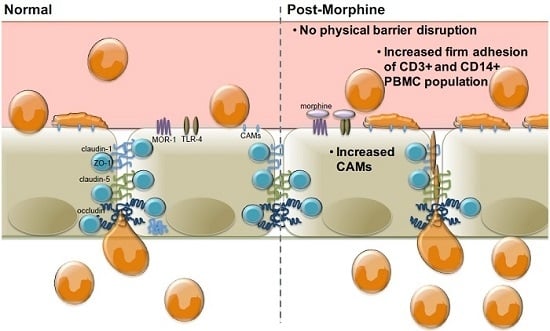
Prolonged Morphine Exposure Induces Increased Firm Adhesion in an in Vitro Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphine Does Not Induce BBB (Blood–Brain Barrier) Leakiness
2.2. Morphine Alters CAM (Cellular Adhesion Molecule) mRNA and Protein Expression
2.3. Morphine Increases PBMC Adhesion
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Model
4.4. FITC-Dextran Permeability Assay
4.5. mRNA and Protein Analysis
4.5.1. RT-PCR
4.5.2. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.6. PBMC Adhesion Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivey, N.S.; MacLean, A.G.; Lackner, A.A. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and the blood–brain barrier. J. Neurovirol. 2009, 15, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strazza, M.; Pirrone, V.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonnemacher, M.R. Breaking down the barrier: The effects of HIV-1 on the blood–brain barrier. Brain Res. 2011, 1399, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, H.C.; Abbott, N.J.; Burek, M.; Cecchelli, R.; Couraud, P.O.; Deli, M.A.; Forster, C.; Galla, H.J.; Romero, I.A.; Shusta, E.V.; et al. In vitro models of the blood–brain barrier: An overview of commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines for their use. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maubert, M.E.; Pirrone, V.; Rivera, N.T.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonnemacher, M.R. Interaction between tat and drugs of abuse during HIV-1 infection and central nervous system disease. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, J.J.; Diamond, M.S. Mechanisms of restriction of viral neuroinvasion at the blood–brain barrier. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 38, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Song, H.L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.X.; Cui, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha affects blood–brain barrier permeability and tight junction-associated occludin in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatovic, S.M.; Keep, R.F.; Andjelkovic, A.V. Brain endothelial cell-cell junctions: How to “open” the blood brain barrier. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossinsky, A.S.; Shivers, R.R. Structural pathways for macromolecular and cellular transport across the blood–brain barrier during inflammatory conditions. Review. Histol. Histopathol. 2004, 19, 535–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Fanning, A.S.; Bridges, A.; Anderson, J.M. Zo-1 stabilizes the tight junction solute barrier through coupling to the perijunctional cytoskeleton. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, R.A.; Mitchell, M.E.; Fondren, G. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in cellular immune reactions in the human central nervous system. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 136, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steffen, B.J.; Butcher, E.C.; Engelhardt, B. Evidence for involvement of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in lymphocyte interaction with endothelium in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the central nervous system in the SJL/J mouse. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bo, L.; Peterson, J.W.; Mork, S.; Hoffman, P.A.; Gallatin, W.M.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Trapp, B.D. Distribution of immunoglobulin superfamily members icam-1, -2, -3, and the beta 2 integrin LFA-1 in multiple sclerosis lesions. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1996, 55, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, R.; Wosik, K.; Berard, J.L.