Susceptibility of Chinese Perch Brain (CPB) Cell and Mandarin Fish to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
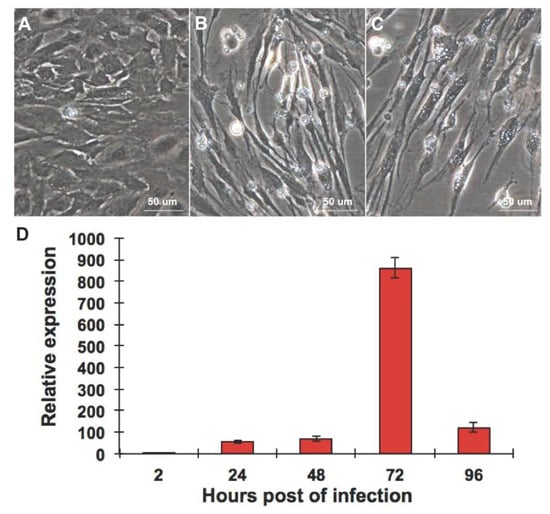
2.1. CPB Cells Are Susceptible to RGNNV
2.2. RGNNV Infection Induced Apoptosis in CPB Cells
2.3. Clinical Signs of Mandarin Fish upon RGNNV Infection
2.4. Histopathology of Mandarin Fish Infected with RGNNV
2.5. Visualization of RGNNV Particles in Brain Tissues of RGNNV-Infected Mandarin Fish
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cells and Virus
4.2. CPB Cell Infection
4.3. Virus RT-PCR and qRT-PCR Assays
4.4. Investigation of Apoptosis in RGNNV-Infected CPB Cells
4.5. Infection of Mandarin Fish with RGNNV
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mori, K.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K.; Arimoto, M.; Mushiake, K.; Furusawa, I. Properties of a new virus belonging to nodaviridae found in larval striped jack (Pseudocaranx dentex) with nervous necrosis. Virology 1992, 187, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerset, I.; Nerland, A.H. Complete sequence of RNA1 and subgenomic RNA3 of Atlantic halibut nodavirus (AHNV). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 58, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, T.; Mise, K.; Takeda, A.; Okinaka, Y.; Mori, K.; Arimoto, M.; Okuno, T.; Nakai, T. Characterization of Striped jack nervous necrosis virus subgenomic RNA3 and biological activities of its encoded protein B2. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2807–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezeth, K.B.; Patel, S.; Henriksen, H.; Szilvay, A.M.; Nerland, A.H. B2 protein from betanodavirus is expressed in recently infected but not in chronically infected fish. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2009, 83, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.C.; Wu, J.L.; Hong, J.R. Betanodavirus non-structural protein B2: A novel necrotic death factor that induces mitochondria-mediated cell death in fish cells. Virology 2009, 385, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.J.; Su, Y.C.; Hong, J.R. Betanodavirus non-structural protein B1: A novel anti-necrotic death factor that modulates cell death in early replication cycle in fish cells. Virology 2009, 385, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Nagai, T.; Nakai, T.; Muroga, K. Genomic classification of fish nodaviruses by molecular phylogenetic analysis of the coat protein gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1633–1636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.K.; Matsuoka, S.; Mori, K.; Okinaka, Y.; Park, S.C.; Nakai, T. Genetic analysis and pathogenicity of betanodavirus isolated from wild redspotted grouper Epinephelus akaara with clinical signs. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, B.L.; Kwang, J.; Moody, N. Betanodavirus infections of teleost fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Nakai, T.; Mori, K.; Arimoto, M.; Furusawa, I. Cloning of the fish cell line SSN-1 for piscine nodaviruses. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2000, 43, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.S.; John, J.A.; Lin, C.H.; Guo, I.C.; Chen, S.C.; Fang, K.; Lin, C.H.; Chang, C.Y. Establishment of cell lines from a tropical grouper, Epinephelus awoara (Temminck & Schlegel), and their susceptibility to grouper irido- and nodaviruses. J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bandin, I.; Olveira, J.G.; Borrego, J.J.; Dopazo, C.P.; Barja, J.L. Susceptibility of the fish cell line SAF-1 to betanodavirus. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, V.; Shukla, R.; Bhonde, R.; Hameed, A.S. Establishment of embryonic cell line from sea bass (Lates calcarifer) for virus isolation. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 137, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, K.; Sumiyoshi, K.; Ariyasu, R.; Yamashita, K.; Zenke, K.; Okinaka, Y. Susceptibilities of medaka (Oryzias latipes) cell lines to a betanodavirus. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarath Babu, V.; Abdul Majeed, S.; Nambi, K.S.; Taju, G.; Madan, N.; Sundar Raj, N.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Comparison of betanodavirus replication efficiency in ten Indian fish cell lines. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, V.S.; Nambi, K.S.; Chandra, V.; Ishaq Ahmed, V.P.; Bhonde, R.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Establishment and characterization of a fin cell line from Indian walking catfish, Clarias batrachus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, A.; The, H.C.; Lam, T.J.; Sin, Y.M. Nodavirus infection in freshwater ornamental fish, guppy, Poicelia reticulata--comparative characterization and pathogenicity studies. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, R.; Okinaka, Y.; Nakai, T. Betanodavirus infection in the freshwater model fish medaka (Oryzias latipes). J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigarre, L.; Cabon, J.; Baud, M.; Heimann, M.; Body, A.; Lieffrig, F.; Castric, J. Outbreak of betanodavirus infection in tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), in freshwater. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keawcharoen, J.; Techangamsuwan, S.; Ponpornpisit, A.; Lombardini, E.D.; Patchimasiri, T.; Pirarat, N. Genetic characterization of a betanodavirus isolated from a clinical disease outbreak in farm-raised tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in Thailand. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanassopoulou, F.; Billinis, C.; Prapas, T. Important disease conditions of newly cultured species in intensive freshwater farms in Greece: First incidence of nodavirus infection in Acipenser sp. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 60, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, R.; Okinaka, Y.; Uematsu, K.; Nakai, T. Screening of freshwater fish species for their susceptibility to a betanodavirus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2007, 77, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.W.; Chao, Y.M.; Guo, T.C.; Santi, N.; Evensen, O.; Kasani, S.K.; Hong, J.R.; Wu, J.L. The interferon response is involved in nervous necrosis virus acute and persistent infection in zebrafish infection model. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Fu, X.; Li, N.; Dong, X.; Zhao, L.; Lan, J.; Ji, W.; Zhou, W.; Ai, T.; Wu, S.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of Mandarin fish brain cells infected with infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus with an emphasis on retinoic acid-inducible gene 1-like receptors and apoptosis pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.C.; Shieh, J.R.; Lin, S.J. Genetic and antigenic analysis of betanodaviruses isolated from aquatic organisms in Taiwan. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 55, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.X.; Dallmann, K.; Kwang, J. Identification of nucleolus localization signal of betanodavirus GGNNV protein alpha. Virology 2003, 306, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Wei, T.; Dallmann, K.; Kwang, J. Induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis by betanodaviruses GGNNV and demonstration of protein alpha as an apoptosis inducer. Virology 2003, 308, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.W.; Wu, T.H.; Jia, T.L.; Hegde, A.; Zhang, R.Q. Development and characterization of a new tropical marine fish cell line from grouper, Epinephelus coioides susceptible to iridovirus and nodavirus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, T.; Mise, K.; Mori, K.; Arimoto, M.; Nakai, T.; Okuno, T. Establishment of an infectious RNA transcription system for Striped jack nervous necrosis virus, the type species of the betanodaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, T.; Okinaka, Y.; Mise, K.; Mori, K.; Arimoto, M.; Okuno, T.; Nakai, T. Identification of host-specificity determinants in betanodaviruses by using reassortants between striped jack nervous necrosis virus and sevenband grouper nervous necrosis virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgard, A.C.; Nerland, A.H.; Fiksdal, I.U.; Patel, S. Atlantic halibut experimentally infected with nodavirus shows increased levels of T-cell marker and IFNgamma transcripts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, S.; Lopez-Jimena, B.; Alonso, M.C.; Garcia-Rosado, E.; Bandin, I. Experimental susceptibility of European sea bass and Senegalese sole to different betanodavirus isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, S.; Olveira, J.G.; Bandin, I. Influence of temperature on Betanodavirus infection in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binesh, C.P. Elevation of temperature and crowding trigger acute viral nervous necrosis in zebra fish, Brachydanio rerio (Hamilton-Buchanan), subclinically infected with betanodavirus. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jimena, B.; Alonso Mdel, C.; Thompson, K.D.; Adams, A.; Infante, C.; Castro, D.; Borrego, J.J.; Garcia-Rosado, E. Tissue distribution of Red Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) genome in experimentally infected juvenile European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Takagi, M.; Miyazaki, T. Histopathological studies on viral nervous necrosis of sevenband grouper, Epinephelus septemfasciatus Thunberg, at the grow-out stage. J. Fish Dis. 2004, 27, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.R. Betanodavirus: Mitochondrial disruption and necrotic cell death. World J. Virol. 2013, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; He, J.G.; Mori, K.I.; Nishioka, T.; Wu, J.L.; Weng, S.; Mushiake, K.; Arimoto, M.; Nakai, T. Mass mortalities associated with viral nervous necrosis in hatchery-reared groupers in the People’s Republic of China. Fish Pathol. 2001, 36, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.M.K.; Nakai, T.; Furusawa, I.; Muroga, K. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of RNA of striped jack nervous necrosis virus (SJNNV). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1994, 18, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, J.; Chen, W.; Fu, X.; Lin, Q.; Chang, O.; Zhao, L.; Lan, J.; Li, N.; Lin, L. Susceptibility of Chinese Perch Brain (CPB) Cell and Mandarin Fish to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050740
Tu J, Chen W, Fu X, Lin Q, Chang O, Zhao L, Lan J, Li N, Lin L. Susceptibility of Chinese Perch Brain (CPB) Cell and Mandarin Fish to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050740
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Jiagang, Wenjie Chen, Xiaozhe Fu, Qiang Lin, Ouqin Chang, Lijuan Zhao, Jiangfeng Lan, Ningqiu Li, and Li Lin. 2016. "Susceptibility of Chinese Perch Brain (CPB) Cell and Mandarin Fish to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050740
APA StyleTu, J., Chen, W., Fu, X., Lin, Q., Chang, O., Zhao, L., Lan, J., Li, N., & Lin, L. (2016). Susceptibility of Chinese Perch Brain (CPB) Cell and Mandarin Fish to Red-Spotted Grouper Nervous Necrosis Virus (RGNNV) Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050740