Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. MicroRNAs in CRC
2.1. Dysregulated Expression of MicroRNAs and Their Putative Roles
2.1.1. Oncogenic miRNAs

| Names | Expression | Targets | Biological Events | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-18a | ↑ | ATM | cell apoptosis, repair of DNA damage, sensitive to genotoxin (etoposide) | [21] |
| miR-21 | ↑ | PTEN, PDCD4 | cell proliferation, prognosis, response to adjuvant chemotherapy | [23,24,25,26] |
| miR-29a | ↑ | KLF4 | cell invasion, metastasis, prognosis | [32] |
| miR-31 | ↑ | FIH-1, RhoBTB1, RASA1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, tumor growth, prognosis | [27,28,29] |
| miR-32 | ↑ | PTEN | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis | [33] |
| miR-92a | ↑ | PTEN | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, clinical stage, lymph node metastases, distant metastases, prognosis | [30,31] |
| miR-95 | ↑ | SNX1 | cell proliferation, tumor growth | [34] |
| miR-96 | ↑ | TP53INP1, FOXO1, FOXO3a | cell proliferation | [35] |
| miR-103 | ↑ | DICER, PTEN | cell proliferation, migration, tumor growth | [36] |
| miR-181a | ↑ | WIF-1, PTEN | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, tumor growth, liver metastasis, metabolic shift, EMT, advanced stage, distant metastasis, prognosis | [37,38] |
| miR-182 | ↑ | - | tumor size, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage, prognosis | [39] |
| miR-196b | ↑ | FAS | cell apoptosis | [40] |
| miR-223 | ↑ | - | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, clinical stage | [41] |
2.1.2. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs
| Names | Expression | Targets | Biological Events | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-18a | - | K-Ras | cell proliferation, anchorage-independent growth | [42] |
| miR-100 | ↓ | RAP1B | cell proliferation, invasion, apoptosis | [54] |
| miR-124 | ↓ | STAT3 | cell proliferation, apoptosis, tumor growth, differentiation, prognosis | [55,56] |
| miR-126 | ↓ | IRS-1, VEGF, CXCR4 | cells proliferation, migration, invasion, cell cycle arrest, angiogenesis, diagnosis | [50,51,52,53] |
| miR-133a | ↓ | FSCN1, LASP1 | cell proliferation, invasion, migration, tumor growth, intrahepatic and pulmonary metastasis, phosphorylation of ERK/MEK | [43,44] |
| miR-133b | ↓ | TBPL1, CXCR4 | cell proliferation, invasion, migration, apoptosis | [45,46] |
| miR-139 | ↓ | IGF-IR, NOTCH1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, tumor growth, cell cycle arrest | [57,58] |
| miR-145 | ↓ | Fascin-1 | cell proliferation, invasion, tumor growth, pulmonary metastasis | [59] |
| miR-148b | ↓ | CCK2R | cell proliferation, tumor growth, tumor size | [60] |
| miR-194 | ↓ | PDK1, AKT2, XIAP, MAP4K4 | cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, cell cycle arrest, tumor growth, tumor size, differentiation, TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, prognosis | [47,48] |
| miR-206 | ↓ | NOTCH3 | cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest | [61] |
| miR-214 | ↓ | FGFR1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, tumor growth, liver metastasis | [62] |
| miR-218 | ↓ | BMI-1 | cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest | [63] |
| miR-224 | ↓ | Cdc42 | cell migration | [64] |
| miR-320a | ↓ | β-catenin, Rac1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, cell cycle arrest | [65,66] |
| miR-342 | ↓ | DNMT1 | cell proliferation, invasion, cell cycle arrest, tumor growth, lung metastasis | [67] |
| miR-375 | ↓ | PIK3CA | cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, tumor growth | [68] |
| miR-378 | ↓ | vimentin | cell proliferation, invasion, tumor growth, tumor size, lymph node metastasis, clinical stage, prognosis | [69] |
| miR-429 | ↓ | Onecut2 | cell migration, invasion, EMT | [70] |
| miR-455 | ↓ | RAF1 | cell proliferation, invasion | [71] |
| miR-638 | ↓ | SOX2 | cell invasion, migration, EMT | [72] |

2.2. MicroRNAs in Clinical Applications
2.2.1. miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for CRC
| Names | Sample Quantity | Expression | Sensitivity | Specificity | Biomarkers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-221 | 595 | ↑ | 62% | 74% | diagnosis | [76] |
| miR-18a | 595 | ↑ | 61% | 69% | diagnosis | [76] |
| miR-223 | 45 | ↑ | 76.5% | 96.4% | diagnosis | [77] |
| miR-451 | 45 | ↑ | 88.2% | 100% | diagnosis | [77] |
| miR-21 | 246 | ↑ | 55.7% | 73.3% | diagnosis | [78] |
| miR-92a | 246 | ↑ | 71.6% | 73.3% | diagnosis | [78] |
| miR-106a | 224 | ↑ | 34.2% | 97.2% | diagnosis | [79] |
| miR-135b | 424 | ↑ | 78% | 68% | diagnosis | [80] |
| miR-144 | 75 | ↑ | 74% | 87% | diagnosis | [81] |
| miR-143 | 51 | ↓ | - | - | diagnosis | [83] |
| miR-145 | 51 | ↓ | - | - | diagnosis | [83] |
| miR-4478 | 56 | ↓ | - | - | diagnosis | [84] |
| miR-1295b-3p | 56 | ↓ | - | - | diagnosis | [84] |
| Names | Samples | Sample Quantity | Expression | Sensitivity | Specificity | Biomarkers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-221 | plasma | 140 | ↑ | 86% | 41% | diagnosis and prognosis | [86] |
| miR-21 | serum | 282 | ↑ | 82.8% | 90.6% | diagnosis and prognosis | [87] |
| miR-106a | plasma | 97 | ↑ | 62.3% | 68.2% | diagnosis | [91] |
| miR-19a | serum | 72 | ↑ | 66.7% | 63.9% | predicting and monitoring resistance to FOLFOX | [92] |
| miR-18a | serum | 56 | ↑ | - | - | diagnosis | [93] |
| miR-29a | serum | 56 | ↑ | - | - | diagnosis | [93] |
| miR-183 | plasma | 179 | ↑ | 73.7% | 88.5% | tumor recurrence, diagnosis and prognosis | [90] |
| miR-126 | tissues | 92 | ↓ | - | - | prognosis | [95] |
| miR-630 | tissues | 206 | ↑ | - | - | prognosis | [96] |
| miR-378 | tissues | 84 | ↓ | - | - | prognosis | [69] |
2.2.2. miRNAs in the Evaluation of Treatment Response in CRC Patients
3. Small Interfering RNAs in CRC
4. Piwi-Interacting RNAs in CRC
5. Long Non-Coding RNAs in CRC
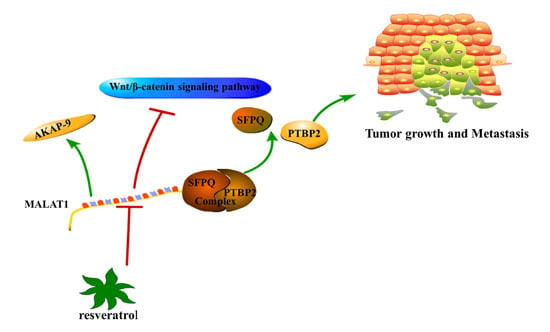
5.1. MALAT1

5.2. HOTAIR
5.3. H19
5.4. CCAT Family
5.5. Other Significant LncRNAs in CRC
| Names | Location | Expression | Biological Events | Putative Roles | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC285194 | Chr3q13.31 | ↓ | tumor size, TNM stage, distant metastasis, prognosis, p53 transcription target, repression of miR-211, cell growth | diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [153,154] |
| uc.73 | Chr2q22.3 | ↓ | overall survival | diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [155] |
| uc.388 | Chr12q13.13 | ↓ | distal location of CRC | diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [155] |
| lincRNA-p21 | Chr6p21.2 | ↓ | higher expression in rectum, stage III tumors, pT and vascular invasion, sensitivity of radiotherapy by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, cell apoptosis, promote pro-apoptosis gene Noxa expression | sensitivity of CRC radiotherapy | [156,157] |
| GAS5 | Chr1q25.1 | ↓ | tumor size, histological grade, TNM stage, prognosis, cell proliferation | prognostic biomarker | [158] |
| ncRAN | Chr17q25.1 | ↓ | histological grade, tumors with liver metastases, prognosis, cell migration, invasion | diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [159] |
| ncRuPAR | Chr5q13.3 | ↓ | lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, Duck’s stage, histological grade, TNM stage, negatively associated with PAR-1 | diagnostic biomarker | [160] |
| MEG3 | Chr14q32.2 | ↓ | histological grade, tumor invasion, TNM stage, prognosis, cell proliferation | diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [161] |
| RP11-462C24.1 | Chr4q25 | ↓ | distant metastasis, prognosis | prognostic biomarker | [162] |
| PRNCR1 | Chr8q24.21 | - | SNPs in PRNCR1 may be involved in the risk of CRC (rs13252298, rs1456315, rs7007694, rs16901946 and rs1456315) | - | [163] |
| PVT-1 | Chr8q24.21 | ↑ | cell proliferation, invasion, apoptosis, prognosis | prognostic biomarker | [164] |
| CRNDE | Chr16q12.2 | ↑ (tissue and plasma) | regulating cellular metabolism by insulin/IGFs, a downstream target of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway or Raf/MAPK pathway | diagnostic biomarker | [165,166] |
| HULC | Chr6p24.3 | ↑ (colorectal hepatic metastasis) | neither expressed in primary CRC samples nor normal tissues but upregulated in colorectal hepatic metastasis | - | [167] |
| PCAT-1 | Chr8q24.21 | ↑ | distant metastasis, prognosis | prognostic biomarker | [168] |
| BANCR | Chr9 | ↑ or ↓ | lymph node metastasis, tumor stage, contribute to cell migration by inducing EMT via an MEK/ERK-dependent mechanism, cell proliferation, apoptosis, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, targeting p21 | therapeutic application | [169,170] |
| UCA1 | Chr19p13.12 | ↑ | cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, tumor size, histological grade, tumor depth, prognosis | diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [171] |
| ATB | Chr14 | - | tumor size, tumor depth, lymphatic invasion, vascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, hematogenous metastases, prognosis | prognostic biomarker | [172] |
| LINC01296 | Chr14q11.2 | ↑ | prognosis | prognostic biomarker | [173] |
| CCAL | - | ↑ | promoting CRC progression and induced multidrug resistance by targeting activator protein 2α, shorter overall survival, worse response to adjuvant chemotherapy | therapeutic application | [174] |
6. Small Nucleolar RNAs in CRC
7. Small Nuclear RNAs in CRC
8. Circular RNAs in CRC
9. Transfer RNAs in CRC
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 2004, 431, 931–945. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzo, A.F.; Lee, E.S. Non-coding RNA: What is functional and what is junk? Front. Genet. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Lam, M.T.; Glass, C.K. Non-coding RNAs as regulators of gene expression and epigenetics. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Roles for noncoding RNAs in cell-fate determination and regeneration. Nat. Struct. Mol. Boil. 2015, 22, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, M.T.; Gupta, S.K.; Thum, T. Noncoding RNAs as regulators of cardiomyocyte proliferation and death. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Peng, J.; Guo, L. Non-Coding RNA: A new tool for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Bajic, V.B.; Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Wang, M.; Ma, N.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, X. Long noncoding RNAs: Novel players in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemani, C.; Weir, H.K.; Carreira, H.; Harewood, R.; Spika, D.; Wang, X.S.; Bannon, F.; Ahn, J.V.; Johnson, C.J.; Bonaventure, A.; et al. Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995–2009: Analysis of individual data for 25,676,887 patients from 279 population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2). Lancet 2015, 385, 977–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.X.; Wang, Z.N. Non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer. Gene 2015, 560, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkhah, R.; Schmitz, U.; Linnebacher, M.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Farazmand, A. MicroRNA-mRNA interactions in colorectal cancer and their role in tumor progression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 54, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, P.; Blasiak, J. The role of microRNA in metastatic colorectal cancer and its significance in cancer prognosis and treatment. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hur, K. MicroRNAs: Promising biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic targets in human colorectal cancer metastasis. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollis, M.; Nair, K.; Vyas, A.; Chaturvedi, L.S.; Gambhir, S.; Vyas, D. MicroRNAs potential utility in colon cancer: Early detection, prognosis, and chemosensitivity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8284–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; di Narzo, A.F.; Mestdagh, P.; Jacobs, B.; Bosman, F.T.; Gustavsson, B.; Majoie, B.; Roth, A.; Vandesompele, J.; Rigoutsos, I.; et al. MicroRNAs in colon cancer: A roadmap for discovery. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3000–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okugawa, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Goel, A. An update on microRNAs as colorectal cancer biomarkers: Where are we and what’s next? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 999–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Wu, D.; Li, P.; Xu, B.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, W. MicroRNA-18a, a member of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster, targets Dicer and suppresses cell proliferation in bladder cancer T24 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morimura, R.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Takeshita, H.; Tsujiura, M.; Nagata, H.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Ikoma, H.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.W.; Dong, Y.J.; Liang, Q.Y.; He, X.Q.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-18a attenuates DNA damage repair through suppressing the expression of ataxia telangiectasia mutated in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Zou, L.; Yang, P.; Wu, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; et al. miR-20b, -21, and -130b inhibit PTEN expression resulting in B7-H1 over-expression in advanced colorectal cancer. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Tao, H.; Jin, W.S. MicroRNA-21 controls hTERT via PTEN in human colorectal cancer cell proliferation. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamichi, N.; Shimomura, R.; Inada, K.; Sakurai, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Fujita, S.; Mizutani, T.; Furukawa, C.; Fujishiro, M.; et al. Locked nucleic acid in situ hybridization analysis of miR-21 expression during colorectal cancer development. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oue, N.; Anami, K.; Schetter, A.J.; Moehler, M.; Okayama, H.; Khan, M.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Mueller, A.; Schad, A.; Shimomura, M.; et al. High miR-21 expression from FFPE tissues is associated with poor survival and response to adjuvant chemotherapy in colon cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Yao, L.Q.; Shi, Q.; Ren, Z.; Ye, L.C.; Xu, J.M.; Zhou, P.H.; Zhong, Y.S. MicroRNA-31 contributes to colorectal cancer development by targeting factor inhibiting HIF-1α (FIH-1). Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.S.; Wu, X.D.; Zhang, S.Q.; Li, C.F.; Yang, L.; Li, D.D.; Zhang, B.G.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.P.; Zhang, B. The tumor suppressor gene RhoBTB1 is a novel target of miR-31 in human colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Yu, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-31 activates the RAS pathway and functions as an oncogenic MicroRNA in human colorectal cancer by repressing RAS p21 GTPase activating protein 1 (RASA1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9508–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Z.; Tian, H.; Zhou, T. MicroRNA-92a functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer by targeting PTEN. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Xia, S.; Tian, H. Overexpression of miR-92a correlates with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Zhu, S.; Leng, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. MicroRNA-29a promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 and E-cadherin via KLF4. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Yang, P.; Tan, W.; Wei, G.; Zhou, Y. MicroRNA-32 (miR-32) regulates phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) expression and promotes growth, migration, and invasion in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liang, L.; Ni, S.; Wang, L.; Sheng, W.; He, X.; Du, X. MicroRNA-95 promotes cell proliferation and targets sorting Nexin 1 in human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wang, W. MicroRNA-96 promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and targets tumor protein p53 inducible nuclear protein 1, forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) and FOXO3a. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Sun, B.; Gao, B.; Wang, Z.; Quan, C.; Wei, F.; Fang, X.D. MicroRNA-103 promotes colorectal cancer by targeting tumor suppressor DICER and PTEN. Int. J Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8458–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Zhan, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xi, J.; Yan, L.; Gu, J. MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor suppressor WIF-1. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Cui, L.; Mei, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D. miR-181a mediates metabolic shift in colon cancer cells via the PTEN/AKT pathway. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Du, L.; Wen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Up-regulation of miR-182 expression in colorectal cancer tissues and its prognostic value. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.S.; Alam, K.J.; Kang, I.H.; Park, W.C.; Seo, G.S.; Choi, S.C.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, H.B.; Yun, K.J.; Chae, S.C. MicroRNA 196B regulates FAS-mediated apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Deng, L.; Cui, Y.; Lu, Y. MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, W.P.; Kwok, T.T. The miR-18a* microRNA functions as a potential tumor suppressor by targeting on K-Ras. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Qian, Q. MicroRNA-133a suppresses colorectal cancer cell invasion by targeting Fascin1. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; An, H.; Wang, B.; Liao, Q.; Li, W.; Jin, X.; Cui, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, L. miR-133a represses tumour growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting LIM and SH3 protein 1 and inhibiting the MAPK pathway. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3924–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, K.M.; Li, X.R. miR-133b acts as a tumor suppressor and negatively regulates TBPL1 in colorectal cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 3767–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.T.; Qian, F.; Fang, K.; Lin, K.Y.; Wang, W.T.; Chen, Y.Q. miR-133b, a muscle-specific microRNA, is a novel prognostic marker that participates in the progression of human colorectal cancer via regulation of CXCR4 expression. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.J.; Ren, L.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Sun, T.T.; Yu, Y.N.; Wang, Y.C.; Yan, T.T.; Zou, W.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. miR-194 deregulation contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis via targeting AKT2 pathway. Theranostics 2014, 4, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Shen, Z.L.; Gao, Z.D.; Zhao, G.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yan, Y.C.; Shen, C.; Jiang, K.W.; et al. miR-194, commonly repressed in colorectal cancer, suppresses tumor growth by regulating the MAP4K4/c-Jun/MDM2 signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, J.E.; Santoro, M.M.; Morton, S.U.; Yu, S.; Yeh, R.F.; Wythe, J.D.; Ivey, K.N.; Bruneau, B.G.; Stainier, D.Y.; Srivastava, D. miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Wang, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Yi, H. Down-regulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer and its clinical significance. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.L.; Ye, S.C.; Wang, H.; Tan, W.K.; Tian, T.; Qiu, Y.M.; Luo, H.S. Down-regulation of miR-126 is associated with colorectal cancer cells proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting IRS-1 via the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Jiang, B. Epigenetic silencing of miR-126 contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1976–1984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, X.; An, P.; Quan, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Luo, H. MicroRNA-126 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer cells by targeting CXCR4 via the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Luo, J.; Hao, H.; Hu, J.; Xie, S.K.; Ren, D.; Rao, B. MicroRNA-100 regulates SW620 colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting RAP1B. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Z.G.; Sun, X.F. Downregulation of microRNA-124 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Yue, X.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wan, J. miR-124 suppresses growth of human colorectal cancer by inhibiting STAT3. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Liang, Q.; Xu, K.; Cui, D.; Jiang, L.; Yin, P.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. miR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, N.; Tsoi, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, C.W.; Wang, K.; Zheng, S.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, F.K.; et al. MicroRNA-139-5p exerts tumor suppressor function by targeting NOTCH1 in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ou, C.; Deng, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, W.; Li, L. MicroRNA-145 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting fascin-1. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yue, Z.; Gao, P.; Xing, C.; Xu, H. MicroRNA-148b suppresses cell growth by targeting cholecystokinin-2 receptor in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Xi, X.Q.; Wu, J.; Wan, Y.Y.; Hui, H.X.; Cao, X.F. MicroRNA-206 attenuates tumor proliferation and migration involving the downregulation of NOTCH3 in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zeng, Z.L.; Wu, W.J.; Zhang, D.S.; Luo, H.Y.; Wang, F.; Qiu, M.Z.; Wang, D.S.; Ren, C.; et al. Identification of microRNA-214 as a negative regulator of colorectal cancer liver metastasis by way of regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 expression. Hepatology 2014, 60, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Dong, Y.; Wu, C.W.; Zhao, Z.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis in colon cancer by downregulating BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, T.W.; Hsu, H.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, W.T.; Cheng, Y.W.; Cheng, C.W. MicroRNA-224 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration by targeting Cdc42. Dis. Markers 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Dong, T.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, A.; Feng, B.; Quan, Y.; Jin, R.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; et al. miR-320a suppresses colorectal cancer progression by targeting Rac1. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Meng, Y.L.; Yan, B.; Bian, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.Z.; et al. MicroRNA-320a suppresses human colon cancer cell proliferation by directly targeting β-catenin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Meng, X.; Ying, X.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, R.; Pan, Z.; Kang, T.; Huang, W. MicroRNA-342 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion by directly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, M.; Jiang, S.; Wang, X. MicroRNA-375 inhibits colorectal cancer growth by targeting PIK3CA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T. miR-378 is an independent prognostic factor and inhibits cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, M. miR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 390, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Dong, W.; Xie, C.; Guo, H. MicroRNA-455 inhibits proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by targeting RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase. Tumour Boil. 2015, 36, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Pan, X.; Fan, P.; He, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Luo, X. Loss of miR-638 in vitro promotes cell invasion and a mesenchymal-like transition by influencing SOX2 expression in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, L.; Lau, W.B.; Lau, B.; Ren, N.; Hu, Y.; Yi, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, S.; et al. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: Small molecules with big functions. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lena, M.; Travaglio, E.; Altomare, D.F. New strategies for colorectal cancer screening. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Ahmed, N.C.; Vos, P.W.; Bonnerup, C.; Atkins, J.N.; Casey, M.; Nuovo, G.J.; Naziri, W.; Wiley, J.E.; Mota, H.; et al. Diagnostic microRNA markers to screen for sporadic human colon cancer in stool: I. Proof of principle. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2013, 10, 93–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yau, T.O.; Wu, C.W.; Dong, Y.; Tang, C.M.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-18a identification in stool as potential biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, L.C.; Chue, X.P.; Koh, P.K.; Cheah, P.Y.; Chan, E.C.; Ho, H.K. Global fecal microRNA profiling in the identification of biomarkers for colorectal cancer screening among Asians. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.W.; Ng, S.S.; Dong, Y.J.; Ng, S.C.; Leung, W.W.; Lee, C.W.; Wong, Y.N.; Chan, F.K.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J. Detection of miR-92a and miR-21 in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for colorectal cancer and polyps. Gut 2012, 61, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Saito, N.; Kakugawa, Y.; Otake, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsumura, Y. Fecal miR-106a is a useful marker for colorectal cancer patients with false-negative results in immunochemical fecal occult blood test. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.W.; Ng, S.C.; Dong, Y.; Tian, L.; Ng, S.S.; Leung, W.W.; Law, W.T.; Yau, T.O.