A Novel Role of Serotonin Receptor 2B Agonist as an Anti-Melanogenesis Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of BW723C86 on Melanin Content in Melan-A Cells and Human Melanocytes
2.2. Effect of BW723C86 on Tyrosinase Activity in Melan-A Cells
2.3. Effect of BW723C86 on the Expression of Melanogenesis-Related Proteins and Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor (MITF)
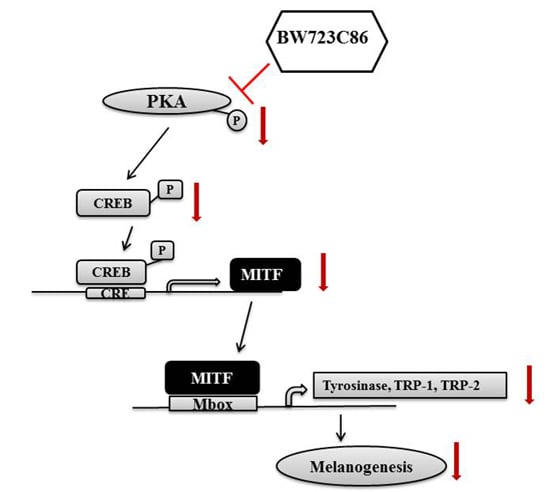
2.4. BW723C86 Downregulated the Protein Kinase A (PKA)/cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB)/MITF Signaling Pathway in Melan-A Cells
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Melanin Assay
3.3. Tyrosinase Activity Assay
3.4. Western Blot Analysis
3.5. RT (Reverse Transcription)-PCR
3.6. Transient Transfection with siRNA
3.7. MITF Promoter Activity Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The regulation of skin pigmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27557–27561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Hearing, V.J. Physiological factors that regulate skin pigmentation. Biofactors 2009, 35, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2003, 16, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Myung, C.H.; Lee, K.R.; Hyun, S.M.; Lee, J.E.; Park, Y.S.; Jeon, S.R.; Park, J.I.; Chang, S.E.; et al. Melanogenesis inhibition of β-lapachone, a natural product from Tabebuia avellanedae, with effective in vivo lightening potency. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.N.; Dwivedi, Y.; Rizavi, H.S.; Ren, X.; Pandey, S.C.; Pesold, C.; Roberts, R.C.; Conley, R.R.; Tamminga, C.A. Higher expression of serotonin 5-HT2a receptors in the postmortem brains of teenage suicide victims. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennett, G.A.; Bright, F.; Trail, B.; Baxter, G.S.; Blackburn, T.P. Effects of the 5-HT2B receptor agonist, BW 723C86, on three rat models of anxiety. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 117, 1443–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennett, G.A.; Ainsworth, K.; Trail, B.; Blackburn, T.P. BW 723C86, a 5-HT2B receptor agonist, causes hyperphagia and reduced grooming in rats. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Semak, I.; Sweatman, T.; Szczesniewski, A.; Wortsman, J. Serotoninergic system in hamster skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Semak, I.; Sweatman, T.; Wortsman, J. Characterization of the serotoninergic system in the C57BL/6 mouse skin. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 3335–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Johansson, O.; Jing, C.; Semak, I.; Slugocki, G.; Wortsman, J. Tryptophan hydroxylase expression in human skin cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1639, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Tobin, D.J. The cutaneous serotoninergic/melatoninergic system: Securing a place under the sun. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Semak, I.; Sweatman, T.; Wortsman, J.; Szczesniewski, A.; Slugocki, G.; McNulty, J.; Kauser, S.; Tobin, D.J.; et al. Serotoninergic and melatoninergic systems are fully expressed in human skin. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlind, K.; Azmitia, E.C.; Slominski, A. The skin as a mirror of the soul: exploring the possible roles of serotonin. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, O.; Liu, P.Y.; Bondesson, L.; Nordlind, K.; Olsson, M.J.; Löntz, W.; Verhofstad, A.; Liang, Y.; Gangi, S. A serotonin-like immunoreactivity is present in human cutaneous melanocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Skobowiat, C.; Zbytek, B.; Slominski, R.M.; Steketee, J.D. Sensing the environment: Regulation of local and global homeostasis by the skin’s neuroendocrine system. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2012, 212, 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Slominski, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Zbytek, B.; Tobin, D.J.; Kauser, S.; Wortsman, J. Functional activity of serotoninergic and melatoninergic systems expressed in the skin. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 196, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Wortsman, J. Expression of genes coding melatonin and serotonin receptors in rodent skin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1680, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, M.