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Ifergan, I.; Kebir, H.; Haqqani, A.S.; Kreymborg, K.; Krug, S.; Moumdjian, R.; et al. Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule promotes leukocyte trafficking into the central nervous system. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.I.; Cayrol, R.; Prat, A. Disruption of central nervous system barriers in multiple sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raine, C.S.; Cannella, B.; Duijvestijn, A.M.; Cross, A.H. Homing to central nervous system vasculature by antigen-specific lymphocytes. II. Lymphocyte/endothelial cell adhesion during the initial stages of autoimmune demyelination. Lab. Investig. 1990, 63, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrithers, M.D.; Visintin, I.; Kang, S.J.; Janeway, C.A., Jr. Differential adhesion molecule requirements for immune surveillance and inflammatory recruitment. Brain 2000, 123, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, S.D.; Aalinkeel, R.; Sykes, D.E.; Reynolds, J.L.; Bindukumar, B.; Fernandez, S.F.; Chawda, R.; Shanahan, T.C.; Schwartz, S.A. Tight junction regulation by morphine and HIV-1 tat modulates blood–brain barrier permeability. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.S.; Ali, S.F. Alterations in blood–brain barrier function by morphine and methamphetamine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 198–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, S.; Saubamea, B.; Cisternino, S.; Marie-Claire, C.; Dauchy, S.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Decleves, X. Effect of chronic exposure to morphine on the rat blood–brain barrier: Focus on the p-glycoprotein. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weksler, B.B.; Subileau, E.A.; Perriere, N.; Charneau, P.; Holloway, K.; Leveque, M.; Tricoire-Leignel, H.; Nicotra, A.; Bourdoulous, S.; Turowski, P.; et al. Blood-brain barrier-specific properties of a human adult brain endothelial cell line. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1872–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, B.P.; Cruz-Orengo, L.; Pasieka, T.J.; Couraud, P.O.; Romero, I.A.; Weksler, B.; Cooper, J.A.; Doering, T.L.; Klein, R.S. Immortalized human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells maintain the properties of primary cells in an in vitro model of immune migration across the blood brain barrier. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 212, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urich, E.; Lazic, S.E.; Molnos, J.; Wells, I.; Freskgard, P.O. Transcriptional profiling of human brain endothelial cells reveals key properties crucial for predictive in vitro blood–brain barrier models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weksler, B.; Romero, I.A.; Couraud, P.O. The hcmec/d3 cell line as a model of the human blood brain barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Potin, S.; Chapy, H.; Crete, D.; Glacial, F.; Ganeshamoorthy, K.; Couraud, P.O.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Decleves, X. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates cyp1b1 but not abcb1 and abcg2 in hcmec/d3 human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells after tcdd exposure. Brain Res. 2015, 1613, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Su, Q.; Zeng, C.; Shang, X. Endophilin-1 regulates blood–brain barrier permeability via EGFR-JNK signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2015, 1606, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couper, F.J.; Logan, B.K. Drugs and Human Performance Fact Sheets. Available online: http://www.nhtsa.gov/People/injury/research/job185drugs/morphine.htm (accessed on 11 December 2015).