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. Identification of microRNA-135b in stool as a potential noninvasive biomarker for colorectal cancer and adenoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalimutho, M.; del Vecchio Blanco, G.; di Cecilia, S.; Sileri, P.; Cretella, M.; Pallone, F.; Federici, G.; Bernardini, S. Differential expression of miR-144* as a novel fecal-based diagnostic marker for colorectal cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.D.; Song, Y.C.; Cao, P.L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Q.; Yan, R.; Diao, D.M.; Cheng, Y.; Dang, C.X. Detection of miR-34a and miR-34b/c in stool sample as potential screening biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.M.; Zhao, R.H.; Li, S.T.; Xie, C.X.; Jiang, H.H.; Ding, W.J.; Du, P.; Chen, W.; Yang, M.; Cui, L. Down-regulation of fecal miR-143 and miR-145 as potential markers for colorectal cancer. Saudi Med. J. 2012, 33, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, R.; Mosakhani, N.; Asadi, J.; Nouraee, N.; Mowla, S.J.; Poustchi, H.; Malekzadeh, R.; Knuutila, S. Decreased expression of fecal miR-4478 and miR-1295b-3p in early-stage colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2014, 15, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Stock, C.; Burwinkel, B.; Brenner, H. Identification and evaluation of plasma microRNAs for early detection of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.X.; Huang, G.L.; Guo, H.Q.; Guo, C.C.; Li, H.; Ye, S.; Ling, S.; Jiang, L.; Tian, Y.; Lin, T.Y. Circulating miR-221 directly amplified from plasma is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer and is correlated with p53 expression. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hur, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basati, G.; Emami Razavi, A.; Abdi, S.; Mirzaei, A. Elevated level of microRNA-21 in the serum of patients with colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, P.; Padilla, D.; Villarejo, P.; Palomino, T.; Nieto, P.; Menendez, J.M.; Rodriguez-Montes, J.A. Prognostic implications of serum microRNA-21 in colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 108, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Li, K.; Zhu, K.; Yan, R.; Dang, C. Plasma miR-183 predicts recurrence and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fan, Z.; Liu, B.; Pei, Y.; Zhao, Z. Expression of plasma miR-106a in colorectal cancer and its clinical significance. J. Southern Med. Univ. 2014, 34, 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Xia, H.W.; Ge, X.J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Tang, Q.L.; Bi, F. Serum miR-19a predicts resistance to FOLFOX chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer cases. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet Vega, A.; Pericay, C.; Moya, I.; Ferrer, A.; Dotor, E.; Pisa, A.; Casalots, A.; Serra-Aracil, X.; Oliva, J.C.; Ruiz, A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal cancer: Circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhong, J.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Jian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W. The expression and clinical significance of microRNAs in colorectal cancer detecting. Tumour Biol. 2014, 36, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, X.; Yang, P.; Yang, J.; An, P.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; et al. Low expression of microRNA-126 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Ji, G. MicroRNA-630 is a prognostic marker for patients with colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 9787–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Hou, Y.; Yuan, T.; Gao, C.; Jia, W.; Yi, X.; Liu, M. MicroRNA-92a as a potential biomarker in diagnosis of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Jin, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.B. MicroRNA-17-5p promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance and tumour metastasis of colorectal cancer by repressing PTEN expression. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2974–2987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Li, N.; Li, X. Dysregulated miR1254 and miR579 for cardiotoxicity in patients treated with bevacizumab in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 5227–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, T.; Tejero, R.; Moreno, I.; Ferrer, G.; Cordeiro, A.; Artells, R.; Navarro, A.; Hernandez, R.; Tapia, G.; Monzo, M. Role of miR-200 family members in survival of colorectal cancer patients treated with fluoropyrimidines. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 109, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Geng, L.; Talmon, G.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-520g confers drug resistance by regulating p21 expression in colorectal cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6215–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.; Gao, F.; Lin, X.; He, L.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L. miR-124 Radiosensitizes human colorectal cancer cells by targeting PRRX1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Sun, K.; Deng, H.J.; Lei, S.T.; Dong, J.Q.; Li, G.X. Anti-miRNA-221 sensitizes human colorectal carcinoma cells to radiation by upregulating PTEN. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 9307–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Feng, B.; Liu, N.; Wu, Q.; Han, Y.; Nie, Y.; Wu, K.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. STIM1, a direct target of microRNA-185, promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Yue, X.; Yang, Q.; Hu, W. HIF-2α mediates hypoxia-induced LIF expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4406–4417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Fu, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Wei, J.; Guo, J. Peroxiredoxin 2 knockdown by RNA interference inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cancer Lett. 2014, 343, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, H.L.; Moran, J.V. Dynamic interactions between transposable elements and their hosts. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Siomi, M.C. Piwi-interacting RNAs: biological functions and biogenesis. Essays Biochem. 2013, 54, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assumpcao, C.B.; Calcagno, D.Q.; Araujo, T.M.; Batista dos Santos, S.E.; Ribeiro dos Santos, A.K.; Riggins, G.J.; Burbano, R.R.; Assumpcao, P.P. The role of piRNA and its potential clinical implications in cancer. Epigenomics 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyano, M.; Stefani, G. PiRNA involvement in genome stability and human cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Guo, J.M.; Xiao, B.X.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.N. piRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer cells. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Xia, L.; Qiu, X.; Gu, D.; Zhu, L.; Jin, J.; Hui, G.; Hua, Q.; Du, M.; Tong, N.; et al. Genetic variants in noncoding PIWI-interacting RNA and colorectal cancer risk. Cancer 2015, 121, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.D.; Qi, P.; Du, X. Long non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer: Implications for pathogenesis and clinical application. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.C.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, J.J.; Xu, J.; Wei, Y. Involvement of long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer: From benchtop to bedside (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.H.; Chen, Y. Targeting long non-coding RNAs in cancers: progress and prospects. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1895–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Vincent, K.; Pichler, M.; Fodde, R.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Slack, F.J.; Calin, G.A. Junk DNA and the long non-coding RNA twist in cancer genetics. Oncogene 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, G.; Gu, D.; Zhu, L.; Hua, Q.; Du, M.; Chu, H.; Tong, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA signature in human colorectal cancer. Gene 2015, 556, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Rong, L.F.; Shi, C.B.; Dong, X.G.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.L.; Wen, H.; He, Z.Y. Screening of lymph nodes metastasis associated lncRNAs in colorectal cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8139–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liang, G.; Yuan, B.; Yang, C.; Gao, R.; Zhou, X. MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014, 36, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Xie, H.Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.M.; Chen, L.M.; Zheng, S.S. Long non-coding RNA MALAT-1 overexpression predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1810–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Tan, D.; Meng, H.; Wang, K.; Bai, Y.; Yang, K. Up-regulation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 contributes to proliferation and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. .Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.T.; Shi, D.B.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, X.X.; Xu, Y.; Tripathi, P.; Gu, W.L.; Cai, G.X.; Cai, S.J. High expression of lncRNA MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3174–3181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Han, Z.; Sui, H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes tumour growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer through binding to SFPQ and releasing oncogene PTBP2 from SFPQ/PTBP2 complex. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yang, M.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. MALAT-1: A long non-coding RNA and its important 3′ end functional motif in colorectal cancer metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Xu, C.; Xie, L.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, Z.G. MALAT1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation/migration/invasion via PRKA kinase anchor protein 9. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athar, M.; Back, J.H.; Tang, X.; Kim, K.H.; Kopelovich, L.; Bickers, D.R.; Kim, A.L. Resveratrol: A review of preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 224, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, L.G.; D’Orazio, J.A.; Pearson, K.J. Resveratrol and cancer: Focus on in vivo evidence. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, R209–R225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Li, M.; Zhu, R. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation in human colorectal carcinoma cells by inducing G1/Sphase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through caspase/cyclinCDK pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Yan, L.; Jiang, H.; Ren, J.; Cai, J.; Li, Q. Resveratrol suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway mediated Snail/E-cadherin expression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Sui, H.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Cai, J.; Qin, J.; Ren, J.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via MALAT1 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Song, X.Q.; Cai, J.P.; Zhang, S. HOTAIR: A cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjari, M.; Salavaty, A. HOTAIR: An oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Wu, Z.; Liao, K.; Zhang, S. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR can serve as a common molecular marker for lymph node metastasis: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 8445–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Sun, H.; He, B.; Pan, Y.; Gao, T.; Chen, J.; Ying, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S. Prognostic value of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in various cancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Large intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an indicator of poor prognosis and a therapeutic target in human cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18985–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Prognostic value of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in digestive system malignancies. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Gu, D.; Ma, G.; Zhu, L.; Hua, Q.; Chu, H.; Tong, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Genetic variants in lncRNA HOTAIR are associated with risk of colorectal cancer. Mutagenesis 2015, 30, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogo, R.; Shimamura, T.; Mimori, K.; Kawahara, K.; Imoto, S.; Sudo, T.; Tanaka, F.; Shibata, K.; Suzuki, A.; Komune, S.; et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6320–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.H.; Wang, X.L.; Tang, H.M.; Jiang, T.; Chen, J.; Lu, S.; Qiu, G.Q.; Peng, Z.H.; Yan, D.W. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a powerful predictor of metastasis and poor prognosis and is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoboda, M.; Slyskova, J.; Schneiderova, M.; Makovicky, P.; Bielik, L.; Levy, M.; Lipska, L.; Hemmelova, B.; Kala, Z.; Protivankova, M.; et al. HOTAIR long non-coding RNA is a negative prognostic factor not only in primary tumors, but also in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, O.; Ariel, I.; Ilan, J.; Lev-Lehman, E.; De-Groot, N.; Hochberg, A. Expression of the imprinted gene H19 in the human fetus. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1994, 38, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Onyango, P.; Brandenburg, S.; Wu, Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Feinberg, A.P. Loss of imprinting in colorectal cancer linked to hypomethylation of H19 and IGF2. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6442–6446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Tang, Z.; Song, G.; Pan, Y.; He, B.; Bao, Q.; Wang, S. Loss of imprinting of IGF2 correlates with hypomethylation of the H19 differentially methylated region in the tumor tissue of colorectal cancer patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matouk, I.J.; Raveh, E.; Abu-lail, R.; Mezan, S.; Gilon, M.; Gershtain, E.; Birman, T.; Gallula, J.; Schneider, T.; Barkali, M.; Richler, C.; et al. Oncofetal H19 RNA promotes tumor metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, W.P.; Ng, E.K.; Ng, S.S.; Jin, H.