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Park Choo, H.Y.; Lee, A.Y.; Lee, C.H. Serotonin induces melanogenesis via serotonin receptor 2A. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Semak, I.; Pisarchik, A.; Sweatman, T.; Szczesniewski, A.; Wortsman, J. Conversion of l-tryptophan to serotonin and melatonin in human melanoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2002, 511, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Kleszczynski, K.; Janjetovic, Z.; Sweatman, T.; Lin, Z.; Li, W.; Reiter, R.J.; Fischer, T.W.; Slominski, A.T. Metabolism of melatonin and biological activity of intermediates of melatoninergic pathway in human skin cells. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2742–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.S.; Kwon, O.S.; Yoon, T.J.; Chung, J.H. Anti-graying effect of the extract of Pueraria thunbergiana via upregulation of cAMP/MITF-M signaling pathway. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 75, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksan, I.; Goding, C.R. Targeting the microphthalmia basic helix–loop–helix–leucine zipper transcription factor to a subset of E-box elements in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6930–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, C.; Khaled, M.; Fisher, D.E. MITF: Master regulator of melanocyte development and melanoma oncogene. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Hong, S.D.; Roh, E.; Jung, S.H.; Cho, W.J.; Park, S.H.; Yoon, D.Y.; Ko, S.M.; Hwang, B.Y.; Hong, J.T.; et al. cAMP-dependent activation of protein kinase A as a therapeutic target of skin hyperpigmentation by diphenylmethylene hydrazinecarbothioamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3434–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Huh, S.; Boo, Y.C.; Hyun, C.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, D. Mechanisms of melanogenesis inhibition by 2,5-dimethyl-4-hydroxy-3(2H)-furanone. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.M.; Lee, S.I.; Choi, S.W.; Moon, S.W.; Boo, Y.C. p-Coumaric acid, a constituent of Sasa quelpaertensis Nakai, inhibits cellular melanogenesis stimulated by α-melanocyte stimulating hormone. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Singh, S.K.; Sarkar, C.; Bera, R.; Ratha, J.; Tobin, D.J.; Bhadra, R. Activation of the MITF promoter by lipid-stimulated activation of p38-stress signalling to CREB. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, M.; Larribere, L.; Bille, K.; Aberdam, E.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R.; Bertolotto, C. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β is activated by cAMP and plays an active role in the regulation of melanogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33690–33697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.R.; Lin, J.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Huang, T.K.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, M.O.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Su, C.C.; Wu, Y.J. Inhibition of melanogenesis by gallic acid: Possible involvement of the PI3K/AKT, MEK/ERK and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in B16F10 cells. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2013, 14, 20443–20458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, E.J.; Park, J.I.; Lee, J.E.; Myung, C.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Chang, S.E.; Hwang, J.S. A Novel Role of Serotonin Receptor 2B Agonist as an Anti-Melanogenesis Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040546
Oh EJ, Park JI, Lee JE, Myung CH, Kim SY, Chang SE, Hwang JS. A Novel Role of Serotonin Receptor 2B Agonist as an Anti-Melanogenesis Agent. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040546
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Eun Ju, Jong Il Park, Ji Eun Lee, Cheol Hwan Myung, Su Yeon Kim, Sung Eun Chang, and Jae Sung Hwang. 2016. "A Novel Role of Serotonin Receptor 2B Agonist as an Anti-Melanogenesis Agent" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040546
APA StyleOh, E. J., Park, J. I., Lee, J. E., Myung, C. H., Kim, S. Y., Chang, S. E., & Hwang, J. S. (2016). A Novel Role of Serotonin Receptor 2B Agonist as an Anti-Melanogenesis Agent. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040546