Ultra-Deep Sequencing Characterization of HCV Samples with Equivocal Typing Results Determined with a Commercial Assay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Ethical Issues
4.3. HCV Genotyping by Commercial Assay
4.4. RNA Extraction
4.5. RT-PCR Amplification for DS and UDPS
4.6. Direct Sequencing (DS) and Ultra-Deep Pyrosequencing (UDPS)
4.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.G.; Willems, B.; Deschênes, M.; Hilzenrat, N.; Mousseau, R.; Sabbah, S. Use of sequence analysis of the NS5B region for routine genotyping of hepatitis C virus with reference to C/E1 and 5′ untranslated region sequences. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Bukh, J.; Combet, C.; Deléage, G.; Enomoto, N.; Feinstone, S.; Halfon, P.; Inchauspé, G.; Kuiken, C.; Maertens, G.; et al. Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2005, 42, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cento, V.; Landonio, S.; De Luca, F.; Di Maio, V.C.; Micheli, V.; Mirabelli, C.; Niero, F.; Magni, C.; Rizzardini, G.; Perno, C.F.; et al. A boceprevir failure in a patient infected with HCV genotype 1g: Importance and limitations of virus genotyping prior to HCV protease-inhibitor-based therapy. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.M. New hepatitis C therapies: The toolbox, strategies, and challenges. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1176–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, V.; Vispo, E.; Poveda, E.; Labarga, P.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; Fernandez-Montero, J.V.; Barreiro, P. Directly acting antivirals against hepatitis C virus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, C.; Ebel, A.; Reinhardt, B.; Merlin, S.; Proust, S.; Roque-Afonso, A.M. Characterization of samples identified as hepatitis C virus Genotype I without subtype by Abbott RealTime HCV Genotype II assay using the new Abbott HCV genotype plus RUO test. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quer, J.; Gregori, J.; Rodríguez-Frias, F.; Buti, M.; Madejon, A.; Perez-del-Pulgar, S.; Garcia-Cehic, D.; Casillas, R.; Blasi, M.; Homs, M.; et al. High-resolution hepatitis C virus subtyping using NS5B deep sequencing and phylogeny, an alternative to current methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solmone, M.; Vincenti, D.; Prosperi, M.C.; Bruselles, A.; Ippolito, G.; Capobianchi, M.R. Use of massively parallel ultradeep pyrosequencing to characterize the genetic diversity of hepatitis B virus in drug-resistant and drug-naive patients and to detect minor variants in reverse transcriptase and hepatitis B S antigen. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selleri, M.; Piralla, A.; Rozera, G.; Giombini, E.; Bartolini, B.; Abbate, I.; Campanini, G.; Rovida, F.; Dossena, L.; Capobianchi, M.R.; et al. Detection of haemagglutinin D222 polymorphisms in influenza A(H1N1)pdm09-infected patients by ultra-deep pyrosequencing. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capobianchi, M.R.; Giombini, E.; Rozera, G. Next-generation sequencing technology in clinical virology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.H.; Liang, C.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lin, C.L.; Su, T.H.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Kao, J.H. Comparison of Abbott RealTime HCV Genotype II with Versant line probe assay 2.0 for hepatitis C virus genotyping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaghefi, P.; Marchadier, E.; Dussaix, E.; Roque-Afonso, A.M. Hepatitis C virus genotyping: Comparison of the Abbott RealTime HCV Genotype II assay and NS5B sequencing. Pathol. Biol. 2010, 58, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Kanda, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Jiang, X.; Miyamura, T.; Nakatani, S.M.; Ono, S.K.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Gonoi, T.; Yokosuka, O. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus subgenotypes 1a and 1b in Japanese patients: Ultra-deep sequencing analysis of HCV NS5B genotype-specific region. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, B.; Giombini, E.; Zaccaro, P.; Selleri, M.; Rozera, G.; Abbate, I.; Comandini, U.V.; Ippolito, G.; Solmone, M.; Capobianchi, M.R. Extent of HCV NS3 protease variability and resistance-associated mutations assessed by next generation sequencing in HCV monoinfected and HIV/HCV coinfected patients. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, B.; Selleri, M.; Garbuglia, A.R.; Giombini, E.; Taibi, C.; Lionetti, R.; D’Offizi, G.; Capobianchi, M.R. HCV NS3 quasispecies in liver and plasma and dynamics of telaprevir-resistant variants in breakthrough patients assessed by UDPS: A case study. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 72, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, B.; Lionetti, R.; Giombini, E.; Sias, C.; Taibi, C.; Montalbano, M.; D’Offizi, G.; McPhee, F.; Hughes, E.A.; Zhou, N.; et al. Dynamics of HCV genotype 4 resistance-associated variants during virologic escape with pIFN/RBV + daclatasvir: A case study using ultra deep pyrosequencing. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 66, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, V.; Gomes-Fernandes, M.; Bascuñana, E.; Casanovas, S.; Saludes, V.; Jordana-Lluch, E.; Matas, L.; Ausina, V.; Martró, E. Accuracy of a commercially available assay for HCV genotyping and subtyping in the clinical practice. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.W.; Balaskas, E.; Furione, M.; Yen, P.H.; Kessler, G.; Scalia, V.; Chui, L.; Sher, G. Comparison and application of a novel genotyping method, semiautomated primer-specific and mispair extension analysis, and four other genotyping assays for detection of hepatitis C virus mixed-genotype infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.P.; Natov, S.N.; Pereira, B.J.; Lau, J.Y. Hepatitis C virus mixed genotype infection in patients on haemodialysis. J. Viral. Hepat. 2000, 7, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagaglio, S.; Uberti-Foppa, C.; Di Serio, C.; Trentini, F.; Andolina, A.; Hasson, H.; Messina, E.; Merli, M.; Porrino, L.; Lazzarin, A.; et al. Dynamic of mixed HCV infection in plasma and PBMC of HIV/HCV patients under treatment With Peg-IFN/Ribavirin. Medicine 2015, 94, e1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). EASL Recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2015. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 199–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wyles, D.; Pockros, P.; Morelli, G.; Younes, Z.; Svarovskaia, E.; Yang, J.C.; Pang, P.S.; Zhu, Y.; McHutchison, J.G.; Flamm, S.; et al. Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus previously treated in clinical trials of sofosbuvir regimens. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, O.; Vijgen, L.; Berke, J.M.; Cummings, M.D.; Fevery, B.; Peeters, M.; De Smedt, G.; Moreno, C.; Picchio, G. Virologic response and characterisation of HCV genotype 2–6 in patients receiving TMC435 monotherapy (study TMC435-C202). J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zopf, S.; Kremer, A.E.; Neurath, M.F.; Siebler, J. Advances in hepatitis C therapy: What is the current state—What come’s next? World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, A.; Meglécz, E.; Pech, N.; Ferreira, S.; Malausa, T.; Martin, J.F. Accuracy and quality assessment of 454 GS-FLX Titanium pyrosequencing. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudia, M.; Emanuela, G.; Barbara, B. Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Lazzaro Spallanzani”—IRCCS, Rome. Unpublished work. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Jaroszewski, L.; Godzik, A. Clustering of highly homologous sequences to reduce the size of large protein databases. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
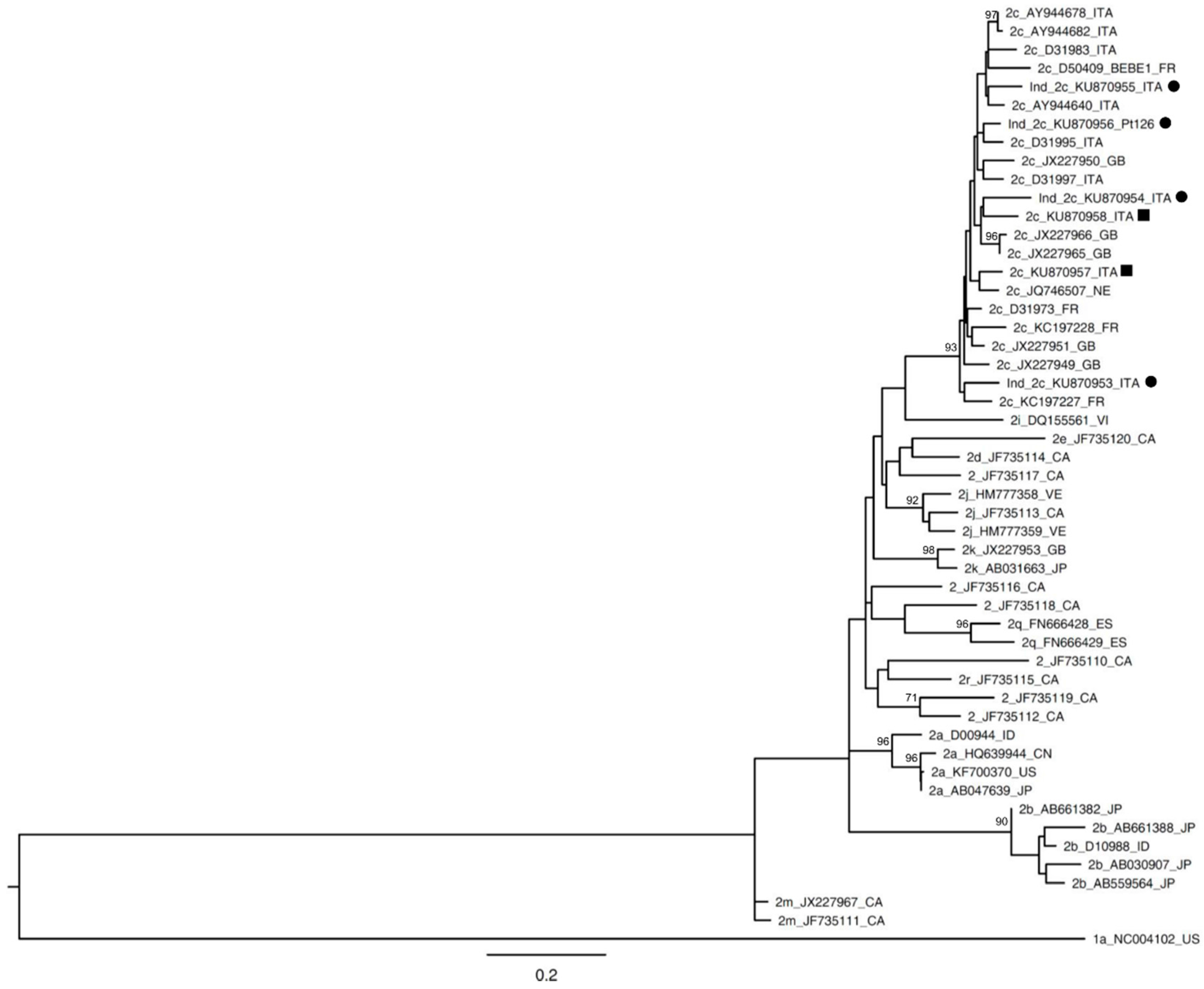