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.; Kwok, T.T. Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissan, A.; Stojadinovic, A.; Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S.; Halle, D.; Grinbaum, R.; Roistacher, M.; Bochem, A.; Dayanc, B.E.; Ritter, G.; Gomceli, I.; et al. Colon cancer associated transcript-1: A novel RNA expressed in malignant and pre-malignant human tissues. Int. J. Cancer. 2012, 130, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaiyan, B.; Ilyayev, N.; Stojadinovic, A.; Izadjoo, M.; Roistacher, M.; Pavlov, V.; Tzivin, V.; Halle, D.; Pan, H.; Trink, B.; et al. Differential expression of colon cancer associated transcript1 (CCAT1) along the colonic adenoma-carcinoma sequence. BMC Cancer 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kam, Y.; Rubinstein, A.; Naik, S.; Djavsarov, I.; Halle, D.; Ariel, I.; Gure, A.O.; Stojadinovic, A.; Pan, H.; Tsivin, V.; et al. Detection of a long non-coding RNA (CCAT1) in living cells and human adenocarcinoma of colon tissues using FIT-PNA molecular beacons. Cancer Lett. 2014, 352, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.B.; Ge, J.; Lu, X.; et al. Human colorectal cancer-specific CCAT1-L lncRNA regulates long-range chromatin interactions at the MYC locus. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Spizzo, R.; Atlasi, Y.; Nicoloso, M.; Shimizu, M.; Redis, R.S.; Nishida, N.; Gafa, R.; Song, J.; Guo, Z.; et al. CCAT2, a novel noncoding RNA mapping to 8q24, underlies metastatic progression and chromosomal instability in colon cancer. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redis, R.S.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Look, M.P.; Tudoran, O.; Ivan, C.; Spizzo, R.; Zhang, X.; de Weerd, V.; Shimizu, M.; Ling, H.; et al. CCAT2, a novel long non-coding RNA in breast cancer: Expression study and clinical correlations. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1748–1762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, L.; Yin, R. CCAT2 is a lung adenocarcinoma-specific long non-coding RNA and promotes invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 5375–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Xu, M.D.; Ni, S.J.; Huang, D.; Wei, P.; Tan, C.; Zhou, X.Y.; Du, X. Low expression of LOC285194 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, Y.Y. LncRNA loc285194 is a p53-regulated tumor suppressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 4976–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, J.; Hankeova, S.; Svoboda, M.; Kiss, I.; Vyzula, R.; Slaby, O. Expression levels of transcribed ultraconserved regions uc.73 and uc.388 are altered in colorectal cancer. Oncology 2012, 82, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. LincRNA-p21 enhances the sensitivity of radiotherapy for human colorectal cancer by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, H.; Fesler, A.; Schee, K.; Fodstad, O.; Flatmark, K.; Ju, J. Clinical significance of long intergenic noncoding RNA-p21 in colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2013, 12, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; He, X.; Zhang, E.; Kong, R.; De, W.; Zhang, Z. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Xu, M.D.; Ni, S.J.; Shen, X.H.; Wei, P.; Huang, D.; Tan, C.; Sheng, W.Q.; Zhou, X.Y.; Du, X. Down-regulation of ncRAN, a long non-coding RNA, contributes to colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion and predicts poor overall survival for colorectal cancer patients. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Gu, W.; Yang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Yue, X.; Gu, Q.; Liu, L. Downregulation of a long noncoding RNA-ncRuPAR contributes to tumor inhibition in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 11329–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.D.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, E.; Kong, R.; Zhang, Z.H.; Guo, R.H. Decreased expression of long noncoding RNA MEG3 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4851–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Zheng, H.; Zhuo, C.; Peng, J.; Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Cai, G.; Cai, S. Low expression of novel lncRNA RP11-462C24.1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Sun, R.; Liang, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Bai, P.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L. Association between polymorphisms in long non-coding RNA PRNCR1 in 8q24 and risk of colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sawada, G.; Kurashige, J.; Uchi, R.; Matsumura, T.; Ueo, H.; Takano, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Sudo, T.; Sugimachi, K.; et al. Amplification of PVT-1 is involved in poor prognosis via apoptosis inhibition in colorectal cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, B.C.; Graham, L.D.; Molloy, P.L. CRNDE, a long non-coding RNA responsive to insulin/IGF signaling, regulates genes involved in central metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, L.D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Brown, G.S.; Ho, T.; Kassir, Z.; Moynihan, A.T.; Vizgoft, E.K.; Dunne, R.; Pimlott, L.; Young, G.P.; et al. Colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE), a novel gene with elevated expression in colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matouk, I.J.; Abbasi, I.; Hochberg, A.; Galun, E.; Dweik, H.; Akkawi, M. Highly upregulated in liver cancer noncoding RNA is overexpressed in hepatic colorectal metastasis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Chen, Y.; Liao, X.; Liu, D.; Li, F.; Ruan, H.; Jia, W. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA PCAT-1 is a novel biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y. BRAF-activated long non-coding RNA contributes to colorectal cancer migration by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jie, D.; Yun, T.; Li, W.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Feng, J. Downregulated Long noncoding RNA BANCR promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells via downregualtion of p21 expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Yuan, H.