Infiltrating Mast Cells Correlate with Angiogenesis in Bone Metastases from Gastric Cancer Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
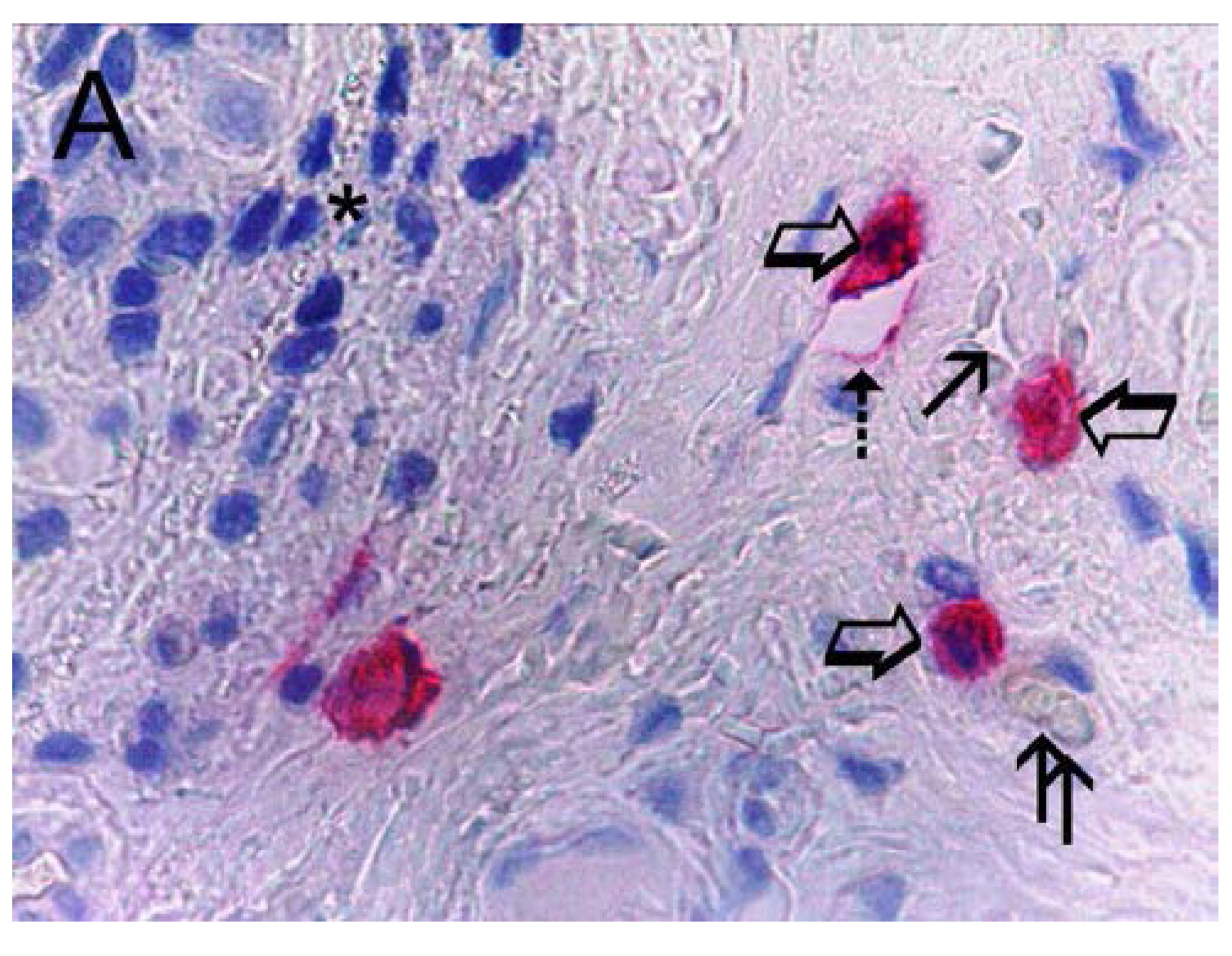
2. Results
| Tissue | MCDPT | MCAPT | MVD | EA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400× (0.19 mm2) | ||||
| 15 Bone metastases | 6.66 ± 2.53 | 147.8 × 10−2 μ2 ± 53.66 | 19.33 ± 7.41 | 180.06 × 10−2 μ2 ± 54.29 |
| 21 Primary tumor | 11.02 ± 4.73 | 223.63 × 10−2 μ2 ± 89.32 | 27.18 ± 9.82 | 231.71 × 10−2 μ2 ± 71.55 |

3. Discussion

4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Patients
| Overall Series | Patients Number (n = 15) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | <65 | 9 |
| >65 | 6 | |
| Sex | Male | 8 |
| Female | 7 | |
| Primary tumour site | Cardia | 2 |
| Lesser curvature | 3 | |
| Greater curvature | 3 | |
| Body and fundus | 4 | |
| Pyloric area | 3 | |
| Stage (TNM) by AJCC classification | T3-4N2-3M1 | 15 |
| Histology | Intestinal type | 7 |
| Diffuse type | 6 | |
| Other | 2 | |
| Grading | G3 | 12 |
| G2 | 3 | |
| Bone metastatic site | Spine | 4 |
| Long bones | 7 | |
| Hip | 4 | |
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Morphometrical Assay


4.5. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.S.; Yi, S.Y.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, J.; Park, J.O.; Park, Y.S.; Jang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Ko, Y.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Clinical outcome of gastric cancer patients with bone marrow metastases. Oncology 2007, 73, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ekinci, A.S.; Bal, O.; Ozatli, T.; Türker, I.; Eşbah, O.; Demirci, A.; Budakoğlu, B.; Arslan, U.Y.; Eraslan, E.; Oksüzoğlu, B. Gastric carcinoma with bone marrow metastasis: A case series. J. Gastric Cancer 2014, 14, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Yamabe, N.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Cheon, G.J.; Ham, J.; Kang, K.S. Stereospecific anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 epimers isolated from heat-processed American ginseng on human gastric cancer cell. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, D.; Raica, M.; Sporea, I.; Tăban, S.; Goldiş, A.; Cornianu, M. Tumor angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2006, 47, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Guidolin, D.; Marzullo, A.; Nico, B.; Annese, T.; Benagiano, V.; Crivellato, E. Mast cells and angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 91, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Irani, A.M.; Schwartz, L.B. Human mast cell heterogeneity. Allergy Proc. 1994, 15, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Marech, I.; Ammendola, M.; Gadaleta, C.; Zizzo, N.; Oakley, C.; Gadaleta, C.D.; Ranieri, G. Possible biological and translational significance of mast cells density in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8910–8920. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.S. Mast-cell responses to pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 787–799. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kawanami, C.; Kishi, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Ohashi, A.; Funasaka, Y.; Okada, A.; Maekawa, T.; He-Yao, W.; et al. Expression of protooncogene c-Kit and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) in gastric carcinoma cell lines. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Ranieri, G.; Basile, A.; Azzariti, A.; Paradiso, A.; Vacca, A. Tumor endothelial markers as a target in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Marech, I.; Patruno, R.; Zizzo, N.; Gadaleta, C.; Introna, M.; Zito, A.F.; Gadaleta, C.D.; Ranieri, G. Masitinib (AB1010), from canine tumor model to human clinical development: Where we are? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 91, 98–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendola, M.; Sacco, R.; Donato, G.; Zuccalà, V.; Russo, E.; Luposella, M.; Vescio, G.; Rizzuto, A.; Patruno, R.; de Sarro, G.; et al. Mast cell positivity to tryptase correlates with metastatic lymph nodes in gastrointestinal cancer patients treated surgically. Oncology 2013, 85, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Starkey, J.R.; Crowle, P.K.; Taubenberger, S. Mast-cell-deficient W/Wv mice exhibit a decreased rate of tumor angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 1988, 42, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendola, M.; Leporini, C.; Marech, I.; Gadaleta, C.D.; Scognamillo, G.; Sacco, R.; Sammarco, G.; de Sarro, G.; Russo, E.; Ranieri, G. Targeting mast cells tryptase in tumor microenvironment: A potential antiangiogenetic strategy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 154702. [Google Scholar]
- Marech, I.; Ammendola, M.; Sacco, R.; Capriuolo, G.S.; Patruno, R.; Rubini, R.; Luposella, M.; Zuccalà, V.; Savino, E.; Gadaleta, C.D.; et al. Serum tryptase, mast cells positive to tryptase and microvascular density evaluation in early breast cancer patients: Possible translational significance. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 534. [Google Scholar]
- Marech, I.; Gadaleta, C.D.; Ranieri, G. Possible prognostic and therapeutic significance of c-Kit expression, mast cell count and microvessel density in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13060–13076. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendola, M.; Sacco, R.; Sammarco, G.; Donato, G.; Montemurro, S.; Ruggieri, E.; Patruno, R.; Marech, I.; Cariello, M.; Vacca, A.; et al. Correlation between serum tryptase, mast cells positive to tryptase and microvascular density in colo-rectal cancer patients: Possible biological-clinical significance. PLoS One 2014, 9, e99512. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendola, M.; Sacco, R.; Sammarco, G.; Donato, G.; Zuccalà, V.; Luposella, M.; Patruno, R.; Marech, I.; Montemurro, S.; Zizzo, N.; et al. Mast cells density positive to tryptase correlates with angiogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients having undergone surgery. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 11, 951957. [Google Scholar]
- Patruno, R.; Marech, I.; Zizzo, N.; Ammendola, M.; Nardulli, P.; Gadaleta, C.; Introna, M.; Capriuolo, G.; Rubini, R.A.; Ribatti, D.; et al. C-Kit expression, angiogenesis, and grading in canine mast cell tumour: A unique model to study c-Kit driven human malignancies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 730246. [Google Scholar]
- Mangia, A.; Malfettone, A.; Rossi, R.; Paradiso, A.; Ranieri, G.; Simone, G.; Resta, L. Tissue remodelling in breast cancer: Human mast cell tryptase as an initiator of myofibroblast differentiation. Histopathology 2011, 58, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, G.; Labriola, A.; Achille, G.; Florio, G.; Zito, A.F.; Grammatica, L.; Paradiso, A. Microvessel density, mast cell density and thymidine phosphorylase expression in oral squamous carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2002, 21, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Malfettone, A.; Silvestris, N.; Saponaro, C.; Ranieri, G.; Russo, A.; Caruso, S.; Popescu, O.; Simone, G.; Paradiso, A.; Mangia, A. High density of tryptase-positive mast cells in human colorectal cancer: A poor prognostic factor related to protease-activated receptor 2 expression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, G. Hot topic: Targeting tumor angiogenesis: An update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 9, 937. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, G.; Passantino, L.; Patruno, R.; Passantino, G.; Jirillo, F.; Catino, A.; Mattioli, V.; Gadaleta, C.; Ribatti, D. The dog mast cell tumour as a model to study the relationship between angiogenesis, mast cell density and tumour malignancy. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 5, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, G.; Patruno, R.; Lionetti, A.; di Summa, A.; Mattioli, E.; Bufo, P.; Pellecchia, A.; Ribatti, D.; Zizzo, N. Endothelial area and microvascular density in a canine non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: An interspecies model of tumor angiogenesis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2005, 46, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Zizzo, N.; Patruno, R.; Zito, F.A.; di Summa, A.; Mattioli, E.; Bufo, P.; Pellecchia, A.; Ribatti, D.; Zizzo, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations from platelets correlate with tumor angiogenesis and grading in a spontaneous canine non-Hodgkin lymphoma model. Leuk. Lymphoma 2010, 51, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Gulubova, M.; Vlaykova, T. Prognostic significance of mast cell number and microvascular density for the survival of patients with primary colorectal cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Nakae, S.; Suto, H.; Kakurai, M.; Sedgwick, J.D.; Tsai, M.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells enhance T cell activation: Importance of mast cell-derived TNF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6467–6472. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Ranieri, G.; Nico, B.; Benagiano, V.; Crivellato, E. Tryptase and chymase are angiogenic in vivo in the chorioallantoic membrane assay. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, R.J.; Meng, H.; Marchese, M.J.; Ren, S.; Schwartz, L.B.; Tonnesen, M.G.; Gruber, B.L. Human mast cells stimulate vascular tube formation. Tryptase is a novel, potent angiogenic factor. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.R.; Ding, Y.; Ricks, T.K.; Gullapalli, A.; Wolfe, B.L.; Trejo, J. Protease-activated receptor-2 is essential for factor VIIa and Xa-induced signaling, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaie, K.; Blatner, N.R.; Khan, M.W.; Gounari, F.; Gounaris, E.; Dennis, K.; Bonertz, A.; Tsai, F.N.; Strouch, M.J.; Cheon, E.; et al. The significant role of mast cells in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Taipale, J.; Lohi, J.; aarinen, J.; Kovanen, P.T.; Keski-Oja, J. Human mast cell chymase and leukocyte elastase release latent transforming growthfactor-β1 from the extracellular matrix of cultured human epithelial and endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4689–4696. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, B. L.; Marchese, M. J.; Suzuki, K.; Schwartz, L.B.; Okada, Y.; Nagase, H.; Ramamurthy, N.S. Synovial procollagenase activation by human mast cell tryptase dependence up on matrixmetallo-proteinase 3 activation. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Stack, M.S.; Johnson, D.A. Human mast cell tryptase activates single-chain urinary-type plasminogen activator (pro-urokinase). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 9416–9419. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Ennas, M. G.; Vacca, A.; Ferreli, F.; Nico, B.; Orru, S.; Sirigu, P. Tumor vascularity and tryptase-positive mast cells correlate with a poor prognosis in melanoma. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez-Bribiesca, L.; Wong, A.; Utrera, D.; Castellanos, E. The role of mast cell tryptase in neoangiogenesis of premalignant and malignant lesions of the uterine cervix. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001, 49, 1061–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendola, M.; Sacco, R.; Sammarco, G.; Donato, G.; Zuccalà, V.; Romano, R.; Luposella, M.; Patruno, R.; Vallicelli, C.; Verdecchia, G.M.; et al. Mast cells positive to tryptase and c-Kit receptor expressing cells correlates with angiogenesis in gastric cancer patients surgically treated. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 703163. [Google Scholar]
