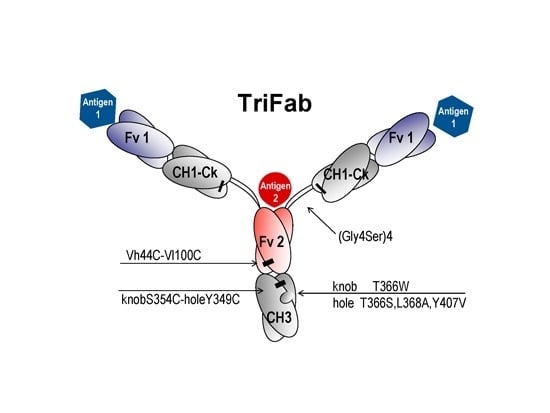
TriFabs—Trivalent IgG-Shaped Bispecific Antibody Derivatives: Design, Generation, Characterization and Application for Targeted Payload Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
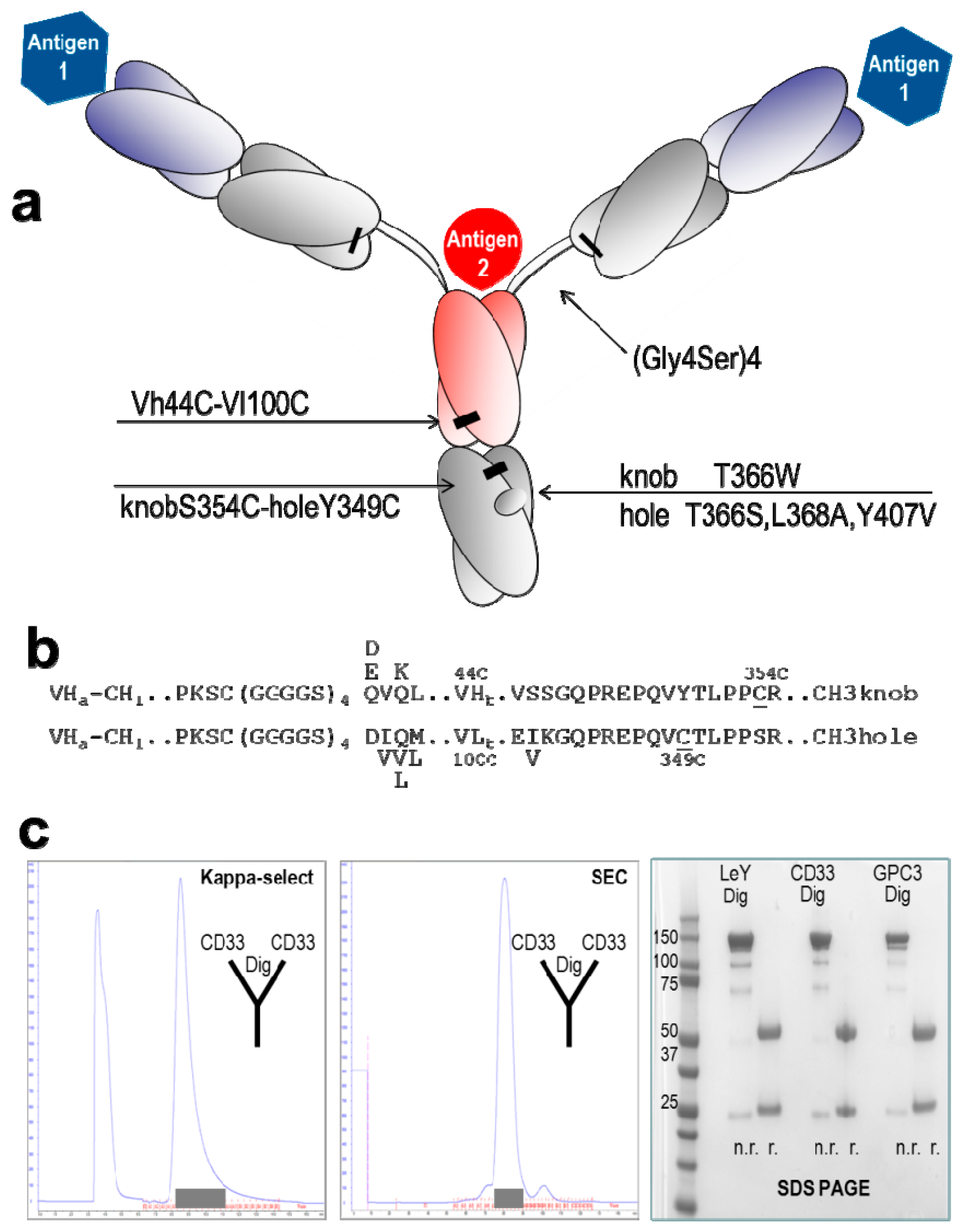
2.1. Design and Generation of TriFabs
2.2. Stability of TriFabs
| TriFab | Tagg (°C) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| CD33-CD33-Bio | 57 | 58 |
| CD33-CD33-Dig | 51 | 66 |
| GPC3-GPC3-Bio | 56 | 58 |
| GPC3-GPC3-Dig | 61 | 65 |
| LeY-LeY-Bio | 52 | 59 |
| LeY-LeY-Dig | 60 | 66 |
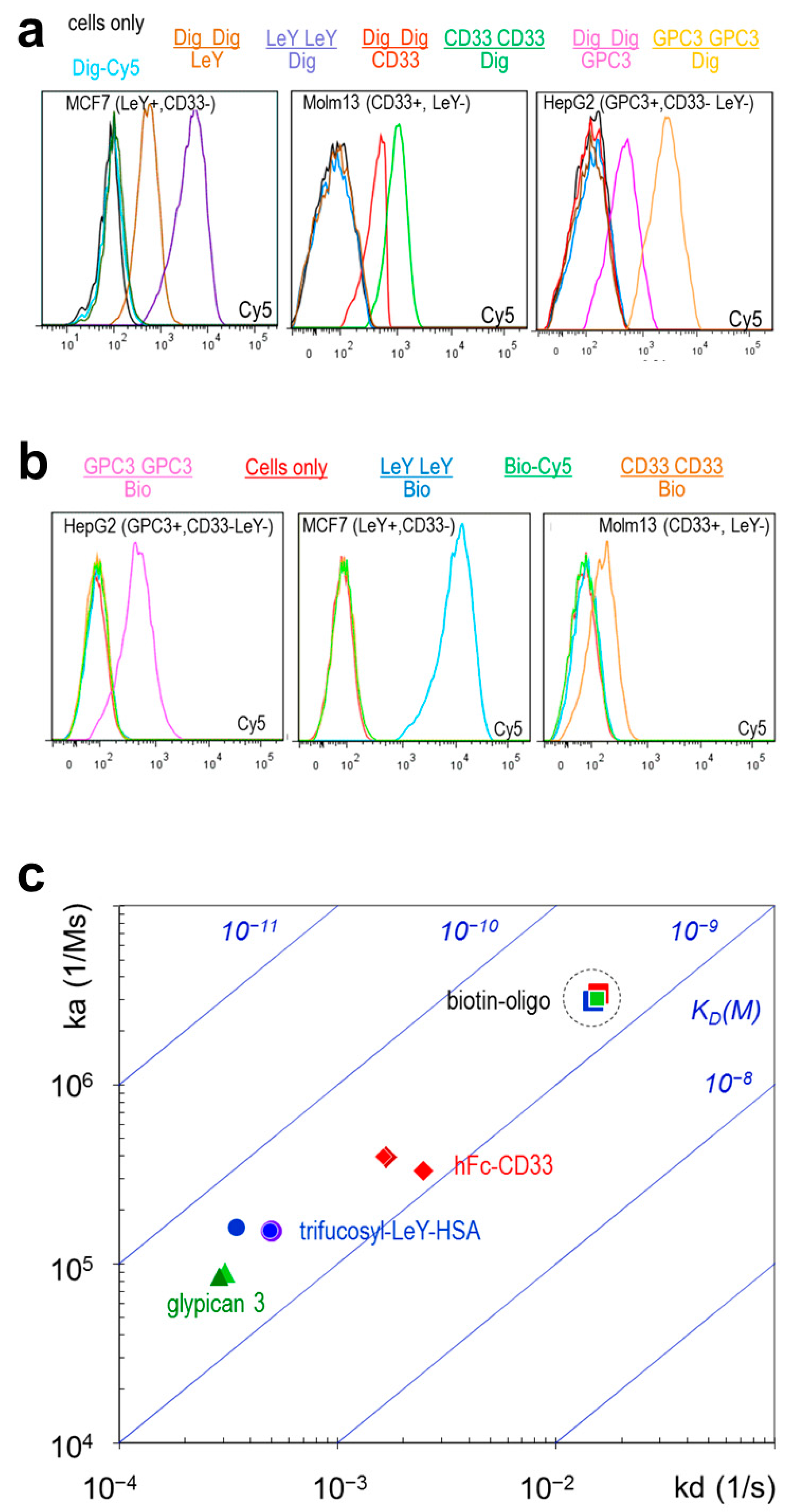
2.3. TriFabs Retain the Binding Properties of Two Antibodies
| Format | SPR | LeY Arm | GPC3 Arm | CD33 Arm | CD33 Stem | Dig Stem | Bio Stem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG | ka (1/Ms) | 1.5 × 105 | 8.5 × 104 | 3.9 × 105 | 1.9 × 105 (Fab) | 6.2 × 105 * | 2.0 × 107 * |
| Kd (1/s) | 5.0 × 10−4 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 1.7 × 10−3 | 6.4 × 10−3 (Fab) | 9.8 × 10−3 × * | 1.0 × 10−2 * | |
| KD (M) | 3.3 × 10−9 | 3.4 × 10−9 | 4.3 × 10−9 | 3.4 × 10−8 (Fab) | 1.6 × 10−8 × * | 6.2 × 10−10 * | |
| TriFab | ka (1/Ms) | 1.5 × 105 | 8.6 × 104 | 4.0 × 105 | 2.4 × 105 | 5.3 × 105 | 2.9 × 106 |
| Kd (1/s) | 4.9 × 10−4 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 1.6 × 10−3 | 7.5 × 10−3 | 5.2 × 10−3 | 1.5 × 10−2 | |
| KD (M) | 3.2 × 10−9 | 3.4 × 10−9 | 4.1 × 10−9 | 3.1 × 10−8 | 9.8 × 10−9 | 5.1 × 10−9 |
2.4. TriFabs Enable Tumor Targeted Payload Delivery of Small Compounds
2.5. TriFabs Enable Tumor Targeted Payload Delivery of Protein Toxins


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Expression of TriFabs
3.2. Purification of TriFabs
3.3. Characterization of TriFabs
3.4. Stability Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kontermann, R.E.; Brinkmann, U. Bispecific antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidle, U.H.; Kontermann, R.E.; Brinkmann, U. Tumor-antigen-binding bispecific antibodies for cancer treatment. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Ying, H.; Grinnell, C.; Bryant, S.; Miller, R.; Clabbers, A.; Bose, S.; McCarthy, D.; Zhu, R.R.; Santora, L.; et al. Simultaneous targeting of multiple disease mediators by a dual-variable-domain immunoglobulin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, S.; Panke, C.; Haas, A.K.; Schanzer, J.; Lau, W.; Croasdale, R.; Hoffmann, E.; Schneider, B.; Auer, J.; Gassner, C.; et al. Bispecific antibody derivatives with restricted binding functionalities that are activated by proteolytic processing. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 25, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Reinhardt, C. Bispecific T-cell engaging antibodies for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4941–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontermann, R.E.; Wing, M.G.; Winter, G. Complement recruitment using bispecific diabodies. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merchant, A.M.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, J.Q.; Goddard, A.; Adams, C.W.; Presta, L.G.; Carter, P. An efficient route to human bispecific IgG. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.; Wu, T.T. Kabat database and its applications: 30 years after the first variability plot. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.; Sustmann, C.; Thomas, M.; Stubenrauch, K.; Croasdale, R.; Schanzer, J.; Brinkmann, U.; Kettenberger, H.; Regula, J.T.; Schaefer, W. Progress in overcoming the chain association issue in bispecific heterodimeric IgG antibodies. MAbs 2012, 4, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, Y.; Brinkmann, U.; Jung, S.H.; Pastan, I.; Lee, B. Disulfide stabilization of antibody Fv: Computer predictions and experimental evaluation. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, S.; Haas, A.K.; Daub, K.; Croasdale, R.; Stracke, J.; Lau, W.; Georges, G.; Josel, H.P.; Dziadek, S.; Hopfner, K.P.; et al. Bispecific digoxigenin-binding antibodies for targeted payload delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8194–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Nakano, K.; Tsunoda, H.; Sugo, I.; Ohizumi, I.; Aburatani, H.; Hamakubo, T.; et al. Anti-glypican 3 antibody as a potential antitumor agent for human liver cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9832–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengl, S.; Hoffmann, E.; Grote, M.; Wagner, C.; Mundigl, O.; Georges, G.; Thorey, I.; Stubenrauch, K.G.; Bujotzek, A.; Josel, H.P.; et al. Hapten-directed spontaneous disulfide shuffling: a universal technology for site-directed covalent coupling of payloads to antibodies. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1763–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, E.; Konkar, A.; Dziadek, S.; Josel, H.P.; Conde-Knape, K.; Kropp, H.; Kling, L.; Stubenrauch, K.; Thorey, I.; Dengl, S.; et al. PK modulation of haptenylated peptides via non-covalent antibody complexation. J. Control. Release 2013, 171, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.; Grote, M.; John, M.; Haas, A.; Bramlage, B.; Ickenstein, L.M.; Jahn-Hofmann, K.; Bauss, F.; Cheng, W.; Croasdale, R.; et al. Targeted siRNA delivery and mRNA knockdown mediated by bispecific digoxigenin-binding antibodies. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feige, M.J.; Hendershot, L.M.; Buchner, J. How antibodies fold. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertz, M.; Buchner, J.; Rief, M. Mechanical stability of the antibody domain CH3 homodimer in different oxidation states. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15085–15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarasch, A.; Koll, H.; Regula, J.T.; Bader, M.; Papadimitriou, A.; Kettenberger, H. Developability assessment during the selection of novel therapeutic antibodies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewert, S.; Huber, T.; Honegger, A.; Plückthun, A. Biophysical properties of human antibody variable domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Hogan, S.; Latypov, R.F.; Narhi, L.O.; Razinkov, V.I. High throughput thermostability screening of monoclonal antibody formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidle, U.H.; Tiefenthaler, G.; Schiller, C.; Weiss, E.H.; Georges, G.; Brinkmann, U. Prospects of bacterial and plant protein-based immunotoxins for treatment of cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2014, 11, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Idusogie, E.E.; Presta, L.G.; Gazzano-Santoro, H.; Totpal, K.; Wong, P.Y.; Ultsch, M.; Meng, Y.G.; Mulkerrin, M.G. Mapping of the C1q binding site on rituxan, a chimeric antibody with a human IgG1 Fc. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4178–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLano, W.L.; Ultsch, M.H.; de vos, A.M.; Wells, J.A. Convergent solutions to binding at a protein-protein interface. Science 2000, 287, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graille, M.; Stura, E.A.; Corper, A.L.; Sutton, B.J.; Taussig, M.J.; Charbonnier, J.B.; Silverman, G.J. Crystal structure of a Staphylococcus aureus protein A domain complexed with the Fab fragment of a human IgM antibody: structural basis for recognition of B-cell receptors and superantigen activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5399–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roopenian, D.C.; Akilesh, S. FcRn: The neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, V.; Palma, E.; Tesar, D.B.; Mundo, E.E.; Bumbaca, D.; Torres, E.K.; Reyes, N.A.; Shen, B.Q.; Fielder, P.J.; Prabhu, S.; et al. Quantitative cumulative biodistribution of antibodies in mice: Effect of modulating binding affinity to the neonatal Fc receptor. MAbs 2014, 6, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Watering, F.C.; Rijpkema, M.; Robillard, M.; Oyen, W.J.; Boerman, O.C. Pretargeted imaging and radioimmunotherapy of cancer using antibodies and bioorthogonal chemistry. Front. Med. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagorsen, D.; Baeuerle, P.A. Immunomodulatory therapy of cancer with T cell-engaging BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonin-Debs, A.L.; Boche, I.; Gille, H.; Brinkmann, U. Development of secreted proteins as biotherapeutic agents. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2004, 4, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.A.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Chang, C.H. Complex and defined biostructures with the dock-and-lock method. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayer, K.; Baumann, A.-L.; Grote, M.; Seeber, S.; Kettenberger, H.; Breuer, S.; Killian, T.; Schäfer, W.; Brinkmann, U. TriFabs—Trivalent IgG-Shaped Bispecific Antibody Derivatives: Design, Generation, Characterization and Application for Targeted Payload Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27497-27507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126037
Mayer K, Baumann A-L, Grote M, Seeber S, Kettenberger H, Breuer S, Killian T, Schäfer W, Brinkmann U. TriFabs—Trivalent IgG-Shaped Bispecific Antibody Derivatives: Design, Generation, Characterization and Application for Targeted Payload Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(11):27497-27507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126037
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayer, Klaus, Anna-Lena Baumann, Michael Grote, Stefan Seeber, Hubert Kettenberger, Sebastian Breuer, Tobias Killian, Wolfgang Schäfer, and Ulrich Brinkmann. 2015. "TriFabs—Trivalent IgG-Shaped Bispecific Antibody Derivatives: Design, Generation, Characterization and Application for Targeted Payload Delivery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 11: 27497-27507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126037
APA StyleMayer, K., Baumann, A. -L., Grote, M., Seeber, S., Kettenberger, H., Breuer, S., Killian, T., Schäfer, W., & Brinkmann, U. (2015). TriFabs—Trivalent IgG-Shaped Bispecific Antibody Derivatives: Design, Generation, Characterization and Application for Targeted Payload Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(11), 27497-27507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126037