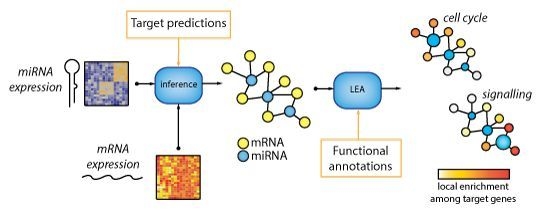
MicroRNA-Target Network Inference and Local Network Enrichment Analysis Identify Two microRNA Clusters with Distinct Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Methods and Materials
2.1. HNSCC Data
2.2. Preliminaries
2.3. Group-Wise Correlation of miRNAs with a Shared Target Gene

2.4. mi-/mRNA Network Inference
2.5. Functional Characterization of miRNA-Target Networks

2.6. Implementation and Availability
2.7. Synthetic Data

2.8. Validation of Network Inference on Experimental HNSCC Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Robust mi-/mRNA Network Inference for Small Sample Sizes
3.2. mi-/mRNA Regulatory Network of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma

3.3. Two Functional Clusters in miRNA-Mediated HPV-Associated Dysregulation

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, B.; Shih, I.; Jones-Rhoades, M.; Bartel, D.; Burge, C. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedel, J.; Klemm, S.; Zheng, Y.; Sahay, A.; Bluthgen, N.; Marks, D.; van Oudenaarden, A. MicroRNA control of protein expression noise. Science 2015, 348, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Maki, M.; Ding, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, L. Genome-wide survey of tissue-specific microRNA and transcription factor regulatory networks in 12 tissues. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barad, O.; Mann, M.; Chapnik, E.; Shenoy, A.; Blelloch, R.; Barkai, N.; Hornstein, E. Efficiency and specificity in microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S. Use of microRNA sponges to explore tissue-specific microRNA functions in vivo. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 873–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquinelli, A. MicroRNAs and their targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, S.; Dietmann, S.; Burk, U.; Brabletz, S.; Lutter, D.; Kowarsch, A.; Mayer, K.; Brabletz, T.; Ruepp, A.; Theis, F.; et al. MicroRNAs coordinately regulate protein complexes. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Conklin, D.; Li, F.; Dai, Z.; Hua, X.; Li, Y.; Xu-Monette, Z.; Young, K.; Xiong, W.; Wysoczynski, M.; et al. The oncogenic microRNA miR-21 promotes regulated necrosis in mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, P.; Nolde, M.; Slack, F. OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 467, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F. Oncomirs—MicroRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerer, I.; Hess, J.; Pitea, A.; Unger, K.; Hieber, L.; Selmansberger, M.; Lauber, K.; Zitzelsberger, H. Integrative analysis of the microRNA-mRNA response to radiochemotherapy in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerer, I.; Niyazi, M.; Unger, K.; Pitea, A.; Zangen, V.; Hess, J.; Atkinson, M.; Belka, C.; Moertl, S.; Zitzelsberger, H. Changes in circulating microRNAs after radiochemotherapy in head and neck cancer patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Peyser, N.D.; Grandis, J.T. Integration of Molecular Targeted Therapy with Radiation in Head and Neck Cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, C.; Braakhuis, B.; Brakenhoff, R. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2011, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stransky, N.; Egloff, A.; Tward, A.; Kostic, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Kryukov, G.; Lawrence, M.; Sougnez, C.; McKenna, A.; et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science 2011, 333, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.; Westra, W. Molecular pathology of head and neck cancer: Implications for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Ad, V.; Palmer, J.; Yang, H.; Cognetti, D.; Curry, J.; Luginbuhl, A.; Tuluc, M.; Campling, B.; Axelrod, R. Current management of locally advanced head and neck cancer: The combination of chemotherapy with locoregional treatments. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, M.; Lauber, K.; Niyazi, M.; Friedl, A.; Li, M.; Maihoefer, C.; Schuettrumpf, L.; Ernst, A.; Niemoeller, O.; Belka, C. Current concepts in clinical radiation oncology. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2014, 53, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, S.; Ang, K.; Vermorken, J.; Haddad, R.; Suarez, C.; Wolf, G.; Hamoir, M.; Machiels, J. Targeted therapies for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Current knowledge and future directions. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psyrri, A.; DiMaio, D. Human papillomavirus in cervical and head-and-neck cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2008, 5, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, C.; Laimins, L. Human papillomavirus in cervical and head-and-neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannone, G.; Santoro, A.; Papagerakis, S.; Muzio, L.L.; Rosa, G.D.; Bufo., P. The role of human papillomavirus in the pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An overview. Infect. Agents Cancer 2011, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Wu, J.; Lee, B.; Farah, C. MicroRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 650218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajer, C.; Garnaes, E.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Norrild, B.; Therkildsen, M.; Glud, M.; Rossing, M.; Lajer, H.; Svane, D.; Skotte, L.; et al. The role of miRNAs in human papilloma virus (HPV)-associated cancers: Bridging between HPV-related head and neck cancer and cervical cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.; Burge, C.; Bartel, D. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D. Human MicroRNA Targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Betel, D.; Koppal, A.; Agius, P.; Sander, C.; Leslie, C. Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, A.R.; Azzam, G.; Wheatley, L.; Tibbit, C.; Rajakumar, T.; McGowan, S.; Stanger, N.; Ewels, P.A.; Taylor, S.; Ponting, C.P.; et al. Understanding functional miRNA-target interactions in vivo by site-specific genome engineering. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gill, R.; Cooper, N.; Yoo, J.; Datta, S. Modeling microRNA-mRNA interactions using PLS regression in human colon cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2011, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausser, J.; Zavolan, M. Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions–beyond repression of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.; Zang, J.; Mele, A.; Darnell, R. Argonaute HITS-CLIP decodes microRNA-mRNA interaction maps. Nature 2009, 460, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Li, J.H.; Shao, P.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Qu, L.H. starBase: A databse for exploring microRNA-mRNA interaction maps from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq data. Nucleic Acid Res. 2011, 39, D202–D209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majoros, W.; Lekprasert, P.; Mukherjee, N.; Skalsky, R.; Corcoran, D.; Cullen, B.R.; Ohler, U. MicroRNA target site identification by integrating sequence and binding information. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshid, M.; Hausser, J.; Zavolan, M.; van Nimwegen, E. A biophysical miRNA-mRNA interaction model infers canonical and noncanonical targets. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Qu, X.; He, W.; He, Y.; Feng, C.; Jia, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, J.; et al. Unraveling the characteristics of microRNA regulation in the developmental and aging process of the human brain. BMC Med. Genom. 2013, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, G.; Coppe, A.; Bisognin, A.; Biasiolo, M.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Romualdi, C. MAGIA, a web-based tool for miRNA and Genes Integrated Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinck, A.; Preusse, M.; Laggerbauer, B.; Lickert, H.; Engelhardt, S.; Theis, F. The human transcriptome is enriched for miRNA-binding sites located in cooperativity-permitting distance. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, W.; Deng, M.; Zhang, C. A Lasso regression model for the construction of microRNA-target regulatory networks. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniategui, A.; Nogales-Cadenas, R.; Vasquez, M.; Arangueren, X.; Luttun, A.; Prosper, F.; Paculal-Montano, A.; Rubio, A. Quantification of miRNA-mRNA Interactions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.; Ayers, S.; Wen, J.; Brandl, M.; Pham, T.; Webb, P.; Chang, C.; Zhou, X. Integrative analysis of next generation sequencing for small non-coding RNAs and transcriptional regulation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. BMC Med. Genom. 2011, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Sass, S.; Mueller, N.; Krebs, S.; Bauersachs, S.; Kaiser, S.; Blum, H.; Thirion, C.; Krause, S.; Theis, F.J.; et al. Integrative Analysis of MicroRNA and mRNA Data Reveals an Orchestrated Function of MicroRNAs in Skeletal Myocyte Differentiation in Response to TNF-Îś or IGF1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldera-Lupa, D.; Kalfalah, F.; Florea, A.; Sass, S.; Kruse, F.; Rieder, V.; Tigges, J.; Fritsche, E.; Krutmann, J.; Busch, H.; et al. Proteome-wide analysis reveals an age-associated cellular phenotype of in situ aged human fibroblasts. Aging 2014, 6, 856–878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kowarsch, A.; Preusse, M.; Marr, C.; Theis, F. miTALOS: Analyzing the tissue-specific regulation of signaling pathways by human and mouse microRNAs. RNA 2011, 17, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.; Kim, B.; Shin, S.; Lee, S. miRGator: An integrated system for functional annotation of microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D146–D152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruepp, A.; Kowarsch, A.; Schmidl, D.; Buggenthin, F.; Brauner, B.; Dunger, I.; Fobo, G.; Frishman, G.; Montrone, C.; Theis, F. PhenomiR: A knowledgebase for microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleazard, T.; Lamb, J.; Griffiths-Jones, S. Bias in microRNA functional enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1592–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, S.; Pitea, A.; Mueller, N.S.; Theis, F.J. The miRlastic R package. Available online: http://icb.helmholtz-muenchen.de/mirlastic (accessed on 14 December 2015).
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamata, T.; Tomari, Y. Making RISC. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.; McCarthy, D.; Smyth, G. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville, S.; Bartel, D. Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 2005, 11, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.; Weissman, J.; Bartel, D. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 43, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D109–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. Int. J. Complex Syst. 2006, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, A.; Orosco, R.; Shen, H.; Egloff, A.; Carter, H.; Hofree, M.; Choueiri, M.; Coffey, C.; Lippman, S.; Hayes, D.; et al. Multi-tiered genomic analysis of head and neck cancer ties TP53 mutation to 3p loss. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, G.; Kreimer, A.; Viscidi, R.; Pawlita, M.; Fakhry, C.; Koch, W.; Westra, W.; Gillison, M. Case-control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, A.; Lin, A.; Xu, W.; Waldron, L.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Shi, W.; Bruce, J.; Huang, S.; O’Sullivan, B.; et al. Potentially prognostic miRNAs in HPV-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Gay, H.; Chernock, R.; Zhang, T.; Luo, J.; Thorstad, W.; Lewis, J.J.; Wang, X. A microRNA expression signature for the prognosis of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, A.; Lenarduzzi, M.; Krushel, T.; Waldron, L.; Pintilie, M.; Shi, W.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Jurisica, I.; O’Sullivan, B.; Waldron, J.; et al. Comprehensive MicroRNA profiling for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Jimeno, A.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Gross, N.; Kulesz-Martin, M.; Wang, D.; et al. Methylation of microRNA-9 is a specific and sensitive biomarker for oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, C.; Nagadia, R.; Pandit, P.; Cooper-White, J.; Banerjee, N.; Dimitrova, N.; Coman, W.; Punyadeera, C. A novel saliva-based microRNA biomarker panel to detect head and neck cancers. Cell Oncol. 2014, 37, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, A.; Hoskins, E.; Wells, S.; Ferris, R.; Khan, S. Alteration of microRNA profiles in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cell lines by human papillomavirus. Head Neck 2011, 33, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, S.; Pitea, A.; Mueller, N.S.; Theis, F.J. MiRlastic on HNSCC dataset. Available online: http://icb.helmholtz-muenchen.de/mirlastic/hnscc (accessed on 14 December 2015).
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-κB: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancroft, C.; Chen, Z.; Yeh, J.; Sunwoo, J.; Yeh, N.; Jackson, S.; Jackson, C.; van Waes, C. Effects of pharmacologic antagonists of epidermal growth factor receptor, PI3K and MEK signal kinases on NF-κB and AP-1 activation and IL-8 and VEGF expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tanji, E.; Makino, N.; Kawata, S.; Furukawa, T. MicroRNAs associated with mitogen-activated protein kinase in human pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenarduzzi, M.; Hui, A.; Alajez, N.; Shi, W.; Williams, J.; Yue, S.; O’Sullivan, B.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-193b enhances tumor progression via down regulation of neurofibromin 1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellman, I.; Yarden, Y. Endocytosis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.; Shahab, S.; Weed, S. Actin cytoskeletal mediators of motility and invasion amplified and overexpressed in head and neck cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietbergen, M.; de Kemp, S.M.; Bloemena, E.; Witte, B.; Brink, A.; de Jong, R.B.; Leemans, C.; Braakhuis, B.; Brakenhoff, R. Cancer stem cell enrichment marker CD98: A prognostic factor for survival in patients with human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jouhi, L.; Datta, N.; Renkonen, S.; Atula, T.; Maekitie, A.; Haglund, C.; Ahmed, A.; Syrjaenen, S.; Grenman, R.; Auvinen, E.; et al. Expression of toll-like receptors in HPV-positive and HPV-negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-an in vivo and in vitro study. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 7755–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador-Molina, A.; Hernandez-Valencia, J.; Lamoyi, E.; Contreras-Paredes, A.; Lizano, M. Role of innate immunity against human papillomavirus (HPV) infections and effect of adjuvants in promoting specific immune response. Viruses 2013, 5, 2624–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautava, J.; Syrjaenen, S. Biology of human papillomavirus infections in head and neck carcinogenesis. Head Neck Pathol. 2012, 6, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pries, R.; Wollenberg, B. Cytokines in head and neck cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.W.; Chang, T.C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.J.; Bahal, R.; Babar, I.A.; Pincus, Z.; Barrera, F.; Liu, C.; Svoronos, A.; Braddock, D.T.; Glazer, P.M.; Engelman, D.M.; et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature 2015, 518, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sass, S.; Pitea, A.; Unger, K.; Hess, J.; Mueller, N.S.; Theis, F.J. MicroRNA-Target Network Inference and Local Network Enrichment Analysis Identify Two microRNA Clusters with Distinct Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30204-30222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226230
Sass S, Pitea A, Unger K, Hess J, Mueller NS, Theis FJ. MicroRNA-Target Network Inference and Local Network Enrichment Analysis Identify Two microRNA Clusters with Distinct Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):30204-30222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226230
Chicago/Turabian StyleSass, Steffen, Adriana Pitea, Kristian Unger, Julia Hess, Nikola S. Mueller, and Fabian J. Theis. 2015. "MicroRNA-Target Network Inference and Local Network Enrichment Analysis Identify Two microRNA Clusters with Distinct Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 30204-30222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226230
APA StyleSass, S., Pitea, A., Unger, K., Hess, J., Mueller, N. S., & Theis, F. J. (2015). MicroRNA-Target Network Inference and Local Network Enrichment Analysis Identify Two microRNA Clusters with Distinct Functions in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 30204-30222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226230