Renalase Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
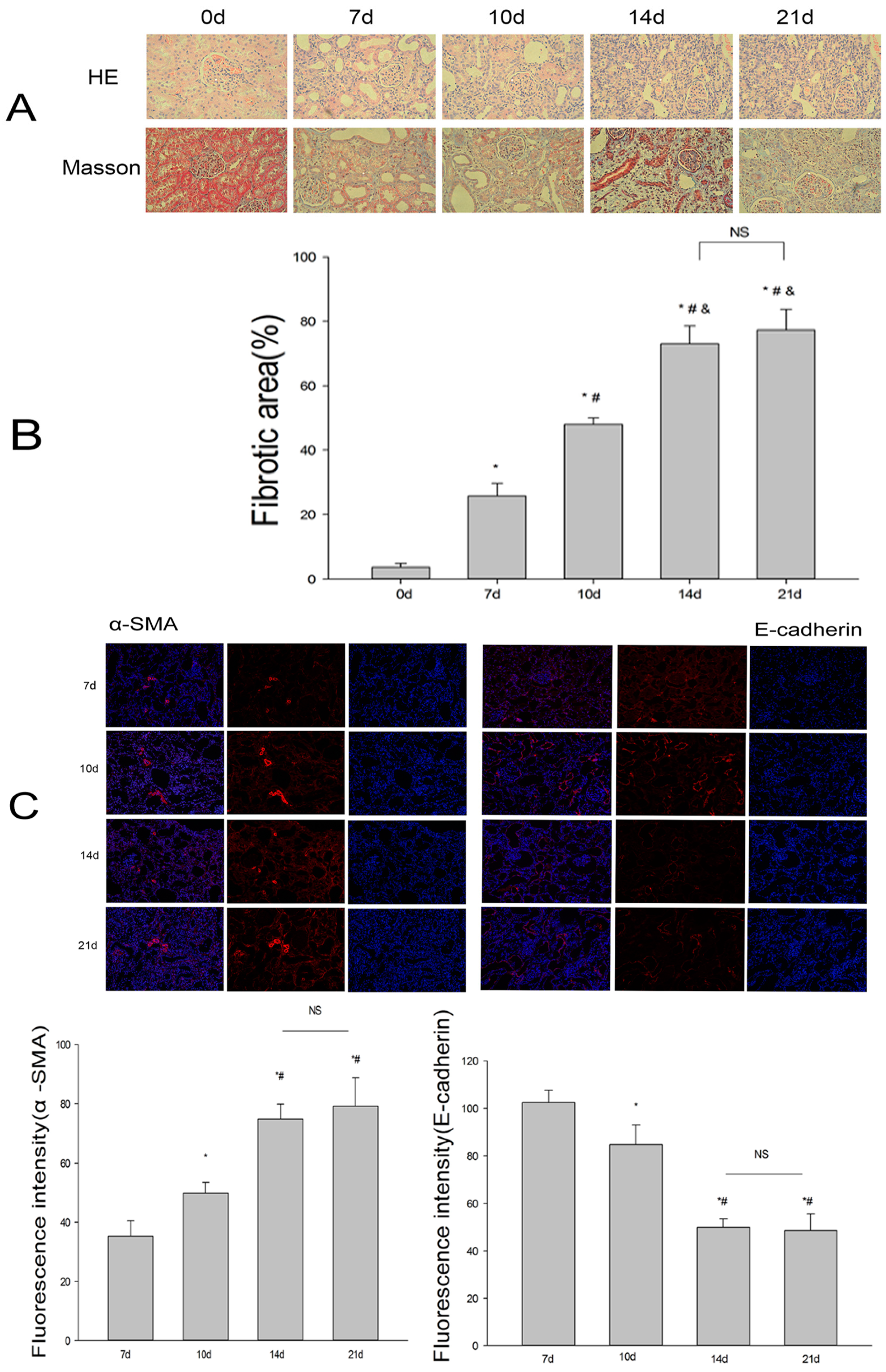
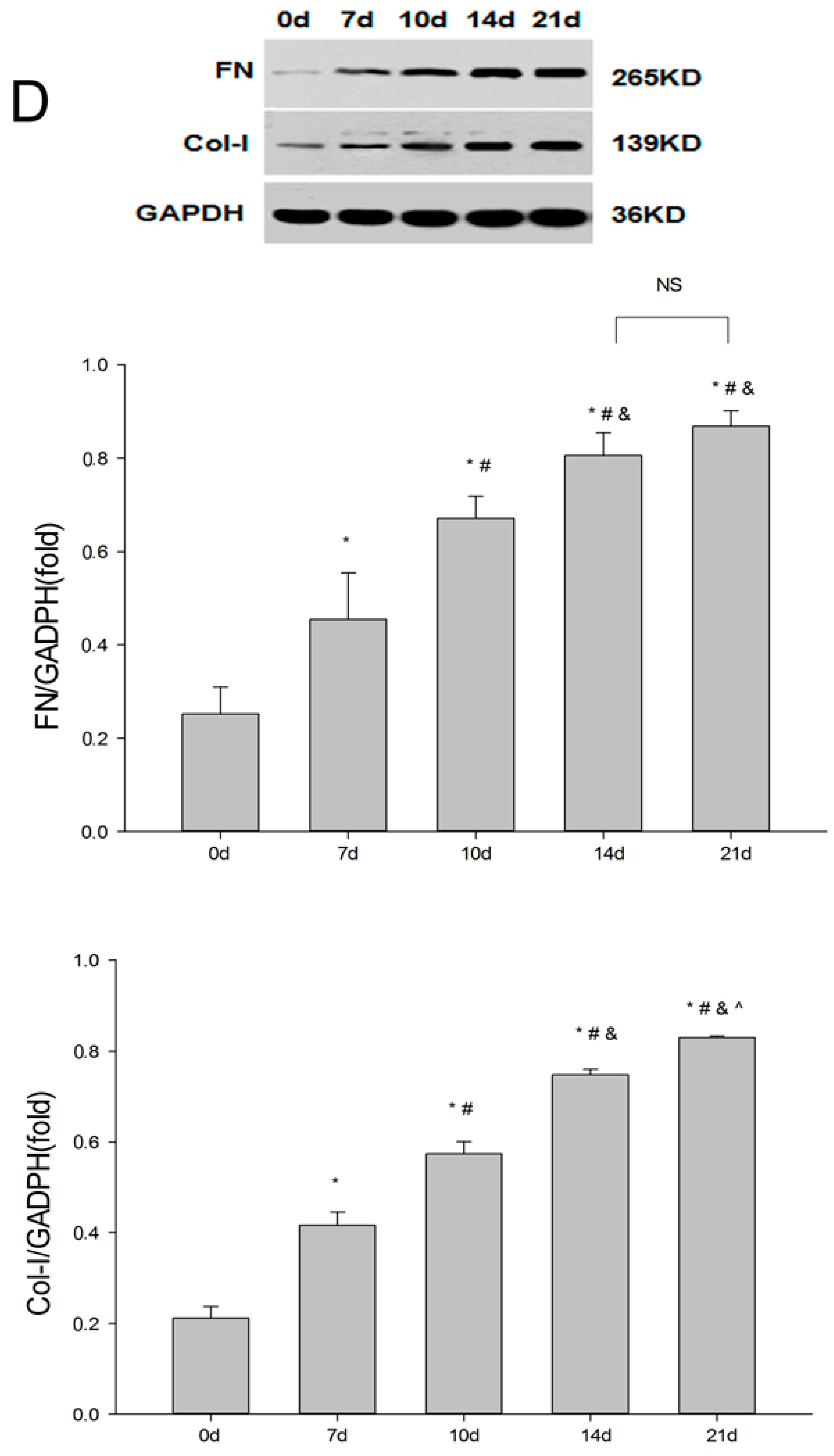
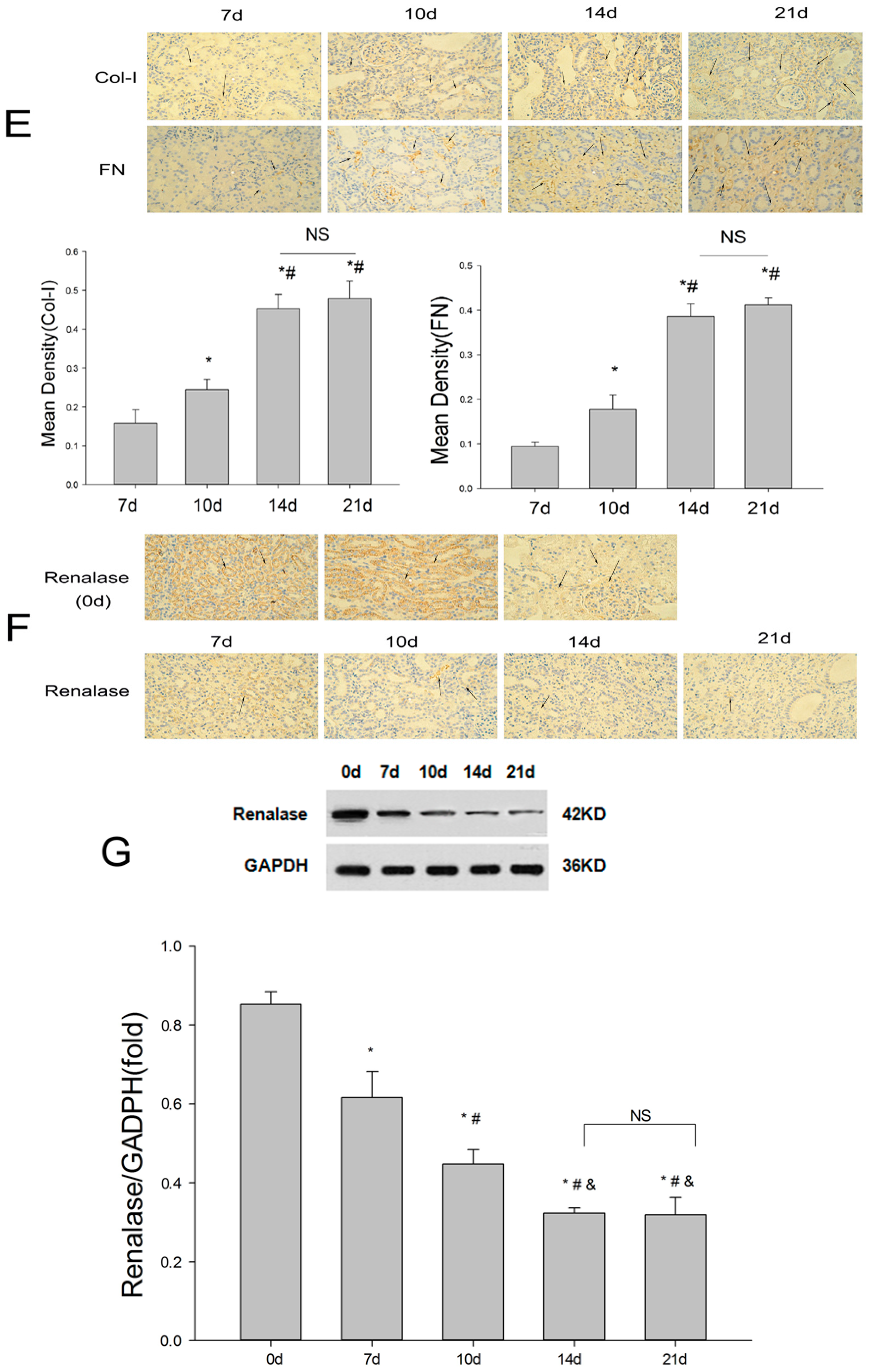
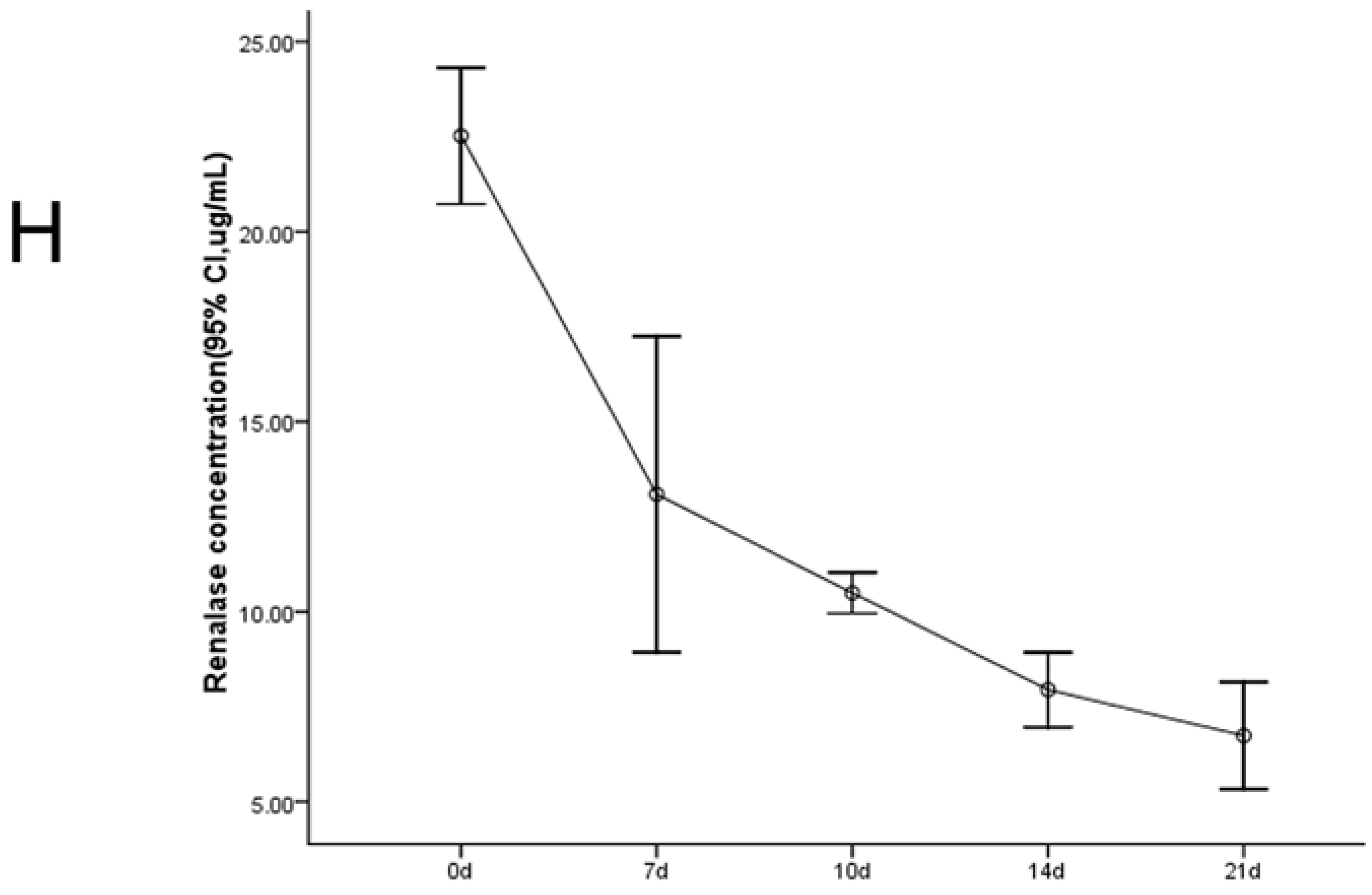
2.1. Establishment of the UUO Model and Expression of Renalase in Rat Kidneys
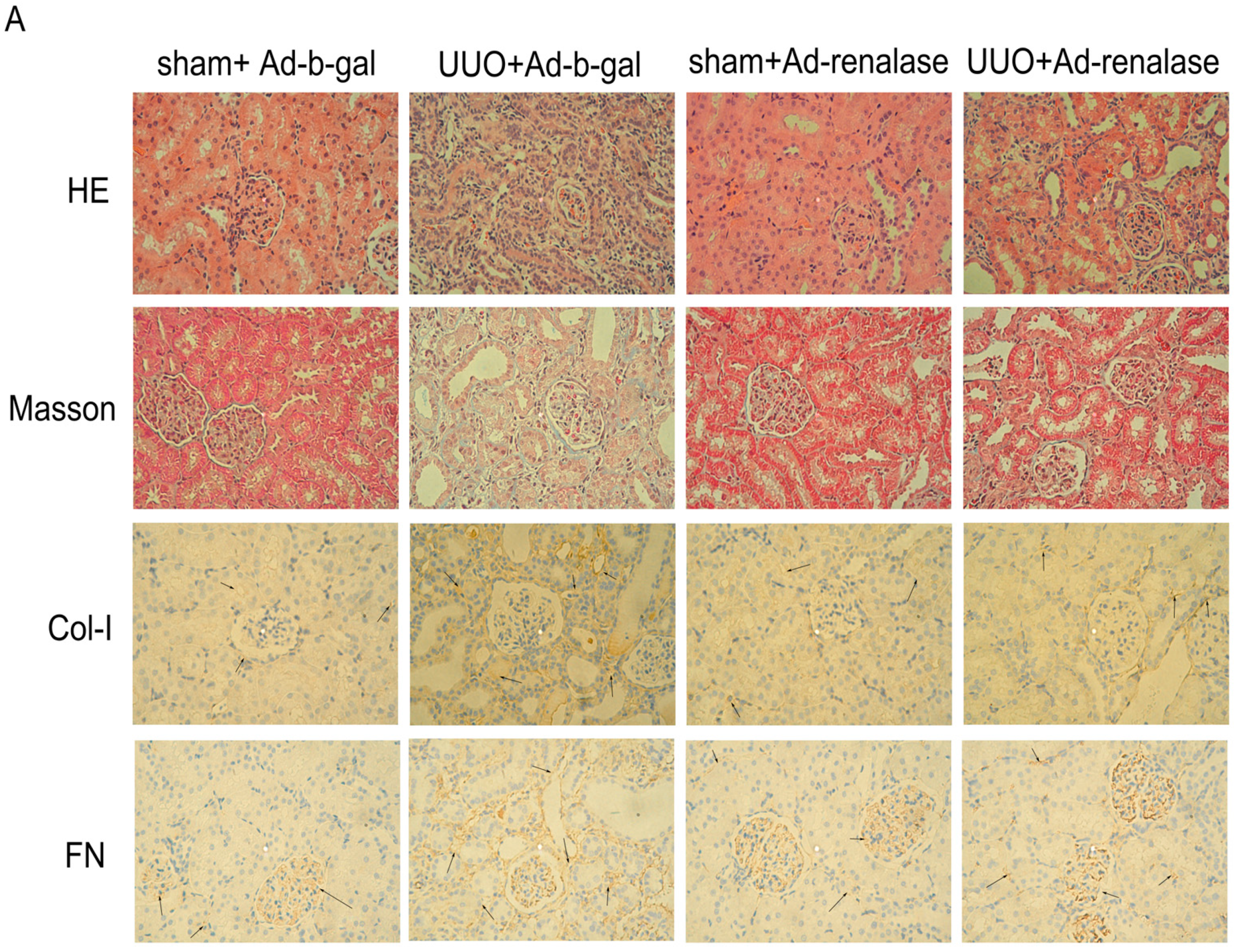
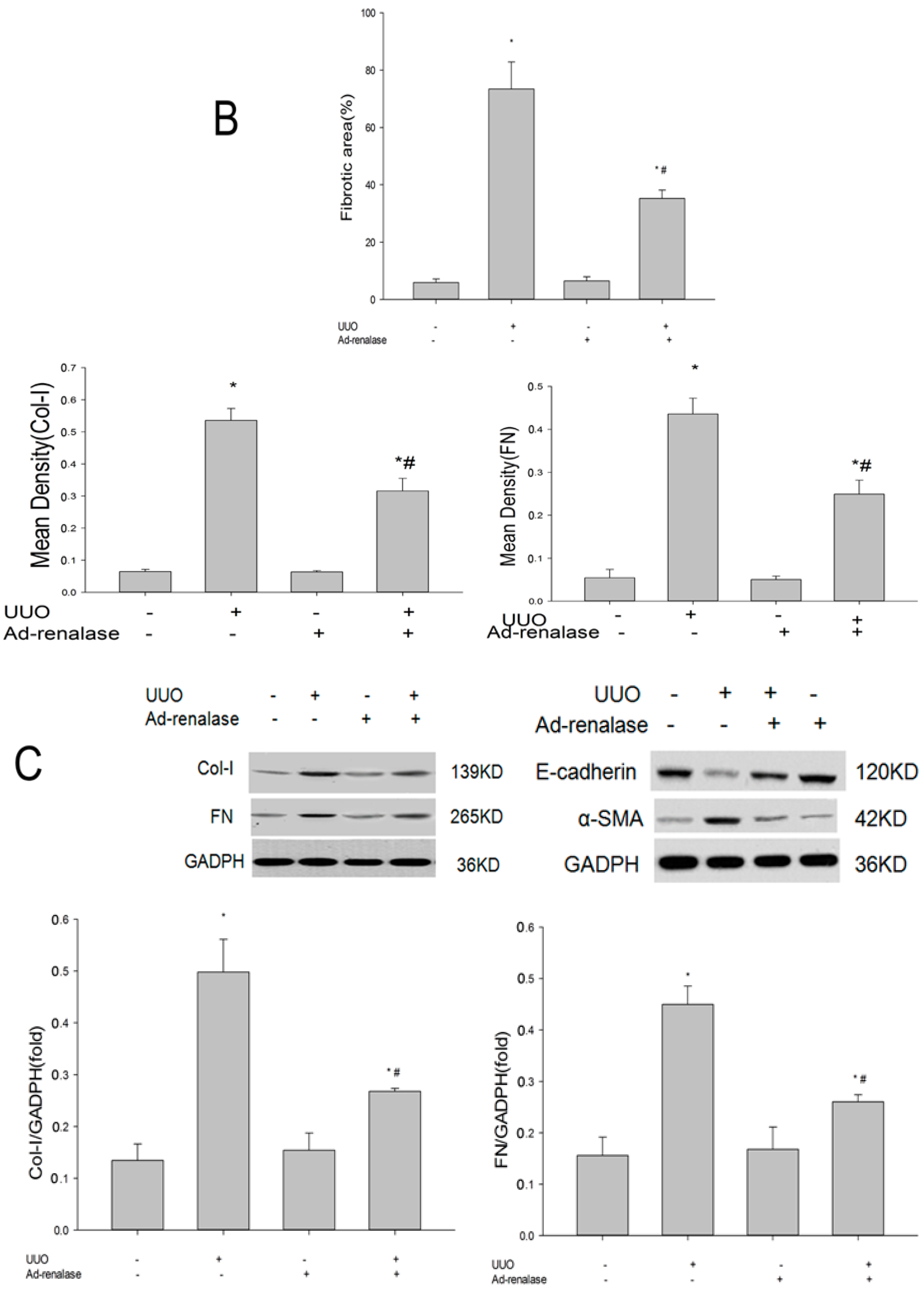
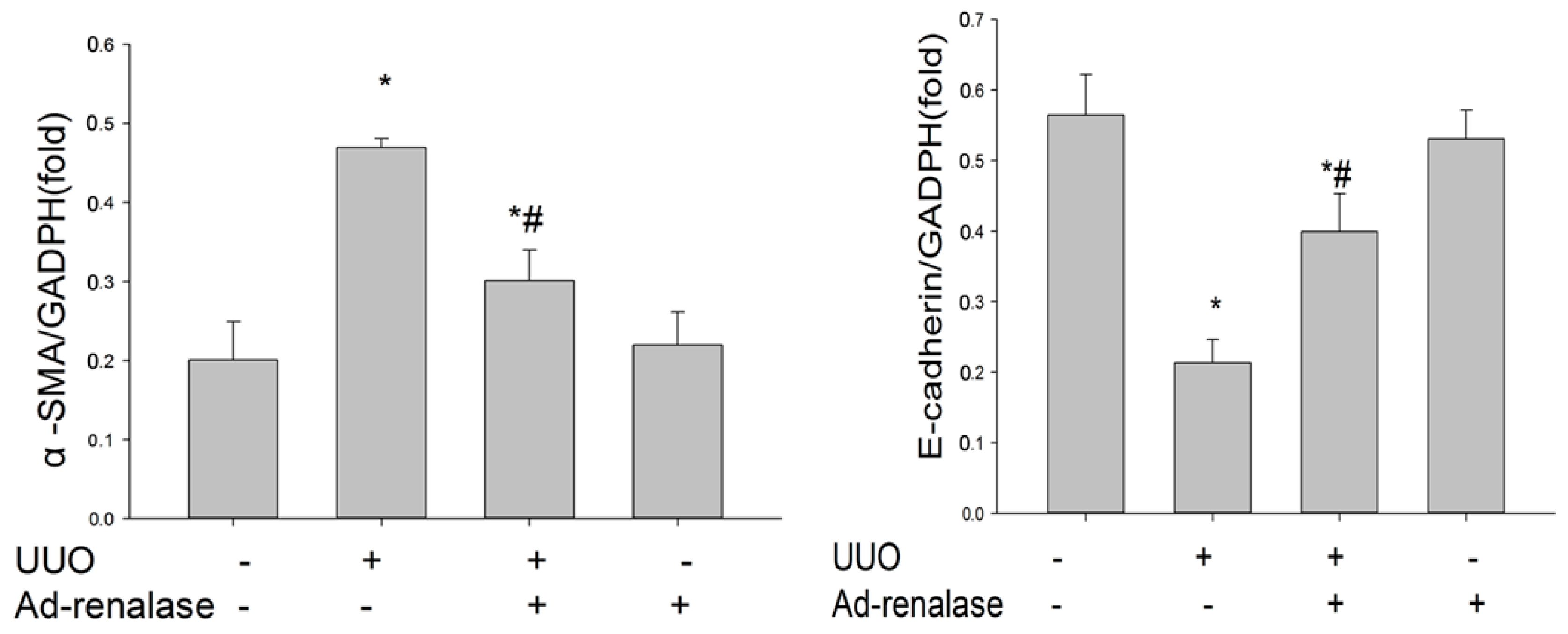
2.2. Renalase Ameliorates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis in the UUO Model
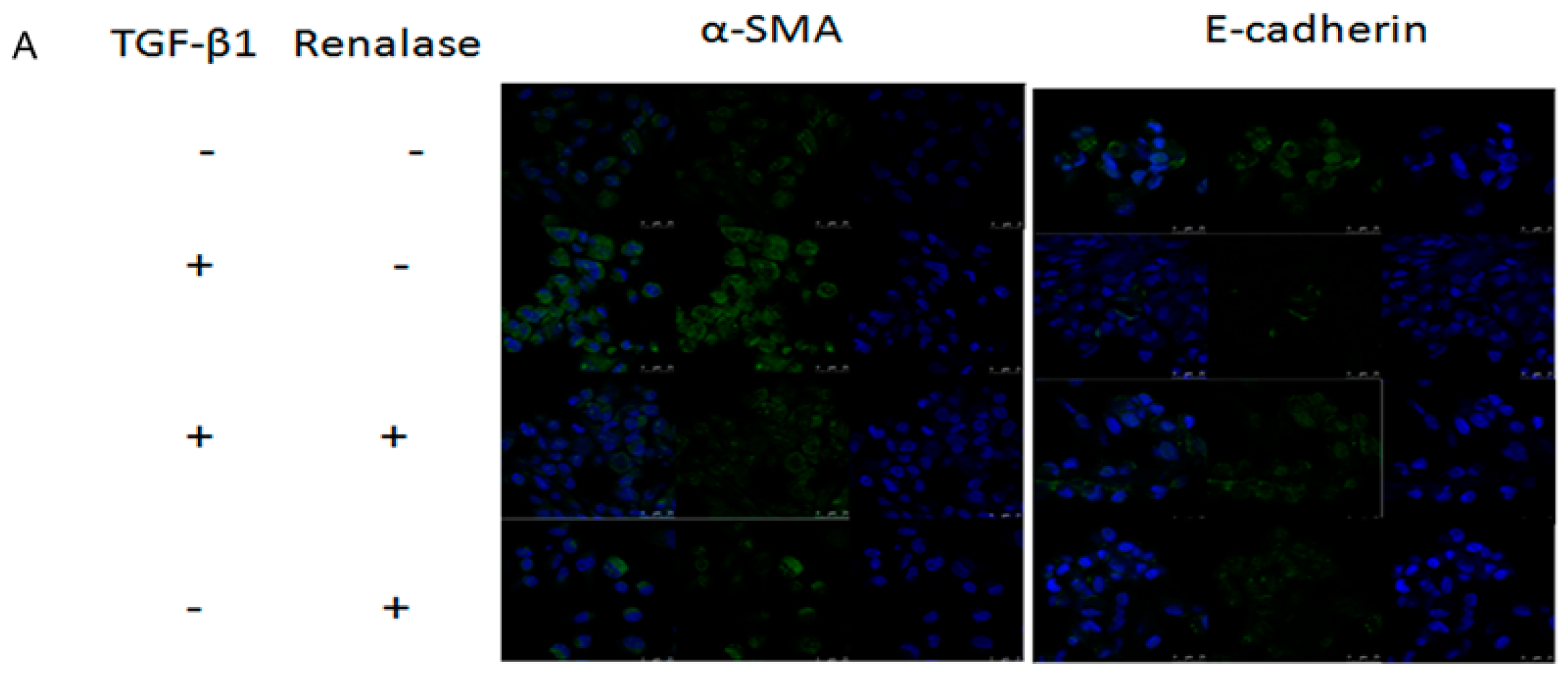
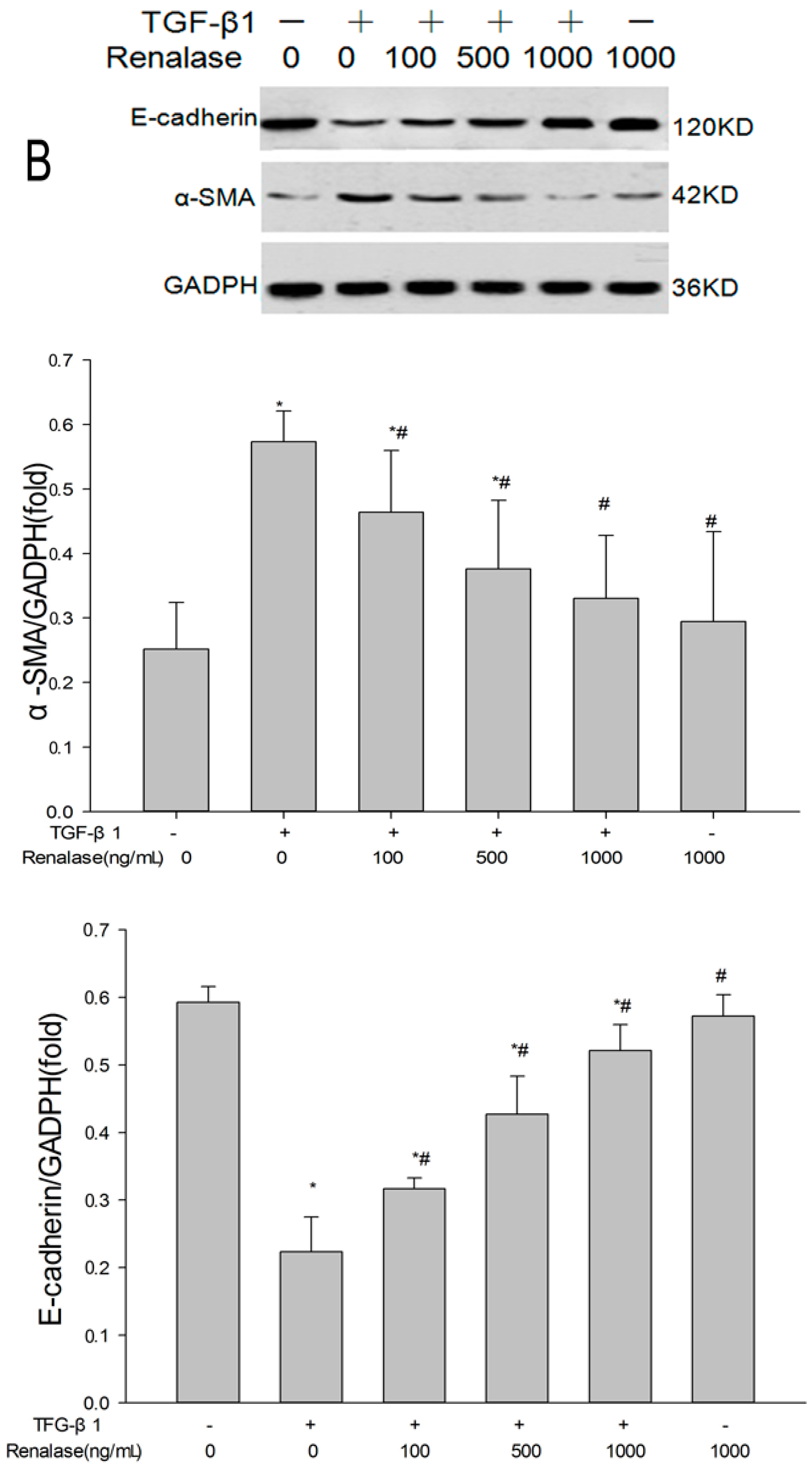
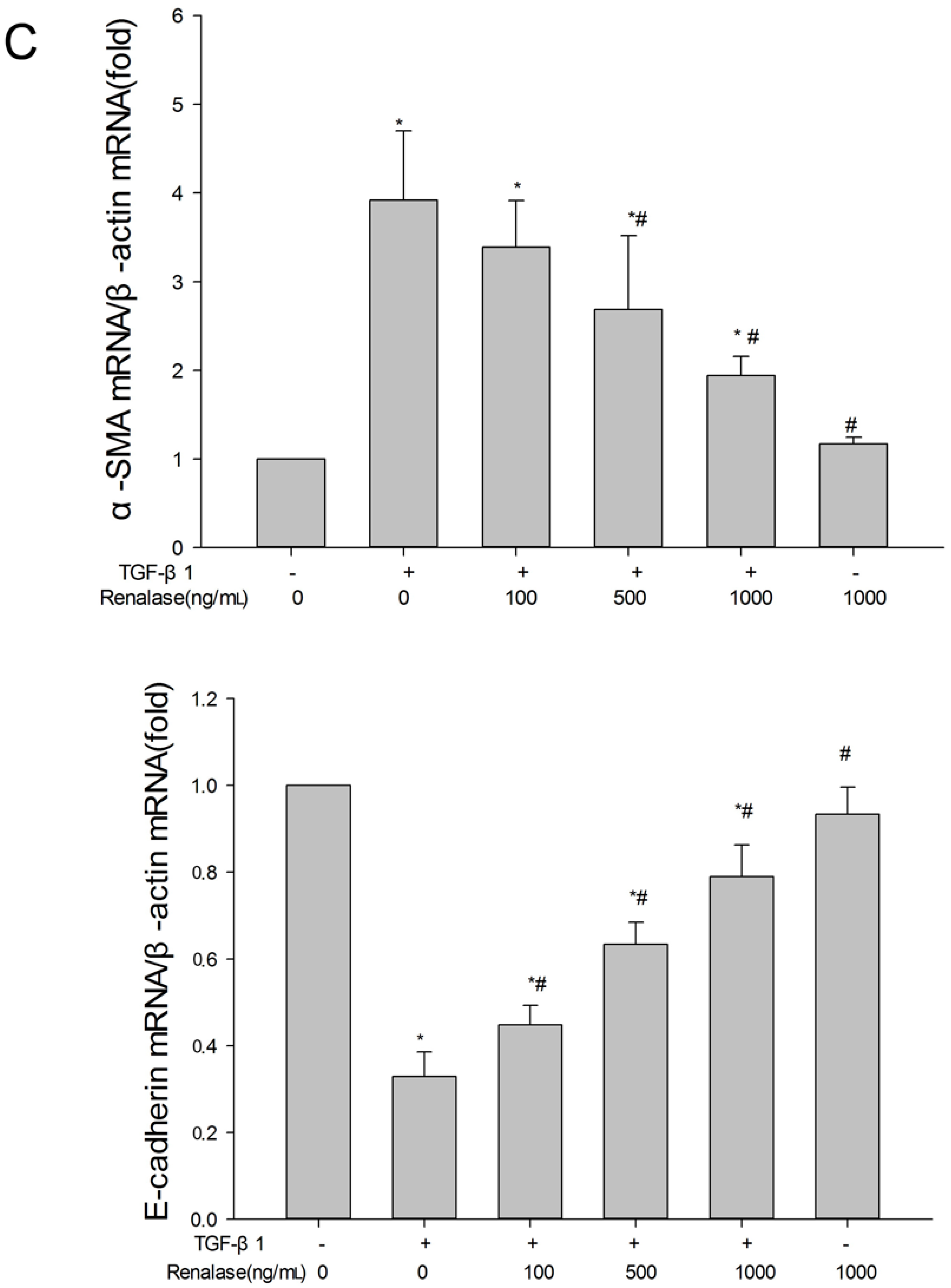
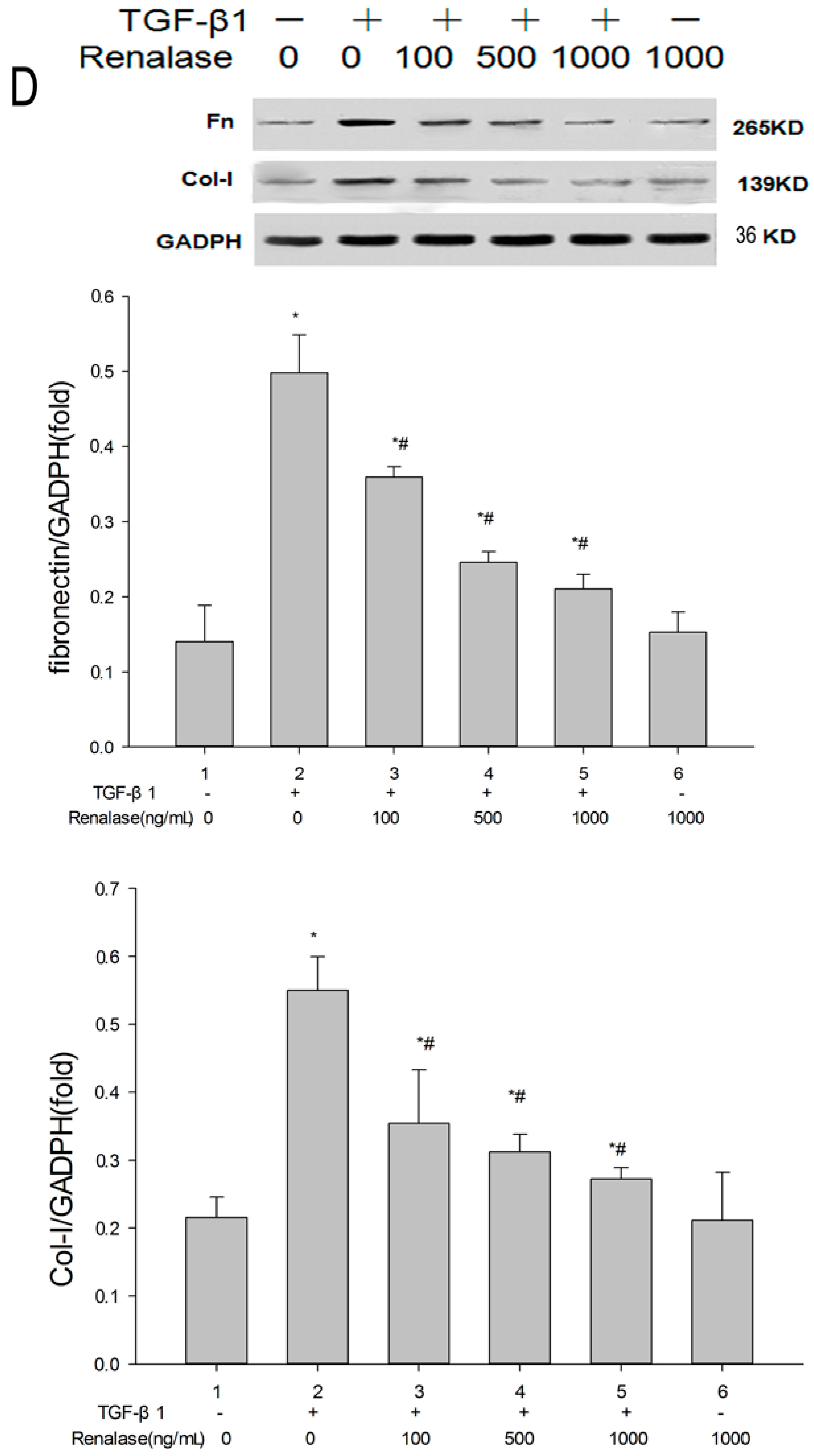
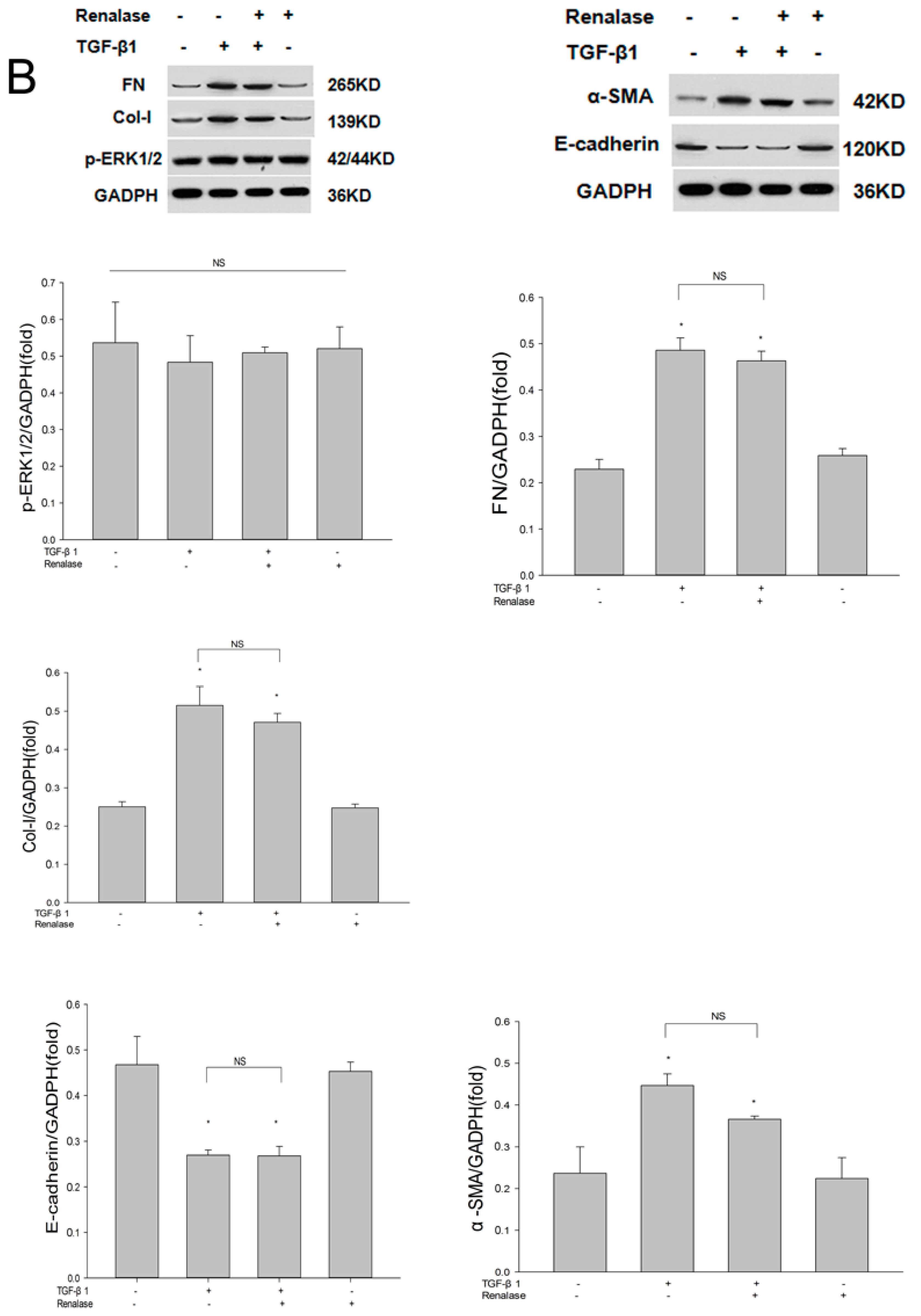
2.3. Renalase Inhibits TGF-β1-Mediated Tubular EMT and Fibrosis In Vitro
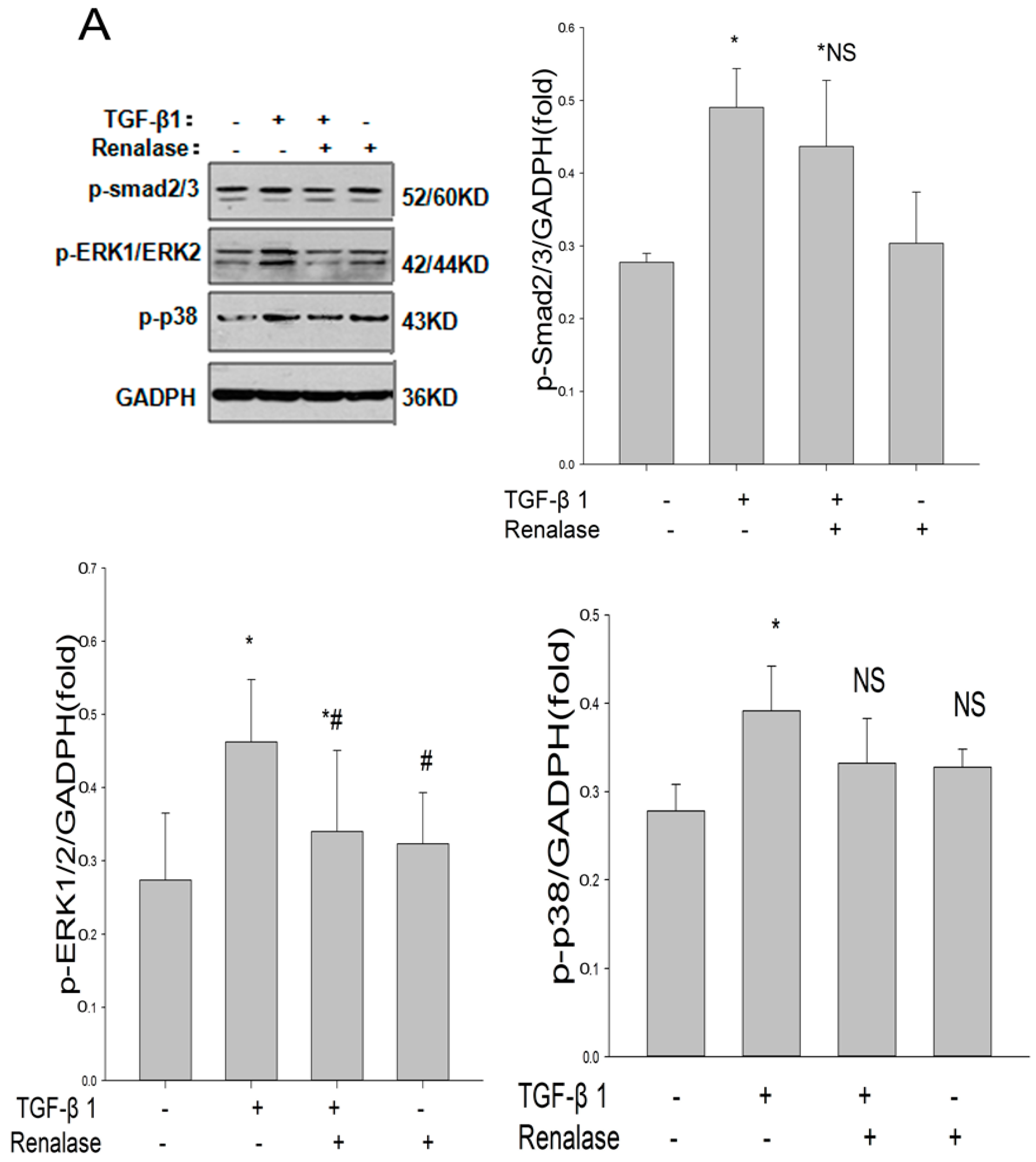
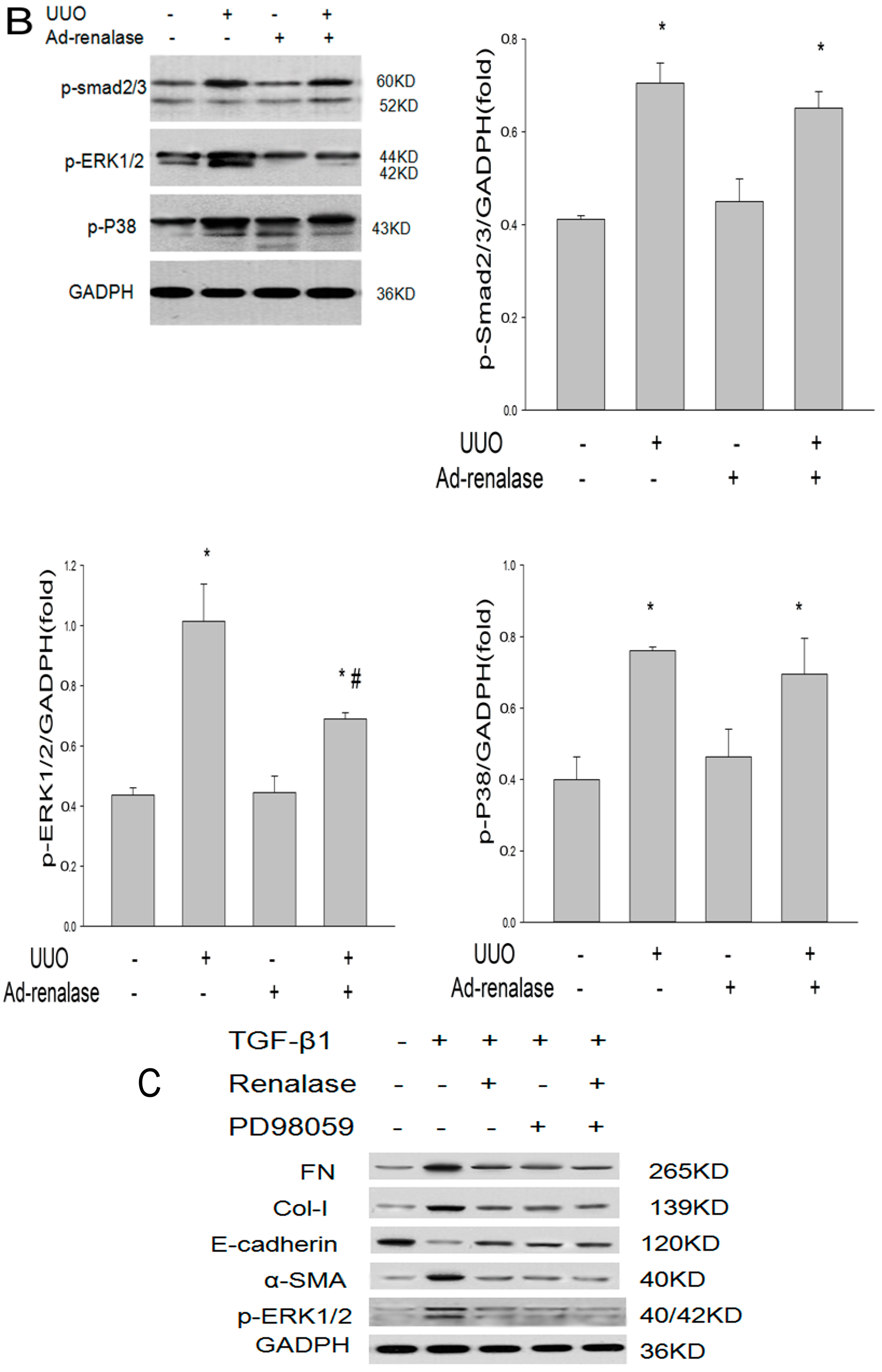
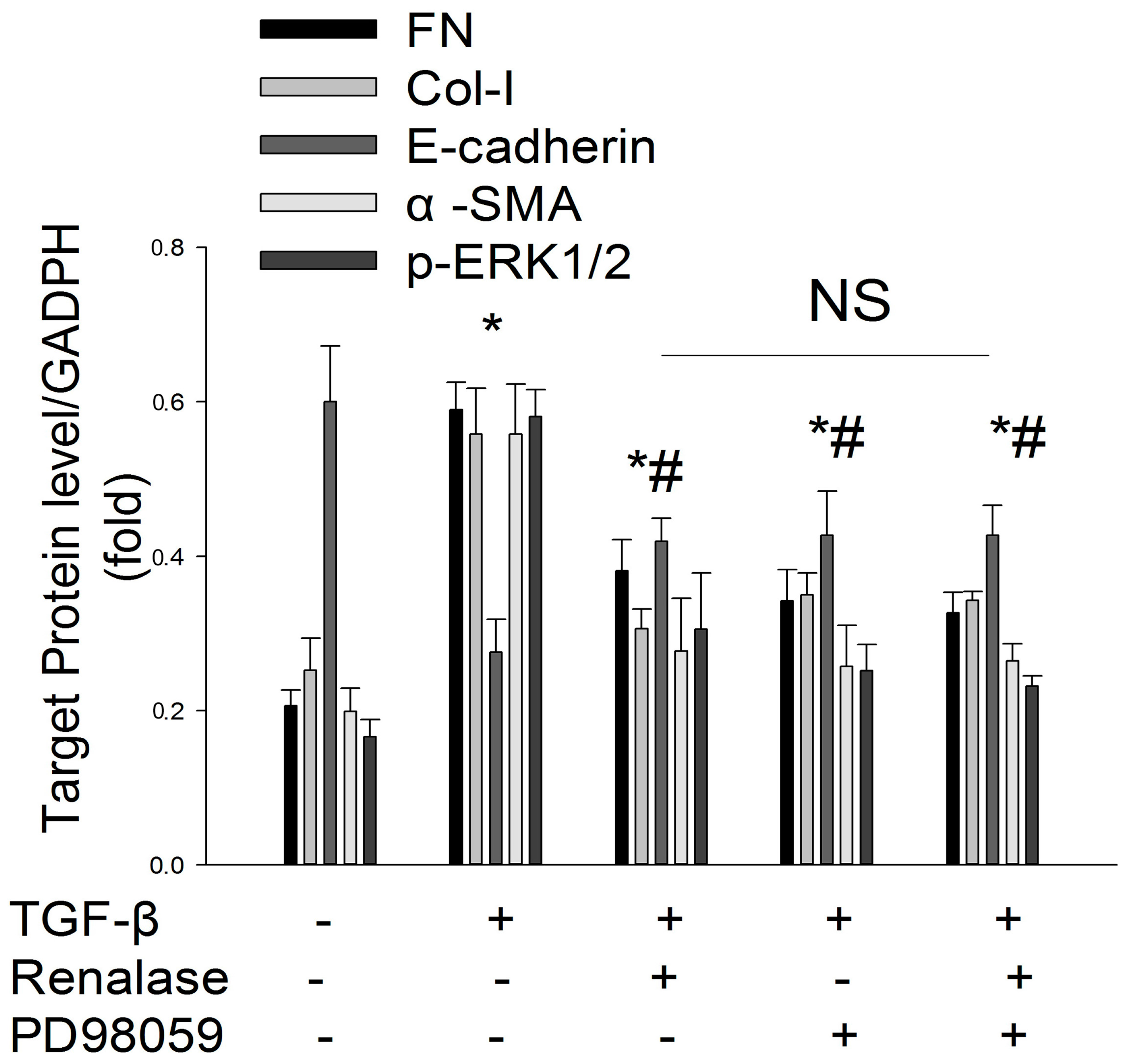
2.4. Renalase Inhibits TGF-β1 Mediated EMT by a Non-Canonical Mechanism
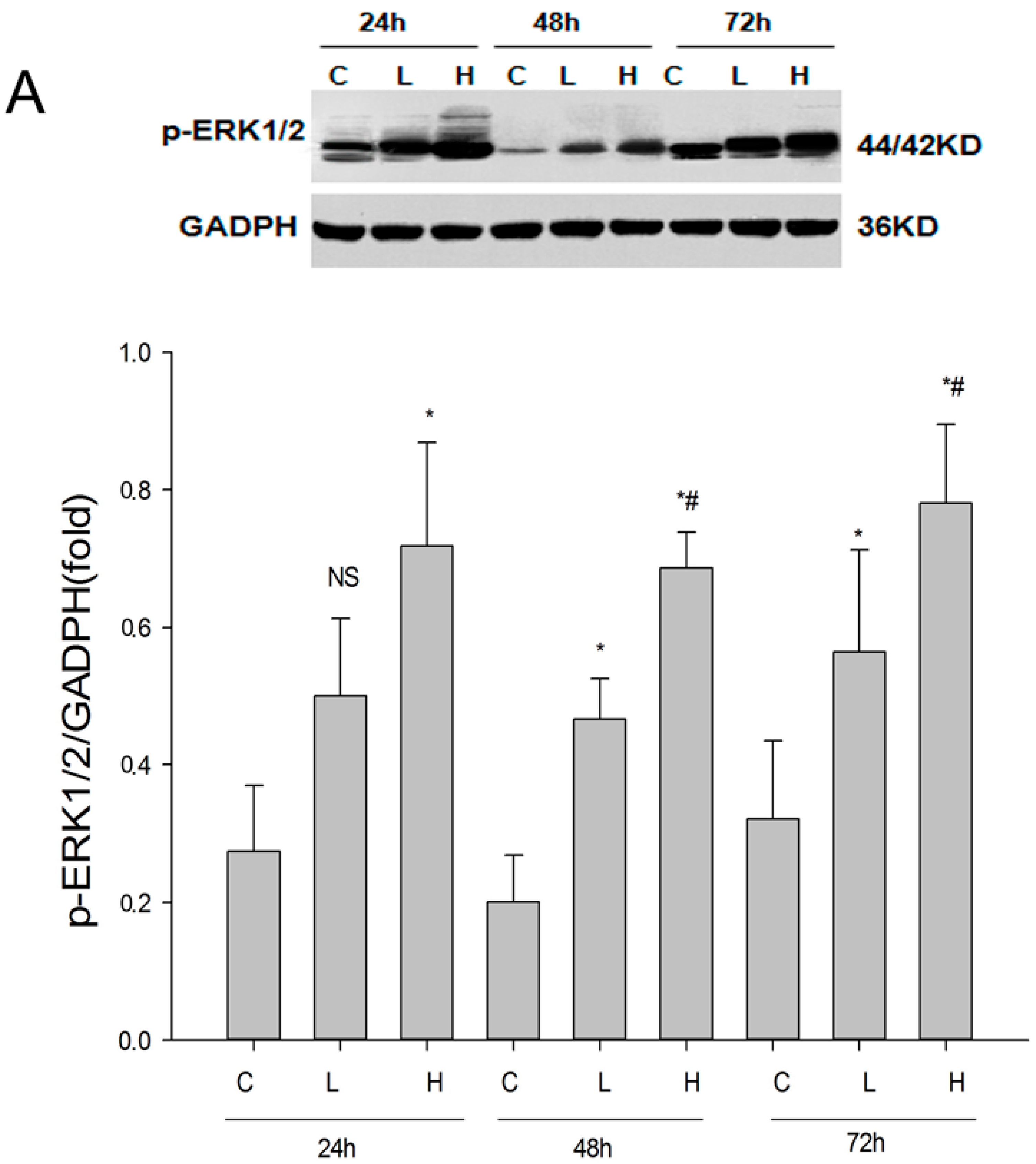
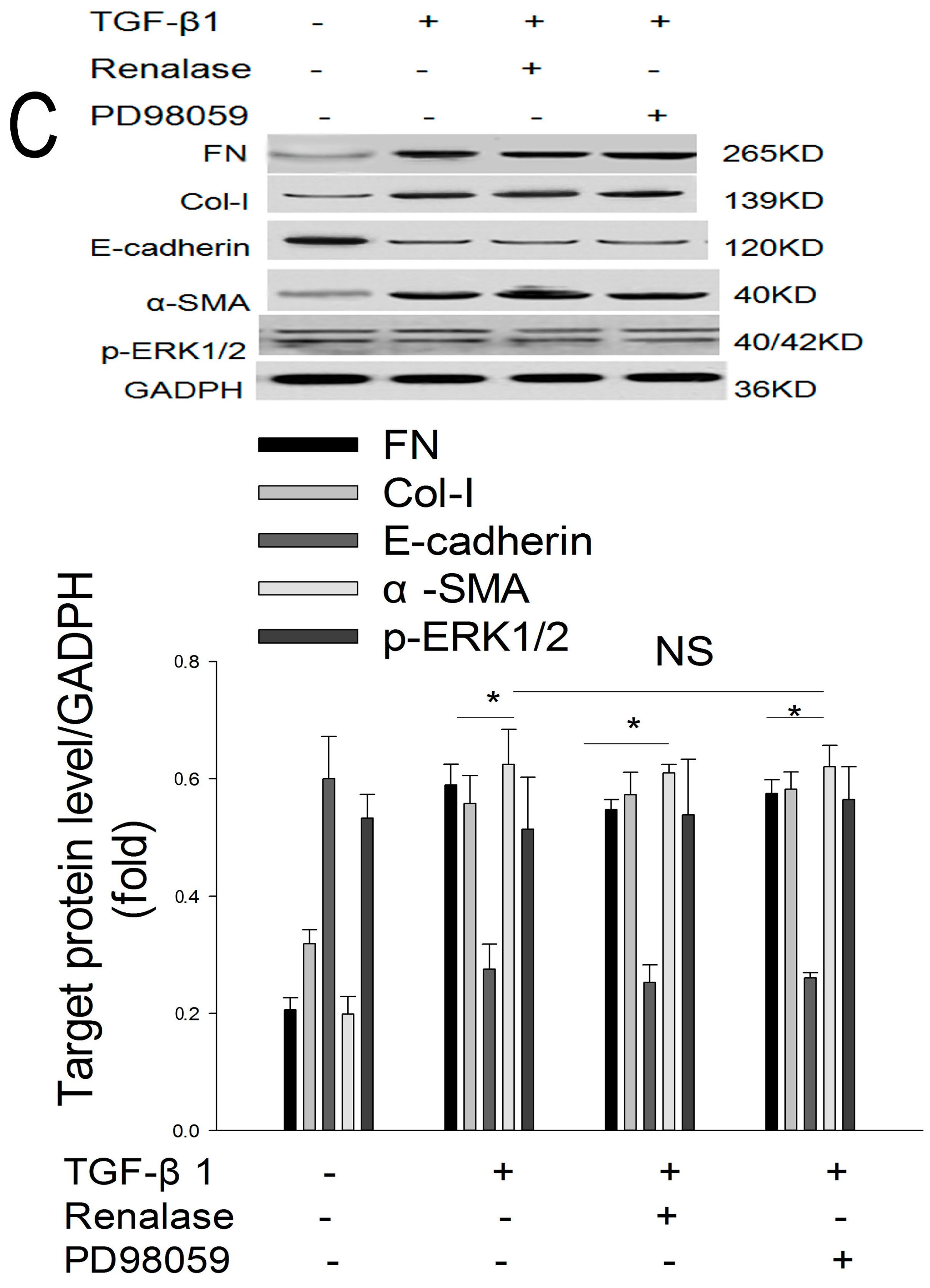
2.5. Role of ERK Signaling Pathway in the Inhibition of EMT by Renalase
