Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
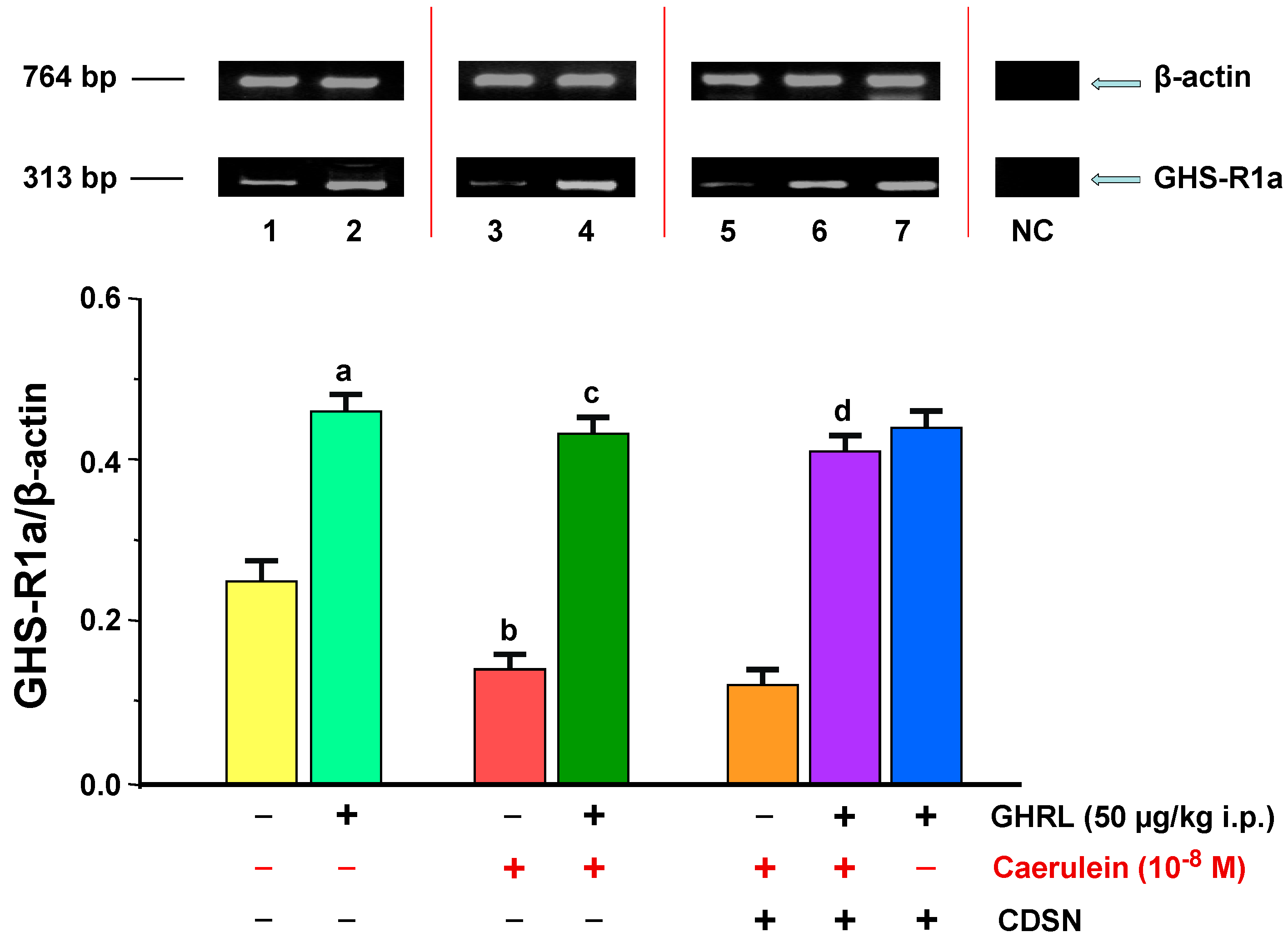
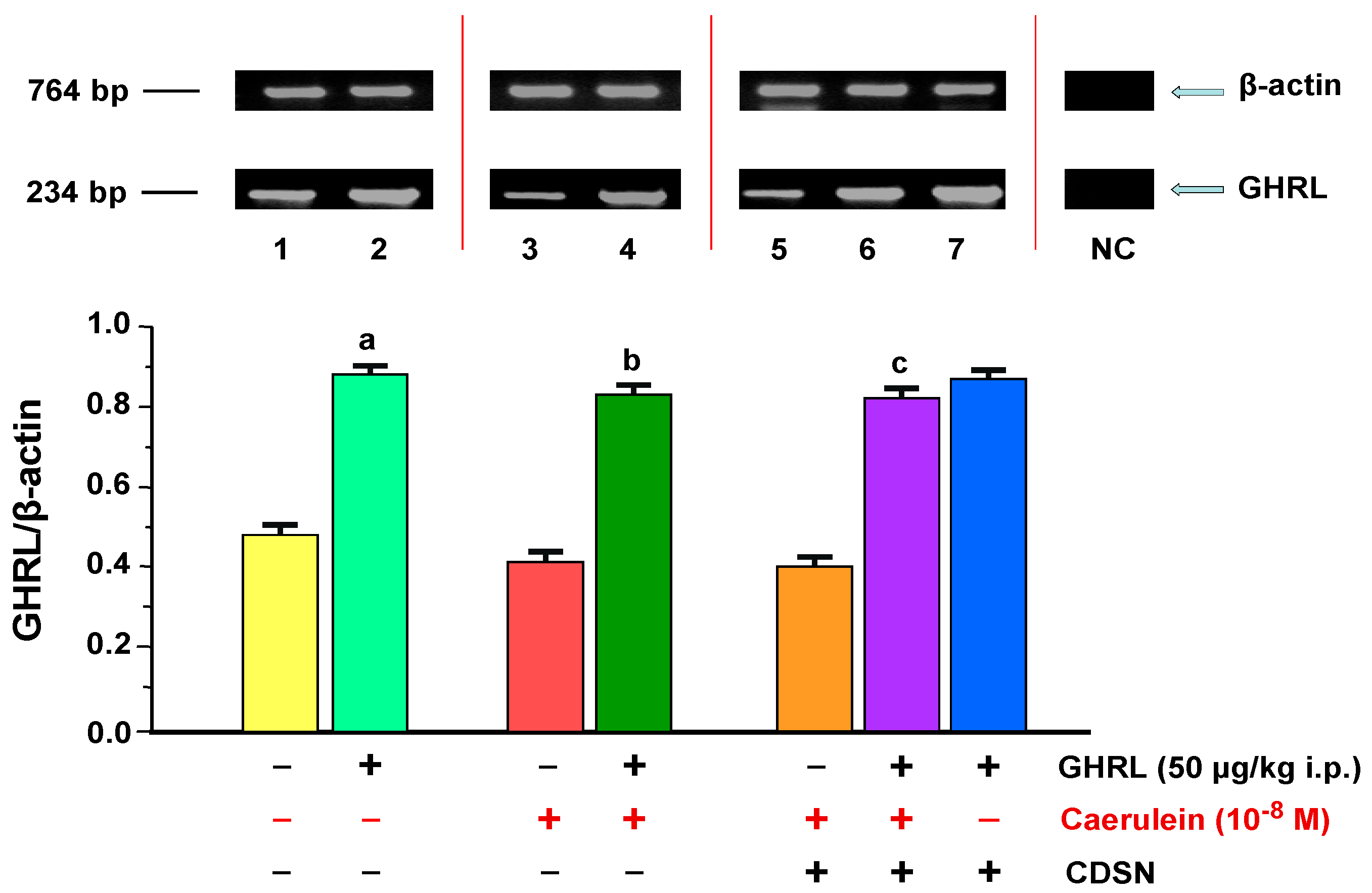
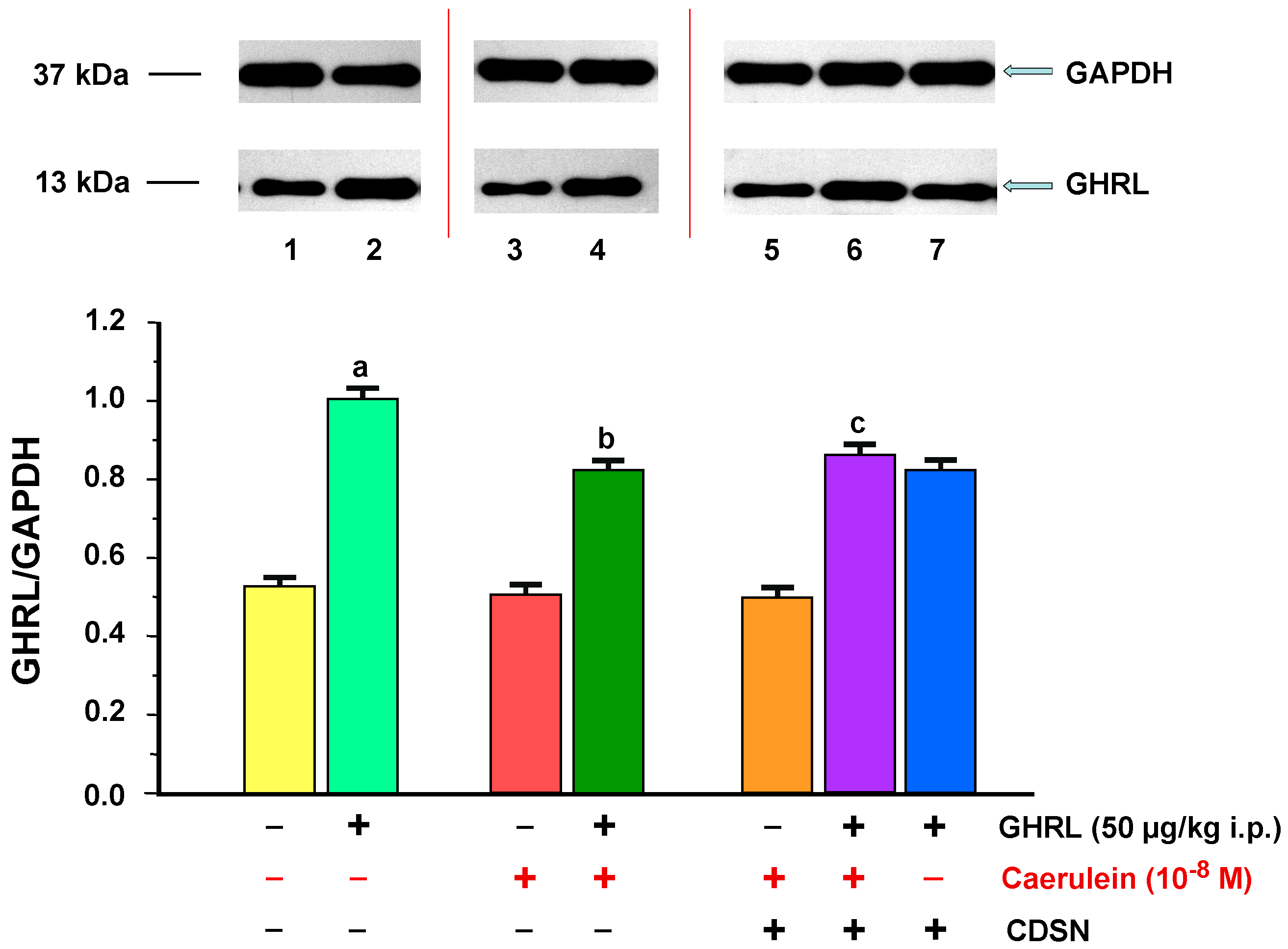
2.1. Influence of Ghrelin Administered Peripherally In Vivo on the GHS-R1a and GHRL Level of Gene Expression and Protein Production in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells with Intact and/or Deactivated Sensory Nerves in Rats in Basic Conditions and after Hyperstimulation with Caerulein in the In Vitro Model
2.1.1. Determination of GHS-R1a Gene Expression and Protein Production
2.1.2. