 and multidrug resistance-related protein 1 in C57BL/6 mice treated with benzene. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 5842–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, S.; Liang, W. Clinical analysis of 43 cases of chronic benzene poisoning. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2005, 153, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Inoue, T. Benzene-induced bone-marrow toxicity: a hematopoietic stem-cell-specific, aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated adverse effect. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedstrom, G.; Thunberg, U.; Berglund, M.; Simonsson, M.; Amini, R.M.; Enblad, G. Low expression of microRNA-129–5p predicts poor clinical outcome in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 97, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, F.; Cao, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, B.; Dong, W.; Gu, W.; Ling, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Identification of circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for detecting acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svasti, S.; Masaki, S.; Penglong, T.; Abe, Y.; Winichagoon, P.; Fucharoen, S.; Umemura, T. Expression of microRNA-451 in normal and thalassemic erythropoiesis. Ann. Hematol. 2010, 89, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmar, F.; Hother, C.; Kulosman, G.; Treppendahl, M.B.; Nielsen, H.M.; Ralfkiaer, U.; Pedersen, A.; Moller, M.B.; Ralfkiaer, E.; de Nully Brown, P.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with combined TP53 mutation and MIR34A methylation: Another “double hit” lymphoma with very poor outcome? Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1912–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchis, M.L.; Ballarino, M.; Salvatori, B.; Puzzolo, M.C.; Bozzoni, I.; Fatica, A. A new molecular network comprising PU.1, interferon regulatory factor proteins and miR-342 stimulates ATRA-mediated granulocytic differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2009, 23, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, E.; Neumann, M.; Schlee, C.; Liebertz, F.; Heesch, S.; Goekbuget, N.; Hoelzer, D.; Baldus, C.D. MicroRNA profiling reveals aberrant microRNA expression in adult ETP-ALL and functional studies implicate a role for miR-222 in acute leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.J.; Feng, D.D.; Luo, X.Q.; Zeng, C.W.; Lin, K.Y.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Zhang, P.; et al. MiR-100 regulates cell differentiation and survival by targeting RBSP3, a phosphatase-like tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2012, 31, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari Moqadam, F.; Lange-Turenhout, E.A.; Aries, I.M.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L. MiR-125b, miR-100 and miR-99a co-regulate vincristine resistance in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Pan, L.; Guo, S.; Wu, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, S. Prognostic role of microRNA-181a/b in hematological malignancies: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debernardi, S.; Skoulakis, S.; Molloy, G.; Chaplin, T.; Dixon-McIver, A.; Young, B.D. MicroRNA miR-181a correlates with morphological sub-class of acute myeloid leukaemia and the expression of its target genes in global genome-wide analysis. Leukemia 2007, 21, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, A.; Nomdedeu, B.; Navarro, A.; Gaya, A.; Gel, B.; Diaz, T.; Valera, S.; Rozman, M.; Belkaid, M.; Montserrat, E.; et al. Hematopoiesis-related microRNA expression in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 1854–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichiorri, F.; Suh, S.S.; Ladetto, M.; Kuehl, M.; Palumbo, T.; Drandi, D.; Taccioli, C.; Zanesi, N.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; et al. MicroRNAs regulate critical genes associated with multiple myeloma pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12885–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.X.; Zhu, W.; Fang, C.; Fan, L.; Zou, Z.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, P.; Hong, M.; Miao, K.R.; Liu, P.; et al. miR-181a/b significantly enhances drug sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via targeting multiple anti-apoptosis genes. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Z.; Li, L.; Lodish, H.F.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; McClellan, S.; Finan, M.A.; Butler, T.W.; Owen, L.B.; Piazza, G.A.; Xi, Y. MiR-181 mediates cell differentiation by interrupting the Lin28 and let-7 feedback circuit. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Rao, D.S.; Gibson, W.S.; Balazs, A.B.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNAs enriched in hematopoietic stem cells differentially regulate long-term hematopoietic output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14235–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchova-Votavova, H.; Yoon, D.; Prchal, J.T. miR-451 enhances erythroid differentiation in K562 cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2010, 51, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.Y.; Tan, K.H.; Sun, R.L.; Yin, L.H.; Zhang, J.; Pu, Y.P. Aberrant Production of Th1/Th2/Th17-Related Cytokines in Serum of C57BL/6 Mice after Short-Term Formaldehyde Exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 10036–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Guo, L.Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.H.; Huang, W.T.; Wang, L.P.; Yang, T.; et al. Comparison of toxicity of benzene metabolite hydroquinone in hematopoietic stem cells derived from murine embryonic yolk sac and adult bone marrow. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, F.; Gutman, D.; Meire, E.; Caceres, M.; Rigoutsos, I.; Bentwich, Z.; Lieberman, J. miR-34a contributes to megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells independently of p53. Blood 2009, 114, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; Tan, K.; Sun, R.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Benzene-Induced Aberrant miRNA Expression Profile in Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells in C57BL/6 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27058-27071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126001
Wei H, Zhang J, Tan K, Sun R, Yin L, Pu Y. Benzene-Induced Aberrant miRNA Expression Profile in Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells in C57BL/6 Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(11):27058-27071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126001
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Haiyan, Juan Zhang, Kehong Tan, Rongli Sun, Lihong Yin, and Yuepu Pu. 2015. "Benzene-Induced Aberrant miRNA Expression Profile in Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells in C57BL/6 Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 11: 27058-27071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126001
APA StyleWei, H., Zhang, J., Tan, K., Sun, R., Yin, L., & Pu, Y. (2015). Benzene-Induced Aberrant miRNA Expression Profile in Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells in C57BL/6 Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(11), 27058-27071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126001