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Sui, H.; Wei, X.L.; Liu, L.; Huang, P.; Zhang, W.J.; Bai, Y.X. UCA1, a long non-coding RNA up-regulated in colorectal cancer influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle distribution. Pathology 2014, 46, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, T.; Uchi, R.; Nambara, S.; Saito, T.; Komatsu, H.; Hirata, H.; Ueda, M.; Sakimura, S.; Takano, Y.; Kurashige, J.; et al. A long noncoding RNA, lncRNA-ATB, is involved in the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.J.; Yan, J.B. Long non-coding RNA LINC01296 is a potential prognostic biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Moyer, M.P.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, N.; et al. Long non-coding RNA CCAL regulates colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway via suppression of activator protein 2α. Gut 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss-Laszlo, Z.; Henry, Y.; Bachellerie, J.P.; Caizergues-Ferrer, M.; Kiss, T. Site-specific ribose methylation of preribosomal RNA: A novel function for small nucleolar RNAs. Cell 1996, 85, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss-Laszlo, Z.; Henry, Y.; Kiss, T. Sequence and structural elements of methylation guide snoRNAs essential for site-specific ribose methylation of pre-rRNA. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, A.M.; Jady, B.E.; Bertrand, E.; Kiss, T. Human box H/ACA pseudouridylation guide RNA machinery. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5797–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.; Contreras, A.; Ruggero, D. Small RNAs with big implications: New insights into H/ACA snoRNA function and their role in human disease. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2015, 6, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appaiah, H.N.; Goswami, C.P.; Mina, L.A.; Badve, S.; Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Liu, Y.; Nakshatri, H. Persistent upregulation of U6:SNORD44 small RNA ratio in the serum of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Y.; Rodriguez, C.; Guo, P.; Sun, X.; Talbot, J.T.; Zhou, W.; Petros, J.; Li, Q.; Vessella, R.L.; Kibel, A.S.; et al. SnoRNA U50 is a candidate tumor-suppressor gene at 6q14.3 with a mutation associated with clinically significant prostate cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Ma, J.; Mannoor, K.; Guarnera, M.A.; Shetty, A.; Zhan, M.; Xing, L.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Genome-wide small nucleolar RNA expression analysis of lung cancer by next-generation deep sequencing. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E623–E629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yang, F.; Ding, C.L.; Zhao, L.J.; Ren, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Qi, Z.T. Small nucleolar RNA 113-1 suppresses tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorenoor, N.; Slaby, O. Small nucleolar RNAs functioning and potential roles in cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallar, S.C.; Kalvakolanu, D.V. Regulation of snoRNAs in cancer: Close encounters with interferon. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013, 33, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, H.E.; Buffa, F.M.; Camps, C.; Ramachandran, A.; Leek, R.; Taylor, M.; Patil, M.; Sheldon, H.; Betts, G.; Homer, J.; et al. The small-nucleolar RNAs commonly used for microRNA normalisation correlate with tumour pathology and prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krell, J.; Frampton, A.E.; Mirnezami, R.; Harding, V.; De Giorgio, A.; Roca Alonso, L.; Cohen, P.; Ottaviani, S.; Colombo, T.; Jacob, J.; et al. Growth arrest-specific transcript 5 associated snoRNA levels are related to p53 expression and DNA damage in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, H.J.; Heyn, H.; Moutinho, C.; Esteller, M. CpG island hypermethylation-associated silencing of small nucleolar RNAs in human cancer. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadkhan, S. snRNAs as the catalysts of pre-mRNA splicing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniskin, A.; Nopel-Dunnebacke, S.; Ahrens, M.; Jensen, S.G.; Zollner, H.; Maghnouj, A.; Wos, A.; Mayerle, J.; Munding, J.; Kost, D.; et al. Circulating U2 small nuclear RNA fragments as a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, E48–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniskin, A.; Nopel-Dunnebacke, S.; Schumacher, B.; Gerges, C.; Bracht, T.; Sitek, B.; Meyer, H.E.; Gerken, G.; Dechene, A.; Schlaak, J.F.; et al. Analysis of U2 small nuclear RNA fragments in the bile differentiates cholangiocarcinoma from primary sclerosing cholangitis and other benign biliary disorders. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.O.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Mo, X.; Li, T.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Damgaard, C.K. Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5609–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Zheng, J.; An, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y. Circular RNA ITCH has inhibitory effect on ESCC by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6001–6013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Reiner, A.T.; Auer, K.; Sukhbaatar, N.; Aust, S.; Bachleitner-Hofmann, T.; Mesteri, I.; Grunt, T.W.; Zeillinger, R.; et al. Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation—Exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, S.J.; Schaack, J.; Cooley, L.; Burke, D.J.; Soll, D. Structure and transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 1985, 19, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.M.; Parker, R. Stressing out over tRNA cleavage. Cell 2009, 138, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, H.; Liu, X.; Nguyen, H.C.; Zhang, S.; Fish, L.; Tavazoie, S.F. Endogenous tRNA-derived fragments suppress breast cancer progression via YBX1 displacement. Cell 2015, 161, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Song, Y.-X.; Ma, B.; Wang, J.-J.; Sun, J.-X.; Chen, X.-W.; Zhao, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-C.; Wang, Z.-N. Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19886-19919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819886
Wang J, Song Y-X, Ma B, Wang J-J, Sun J-X, Chen X-W, Zhao J-H, Yang Y-C, Wang Z-N. Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):19886-19919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819886
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jun, Yong-Xi Song, Bin Ma, Jia-Jun Wang, Jing-Xu Sun, Xiao-Wan Chen, Jun-Hua Zhao, Yu-Chong Yang, and Zhen-Ning Wang. 2015. "Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 19886-19919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819886
APA StyleWang, J., Song, Y.-X., Ma, B., Wang, J.-J., Sun, J.-X., Chen, X.-W., Zhao, J.-H., Yang, Y.-C., & Wang, Z.-N. (2015). Regulatory Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 19886-19919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819886