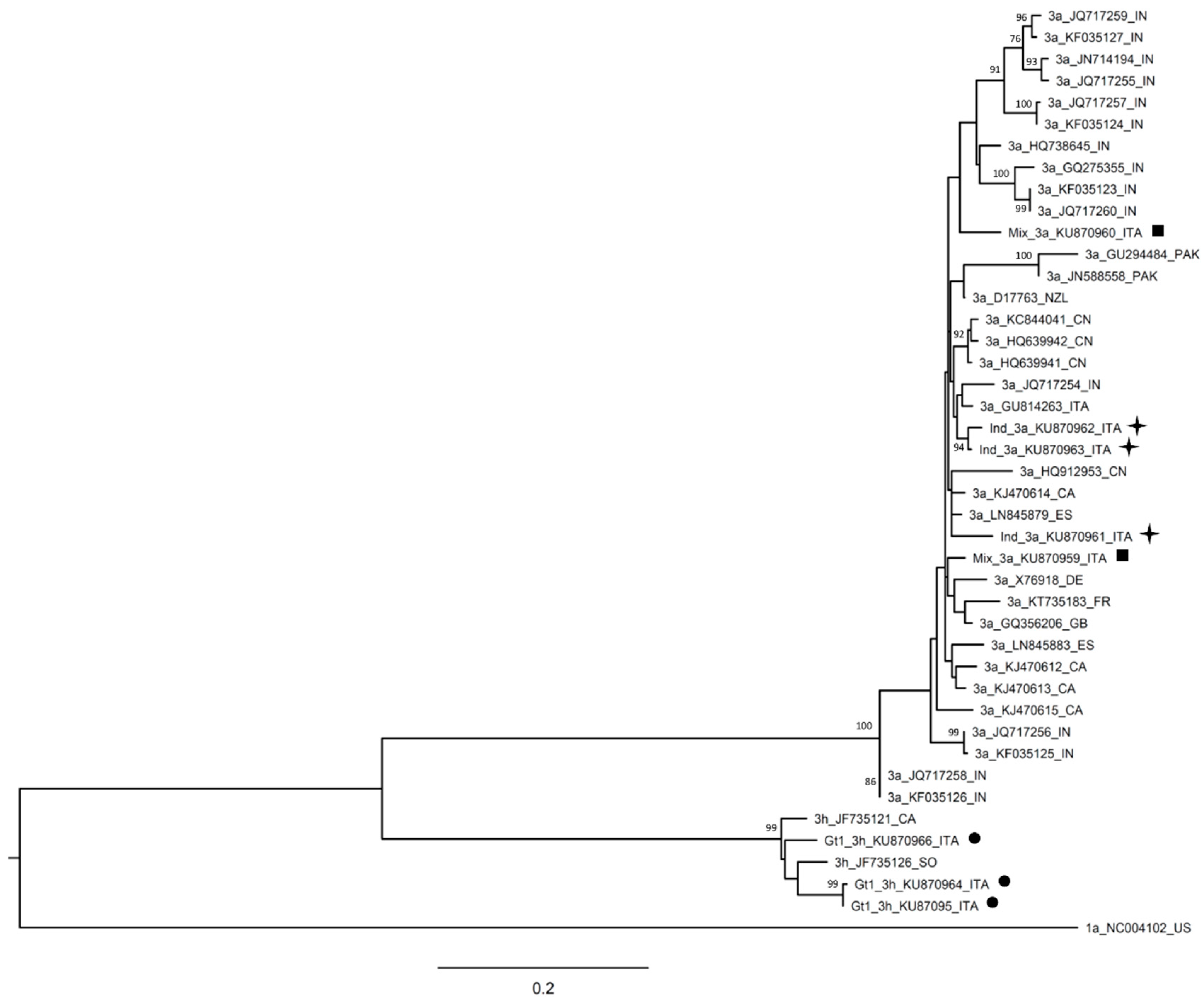
| Patient Code | HCV RNA | Date of Collection | Abbott RealTime HCV Genotype II | DS | UDPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt 12 | 2.25 × 106 | 17 May 2013 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 108 | 5.63 × 103 | 26 February 2015 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 29 | 1.58 × 104 | 02 November 2013 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 10 | 1.50 × 105 | 13 May 2013 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 17 | 6.87 × 104 | 06 July 2013 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 22 | 1.88 × 105 | 31 August 2013 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 141 | 5.71 × 103 | 7 August 2015 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 142 | 4.49 × 104 | 7 August 2015 | 1 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 53 | 1.70 × 106 | 29 April 2014 | 1 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 8 | 7.06 × 106 | 15 February 2013 | 1 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 13 | 2.31 × 105 | 3 June 2013 | 1 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 14 | 9.12 × 106 | 12 June 2013 | 1 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 23 | 7.90 × 106 | 13 September 2013 | 1 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 133 | 2.63 × 106 | 10 June 2015 | 1 | 1e | 1e + 1a |
| Pt 49–59a | 7.72 × 105 | 31 March 2014 | 1 | 3h | 3h |
| Pt 49–59b | 4.53 × 105 | 20 June 2014 | 1 | 3h | 3h |
| Pt 77 | 6.77 × 106 | 15 September 2014 | 1 | 3h | 3h |
| Pt 54–127a | 4.94 × 106 | 2 May 2014 | 1a + 3 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 54–127b | 2.68 × 106 | 12 June 2015 | 1a + 3 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 81 | 6.27 × 106 | 29 September 2014 | 1a + 3 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 44 | 3.93 × 106 | 25 February 2014 | 1a + 4 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 128 | 5.25 × 105 | 17 June 2015 | 1a + 4 | 1a | 1a |
| Pt 55 | 6.49 × 106 | 15 May 2014 | 1a + 4 | 1a | NR |
| Pt 92 | 1.96 × 105 | 4 December 2014 | 1b + 3 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 18 | 3.72 × 104 | 5 August 2013 | 1b + 2 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 97 | 1.31 × 105 | 19 December 2014 | 1b + 2 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 115 | 5.32 × 105 | 17 March 2015 | 1b + 4 | 1b | 1b |
| Pt 76 | 2.83 × 106 | 12 September 2014 | 3 + 4 | 3a | 3a |
| Pt 46 | 1.04 × 105 | 20 March 2014 | 3 + 4 | 3a | 3a |
| Pt 16–50a | 6.26 × 105 | 2 July 2013 | 1 + 4 | 4m | 4m |
| Pt 16–50b | 1.21 × 106 | 1 April 2014 | 1 + 4 | 4m | 4m |
