Expression of PD-1 Molecule on Regulatory T Lymphocytes in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study Population
| Pt | Sex | Age of Disease Onset | Actual Age | Duration of Disease | Associated Diseases | Islet-Related Abs | Other Abs | HbA1c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 3 | 16 | 13 | GADA: 0.1; IA2: 0.1 | TPO: <28.0; Tg: <20; tTGA: 0.2 | 69 | |
| 2 | F | 10 | 27 | 17 | AT | GADA: 0.4; IA2: 4.6 | TPO: >1300; Tg: | 72 |
| 3 | F | 6 | 22 | 16 | AT; AG | GADA: 17.0; IA2: 1.0 | TPO: >1300; Tg: 27.7; tTGA: 0.2; PCA pos | 73 |
| 4 | F | 4 | 16 | 12 | AT; vitiligo | GADA: 0.1; IA2: 2.7 | TPO: <28.0; Tg: <20.0; tTGA: 0.2 | 85 |
| 5 | F | 2 | 12 | 10 | AT | GADA: 0.3; IA2: 1.5 | TPO: 266.7; Tg: <20.0; tTGA: 0.2 | 78 |
| 6 | F | 3 | 20 | 17 | GADA: 1.6; IA2: 1.6 | TPO: <28.0; Tg: <20.0; tTGA: 0.2 | 72 | |
| 7 | M | 1 | 13 | 12 | AT | GADA: 1.3; IA2: 0.1 | TPO: 498.9; Tg: <20.0; tTGA: 0.3 | 62 |
| 8 | M | 3 | 19 | 16 | Basedow | GADA: 0.9; IA2: 0.4 | TPO: <28.0; Tg: 24.0; tTGA: 0.2 | 64 |
| 9 | F | 10 | 24 | 14 | AT; AG; vitiligo | GADA: 120.0; IA2: 2.6 | TPO: >1300; Tg: 397.0; tTGA: 0.9; PCA pos | 93 |
| 10 | F | 4 | 15 | 11 | CD; vitiligo | GADA: 2.3; IA2: 0.1 | TPO: <28.0; Tg: <20.0; tTGA: 0.5 | 70 |
2.2. Analysis of T Regulatory and T Effector Cell Subsets after Four and Six Days of Culture under Standard Basal Conditions
PD-1 Expression
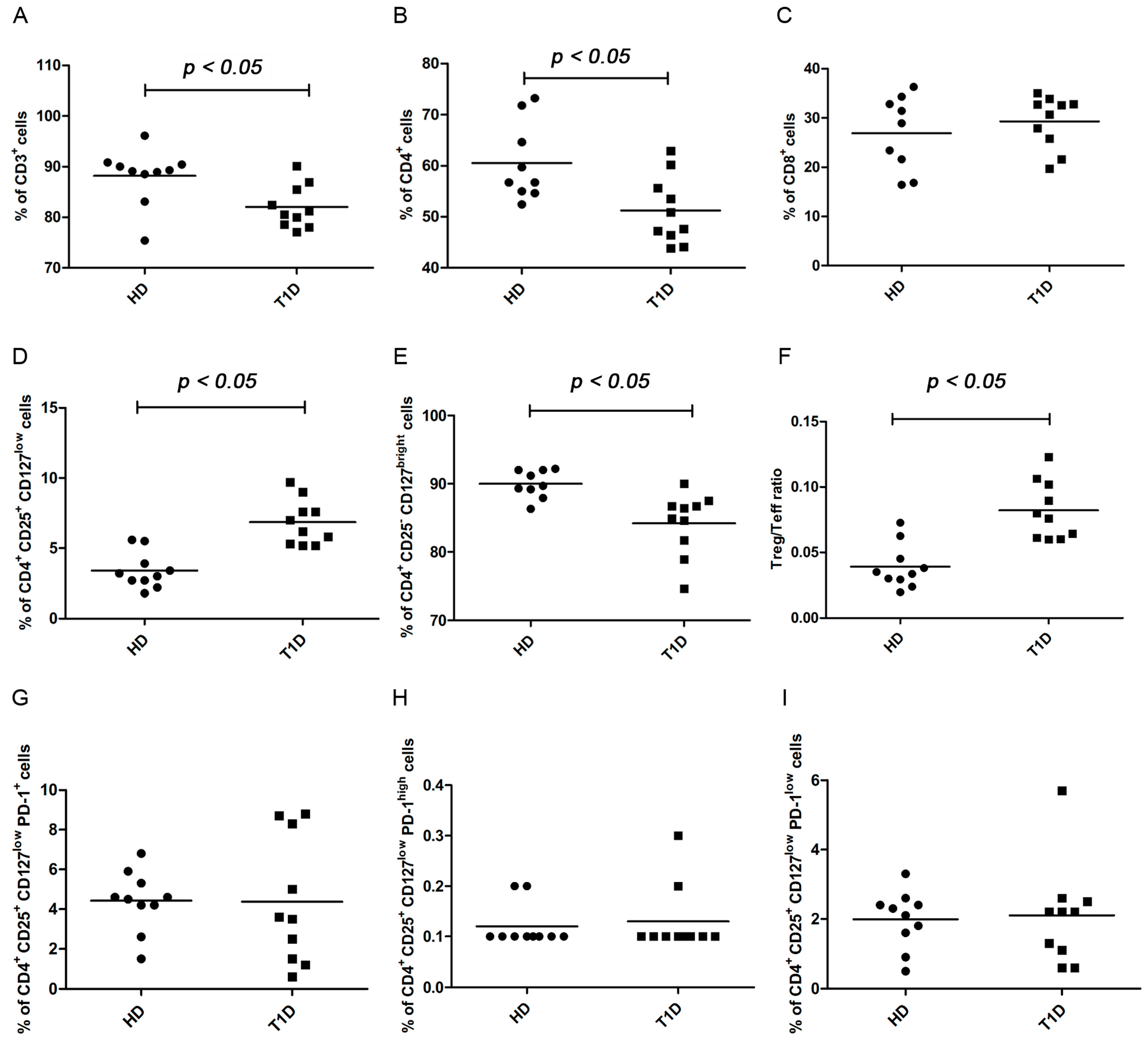
2.3. Analysis of T Regulatory and T Effector Cell Subsets after Four and Six Days of CD3/CD28 Costimulation

PD-1 Expression



2.4. Treg Immunosuppressive Function
2.5. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Cell Preparation
3.3. Stimulation of PBMC with CD3/CD28-Coated Beads and Proliferation Assay
3.4. FACS
3.5. Cytokine Quantification
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fierabracci, A. The potential of multimer technologies in type 1 diabetes prediction strategies. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierabracci, A. Recent insights into the role and molecular mechanisms of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene in autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, A.L.; Vendrame, F.; Dotta, F.; Gottlieb, P.A. CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in human autoimmune diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2005, 24, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Xiang, Y.; Chang, C.; Zhou, Z. Alteration of regulatory T cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 47, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukreja, A.; Cost, G.; Marker, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Z.; Lin-Su, K.; Ten, S.; Sanz, M.; Exley, M.; Wilson, B.; et al. Multiple immuno-regulatory defects in type-1 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindley, S.; Dayan, C.M.; Bishop, A.; Roep, B.O.; Peakman, M.; Tree, T.I. Defective suppressor function in CD4(+)CD25(+) T-cells from patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczyński, W.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Stasiak-Barmuta, A.; Urban, R.; Iłendo, E.; Urban, M.; Hryszko, M.; Kretowski, A.; Górska, M. Diminished expression of ICOS, GITR and CTLA-4 at the mRNA level in T regulatory cells of children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2009, 56, 361–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawson, J.M.; Tremble, J.; Dayan, C.; Beyan, H.; Leslie, R.D.G.; Peakman, M.; Tree, T.I. Increased resistance to CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusko, T.M.