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Models
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.3. Transient Transfection
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Semi-Quantitative Assessment of Renal Fibrosis
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| RIF | Renal interstitial fibrosis |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor-β1 |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| UUO | Unilateral ureteral obstruction |
| MTS | Masson’s trichrome staining |
| HK-2 | Human proximal tubule epithelial cells |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Eddy, A.A. Overview of the cellular and molecular basis of kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. Suppl. (2011) 2014, 4, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragiadaki, M.; Mason, R.M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal fibrosis—Evidence for and against. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 92, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunotto, M.; Budd, D.C.; Gabbiani, G.; Meier, M.; Formentini, I.; Hartmann, G.; Pomposiello, S.; Moll, S. Epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk alteration in kidney fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.M.; Tang, P.M.; Li, J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desir, G.V.; Wang, L.; Peixoto, A.J. Human renalase: A review of its biology, function, and implications for hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2012, 6, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennebry, S.C.; Eikelis, N.; Socratous, F.; Desir, G.; Lambert, G.; Schlaich, M. Renalase, a novel soluble FAD-dependent protein, is synthesized in the brain and peripheral nerves. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Velazquez, H.; Moeckel, G.; Chang, J.; Ham, A.; Lee, H.T.; Safirstein, R.; Desir, G.V. Renalase prevents AKI independent of amine oxidase activity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Velazquez, H.; Chang, J.; Safirstein, R.; Desir, G.V. Identification of a receptor for extracellular renalase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, P.; Velazquez, H.; Yao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Peixoto, A.; Crowley, S.; Desir, G.V. Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Velazquez, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Desir, G.V. Catecholamines regulate the activity, secretion, and synthesis of renalase. Circulation 2008, 117, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desir, G.V. Renalase deficiency in chronic kidney disease, and its contribution to hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buraczynska, M.; Zukowski, P.; Buraczynska, K.; Mozul, S.; Ksiazek, A. Renalase gene polymorphisms in patients with type 2 diabetes, hypertension and stroke. Neuromol. Med. 2011, 13, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzaneh-Far, R.; Desir, G.V.; Na, B.; Schiller, N.B.; Whooley, M.A. A functional polymorphism in renalase (Glu37Asp) is associated with cardiac hypertrophy, dysfunction, and ischemia: Data from the heart and soul study. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Xing, T.; Wang, F.; Wang, N. Renalase protects against contrast-induced nephropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Xing, T.; Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Peng, C.; Liu, G.; Wang, N. Renalase contributes to the renal protection of delayed ischaemic preconditioning via the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1β. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Velazquez, H.; Wang, P.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Sampaio-Maia, B.; Quelhas-Santos, J.; Russell, K.; Russell, R.; et al. Renalase deficiency aggravates ischemic myocardial damage. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Wang, P.; Tang, L.; Baroni, S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Desir, G.V. Renalase protects against ischemic AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strutz, F.M. EMT and proteinuria as progression factors. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, L.; Miao, N.; Wang, N. Renalase attenuates hypertension, renal injury and cardiac remodelling in rats with subtotal nephrectomy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaupre, B.A.; Hoag, M.R.; Moran, G.R. Renalase does not catalyze the oxidation of catecholamines. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 579, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, F.C. Renalase, a catecholamine-metabolizing hormone from the kidney. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennuni, S.; Rubattu, S.; Pierelli, G.; Tocci, G.; Fofi, C.; Volpe, M. Hypertension and kidneys: Unraveling complex molecular mechanisms underlying hypertensive renal damage. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2014, 28, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Beddhu, S.; Lewis, J.B.; Toto, R.D.; Cheung, A.K. Managing hypertension in patients with CKD: A marathon, not a SPRINT. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, A.B.; Colvin, R.B. Renal interstitial fibrosis: Mechanisms and evaluation. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Hou, F.F.; Nie, J. AOPPs and the progression of kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. (2011) 2014, 4, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Huang, K.; Huang, D.; Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; et al. Renalase is a novel target gene of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in protection against cardiac ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 105, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Jin, J.; Zhang, W.; Grenz, A.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Tao, L.; et al. Elevated endothelial hypoxia-inducible factor-1α contributes to glomerular injury and promotes hypertensive chronic kidney disease. Hypertension 2015, 66, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Luo, G.; Fang, Q.; Sun, Z. Stable expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Renal fibrosis: New insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Becker, B.N.; Hoffmann, F.M.; Mertz, J.E. Complete reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal transition requires inhibition of both ZEB expression and the Rho pathway. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneyama, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Aoyagi, D.; Ehara, T. Tranilast modulates fibrosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and peritubular capillary injury in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats. Pathology 2010, 42, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.Y.; Diao, Z.L.; Zhang, D.L.; Zheng, J.F.; Zhang, Q.D.; Ding, J.X.; Liu, W.H. The regulatory peptide apelin: A novel inhibitor of renal interstitial fibrosis. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Dai, C.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y. Role for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W. Renalase Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050855
Wu Y, Wang L, Deng D, Zhang Q, Liu W. Renalase Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(5):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050855
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yiru, Liyan Wang, Dai Deng, Qidong Zhang, and Wenhu Liu. 2017. "Renalase Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 5: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050855
APA StyleWu, Y., Wang, L., Deng, D., Zhang, Q., & Liu, W. (2017). Renalase Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(5), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050855