| Pt 104 | 1.14 × 106 | 4 February 2015 | 1a + 4 | 4d | 4d |
| Pt 89–114a | 6.10 × 106 | 24 October 2014 | 1 + 4 | 4d | 4d |
| Pt 89–114b | 2.77 × 106 | 10 March 2015 | 1a + 4 | 4d | 4d + 1a |
| Pt 41 | 2.15 × 106 | 15 January 2014 | ind | 2c | 2c |
| Pt 84 | 7.57 × 104 | 2 October 2014 | ind | 2c | 2c |
| Pt 126 | 1.83 × 105 | 24 April 2015 | ind | 2c | 2c |
| Pt 123 | 3.11 × 106 | 9 May 2015 | ind | 2c | 2c |
| Pt 102 | 8.92 × 104 | 2 February 2015 | ind | 3a | 3a |
| Pt 103 | 3.97 × 106 | 2 February 2015 | ind | 3a | 3a |
| Pt 56 | 6.17 × 103 | 24 May 2014 | ind | 4d | 4d |
| Pt 94 | 1.01 × 104 | 10 December 2014 | ind | 6n | 6n |
| Pt 68 | 2.53 × 105 | 28 July 2014 | ind | 3a | 3a + 3h |
| Genotype Identified by Abbott | Number of Samples Tested by Abbott | Number of Samples Identified by DS (Type of Infection) | Number of Samples Identified by UDPS | Concordance (UDPS vs. DS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 | 17 (mono-infection) | 16 mono-infection | 94% |
| 1 co-infection: 1e + 1a | ||||
| co-infection | 17 | 17 (mono-infection) | 15 mono-infection | 88% |
| 1 co-infection: 4d + 1a | ||||
| Indeterminate | 9 | 9 (mono-infection) | 8 mono-infection | 89% |
| 1 co-infection: 3a + 3h | ||||
| Total | 43 | 43 | 42 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minosse, C.; Giombini, E.; Bartolini, B.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Garbuglia, A.R. Ultra-Deep Sequencing Characterization of HCV Samples with Equivocal Typing Results Determined with a Commercial Assay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101679
Minosse C, Giombini E, Bartolini B, Capobianchi MR, Garbuglia AR. Ultra-Deep Sequencing Characterization of HCV Samples with Equivocal Typing Results Determined with a Commercial Assay. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(10):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101679
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinosse, Claudia, Emanuela Giombini, Barbara Bartolini, Maria R. Capobianchi, and Anna R. Garbuglia. 2016. "Ultra-Deep Sequencing Characterization of HCV Samples with Equivocal Typing Results Determined with a Commercial Assay" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 10: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101679
APA StyleMinosse, C., Giombini, E., Bartolini, B., Capobianchi, M. R., & Garbuglia, A. R. (2016). Ultra-Deep Sequencing Characterization of HCV Samples with Equivocal Typing Results Determined with a Commercial Assay. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(10), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101679