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Clare-Salzler, M.J.; Schatz, D.A.; Atkinson, M.A. Functional defects and the influence of age on the frequency of CD4+ CD25+ T-cells in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniuszko, M.; Glowinska-Olszewska, B.; Rusak, M.; Jeznach, M.; Grubczak, K.; Lipinska, D.; Milewski, R.; Milewska, A.J.; Dabrowska, M.; Jablonska, E.; et al. Decreased CD127 expression on CD4+ T-cells and elevated frequencies of CD4+CD25+CD127− T-cells in children with long-lasting type 1 diabetes. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 459210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menart-Houtermans, B.; Rütter, R.; Nowotny, B.; Rosenbauer, J.; Koliaki, C.; Kahl, S.; Simon, M.C.; Szendroedi, J.; Schloot, N.C.; Roden, M.; et al. Leukocyte profiles differ between type 1 and type 2 diabetes and are associated with metabolic phenotypes: Results from the German Diabetes Study (GDS). Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusko, T.; Wasserfall, C.; McGrail, K.; Schatz, R.; Viener, H.L.; Schatz, D.; Haller, M.; Rockell, J.; Gottlieb, P.; Clare-Salzler, M.; et al. No alterations in the frequency of FOXP3+ regulatory T-cells in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2007, 56, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Rieck, M.; Sanda, S.; Pihoker, C.; Greenbaum, C.; Buckner, J.H. The effector T cells of diabetic subjects are resistant to regulation via CD4+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7350–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, P.; Scirpoli, M.; Maffi, P.; Piemonti, L.; Secchi, A.; Bonifacio, E.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Battaglia, M. Rapamycin monotherapy in patients with type 1 diabetes modifies CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T-cells. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glisic-Milosavljevic, S.; Waukau, J.; Jailwala, P.; Jana, S.; Khoo, H.-J.; Albertz, H.; Woodliff, J.; Koppen, M.; Alemzadeh, R.; Hagopian, W.; et al. At-risk and recent-onset type 1 diabetic subjects have increased apoptosis in the CD4+CD25+ T-cell fraction. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughson, A.; Bromberg, I.; Johnson, B.; Quataert, S.; Jospe, N.; Fowell, D.J. Uncoupling of proliferation and cytokines from suppression within the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T-cell compartment in the 1st year of human type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glisic, S.; Ehlenbach, S.; Jailwala, P.; Waukau, J.; Jana, S.; Ghosh, S. Inducible regulatory T cells (iTregs) from recent-onset type 1 diabetes subjects show increased in vitro suppression and higher ITCH levels compared with controls. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClymont, S.A.; Putnam, A.L.; Lee, M.R.; Esensten, J.H.; Liu, W.; Hulme, M.A.; Woodliff, J.; Koppen, M.; Alemzadeh, R.; Hagopian, W.; et al. Plasticity of human regulatory T cells in healthy subjects and patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3918–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Shen, Y.-W.; Lee, W.-H.; Wang, D.; Paz, S.; Kandeel, F.; Liu, C.P. Foxp3+ Treg expanded from patients with established diabetes reduce Helios expression while retaining normal function compared to healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwaha, A.K.; Crome, S.Q.