Metagenomic Analysis of Upwelling-Affected Brazilian Coastal Seawater Reveals Sequence Domains of Type I PKS and Modular NRPS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Metagenomic Reads Assembly
2.2. Screening of NRPS and PKS Domains
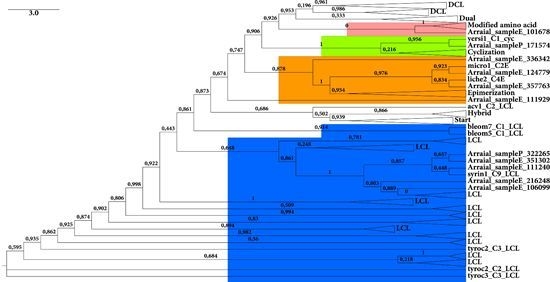
2.2.1. KS Domain
| Sample | KS Modular (Total Hits) | KS Iterative (Total Hits) | KS Modular (Confirmed by Blast) | KS Iterative (Confirmed by Blast) | KS Modular (Classified by NapDos) | KS Iterative (Classified by NapDos) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample P | 28 | 21 | 13 (46.42%) | 6 (28.57%) | 23 (78.57%) | 15 (71.42%) |
| Sample E | 37 | 16 | 27 (72.97%) | 9 (56.25%) | 34 (91.89%) | 12 (75%) |
| Total | 65 | 37 | 40 | 15 | 57 | 27 |


2.2.2. C Domain

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Metagenomic Reads Assembly
3.3. Screening for Genes of NRPS C Domain and Type I PKS KS Domains
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, J.J.; Spear, J.R.; Pace, N.R. Geobiology of a microbial endolithic community in the Yellowstone geothermal environment. Nature 2005, 434, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, T.; Abe, T.; Ikemura, T.; Watanabe, K. Substrate-induced gene-expression screening of environmental metagenome libraries for isolation of catabolic genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoracci, G.B.; Nascimento, J.R.; Cabral, A.S.; Paranhos, R.; Valentin, J.L.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L. Structuring of bacterioplankton diversity in a large tropical bay. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade-Silva, A.E.; Rua, C.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Dutilh, B.E.; Moreira, A.P.B.; Edwards, R.A.; Hajdu, E.; Lobo-Hajdu, G.; Vasconcelos, A.T.; Berlinck, R.G.; et al. Taxonomic and functional microbial signatures of the endemic marine sponge Arenosclera brasiliensis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cury, J.C.; Araujo, F.V.; Coelho-Souza, S.A.; Peixoto, R.S.; Oliveira, J.A.L.; Santos, H.F.; Dávila, A.M.; Rosado, A.S. Microbial diversity of a Brazilian coastal region influenced by an upwelling system and anthropogenic activity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.E.L.; Gonçalves, J.E.A.; Coutinho, R. Ship hulls and oil platforms as potential vectors to marine species introduction. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 39, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar]
- López, M.S.; Coutinho, R. Positive interaction between the native macroalgae Sargassum sp. and the exotic bivalve Isognomon bicolor? Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 58, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Souza, S.A.; Pereira, G.C.; Coutinho, R.; Guimarães, J.R. Yearly variation of bacterial production in the Arraial do Cabo protection area (Cabo Frio upwelling region): An evidence of anthropogenic pressure. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Gibbons, T.; Ghodsi, M.; Treangen, T.; Pop, M. Accurate and fast estimation of taxonomic profiles from metagenomic shotgun sequences. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-J.; Hao, Z.-Y.; Zeng, R.; Shen, P.-H.; Li, J.-F.; Wu, B. Characterization of a novel serine protease inhibitor gene from a marine metagenome. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokhale, R.S.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Mohanty, D. Versatility of polyketide synthases in generating metabolic diversity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koglin, A.; Walsh, C.T. Structural insights into nonribosomal peptide enzymatic assembly lines. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R.; Kumari, R.; Kaur, H.; Khanna, R.; Dhingra, N.; Tuteja, D. Regulation and manipulation of the gene clusters encoding type-I PKSs. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, D.E. Harnessing the Biosynthetic Code: Combinations, Permutations, and Mutations. Science 1998, 282, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Peng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Functional gene-guided discovery of type II polyketides from culturable actinomycetes associated with soft coral Scleronephthya sp. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoe, T.A.; Stephens, T.; Noonan, B.P.; Calestani, C. A novel group of type I polyketide synthases (PKS) in animals and the complex phylogenomics of PKSs. Gene 2007, 392, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Stenico, M.E.; Silva, C.S.P.; Lorenzi, A.S.; Shishido, T.K.; Etchegaray, A.; Lira, S.P.; Moraes, L.A.; Fiore, M.F. Non-ribosomal peptides produced by Brazilian cyanobacterial isolates with antimicrobial activity. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 166, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.M.; Smith, C.B.; Tolar, B.; Hollibaugh, J.T. Analysis of composition and structure of coastal to mesopelagic bacterioplanktoncommunities in the northern gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, R.E.; Rogers, A.D.; Billett, D.S.M.; Smale, D.A.; Pearce, D.A. Patterns of marine bacterioplankton biodiversity in the surface waters of the Scotia Arc, Southern Ocean. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.C.K.; Zhang, R.; Brodie, E.L.; Piceno, Y.M.; Andersen, G.; Liu, W.T. Biogeography of bacterioplankton in the tropical seawaters of Singapore. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desriac, F.; Jégou, C.; Balnois, E.; Brillet, B.; Le Chevalier, P.; Fleury, Y. Antimicrobial peptides from marine proteobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3632–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, A.P.; Bondoso, J.; Gaspar, H.; Xavier, J.R.; Monteiro, M.C.; de la Cruz, M.; Oves-Costales, D.; Vicente, F.; Lage, O.M. Antimicrobial activity of heterotrophic bacterial communities from the marine sponge Erylus discophorus (Astrophorida, Geodiidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneemann, I.; Nagel, K.; Kajahn, I.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Comprehensive investigation of marine actinobacteria associated with the sponge Halichondria panicea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3702–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Schlingloff, A.; Bernhard, M.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Antagonistic activity of bacteria isolated from organic aggregates of the German Wadden Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, T.; Gram, L.; Grossart, H.-P.; Kessler, D.; Muller, R.; Simon, M.; Wenzel, S.C.; Brinkhoff, T. Bacteria of the Roseobacter clade show potential for secondary metabolite production. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, P.J.; Hunt, A.L.; Rostoll, K.; van der Walt, J.J.; Graz, C.J. The biological activity of selected cyclic dipeptides. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1998, 50, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slightom, R.N.; Buchan, A. Surface colonization by marine roseobacters: Integrating genotype and phenotype. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6027–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cude, W.N.; Mooney, J.; Tavanaei, A.A.; Hadden, M.K.; Frank, A.M.; Gulvik, C.A.; May, A.L.; Buchan, A. Production of the antimicrobial secondary metabolite indigoidine contributes to competitive surface colonization by the marine roseobacter Phaeobacter sp. strain Y4I. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Madan, A. CAP3: A DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, B.; Ding, R.; Li, Y.; Duan, L.; Zhu, H. A de novo metagenomic assembly program forshotgun DNA reads. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namiki, T.; Hachiya, T.; Tanaka, H.; Sakakibara, Y. MetaVelvet: An extension of Velvet assembler to de novo metagenome assembly from short sequence reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afiahayati; Sato, K.; Sakakibara, Y. An extended genovo metagenomic assembler by incorporating paired-end information. Peer J. 2013, 1, e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, R.M.; Mohammed, M.H.; Mande, S.S. MetaCAA: A clustering-aided methodology for efficient assembly of metagenomic datasets. Genomics 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavromatis, K.; Ivanova, N.; Barry, K.; Shapiro, H.; Goltsman, E.; McHardy, A.C.; Rigoutsos, I.; Salamov, A.; Korzeniewski, F.; Land, M.; et al. Use of simulated data sets to evaluate the fidelity of metagenomic processing methods. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatelli, M.; Moya, A. Evaluating the fidelity of de novo short read metagenomic assembly using simulated data. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.; Codling, C.E.; Jones, B.V.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Marchesi, J.R. Diversity of microbes associated with the marine sponge, Haliclona simulans, isolated from Irish waters and identification of polyketide synthase genes from the sponge metagenome. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade-Silva, A.E.; Rua, C.P.J.; Andrade, B.G.N.; Vicente, A.C.P.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Berlinck, R.G.; Thompson, F.L. Polyketide synthase gene diversity within the microbiome of the sponge Arenosclera brasiliensis, endemic to the Southern Atlantic Ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerstner, K.U.; Doerks, T.; Creevey, C.J.; Doerks, A.; Bork, P. A Computational screen for type I polyketide synthases in metagenomics shotgun data. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziemert, N.; Podell, S.; Penn, K.; Badger, J.H.; Allen, E.; Jensen, P.R. The natural product domain seeker NaPDoS: A Phylogeny based bioinformatic tool to classify secondary metabolite gene diversity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenke-Kodama, H.; Sandmann, A.; Muller, R.; Dittmann, E. Evolutionary implications of bacterial polyketide synthases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tringe, S.G.; von Mering, C.; Kobayashi, A.; Salamov, A.A.; Chen, K.; Chang, H.W.; Podar, M.; Short, J.M.; Mathur, E.J.; Detter, J.C.; et al. Comparative metagenomics of microbial communities. Science 2005, 308, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelsman, J.; Rondon, M.R.; Brady, S.F.; Clardy, J.; Goodman, R.M. Molecular biological access to the chemistry of unknown soil microbes: A new frontier for natural products. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, R245–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, J.C.; Remington, K.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Halpern, A.L.; Rusch, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Wu, D.; Paulsen, I.; Nelson, K.E.; Nelson, W.; et al. Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 2004, 304, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, K.M. Biosynthesis of natural products by microbial iterative hybrid PKS–NRPS. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 18228–18247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.; Rajbhandari, I.; Wesson, K. Competition-mediated antibiotic induction in the marine bacterium Streptomyces tenjimariensis. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 41, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão-Dumaresq, A.S.; Fróes, A.M.; Cuadrat, R.R.C.; Silva, F.P.; Dávila, A.M.R. Towards a comprehensive search of putative chitinases sequences in environmental metagenomic databases. Nat. Sci. 2014, 6, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPSIDB. Available online: http://gate.smallsoft.co.kr:8080/pks/mapsidb (accessed on 5 October 2015).
- NRPSDB. Available online: http://linux1.nii.res.in/~zeeshan/webpages/home.html (accessed on 5 October 2015).
- Ansari, M.Z.; Yadav, G.; Gokhale, R.S.; Mohanty, D. NRPS-PKS: A knowledge-based resource for analysis of NRPS/PKS megasynthases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W405–W413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NapDOS. Available online: http://npdomainseeker.ucsd.edu/ (accessed on 5 October 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuadrat, R.R.C.; Cury, J.C.; Dávila, A.M.R. Metagenomic Analysis of Upwelling-Affected Brazilian Coastal Seawater Reveals Sequence Domains of Type I PKS and Modular NRPS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28285-28295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226101
Cuadrat RRC, Cury JC, Dávila AMR. Metagenomic Analysis of Upwelling-Affected Brazilian Coastal Seawater Reveals Sequence Domains of Type I PKS and Modular NRPS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):28285-28295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226101
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuadrat, Rafael R. C., Juliano C. Cury, and Alberto M. R. Dávila. 2015. "Metagenomic Analysis of Upwelling-Affected Brazilian Coastal Seawater Reveals Sequence Domains of Type I PKS and Modular NRPS" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 28285-28295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226101
APA StyleCuadrat, R. R. C., Cury, J. C., & Dávila, A. M. R. (2015). Metagenomic Analysis of Upwelling-Affected Brazilian Coastal Seawater Reveals Sequence Domains of Type I PKS and Modular NRPS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 28285-28295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226101