- Zhang, E.Y.; Xiong, J.; Parker, B.L.; Chen, A.Y.; Fields, P.E.; Ma, X.; Qiu, J.; Yankee, T.M. Depletion and recovery of lymphoid subsets following morphine administration. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.Y.; Baik, E.J.; Lee, S.H. Prostaglandin e(2)-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression is mediated by camp/epac signaling modules in bend.3 brain endothelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, H.F.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions in inflammation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernot, D.; Peiretti, F.; Canault, M.; Juhan-Vague, I.; Nalbone, G. Upregulation of TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 surface expression by adenylate cyclase-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M.; Kemp, B.; Hauptmann, S.; Rath, W. Parturition: Steroids, prostaglandin e2, and expression of adhesion molecules by endothelial cells. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 89, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Awar, L.; McMickle, A.; Bai, F.; Nagarajan, A.; Yu, S. IL-17 induces expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule through signaling pathway of NF-κb, but not Akt1 and TAK1 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 77, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J. HIV gp120 induces endothelial dysfunction in tumour necrosis factor-a-activated porcine and human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stins, M.F.; Pearce, D.; di Cello, F.; Erdreich-Epstein, A.; Pardo, C.A.; Sik Kim, K. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human brain endothelial cells by HIV-1 gp120: Role of CD4 and chemokine coreceptors. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.A.; Kim, C.; Gupta, S.K.; Rajashekhar, G.; Rehman, J.; Clauss, M. Pentoxifylline reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha and HIV-induced vascular endothelial activation. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2012, 28, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Kim, K.; Duan, M.; Hayashi, T.; Guo, M.; Morgello, S.; Prat, A.; Wang, J.; Su, T.P.; Buch, S. Cocaine hijacks sigma1 receptor to initiate induction of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule: Implication for increased monocyte adhesion and migration in the cns. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5942–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.; Heasman, S.J.; Alvarez, J.I.; Prat, A.; Lyck, R.; Engelhardt, B. Review: Leucocyte-endothelial cell crosstalk at the blood–brain barrier: A prerequisite for successful immune cell entry to the brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2011, 37, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Loram, L.C.; Ramos, K.; de Jesus, A.J.; Thomas, J.; Cheng, K.; Reddy, A.; Somogyi, A.A.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Watkins, L.R.; et al. Morphine activates neuroinflammation in a manner parallel to endotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6325–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, R.; Roy, S. Chronic morphine and HIV-1 tat promote differential central nervous system trafficking of CD3+ and Ly6C+ immune cells in a murine streptococcus pneumoniae infection model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.H.; Tsai, R.Y.; Wong, C.S. Role of neuroinflammation in morphine tolerance: Effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwan 2012, 50, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, P.M.; Ramos, K.M.; Rodgers, K.M.; Wang, X.