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Berg, K.B.; Qin, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Xu, L.; Priatel, J.J.; Levings, M.K.; Tan, R. Cutting edge: Increased IL-17-secreting T cells in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3814–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, N.; Martínez-Arconada, M.J.; Granada, M.L.; Soldevila, B.; Cantón, A.; Mate, J.L.; Sanmartí, A.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.M. Regulatory T cells in type 1 diabetic patients with autoimmune chronic atrophic gastritis. Endocrine 2009, 35, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseda, F.; Imagawa, A.; Murase-Mishiba, Y.; Terasaki, J.; Hanafusa, T. CD4+ CD45RA− FoxP3high activated regulatory T cells are functionally impaired and related to residual insulin-secreting capacity in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badami, E.; Sorini, C.; Coccia, M.; Usuelli, V.; Molteni, L.; Bolla, A.M.; Scavini, M.; Mariani, A.; King, C.; Bosi, E.; et al. Defective differentiation of regulatory FoxP3+ T cells by small-intestinal dendritic cells in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, A.; Socci, C.; Stabilini, A.; Valle, A.; Monti, P.; Piemonti, L.; Nano, R.; Olek, S.; Maffi, P.; Scavini, M.; et al. Expansion of Th17 cells and functional defects in T regulatory cells are key features of the pancreatic lymph nodes in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Putnam, A.L.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Szot, G.L.; Lee, M.R.; Zhu, S.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Kapranov, P.; Gingeras, T.R.; Fazekas de St Groth, B.; et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, H.; Sakaguchi, S. Genetic and epigenetic basis of Treg cell development and function: From a FoxP3-centered view to an epigenome-defined view of natural Treg cells. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 259, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, K.; Onishi, Y.; Prieto-Martin, P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Miyara, M.; Fehervari, Z.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. CTLA-4 control over Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function. Science 2008, 322, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, K.M.; Deaglio, S.; Gao, W.; Friedman, D.; Strom, T.B.; Robson, S.C. CD39 and control of cellular immune responses. Purinergic Signal 2007, 3, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-T.; Workman, C.J.; Flies, D.; Pan, X.; Marson, A.L.; Zhou, G.; Hipkiss, E.L.; Ravi, S.; Kowalski, J.; Levitsky, H.I.; et al. Role of LAG-3 in regulatory T cells. Immunity 2004, 21, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garín, M.I.; Chu, C.-C.; Golshayan, D.; Cernuda-Morollón, E.; Wait, R.; Lechler, R.I. Galectin-1: A key effector of regulation mediated by CD4+CD25+ T cells. Blood 2007, 109, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.O.; Wan, Y.Y.; Sanjabi, S.; Robertson, A.-K.L.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 99–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Cai, S.F.; Fehniger, T.A.; Song, J.; Collins, L.I.; Piwnica-Worms, D.R.; Ley, T.J. Granzyme B and perforin are important for regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of tumor clearance. Immunity 2007, 27, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-S.; Wang, J.; Shen, D.-F.; Yuan, X.-L.; Dong, P.; Li, M.-X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, F.M.; Ge, H.L.; Xu, D. CD4(+)CD25(+)CD127(low/-) regulatory T cells express Foxp3 and suppress effector T cell proliferation and contribute to gastric cancers progression. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 131, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Delfino, D.V.; Fierabracci, A. Recent insights into the role of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in immunological tolerance and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleman, L.J.; van Puijenbroek, A.A.; Shu, K.M.; Nadler, L.M.; Boussiotis, V.A. CD28 costimulation mediates down-regulation of p27kip1 and cell cycle progression by activation of the PI3K/PKB signaling pathway in primary human T cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, A.; Okino, S.T.; Liao, J.; Nakatani, K.; Li, J.; Whitlock, J.P.; Roth, R.A. Regulation of GLUT1 gene transcription by the serine/threonine kinase Akt1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20281–20286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, R.V.; Chemnitz, J.M.; Frauwirth, K.A.; Lanfranco, A.R.; Braunstein, I.; Kobayakshi, S.V.; Linsley, P.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Riley, J.L. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9543–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, R.V.; Reif, K.; Smith, G.; Sansom, D.M.; Hemmings, B.A.; Ward, S.G. Ligation of the T cell co-stimulatory receptor CD28 activates the serine-threonine protein kinase protein kinase B. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frauwirth, K.A.; Riley, J.L.; Harris, M.H.; Parry, R.V.; Rathmell, J.C.; Plas, D.R.; Yamazaki, T.; Azuma, M.; Iwai, H.; Khoury, S.J. The CD28 signaling pathway regulates glucose metabolism. Immunity 2002, 16, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Salama, A.D.; Chitnis, T.; Smith, R.N.; Yagita, H.; Akiba, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Azuma, M.; Iwai, H.; Khoury, S.J.; et al. The programmed death-1 (PD-1) pathway regulates autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatachi, S.; Iwai, Y.; Kawano, S.; Morinobu, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Koshiba, M.; Yamazaki, T.; Azuma, M.; Iwai, H.; Khoury, S.J. CD4+ PD-1+ T cells accumulate as unique anergic cells in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kawano, S.; Hatachi, S.; Kurimoto, C.; Okazaki, T.; Iwai, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Azuma, M.; Iwai, H.; Khoury, S.J.; et al. Enhanced expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 in salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertias, G.K.; Nakou, M.; Choulaki, C.; Raptopoulos, A.; Papadimitraki, E.; Goulielmos, G.; Kritikos, H.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Tzardi, M.; Kardassis, D.; et al. Genetic, immunologic, and immunohistochemical analysis of the programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lili, Y.; Yi, W.; Ji, Y.; Yue, S.; Weimin, S.; Ming, L. Global activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes correlates with an impairment in regulatory T cells in patients with generalized vitiligo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tembhre, M.K.; Parihar, A.S.; Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Gupta, S. Alteration in regulatory T cells and programmed death (PD)1 expressing regulatory T cells in active generalized vitiligo and their clinical correlation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, Y.; Jie, X.; Ihara, K.; Nomura, A.; Kanemitsu, S.; Takada, H.; Hara, T. Phenotypic and genetic analyses of T-cell-mediated immunoregulation in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, R.; Haseda, F.; Tsutsumi, C.; Hiromine, Y.; Noso, S.; Kawabata, Y.; Mitsui, S.; Terasaki, J.; Ikegami, H.; Imagawa, A.; et