Mblk-1 Transcription Factor Family: Its Roles in Various Animals and Regulation by NOL4 Splice Variants in Mammals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Honeybees Exhibit Highly Organized Social Behavior and Have Enlarged Mushroom Bodies (MBs)
3. Mblk-1 Is Preferentially Expressed in Honeybee MBs
4. Drosophila Homolog E93 Is Involved in Regulation of Development and Morphogenesis
5. LCoR, the Human Homolog of Mblk-1, Interacts with Multiple Cofactors and Modulates Transcription Activities
6. The Mouse Homologs Mlr1 and Mlr2 Have Transactivation Activities and Show Different Expression Patterns
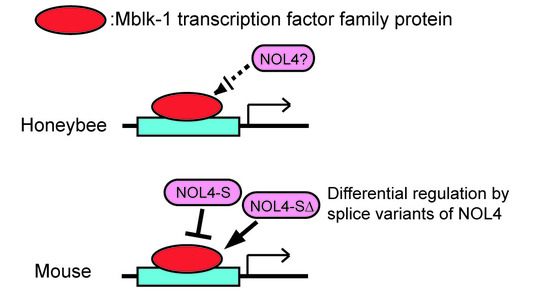
7. Mlr1, Mlr2 Interact with Multiple Cofactors Including a Conserved Nucleolar Protein NOL4
8. Splicing Variants of NOL4 Differentially Affect the Transactivation Activities of Mlr1 and Mlr2
9. Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kandel, E.R. The molecular biology of memory: cAMP, PKA, CRE, CREB-1, CREB-2, and CPEB. Mol. Brain 2012, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhina, V.; Arey, R.N.; Kaletsky, R.; Kauffman, A.; Stein, G.; Keyes, W.; Xu, D.; Murphy, C.T. Genome-wide functional analysis of CREB/long-term memory-dependent transcription reveals distinct basal and memory gene expression programs. Neuron 2015, 85, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.P.; Littleton, J.T. Transmission, development, and plasticity of synapses. Genetics 2015, 2, 345–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Kage, E.; Sawata, M.; Kamikouchi, A.; Ohashi, K.; Ohara, M.; Fujiyuki, T.; Kunieda, T.; Sekimizu, K.; Natori, S.; et al. Identification of a novel gene, Mblk-1, that encodes a putative transcription factor expressed preferentially in the large-type kenyon cells of the honeybee brain. Insect Mol. Biol. 2001, 10, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, M.L. The Biology of the Honey Bee; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Seeley, T.D. The Wisdom of the Hive: The Social Physiology of Honey Bee Colonies; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Von Frisch, K. The Dance Language and Orientation of Bees; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg, M. Mushroom body memoir: From maps to models. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, R.; Leboulle, G.; Eisenhardt, D. Small brains, bright minds. Cell 2006, 124, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, M.; Menzel, R. Learning and memory in the honeybee. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farris, S.M.; Robinson, G.E.; Fahrbach, S.E. Experience- and age-related outgrowth of intrinsic neurons in the mushroom bodies of the adult worker honeybee. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 6395–6404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ismail, N.; Robinson, G.E.; Fahrbach, S.E. Stimulation of muscarinic receptors mimics experience-dependent plasticity in the honey bee brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiya, T.; Kunieda, T.; Kubo, T. Increased neural activity of a mushroom body neuron subtype in the brains of forager honeybees. PLoS ONE 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiya, T.; Kubo, T. Dance type and flight parameters are associated with different mushroom body neural activities in worker honeybee brains. PLoS ONE 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strausfeld, N.J.; Hansen, L.; Li, Y.; Gomez, R.S.; Ito, K. Evolution, discovery, and interpretations of arthropod mushroom bodies. Learn. Mem. 1998, 5, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mobbs, P. The brain of the honeybee apis mellifera. I. The connections and spatial organization of the mushroom bodies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1982, 298, 309–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Grübel, K.; Busch, S.; Friedrich, A.B.; Siwanowicz, I.; Tanimoto, H. The mushroom body of adult Drosophila characterized by GAL4 drivers. J. Neurogenet. 2009, 23, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamikouchi, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Sawata, M.; Ohashi, K.; Natori, S.; Kubo, T. Preferential expression of the gene for a putative inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor homologue in the mushroom bodies of the brain of the worker honeybee Apis mellifera L. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 242, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamikouchi, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Sawata, M.; Natori, S.; Kubo, T. Concentrated expression of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and protein kinase C in the mushroom bodies of the brain of the honeybee Apis mellifera L. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 417, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Fujiyuki, T.; Shirai, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Kamikouchi, A.; Fujinawa, Y.; Kato, A.; Tsujimoto, A.; Kubo, T. Identification of genes expressed preferentially in the honeybee mushroom bodies by combination of differential display and cDNA microarray. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. Inositol triphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 1993, 361, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adasme, T.; Haeger, P.; Paula-Lima, A.C.; Espinoza, I.; Casas-Alarcón, M.M.; Carrasco, M.A.; Hidalgo, C. Involvement of ryanodine receptors in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial memory formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayanagi-Kiya, S.; Misawa-Hojo, K.; Kiya, T.; Kunieda, T.; Kubo, T. Splicing variants of NOL4 differentially regulate the transcription activity of Mlr1 and Mlr2 in cultured cells. Zool. Sci. 2014, 31, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Kunieda, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Kubo, T. DNA-binding properties of Mblk-1, a putative transcription factor from the honeybee. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.M.; Kunieda, T.; Kubo, T. The activity of Mblk-1, a mushroom body-selective transcription factor from the honeybee, is modulated by the Ras/MAPK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 18689–18694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, C.W.; Cziko, A.M.; Robinson, G.E. Gene expression profiles in the brain predict behavior in individual honey bees. Science 2003, 302, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baehrecke, E.H.; Thummel, C.S. The Drosophila E93 gene from the 93F early puff displays stage- and tissue-specific regulation by 20-hydroxyecdysone. Dev. Biol. 1995, 171, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Wendel, D.P.; Reid, P.; Lam, G.; Thummel, C.S.; Baehrecke, E.H. E93 directs steroid-triggered programmed cell death in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Duncan, D.M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Duncan, I. Control of target gene specificity during metamorphosis by the steroid response gene E93. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2949–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ureña, E.; Manjón, C.; Franch-Marro, X.; Martín, D. Transcription factor E93 specifies adult metamorphosis in hemimetabolous and holometabolous insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7024–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.; Alkhori, L.; Schleiffer, A.; Brochtrup, A.; Hummel, T.; Alenius, M. Combinatorial activation and repression by seven transcription factors specify Drosophila odorant receptor expression. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweck, H.K.M.; Ebrahim, S.A.M.; Thoma, M.; Mohamed, A.A.M.; Keesey, I.W.; Trona, F.; Lavista-Lianos, S.; Svatoš, A.; Sachse, S.; Knaden, M.; et al. Pheromones mediating copulation and attraction in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Cao, D.S.; Sethi, S.; Zheng, Z.; Chin, J.S.; Chakraborty, T.S.; Shepherd, A.K.; Nguyen, C.A.; Yew, J.Y.; Su, C.Y.; et al. Hormonal modulation of pheromone detection enhances male courtship success. Neuron 2016, 90, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kage, E.; Hayashi, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Hirotsu, T.; Kunitomo, H.; Inoue, T.; Arai, H.; Iino, Y.; Kubo, T. MBR-1, a novel helix-turn-helix transcription factor, is required for pruning excessive neurites in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Hirotsu, T.; Iwata, R.; Kage-Nakadai, E.; Kunitomo, H.; Ishihara, T.; Iino, Y.; Kubo, T. A trophic role for Wnt-Ror kinase signaling during developmental pruning in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heery, D.M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Hoare, S.; Parker, M.G. A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 1997, 387, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, I.; Bastien, Y.; Wai, T.; Nygard, K.; Lin, R.; Cormier, O.; Lee, H.S.; Eng, F.; Bertos, N.R.; Pelletier, N.; et al. Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor LcoR functions by histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M. Estrogen receptor α and β in health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 4, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asim, M.; Hafeez, B.B.