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Lewis, M.T.; Morgan, K.N.; Kroll, J.L.; Taylor, F.R.; Strand, K.A.; et al. Activation of adult rat cns endothelial cells by opioid-induced toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling induces proinflammatory, biochemical, morphological, and behavioral sequelae. Neuroscience 2014, 280, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leow-Dyke, S.; Allen, C.; Denes, A.; Nilsson, O.; Maysami, S.; Bowie, A.G.; Rothwell, N.J.; Pinteaux, E. Neuronal toll-like receptor 4 signaling induces brain endothelial activation and neutrophil transmigration in vitro. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, S.M.; Park, T.Y.; Park, H.S.; Baik, E.J.; Lee, S.H. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of ICAM-1 through modulation of toll-like receptor-4 signaling in brain endothelial cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, C.; Dietz, K.; Schleich, A.; Schlaszus, H.; Stoll, M.; Meyermann, R.; Mittelbronn, M. Immune surveillance of the normal human cns takes place in dependence of the locoregional blood-brain barrier configuration and is mainly performed by CD3+/CD8+ lymphocytes. Neuropathology 2011, 31, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryce, G.; Male, D.; Campbell, I.; Greenwood, J. Factors controlling T-cell migration across rat cerebral endothelium in vitro. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 75, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G.; Grimes, T.; Brankin, B.; Mabruk, M.J.; Hosie, M.J.; Jarrett, O.; Callanan, J.J. Neuropathology associated with feline immunodeficiency virus infection highlights prominent lymphocyte trafficking through both the blood-brain and blood-choroid plexus barriers. J. Neurovirol. 2005, 11, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Fincke, J.E.; Legido, A.; Lischner, H.W.; de Chadarevian, J.P.; Kaye, E.M.; Platsoucas, C.D.; Oleszak, E.L. Angiocentric CD3+ T-cell infiltrates in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated central nervous system disease in children. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1999, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

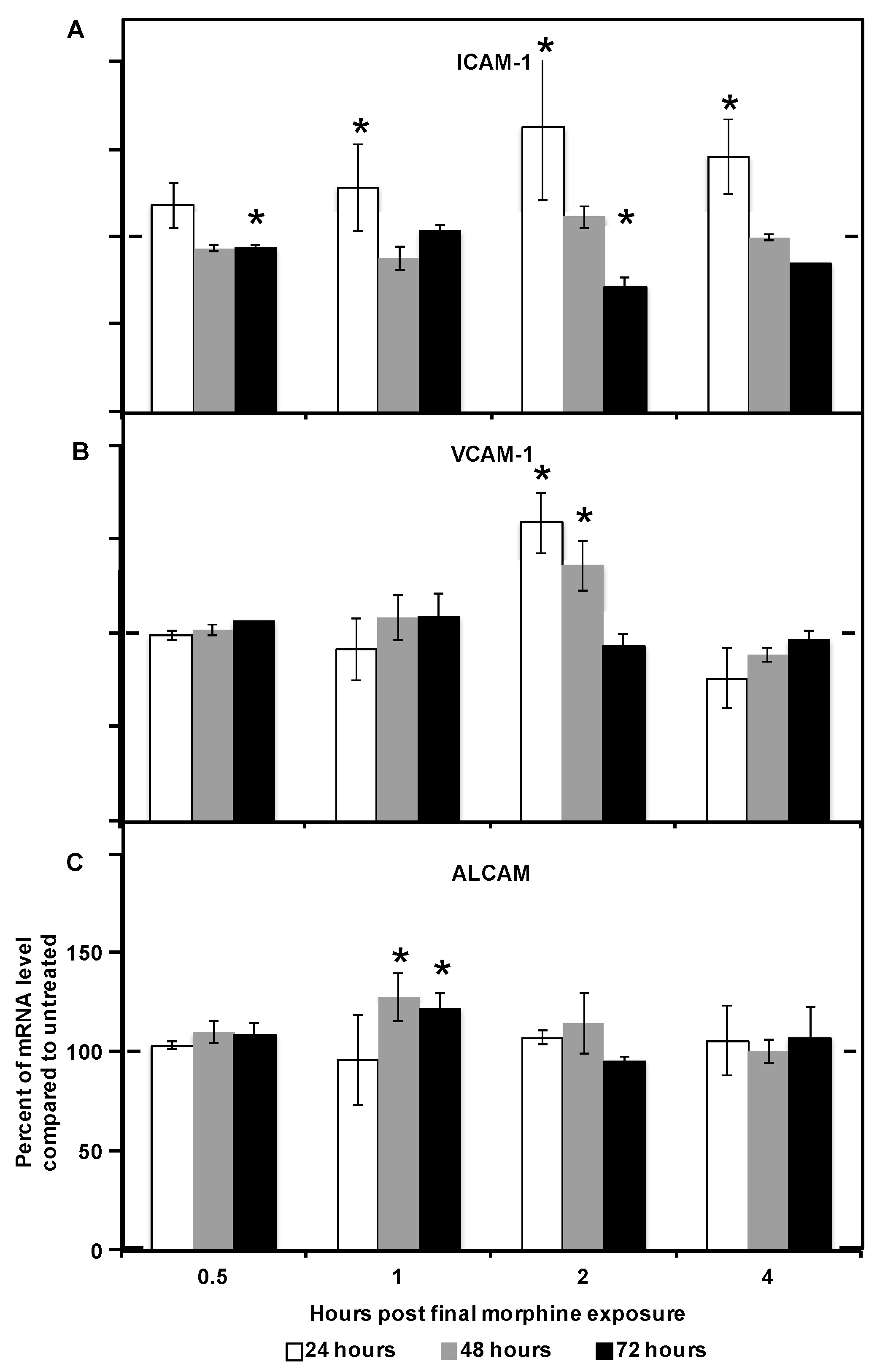



| CAM Examined | Number of Expressors | MFI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | p Value | R2 | p Value | |
| ICAM-1 | 0.983 | 0.017 | 0.962 | 0.038 |
| VCAM-1 | 0.998 | 0.002 | −0.258 | 0.742 |
| ALCAM | 0.998 | 0.012 | 0.982 | 0.018 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strazza, M.; Pirrone, V.; Wigdahl, B.; Dampier, W.; Lin, W.; Feng, R.; Maubert, M.E.; Weksler, B.; Romero, I.A.; Couraud, P.-O.; et al. Prolonged Morphine Exposure Induces Increased Firm Adhesion in an in Vitro Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060916
Strazza M, Pirrone V, Wigdahl B, Dampier W, Lin W, Feng R, Maubert ME, Weksler B, Romero IA, Couraud P-O, et al. Prolonged Morphine Exposure Induces Increased Firm Adhesion in an in Vitro Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060916
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrazza, Marianne, Vanessa Pirrone, Brian Wigdahl, Will Dampier, Wei Lin, Rui Feng, Monique E. Maubert, Babette Weksler, Ignacio A. Romero, Pierre-Olivier Couraud, and et al. 2016. "Prolonged Morphine Exposure Induces Increased Firm Adhesion in an in Vitro Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060916
APA StyleStrazza, M., Pirrone, V., Wigdahl, B., Dampier, W., Lin, W., Feng, R., Maubert, M. E., Weksler, B., Romero, I. A., Couraud, P.-O., & Nonnemacher, M. R. (2016). Prolonged Morphine Exposure Induces Increased Firm Adhesion in an in Vitro Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060916