- Acikalin, M.F.; Oner, U.; Topcu, I.; Yasar, B.; Kiper, H.; Colak, E. Tumour angiogenesis and mast cell density in the prognostic assessment of colorectal carcinomas. Dig. Liver Dis. 2005, 37, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kakeji, Y.; Maehara, Y.; Sumiyoshi, Y.; Oda, O.; Emi, Y. Angiogenesis as a target for gastric cancer. Surgery 2002, 131, S48–S54. [Google Scholar]
- Kakeji, Y.; Koga, T.; Sumiyoshi, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Oda, S.; Maehara, Y.; Sugimachi, K. Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 21, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dutta, D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Karmakar, R.; Barui, G. Evaluation of endoscopic biopsy in gastric lesions with a special reference to the significance of mast cell density. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2009, 52, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico, L.; Satolli, M.A.; Mecca, C.; Castiglione, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; D'Amelio, P.; Garino, M.; De Giuli, M.; Sandrucci, S.; Ferracini, R.; et al. Bone metastases in gastric cancer follow a RANKL-independent mechanism. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, S.J.; Nakae, S.; Tsai, M. Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestris, N.; Pantano, F.; Ibrahim, T.; Gamucci, T.; de Vita, F.; di Palma, T.; Pedrazzoli, P.; Barni, S.; Bernardo, A.; Febbraro, A.; et al. Natural history of malignant bone disease in gastric cancer: Final results of a multicenter bone metastasis survey. PLoS One 2013, 28, e74402. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ammendola, M.; Marech, I.; Sammarco, G.; Zuccalà, V.; Luposella, M.; Zizzo, N.; Patruno, R.; Crovace, A.; Ruggieri, E.; Zito, A.F.; et al. Infiltrating Mast Cells Correlate with Angiogenesis in Bone Metastases from Gastric Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3237-3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023237
Ammendola M, Marech I, Sammarco G, Zuccalà V, Luposella M, Zizzo N, Patruno R, Crovace A, Ruggieri E, Zito AF, et al. Infiltrating Mast Cells Correlate with Angiogenesis in Bone Metastases from Gastric Cancer Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(2):3237-3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023237
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmmendola, Michele, Ilaria Marech, Giuseppe Sammarco, Valeria Zuccalà, Maria Luposella, Nicola Zizzo, Rosa Patruno, Alberto Crovace, Eustachio Ruggieri, Alfredo Francesco Zito, and et al. 2015. "Infiltrating Mast Cells Correlate with Angiogenesis in Bone Metastases from Gastric Cancer Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 2: 3237-3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023237
APA StyleAmmendola, M., Marech, I., Sammarco, G., Zuccalà, V., Luposella, M., Zizzo, N., Patruno, R., Crovace, A., Ruggieri, E., Zito, A. F., Gadaleta, C. D., Sacco, R., & Ranieri, G. (2015). Infiltrating Mast Cells Correlate with Angiogenesis in Bone Metastases from Gastric Cancer Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(2), 3237-3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023237