al. Low PD-1 expression in peripheral CD4+ T-cells in Japanese patients with autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C.; Hansen, D.; Husby, S.; Jacobsen, B.B.; Lillevang, S.T. Association of a putative regulatory polymorphism in the PD-1 gene with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Tissue Antigens 2003, 62, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, R.; Ihara, K.; Miyako, K.; Kuromaru, R.; Inuo, M.; Kohno, H.; Matsuura, N.; Yoshimura, A.; Hara, T. PD-1 gene haplotype is associated with the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Japanese children. Hum. Genet. 2007, 121, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, A.L.; Brusko, T.M.; Lee, M.R.; Liu, W.; Szot, G.L.; Ghosh, T.; Atkinson, M.A.; Bluestone, J.A. Expansion of human regulatory T-cells from patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.; La Cava, A.; Hahn, B.H. Blockade of programmed death-1 in young (New Zealand Black x New Zealand White)F1 mice promotes the suppressive capacity of CD4+ regulatory T cells protecting from lupus-like disease. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5402–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, G.; Shufesky, W.J.; Tokita, D.; Morelli, A.E.; Thomson, A.W. Regulated compartmentalization of programmed cell death-1 discriminates CD4+CD25+ resting regulatory T cells from activated T cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 2808–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, D.; Paroli, M.; Francavilla, V.; Videtta, M.; Morrone, S.; Labbadia, G.; Atkinson, M.A.; Bluestone, J.A. PD-L1 negatively regulates CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs by limiting STAT-5 phosphorylation in patients chronically infected with HCV. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotot, J.; Gottschalk, C.; Leopold, S.; Knolle, P.A.; Yagita, H.; Kurts, C.; Ludwig-Portugall, I. Regulatory T cells use programmed death 1 ligands to directly suppress autoreactive B cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10468–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yoshida, T.; Nakaki, F.; Hiai, H.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. Establishment of NOD-Pdcd1-/- mice as an efficient animal model of type I diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11823–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauken, K.E.; Jenkins, M.K.; Azuma, M.; Fife, B.T. PD-1, but not PD-L1, expressed by islet-reactive CD4+ T cells suppresses infiltration of the pancreas during type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2859–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nervi, S.; Atlan-Gepner, C.; Fossat, C.; Vialettes, B. Constitutive impaired TCR/CD3-mediated activation of T cells in IDDM patients co-exist with normal co-stimulation pathways. J. Autoimmun. 1999, 13, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tree, T.I.M.; Roep, B.O.; Peakman, M. A mini meta-analysis of studies on CD4+CD25+ T cells in human type 1 diabetes: Report of the Immunology of Diabetes Society T Cell Workshop. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1079, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.A.; Cerosaletti, K.; Bollyky, P.L.; Tatum, M.; Shilling, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Pihoker, C.; Sanda, S.; Greenbaum, C.; et al. Defects in IL-2R signaling contribute to diminished maintenance of FOXP3 expression in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cells of type 1 diabetic subjects. Diabetes 2010, 59, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalek, J.; Vrabelova, Z.; Hrotekova, Z.; Kyr, M.; Pejchlova, M.; Kolouskova, S.; Faresjö, M.; Stechova, K. Immune regulatory T cells in siblings of children suffering from type 1 diabetes mellitus. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006, 64, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xufré, C.; Costa, M.; Roura-Mir, C.; Codina-Busqueta, E.; Usero, L.; Pizarro, E.; Faresjö, M.; Stechova, K. Low frequency of GITR+ T cells in ex vivo and in vitro expanded Treg cells from type 1 diabetic patients. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Podolsky, R.; Hopkins, D.; Makala, L.H.C.; Muir, A.; She, J.X. APC dysfunction is correlated with defective suppression of T cell proliferation in human type 1 diabetes. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, M.A.; Lohmann, T.; Gabler, C.; Blank, N.; Kalden, J.R.; Lorenz, H.-M. Defective suppressor function of human CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type II. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianchecchi, E.; Crinò, A.; Giorda, E.; Luciano, R.; Perri, V.; Lo Russo, A.; Cappa, M.; Rosado, M.M.; Fierabracci, A. Altered B cell homeostasis and Toll-like receptor 9-driven response in Type 1 diabetes carriers of the C1858T PTPN22 allelic variant: Implications in the disease pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fattore, A.; Luciano, R.; Pascucci, L.; Goffredo, B.M.; Giorda, E.; Scapaticci, M.; Fierabracci, A.; Muraca, M. Immunoregulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on t lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.; Fouser, L.A.; Jussif, J.; Fitz, L.; Deng, B.; Wood, C.R.; Collins, M.; Honjo, T.; Freeman, G.J.; Carreno, B.M. PD-1:PD-L inhibitory pathway affects both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and is overcome by IL-2. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraut, J.; Grigore, E.I.; Jean-Louis, F.; Khelifa, S.H.; Durand, C.; Verrecchia, F.; Farge, D.; Michel, L. Peripheral blood regulatory T cells in patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis (SSc) before and after autologous hematopoietic SCT: A pilot study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014, 49, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perri, V.; Russo, B.; Crinò, A.; Schiaffini, R.; Giorda, E.; Cappa, M.; Rosado, M.M.; Fierabracci, A. Expression of PD-1 Molecule on Regulatory T Lymphocytes in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22584-22605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160922584
Perri V, Russo B, Crinò A, Schiaffini R, Giorda E, Cappa M, Rosado MM, Fierabracci A. Expression of PD-1 Molecule on Regulatory T Lymphocytes in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(9):22584-22605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160922584
Chicago/Turabian StylePerri, Valentina, Benedetta Russo, Antonino Crinò, Riccardo Schiaffini, Ezio Giorda, Marco Cappa, Maria Manuela Rosado, and Alessandra Fierabracci. 2015. "Expression of PD-1 Molecule on Regulatory T Lymphocytes in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 9: 22584-22605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160922584
APA StylePerri, V., Russo, B., Crinò, A., Schiaffini, R., Giorda, E., Cappa, M., Rosado, M. M., & Fierabracci, A. (2015). Expression of PD-1 Molecule on Regulatory T Lymphocytes in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(9), 22584-22605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160922584







