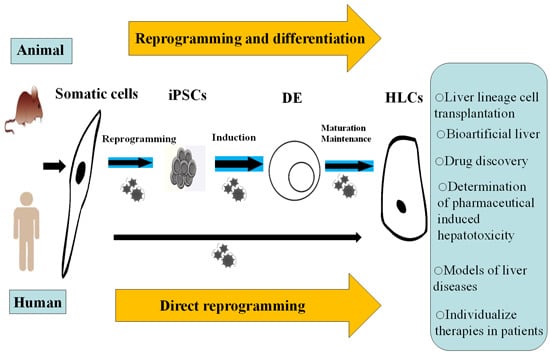
Two Effective Routes for Removing Lineage Restriction Roadblocks: From Somatic Cells to Hepatocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Reprogramming Somatic Cells to Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSCs)
3. The Hepatic Differentiation Abilities of Different Sources Vary
4. The Characteristics of iPSC-Derived Hepatocyte-Like Cells (HLCs)

5. In Vitro Differentiation of iPSCs to HLCs

5.1. Differentiation to Immature HLCs
5.2. Maturation of iPSC-Derived Hepatic Lineage Cells
5.3. Three-Dimensional (3D) Culture for Hepatic Differentiation
| Species | Cell Type | Target Cell | 2D/3D Culture | Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | iPSCs | Definitive endoderm | Poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffold | Reduced cell stress, rapid cell adaption, and high viability, growth, and differentiation | [63] |
| Human | iPSCs | Definitive endoderm | CHIR99021/Wnt3A ligand under feeder- and serum-free conditions | Easier handling and higher efficiency | [55] |
| Human | iPSCs | Hepatoblasts | Serum/feeder cell-free chemically defined conditions | Faster transition, more functional and higher efficiency | [65] |
| Mouse | iPSCs | HLCs | 3D micro-cavitary hydrogel system | Nutrient exchange enhancement, greater living space, faster transition, and higher efficiency | [81] |
| Human | iPSCs | HLCs | Nanofiber scaffolds | More functional and higher efficiency | [82] |
| Human | iPSCs | HLCs | 3D micropattern plate | More functional, higher efficiency, large number of HLCs for industrial and clinical applications | [83] |
| Human | iPSCs | HLCs | Scalable stirred-suspension bioreactor | Multiple features of primary hepatocytes and persistent function in vivo | [84] |
| Mouse | iPSCs | HLCs | Combination of a bioreactor module with a 0.2 μm pore membrane | Act as a promising option for bioartificial liver systems | [85] |
| Human | iPSCs | HLCs | 3D collagen matrices compatible with high-throughput screening | Promote functional maturation and improve functional longevity to over 75 days | [86] |
| Human | iPSCs | HLCs | A micro-patterned co-culture platform | Promote functional maturation and improve functional longevity to over four weeks | [87] |
| Human | iPSC derived-hepatoblasts | HLCs | Combination of 3D cell aggregation and cAMP signaling | Comparable function to primary human hepatocytes, more simple and reproducible | [88] |
| Human | iPSC derived-hepatoblasts | HLCs | Human laminin 111-coated dish | Longevity of more than 3 months | [89] |
| Human | iPSCs | Liver bud | Coculture with endothelial cells and mesenchymal stem cells, and then mixed cells are plated onto a presolidified matrix | Fast formation of liver bud and act as a functional liver in vivo | [90] |
6. Direct Reprogramming as an Alternative
7. In Vivo Hepatic Differentiation of iPSCs
8. The Potential Applications of iPSC-Derived HLCs
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESCs | embryonic stem cells |
| iPSCs | induced pluripotent stem cells |
| HLCs | hepatocyte-like cells |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| ICG | indocyanine green |
| mKO1 | monomeric Kusabira-Orange |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| SSCs | spermatogonial stem cells |
| AAT | alpha-1 antitrypsin |
References
- Kmiec, Z. Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2001, 161, 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, S.A.; Keeffe, E.B. Chronic viral hepatitis: Epidemiology, molecular biology, and antiviral therapy. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.; Strom, S.C.; Sokal, E.; Fox, I.J. Human hepatocyte transplantation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 640, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Nagata, H.; Miyakawa, S.; Fox, I.J. Review of hepatocyte transplantation. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2009, 16, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Ying, L.; Galvao, A.M.; Mills, J.A.; Lin, H.C.; Kotton, D.N.; Shen, S.S.; Nostro, M.C.; Lu, L.; Choi, J.K.; et al. Self-renewing endodermal progenitor lines generated from human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afanassieff, M.; Tapponnier, Y.; Savatier, P. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells in rabbits. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, E.; Nemes, C.; Davis, R.P.; Ujhelly, O.; Klincumhom, N.; Polgar, Z.; Muenthaisong, S.; Pirity, M.K.; Dinnyes, A. Generation of transgene-free mouse induced pluripotent stem cells using an excisable lentiviral system. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Freed, C.R. Adenoviral gene delivery can reprogram human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, K.; Sano, M.; Ohtaka, M.; Furuta, B.; Umemura, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Ikehara, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Segawa, H.; Takayasu, S.; et al. Development of defective and persistent Sendai virus vector: A unique gene delivery/expression system ideal for cell reprogramming. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 4760–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Liu, T.; Song, K.; Li, X.; Ge, D. Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from human adipose-derived stem cells using a non-viral polycistronic plasmid in feeder-free conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Hung, S.S.; Lim, S.Y.; Wong, R.C.; Ko, M.S. Efficient generation of integration-free human induced pluripotent stem cells from keratinocytes by simple transfection of episomal vectors. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, F.; Wilson, K.D.; Sun, N.; Gupta, D.M.; Huang, M.; Panetta, N.J.; Chen, Z.Y.; Robbins, R.C.; Li, Z.; Kay, M.A.; et al. A nonviral minicircle vector for deriving human iPS cells. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, B.C.; Heinimann, K.; Miny, P.; Iezzi, G.; Glatz, K.; Scherberich, A.; Zulewski, H.; Fussenegger, M. mRNA transfection-based, feeder-free, induced pluripotent stem cells derived from adipose tissue of a 50-year-old patient. Metab. Eng. 2013, 18, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, S.; Joo, J.Y.; Zhu, S.; Han, D.W.; Lin, T.; Trauger, S.; Bien, G.; Yao, S.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells using recombinant proteins. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Ding, S. Brief report: Combined chemical treatment enables Oct4-induced reprogramming from mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Ambasudhan, R.; Yuan, X.; Li, W.; Hilcove, S.; Abujarour, R.; Lin, X.; Hahm, H.S.; Hao, E.; Hayek, A.; et al. A chemical platform for improved induction of human iPSCs. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montserrat, N.; Nivet, E.; Sancho-Martinez, I.; Hishida, T.; Kumar, S.; Miquel, L.; Cortina, C.; Hishida, Y.; Xia, Y.; Esteban, C.R.; et al. Reprogramming of human fibroblasts to pluripotency with lineage specifiers. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Heo, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Jun, E.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, A.; Kim, J.; Whang, K.Y.; Kang, Y.K.; Yeo, S.; et al. Reprogramming fibroblasts into induced pluripotent stem cells with Bmi1. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samavarchi-Tehrani, P.; Golipour, A.; David, L.; Sung, H.K.; Beyer, T.A.; Datti, A.; Woltjen, K.; Nagy, A.; Wrana, J.L. Functional genomics reveals a BMP-driven mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in the initiation of somatic cell reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montserrat, N.; de Onate, L.; Garreta, E.; Gonzalez, F.; Adamo, A.; Eguizabal, C.; Hafner, S.; Vassena, R.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Generation of feeder-free pig induced pluripotent stem cells without Pou5f1. Cell Transpl. 2012, 21, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Yan, S.; Fu, C.; Wei, A. The histone acetyltransferase MOF promotes induces generation of pluripotent stem cells. Cell. Reprogram. 2015, 17, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Niu, B.; Zhu, H.; He, X.; Bai, C.; Li, G.; Hua, J. PRMT5 enhances generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from dairy goat embryonic fibroblasts via down-regulation of p53. Cell Prolif. 2015, 48, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingold, J.A.; Fidalgo, M.; Guallar, D.; Lau, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, H.; Faiola, F.; Huang, X.; Lee, D.F.; Waghray, A.; et al. A genome-wide RNAi screen identifies opposing functions of Snai1 and Snai2 on the Nanog dependency in reprogramming. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodsizadeh, A.; Taei, A.; Totonchi, M.; Seifinejad, A.; Gourabi, H.; Pournasr, B.; Aghdami, N.; Malekzadeh, R.; Almadani, N.; Salekdeh, G.H.; et al. Generation of liver disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells along with efficient differentiation to functional hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2010, 6, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chichagova, V.; Sanchez-Vera, I.; Armstrong, L.; Steel, D.; Lako, M. