Synergetic Effects of PARP Inhibitor AZD2281 and Cisplatin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Vitro and in Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of the Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase (PARP)-1 Inhibitor AZD2281
2.2. Relative Survival Assay
2.3. Effects of AZD2281 and Cisplatin on Cell Cycle
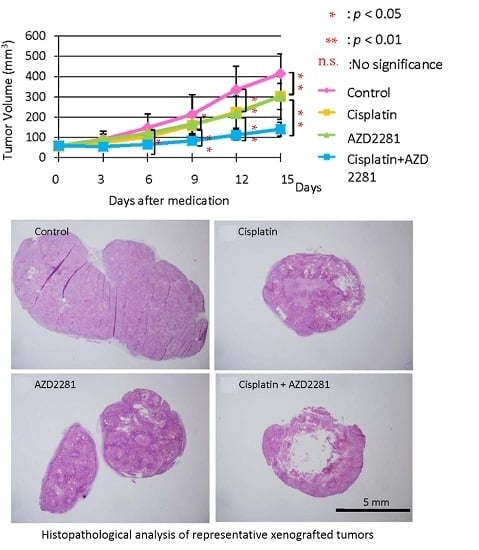
2.4. In Vivo Effects of AZD2281 with Cisplatin on Xenografted Tumor Growth
2.5. Histopathological Analysis Reveals that the Combination of Cisplatin and AZD2281 Decreases Proliferation Potential and Increases Necrosis in Tumors
2.6. Results of Analysis of Western Blotting
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Culture of Cell Lines Derived from Oral Carcinoma
4.2. MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) Assay
4.3. Survival Assay
4.4. Combination Index Analysis
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Animal Model
4.7. Animal Experimental Protocol
4.8. Histopathological Analysis
4.9. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.10. Immunohistochemistry
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashibe, M.; Brennan, P.; Chuang, S.C.; Boccia, S.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; dal Maso, L.; Daudt, A.W.; Fabianova, E.; et al. Interaction between tobacco and alcohol use and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the international head and neck cancer epidemiology consortium. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, A.M.; Blot, W.J.; Greenberg, R.S.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Austin, D.F.; Preston-Martin, S.; Winn, D.M.; Bernstein, L.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Familial risk in oral and pharyngeal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1994, 30B, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katanoda, K.; Hori, M.; Matsuda, T.; Shibata, A.; Nishino, Y.; Hattori, M.; Soda, M.; Ioka, A.; Sobue, T.; Nishimoto, H. An updated report on the trends in cancer incidence and mortality in japan, 1958–2013. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol 2015, 45, 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, R.I.; Shin, D.M. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, D.G.; Ang, K.K.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.A.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; Cmelak, A.J.; Colevas, A.D.; Dunphy, F.; Eisele, D.W.; et al. Head and neck cancers, version 2.2013. Featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Can. Netw. 2013, 11, 917–923. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Schmitz, K.R.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Wiltzius, J.J.; Kussie, P.; Ferguson, K.M. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnam, K.; Low, J.A. Current development of clinical inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in oncology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, R.; Jones, C.; Middleton, M.; Wilson, R.; Evans, J.; Olsen, A.; Curtin, N.; Boddy, A.; McHugh, P.; Newell, D.; et al. Phase I study of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, AG014699, in combination with temozolomide in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7917–7923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Conte, G.; Sessa, C.; von Moos, R.; Vigano, L.; Digena, T.; Locatelli, A.; Gallerani, E.; Fasolo, A.; Tessari, A.; Cathomas, R.; et al. Phase I study of olaparib in combination with liposomal doxorubicin in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Tolaney, S.M.; Birrer, M.; Fleming, G.F.; Buss, M.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Lee, H.; Whalen, C.; Tyburski, K.; Winer, E.; et al. A phase I trial of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib (AZD2281) in combination with the anti-angiogenic cediranib (AZD2171) in recurrent epithelial ovarian or triple-negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.E.; Hochegger, H.; Takeda, S.; Caldecott, K.W. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 accelerates single-strand break repair in concert with poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 5597–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, N.; Turner, N.C.; Lord, C.J.; Kluzek, K.; Bialkowska, A.; Swift, S.; Giavara, S.; O’Connor, M.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Zdzienicka, M.Z.; et al. Deficiency in the repair of DNA damage by homologous recombination and sensitivity to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8109–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Morris, J.; Ji, J.; Takeda, S.; Doroshow, J.H.; Pommier, Y. Rationale for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors in combination therapy with camptothecins or temozolomide based on PARP trapping versus catalytic inhibition. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 349, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lippard, S.J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardnell, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Diao, L.; Fan, Y.H.; Masrorpour, F.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Mills, G.B.; Minna, J.D.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Proteomic markers of DNA repair and PI3K pathway activation predict response to the PARP inhibitor BMN 673 in small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ui, T.; Morishima, K.; Saito, S.; Sakuma, Y.; Fujii, H.; Hosoya, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Aburatani, H.; Fukayama, M.; Niki, T.; et al. The HSP90 inhibitor 17-n-allylamino-17-demethoxy geldanamycin (17-AAG) synergizes with cisplatin and induces apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines via the Akt/XIAP pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuang, H.C.; Kapuriya, N.; Kulp, S.K.; Chen, C.S.; Shapiro, C.L. Differential anti-proliferative activities of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastak, K.; Alli, E.; Ford, J.M. Synergistic chemosensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer cell lines to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition, gemcitabine, and cisplatin. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7970–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottenberg, S.; Jaspers, J.E.; Kersbergen, A.; van der Burg, E.; Nygren, A.O.; Zander, S.A.; Derksen, P.W.; de Bruin, M.; Zevenhoven, J.; Lau, A.; et al. High sensitivity of BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors to the PARP inhibitor AZD2281 alone and in combination with platinum drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17079–17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, J.C.; Feng, F.Y.; Han, S.; Patel, S.; Goyal, S.V.; Bou-Maroun, L.M.; Liu, M.; Lonigro, R.; Prensner, J.R.; Tomlins, S.A.; et al. PARP-1 inhibition as a targeted strategy to treat ewing's sarcoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, R.A.; Rozanska, A.L.; Thomas, H.D.; Mulligan, E.A.; Drew, Y.; Castelbuono, D.J.; Hostomsky, Z.; Plummer, E.R.; Boddy, A.V.; Tweddle, D.A.; et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 enhances temozolomide and topotecan activity against childhood neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinic, P.; Levine, D.A. New insights into PARP inhibitors’ effect on cell cycle and homology-directed DNA damage repair. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishel, M.L.; Newell, D.R.; Griffin, R.J.; Davison, R.; Wang, L.Z.; Curtin, N.J.; Zuhowski, E.G.; Kasza, K.; Egorin, M.J.; Moschel, R.C.; et al. Effect of cell cycle inhibition on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.A.; Schwartz, G.K. Cell cycle-mediated drug resistance: An emerging concept in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddik, Z.H. Cisplatin: Mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7265–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robu, M.; Shah, R.G.; Petitclerc, N.; Brind’Amour, J.; Kandan-Kulangara, F.; Shah, G.M. Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in the removal of UV-induced DNA lesions by nucleotide excision repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.M.; Popp, O.; Gebhard, D.; Veith, S.; Fischbach, A.; Beneke, S.; Leitenstorfer, A.; Bergemann, J.; Scheffner, M.; Ferrando-May, E.; et al. Poly(ADP-ribose)-mediated interplay of XPA and PARP1 leads to reciprocal regulation of protein function. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 3625–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, T.; Cui, S.; Gu, Y.; Bian, C.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z. Poly(ADP-ribose) protects vascular smooth muscle cells from oxidative DNA damage. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, C.; Volpe, M.; Botta, G.; Scamardella, E.; Perruolo, G.; Gillespie, D.; Libertini, S.; Portella, G. PARP inhibitor olaparib increases the oncolytic activity of dl922-947 in in vitro and in vivo model of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, A.L.; Zeng, W.S.; Luo, S.Q.; Bai, X.C. Hydrogen peroxide induces G2 cell cycle arrest and inhibits cell proliferation in osteoblasts. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan, B.D.; Gibbons, S.; Tejpal, N.; Stepkowski, S.M.; Chou, T.C. Synergistic interactions of cyclosporine and rapamycin to inhibit immune performances of normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Transplantation 1991, 51, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, S.H.; Chang, H.H.; Tsai, J.Y.; Hung, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiang, C.P.; Liu, C.M.; Kuo, M.Y. Expression of Cyr61 (CCN1) in human oral squamous cell carcinoma: An independent marker for poor prognosis. Head. Neck. 2010, 32, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasukawa, M.; Fujihara, H.; Fujimori, H.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamada, H.; Nakayama, R.; Yamamoto, N.; Kishi, Y.; Hamada, Y.; Masutani, M. Synergetic Effects of PARP Inhibitor AZD2281 and Cisplatin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Vitro and in Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030272
Yasukawa M, Fujihara H, Fujimori H, Kawaguchi K, Yamada H, Nakayama R, Yamamoto N, Kishi Y, Hamada Y, Masutani M. Synergetic Effects of PARP Inhibitor AZD2281 and Cisplatin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Vitro and in Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(3):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030272
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasukawa, Masaaki, Hisako Fujihara, Hiroaki Fujimori, Koji Kawaguchi, Hiroyuki Yamada, Ryoko Nakayama, Nanami Yamamoto, Yuta Kishi, Yoshiki Hamada, and Mitsuko Masutani. 2016. "Synergetic Effects of PARP Inhibitor AZD2281 and Cisplatin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Vitro and in Vivo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 3: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030272
APA StyleYasukawa, M., Fujihara, H., Fujimori, H., Kawaguchi, K., Yamada, H., Nakayama, R., Yamamoto, N., Kishi, Y., Hamada, Y., & Masutani, M. (2016). Synergetic Effects of PARP Inhibitor AZD2281 and Cisplatin in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Vitro and in Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(3), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030272