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Gerlach, C.; Patz, M.; Mukhtar, H.; Baniahmad, A. Ligand-dependent corepressor acts as a novel androgen receptor corepressor, inhibits prostate cancer growth, and is functionally inactivated by the Src protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37108–37117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, M.R.; Verway, M.; An, B.S.; DiFeo, A.; Bismar, T.A.; Ann, D.K.; Martignetti, J.A.; Shalom-Barak, T.; White, J.H. Ligand-dependent corepressor (LcoR) recruitment by Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) regulates expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CDKN1A gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8662–8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palijan, A.; Fernandes, I.; Bastien, Y.; Tang, L.; Verway, M.; Kourelis, M.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.E.; Li, Z.; Bourdeau, V.; Mader, S.; et al. Function of histone deacetylase 6 as a cofactor of nuclear receptor coregulator LcoR. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30264–30274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, M.R.; Verway, M.; Benslama, R.O.; Birlea, M.; Bouttier, M.; Dimitrov, V.; Mader, S.; White, J.H. Ligand-dependent corepressor contributes to transcriptional repression by C2H2 zinc-finger transcription factor ZBRK1 through association with KRAB-associated protein-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7012–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basilico, C.; Moscatelli, D. The FGF family of growth factors and oncogenes. Adv. Cancer Res. 1992, 59, 115–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palijan, A.; Fernandes, I.; Verway, M.; Kourelis, M.; Bastien, Y.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.E.; Sacheli, A.; Bourdeau, V.; Mader, S.; White, J.H. Ligand-dependent corepressor LcoR is an attenuator of progesterone-regulated gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30275–30287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunieda, T.; Park, J.M.; Takeuchi, H.; Kubo, T. Identification and characterization of Mlr1,2: Two mouse homologues of Mblk-1, a transcription factor from the honeybee brain. FEBS Lett. 2003, 535, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolma, A.; Yin, Y.; Nitta, K.R.; Dave, K.; Popov, A.; Taipale, M.; Enge, M.; Kivioja, T.; Morgunova, E.; Taipale, J. DNA-dependent formation of transcription factor pairs alters their binding specificity. Nature 2015, 527, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampfel, G.; Kazmar, T.; Frank, O.; Wienerroither, S.; Reiter, F.; Stark, A. Transcriptional regulators form diverse groups with context-dependent regulatory functions. Nature 2015, 528, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.; Crossley, M. The CtBP family: Enigmatic and enzymatic transcriptional co-repressors. Bioessays 2001, 23, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, N.; Kondo, M.; Seki, N.; Yano, K.; Oda, T.; Masuho, Y.; Muramatsu, M. NOLP: Identification of a novel human nucleolar protein and determination of sequence requirements for its nucleolar localization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 252, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, S.; Barrodia, P.; Swain, R.K. Nucleolar protein 4-like has a complex expression pattern in zebrafish embryos. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 60, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.D.; Kirilyuk, A.; Li, J.V.; Zhang, W.; Lahusen, T.; Schmidt, M.O.; Oh, A.S.; Wellstein, A.; Riegel, A.T. Role of the nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1-Δ4 splice variant in the control of gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26813–26827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Ohmori, S.; Ito, T.; Seo, H. A splicing variant of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-1 (SRC-1E): The major isoform of SRC-1 to mediate thyroid hormone action. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takayanagi-Kiya, S.; Kiya, T.; Kunieda, T.; Kubo, T. Mblk-1 Transcription Factor Family: Its Roles in Various Animals and Regulation by NOL4 Splice Variants in Mammals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020246
Takayanagi-Kiya S, Kiya T, Kunieda T, Kubo T. Mblk-1 Transcription Factor Family: Its Roles in Various Animals and Regulation by NOL4 Splice Variants in Mammals. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020246
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakayanagi-Kiya, Seika, Taketoshi Kiya, Takekazu Kunieda, and Takeo Kubo. 2017. "Mblk-1 Transcription Factor Family: Its Roles in Various Animals and Regulation by NOL4 Splice Variants in Mammals" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020246
APA StyleTakayanagi-Kiya, S., Kiya, T., Kunieda, T., & Kubo, T. (2017). Mblk-1 Transcription Factor Family: Its Roles in Various Animals and Regulation by NOL4 Splice Variants in Mammals. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020246