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells using RNA-based Sendai virus system and pluripotency validation of the resulting cell population. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Han, Q.; Qin, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Song, H.; Yang, D.; Peng, M.; et al. Toward an optimized culture medium for the generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31066–31072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakada, A.; Shigeno, K.; Nakamura, T. Accelerated generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells with retroviral transduction and chemical inhibitors under physiological hypoxia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Okita, K.; Ichisaka, T.; Yamanaka, S. Hypoxia enhances the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elanzew, A.; Sommer, A.; Pusch-Klein, A.; Brustle, O.; Haupt, S. A reproducible and versatile system for the dynamic expansion of human pluripotent stem cells in suspension. Biotechnol. J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Bru, P.; Roelandt, P.; Narain, N.; Pauwelyn, K.; Notelaers, T.; Shimizu, T.; Ott, M.; Verfaillie, C. Directed differentiation of murine-induced pluripotent stem cells to functional hepatocyte-like cells. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, Y.; Mich-Basso, J.D.; Lin, B.; Yang, L. High efficient differentiation of functional hepatocytes from porcine induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansel, M.C.; Gramignoli, R.; Blake, W.; Davila, J.; Skvorak, K.; Dorko, K.; Tahan, V.; Lee, B.R.; Tafaleng, E.; Guzman-Lepe, J.; et al. Increased reprogramming of human fetal hepatocytes compared with adult hepatocytes in feeder-free conditions. Cell Transpl. 2014, 23, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiwara, M.; Aoi, T.; Okita, K.; Takahashi, R.; Inoue, H.; Takayama, N.; Endo, H.; Eto, K.; Toguchida, J.; Uemoto, S.; et al. Donor-dependent variations in hepatic differentiation from human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12538–12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ye, Z.; Kim, Y.; Sharkis, S.; Jang, Y.Y. Generation of endoderm-derived human induced pluripotent stem cells from primary hepatocytes. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Seo, D.; Choi, D.; Park, K.Y.; Holczbauer, A.; Marquardt, J.U.; Conner, E.A.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Contribution of hepatic lineage stage-specific donor memory to the differential potential of induced mouse pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basma, H.; Soto-Gutierrez, A.; Yannam, G.R.; Liu, L.; Ito, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Ellis, E.; Carson, S.D.; Sato, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Differentiation and transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snykers, S.; de Kock, J.; Rogiers, V.; Vanhaecke, T. In vitro differentiation of embryonic and adult stem cells into hepatocytes: State of the art. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 577–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.E.; Fleming, H.E.; Khetani, S.R.; Bhatia, S.N. Pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulvestad, M.; Nordell, P.; Asplund, A.; Rehnstrom, M.; Jacobsson, S.; Holmgren, G.; Davidson, L.; Brolen, G.; Edsbagge, J.; Bjorquist, P.; et al. Drug metabolizing enzyme and transporter protein profiles of hepatocytes derived from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharvand, H.; Hashemi, S.M.; Shahsavani, M. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells in a serum-free adherent culture condition. Differentiation 2008, 76, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, M.; Yamashita, A.; Tagawa, Y. Mitochondrial development of the in vitro hepatic organogenesis model with simultaneous cardiac mesoderm differentiation from murine induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Amiot, B.P.; Rinaldo, P.; Duncan, S.A.; Nyberg, S.L. Hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells: Relevance to cellular therapies. Stem Cell Res. 2012, 9, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.Y.; Liu, W.; Qiu, D.B.; Hei, Z.Q.; Ying, Q.L.; Chen, G.H. Efficient derivation of functional hepatocytes from mouse induced pluripotent stem cells by a combination of cytokines and sodium butyrate. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 2011, 124, 3786–3793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Si-Tayeb, K.; Noto, F.K.; Nagaoka, M.; Li, J.; Battle, M.A.; Duris, C.; North, P.E.; Dalton, S.; Duncan, S.A. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology 2010, 51, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touboul, T.; Hannan, N.R.; Corbineau, S.; Martinez, A.; Martinet, C.; Branchereau, S.; Mainot, S.; Strick-Marchand, H.; Pedersen, R.; di Santo, J.; et al. Generation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells under chemically defined conditions that recapitulate liver development. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yong, J.; Duo, S.; Song, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, H.; et al. Efficient generation of hepatocyte-like cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Duan, Y.; Tschudy-Seney, B.; Roll, G.; Behbahan, I.S.; Ahuja, T.P.; Tolstikov, V.; Wang, C.; McGee, J.; Khoobyari, S.; et al. Highly efficient differentiation of functional hepatocytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjogren, A.K.; Liljevald, M.; Glinghammar, B.; Sagemark, J.; Li, X.Q.; Jonebring, A.; Cotgreave, I.; Brolen, G.; Andersson, T.B. Critical differences in toxicity mechanisms in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes, hepatic cell lines and primary hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si-Tayeb, K.; Lemaigre, F.P.; Duncan, S.A. Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravalli, R.N.; Cressman, E.N.; Steer, C.J. Hepatic differentiation of porcine induced pluripotent stem cells in vitro. Vet. J. 2012, 194, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, A.; Otsuka, M.; Kogiso, T.; Kojima, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tateishi, R.; Kato, N.; Shiina, S.; Yoshida, H.; Omata, M.; et al. Direct differentiation of hepatic cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells using a limited number of cytokines. Hepatol. Int. 2011, 5, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Shinozaki, F.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sueishi, M.; Yoshida, T. Single-step protocol for the differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells into hepatic progenitor-like cells. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itaba, N.; Wairagu, P.M.; Aramaki, N.; Yasui, T.; Matsumi, Y.; Kono, Y.; Phan, A.N.; Otsu, M.; Kunisada, T.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Nuclear receptor gene alteration in human induced pluripotent stem cells with hepatic differentiation propensity. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, E408–E419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, H.; Mizuno, K.; Terada, R.; Miura, T.; Ohnuma, K.; Takahashi, S.; Asashima, M.; Michiue, T. Improved efficiency of definitive endoderm induction from human induced pluripotent stem cells in feeder and serum-free culture system. Vitro. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2015, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavon, N. Generation of hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 640, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Takebe, T.; Sekine, K.; Koike, H.; Zheng, Y.; Taniguchi, H. Identification of proliferating human hepatic cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, A.B.; D’Amour, K.A.; Jones, K.L.; Krishnamoorthy, M.; Kulik, M.J.; Reynolds, D.M.; Sheppard, A.M.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Baetge, E.E.; et al. Activin a efficiently specifies definitive endoderm from human embryonic stem cells only when phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling is suppressed. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duboc, V.; Lapraz, F.; Saudemont, A.; Bessodes, N.; Mekpoh, F.; Haillot, E.; Quirin, M.; Lepage, T. Nodal and BMP2/4 pattern the mesoderm and endoderm during development of the sea urchin embryo. Development 2010, 137, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, K.; Takebe, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Nakauchi, H.; Taniguchi, H. Highly efficient generation of definitive endoderm lineage from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.P.; Yu, C.Y.; Chen, H.F.; Chen, P.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Lin, S.J.; Huang, S.T.; Chan, W.H.; Ueng, T.H.; Ho, H.N.; et al. Factors from human embryonic stem cell-derived fibroblast-like cells promote topology-dependent hepatic differentiation in primate embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33510–33519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvoro, A.; Devito, L.; Milton, F.A.; Noli, L.; Zhang, A.; Filippi, C.; Sakai, K.; Suh, J.H.; Dhawan, A.; Sakai, T.; et al. A thyroid hormone receptor/KLF9 axis in human hepatocytes and pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoveizi, E.; Khodadadi, S.; Tavakol, S.; Karima, O.; Nasiri-Khalili, M.A. Small molecules differentiate definitive endoderm from human induced pluripotent stem cells on PCL scaffold. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Shinozaki, F.; Motoyoshi, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishige, N. An optimal medium supplementation regimen for initiation of hepatocyte differentiation in human induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, M.; Kawabata, K.; Takayama, K.; Tashiro, K.; Sakurai, F.; Katayama, K.; Toyoda, M.; Akutsu, H.; Miyagawa, Y.; Okita, H.; et al. Efficient generation of hepatoblasts from human ES cells and iPS cells by transient overexpression of homeobox gene HEX. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.E.; Linehan, J.L.; Painschab, M.S.; Hu, W.S.; Verfaillie, C.M.; Kaufman, D.S. Defined conditions for development of functional hepatic cells from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2005, 14, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, T.; Takahashi, S.; Numata, Y.; Narita, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Kondo, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Ohmori, S.; Nagata, K. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 activates the transcription of CYP3A4 in hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 28, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Inamura, M.; Kawabata, K.; Sugawara, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Higuchi, M.; Nagamoto, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Tashiro, K.; Sakurai, F.; et al. Generation of metabolically functioning hepatocytes from human pluripotent stem cells by FOXA2 and HNF1α transduction. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Inamura, M.; Kawabata, K.; Katayama, K.; Higuchi, M.; Tashiro, K.; Nonaka, A.; Sakurai, F.; Hayakawa, T.; Furue, M.K.; et al. Efficient generation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells by HNF4α transduction. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yamazoe, T.; Shiraki, N.; Higuchi, Y.; Tokieda, K.; Kume, K.; Mitani, K.; Kume, S. Albumin gene targeting in human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells with helper-dependent adenoviral vector to monitor hepatic differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 10, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Luo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Shu, G.; Lou, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Hepatectomised patient sera promote hepatocyte differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ross, N.T.; Logan, D.J.; Thomas, D.; Duncan, S.A.; North, T.E.; Goessling, W.; Carpenter, A.E.; Bhatia, S.N. Identification of small molecules for human hepatocyte expansion and iPS differentiation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Iwao, T.; Yoshihashi, S.; Mimori, K.; Ogihara, R.; Nagata, K.; Kurose, K.; Saito, M.; Niwa, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid promotes the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Yoshihashi, S.; Mimori, K.; Ogihara, R.; Kanehama, Y.; Maki, Y.; Enosawa, S.; Kurose, K.; Iwao, T.; Nakamura, K.; et al. Selective culture method for hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2014, 29, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avior, Y.; Levy, G.; Zimerman, M.; Kitsberg, D.; Schwartz, R.; Sadeh, R.; Moussaieff, A.; Cohen, M.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Nahmias, Y. Microbial-derived lithocholic acid and vitamin K2 drive the metabolic maturation of pluripotent stem cells-derived and fetal hepatocytes. Hepatology 2015, 62, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siller, R.; Greenhough, S.; Naumovska, E.; Sullivan, G.J. Small-molecule-driven hepatocyte differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 4, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Yanagi, S.; Kato, C.; Takashima, R.; Kobayashi, E.; Hagiwara, K.; Ochiya, T. Human induced hepatic lineage-oriented stem cells: Autonomous specification of human iPS cells toward hepatocyte-like cells without any exogenous differentiation factors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, H.L.; Cui, C.B.; Wauthier, E.; Barbier, C.; Costello, M.J.; Moss, N.; Yamauchi, M.; Sricholpech, M.; Gerber, D.; et al. Paracrine signals from mesenchymal cell populations govern the expansion and differentiation of human hepatic stem cells to adult liver fates. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, J.; Martin, B.L.; Kimelman, D.; Shin, D. Wnt/β-catenin signaling cell-autonomously converts non-hepatic endodermal cells to a liver fate. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungrin, M.D.; Joshi, C.; Nica, A.; Bauwens, C.; Zandstra, P.W. Reproducible, ultra high-throughput formation of multicellular organization from single cell suspension-derived human embryonic stem cell aggregates. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, T.T.; Ho, L.W.; Wang, D.A. Hepatogenesis of murine induced pluripotent stem cells in 3D micro-cavitary hydrogel system for liver regeneration. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6659–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazoe, T.; Shiraki, N.; Kume, S. Hepatic differentiation from murine and human iPS cells using nanofiber scaffolds. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R.; Takebe, T.; Miyazaki, L.; Takayama, M.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Enomura, M.; Zheng, Y.W.; Sekine, K.; Taniguchi, H. Efficient hepatic differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells in a three-dimensional microscale culture. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1210, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vosough, M.; Omidinia, E.; Kadivar, M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Pournasr, B.; Aghdami, N.; Baharvand, H. Generation of functional hepatocyte-like cells from human pluripotent stem cells in a scalable suspension culture. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2693–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamuro, M.; Shiraha, H.; Nakaji, S.; Furutani, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Takaki, A.; Yamamoto, K. A preliminary study for constructing a bioartificial liver device with induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Biomed. Eng. Online 2012, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieseck, R.L., 3rd; Hannan, N.R.; Bort, R.; Hanley, N.A.; Drake, R.A.; Cameron, G.W.; Wynn, T.A.; Vallier, L. Maturation of induced pluripotent stem cell derived hepatocytes by 3D-culture. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, D.R.; Ware, B.R.; Davidson, M.D.; Allsup, S.R.; Khetani, S.R. Enhancing the functional maturity of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived human hepatocytes by controlled presentation of cell–cell interactions in vitro. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Surapisitchat, J.; Virtanen, C.; Ogawa, M.; Niapour, M.; Sugamori, K.S.; Wang, S.; Tamblyn, L.; Guillemette, C.; Hoffmann, E.; et al. Three-dimensional culture and cAMP signaling promote the maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Development 2013, 140, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Nagamoto, Y.; Mimura, N.; Tashiro, K.; Sakurai, F.; Tachibana, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Kawabata, K.; Mizuguchi, H. Long-term self-renewal of human ES/iPS-derived hepatoblast-like cells on human laminin 111-coated dishes. Stem Cell Rep. 2013, 1, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, T.; Zhang, R.R.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Yoshizawa, E.; Enomura, M.; Koike, N.; Sekine, K.; Taniguchi, H. Generation of a vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, T.; Sekine, K.; Enomura, M.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Ogaeri, T.; Zhang, R.R.; Ueno, Y.; Zheng, Y.W.; Koike, N.; et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature 2013, 499, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, T.; Enver, T. Forcing cells to change lineages. Nature 2009, 462, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Rezvani, M.; Harbell, J.; Mattis, A.N.; Wolfe, A.R.; Benet, L.Z.; Willenbring, H.; Ding, S. Mouse liver repopulation with hepatocytes generated from human fibroblasts. Nature 2014, 508, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, J.; Song, N.; Xiang, C.; Xu, J.; Hou, Z.; Su, X.; Liu, B.; Jiang, T.; et al. Human hepatocytes with drug metabolic function induced from fibroblasts by lineage reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; He, Z.; Ji, S.; Sun, H.; Xiang, D.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hui, L. Induction of functional hepatocyte-like cells from mouse fibroblasts by defined factors. Nature 2011, 475, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, S.; Suzuki, A. Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors. Nature 2011, 475, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeonov, K.P.; Uppal, H. Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by synthetic modified mRNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hai, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Direct transdifferentiation of spermatogonial stem cells to morphological, phenotypic and functional hepatocyte-like cells via the ERK1/2 and Smad2/3 signaling pathways and the inactivation of cyclin A, cyclin B and cyclin E. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantz, T.; Bleidissel, M.; Stehling, M.; Scholer, H.R. In vitro differentiation of reprogrammed murine somatic cells into hepatic precursor cells. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Huang, H.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Tsai, P.H.; Jeng, S.Y.; Hung, S.I.; Hsieh, J.H.; Huang, H.S.; Chiou, S.H.; et al. Investigation of hepatoprotective activity of induced pluripotent stem cells in the mouse model of liver injury. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 219060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Kim, Y.; Sharkis, S.; Marchionni, L.; Jang, Y.Y. In vivo liver regeneration potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells from diverse origins. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 82ra39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Sauer, V.; Chang, C.J.; Han, B.; Tchaikovskaya, T.; Avsar, Y.; Tafaleng, E.; et al. Amelioration of hyperbilirubinemia in gunn rats after transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasiddaiah, A.; Moreno, D.; Guembe, L.; Prieto, J.; Aldabe, R. Hepatic differentiation of mouse iPS cells and analysis of liver engraftment potential of multistage iPS progeny. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 69, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamoto, Y.; Takayama, K.; Tashiro, K.; Tateno, C.; Sakurai, F.; Tachibana, M.; Kawabata, K.; Ikeda, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, H. Efficient engraftment of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells in uPA/SCID mice by overexpression of FNK, a Bcl-xL mutant gene. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.C.; Cheng, L.Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chiou, S.H.; Tsai, P.H.; Huo, T.I.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, F.Y. The role of interferon-γ inducible protein-10 in a mouse model of acute liver injury post induced pluripotent stem cells transplantation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.M.; Liao, Y.W.; Chiang, C.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Lai, Y.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Chen, H.L.; Jeng, S.Y.; Hsieh, J.H.; Peng, C.H.; et al. Improvement of carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic failure by transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cells without reprogramming factor c-Myc. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3598–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Chien, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.F.; Chang, Y.L.; Chiang, C.H.; Jeng, S.Y.; Chang, C.M.; Wang, M.L.; Chen, L.K.; et al. Reprogramming induced pluripotent stem cells in the absence of c-Myc for differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Li, H.Y.; Larsson, M.; Wu, W.W.; Chien, C.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Chu, P.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Lo, W.L.; et al. Synergistic effects of carboxymethyl-hexanoyl chitosan, cationic polyurethane-short branch PEI in miR122 gene delivery: Accelerated differentiation of iPSCs into mature hepatocyte-like cells and improved stem cell therapy in a hepatic failure model. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wenum, M.; Chamuleau, R.A.; van Gulik, T.M.; Siliakus, A.; Seppen, J.; Hoekstra, R. Bioartificial livers in vitro and in vivo: Tailoring biocomponents to the expanding variety of applications. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taapken, S.M.; Nisler, B.S.; Newton, M.A.; Sampsell-Barron, T.L.; Leonhard, K.A.; McIntire, E.M.; Montgomery, K.D. Karotypic abnormalities in human induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekhoubad, S.; Bock, C.; de Boer, A.S.; Kiskinis, E.; Meissner, A.; Eggan, K. Erosion of dosage compensation impacts human iPSC disease modeling. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetto, M.C.; Carromeu, C.; Acab, A.; Yu, D.; Yeo, G.W.; Mu, Y.; Chen, G.; Gage, F.H.; Muotri, A.R. A model for neural development and treatment of Rett syndrome using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell 2010, 143, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaerkady, R.; Kerr, C.L.; Kandasamy, K.; Marimuthu, A.; Gearhart, J.D.; Pandey, A. Comparative proteomics of human embryonic stem cells and embryonal carcinoma cells. Proteomics 2010, 10, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, O.; Habib, G.; Choi, H.W.; Hong, K.S.; Do, J.T.; Moon, S.H.; Chung, H.M. An improved method for the derivation of high quality iPSCs in the absence of c-Myc. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 3190–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, F.K.; Determan, M.R.; Cai, J.; Cayo, M.A.; Mallanna, S.K.; Duncan, S.A. Aneuploidy is permissive for hepatocyte-like cell differentiation from human induced pluripotent stem cells. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.J.; Hay, D.C.; Park, I.H.; Fletcher, J.; Hannoun, Z.; Payne, C.M.; Dalgetty, D.; Black, J.R.; Ross, J.A.; Samuel, K.; et al. Generation of functional human hepatic endoderm from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology 2010, 51, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Einhorn, S.; Venkatarangan, L.; Miller, M.; Mann, D.A.; Watkins, P.B.; LeCluyse, E. Morphological and functional characterization and assessment of iPSC-derived hepatocytes for in vitro toxicity testing. Toxicol. Sci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Takayama, K.; Kondoh, M.; Sakurai, F.; Tani, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Matsuura, Y.; Mizuguchi, H.; Yagi, K. Use of human hepatocyte-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells as a model for hepatocytes in hepatitis C virus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 416, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, S.T.; Corbineau, S.; Hannan, N.; Marciniak, S.J.; Miranda, E.; Alexander, G.; Griffin, J.; Huang-Doran, I.; Ahrlund-Richter, L.; Skepper, J.; et al. Modeling inherited metabolic disorders of the liver using human induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3127–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.A.; Ying, L.; Liesa, M.; Segeritz, C.P.; Mills, J.A.; Shen, S.S.; Jean, J.; Lonza, G.C.; Liberti, D.C.; Lang, A.H.; et al. Emergence of a stage-dependent human liver disease signature with directed differentiation of α-1 antitrypsin-deficient iPS cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 4, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.M.; Kim, Y.; Shim, J.S.; Park, J.T.; Wang, R.H.; Leach, S.D.; Liu, J.O.; Deng, C.; Jang, Y.Y.; Ye, Z. Efficient drug screening and gene correction for treating liver disease using patient-specific stem cells. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.; Qu, J.; Li, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kim, N.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Belmonte, J.C. Establishment of hepatic and neural differentiation platforms of Wilson’s disease specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldner, F.; Laganiere, J.; Cheng, A.W.; Hockemeyer, D.; Gao, Q.; Alagappan, R.; Khurana, V.; Golbe, L.I.; Myers, R.H.; Lindquist, S.; et al. Generation of isogenic pluripotent stem cells differing exclusively at two early onset Parkinson point mutations. Cell 2011, 146, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayo, M.A.; DeLaForest, A.; Noto, F.K.; Nagaoka, M.; Clark, B.S.; Collery, R.F.; Si-Tayeb, K.; Cai, J.; Duncan, S.A. JD induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes faithfully recapitulate the pathophysiology of familial hypercholesterolemia. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.L.; Sullivan, G.J.; Sun, P.; Park, I.H. Humanized murine model for HBV and HCV using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Li, L. Two Effective Routes for Removing Lineage Restriction Roadblocks: From Somatic Cells to Hepatocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20873-20895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920873
Hu C, Li L. Two Effective Routes for Removing Lineage Restriction Roadblocks: From Somatic Cells to Hepatocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(9):20873-20895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920873
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Chenxia, and Lanjuan Li. 2015. "Two Effective Routes for Removing Lineage Restriction Roadblocks: From Somatic Cells to Hepatocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 9: 20873-20895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920873
APA StyleHu, C., & Li, L. (2015). Two Effective Routes for Removing Lineage Restriction Roadblocks: From Somatic Cells to Hepatocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(9), 20873-20895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160920873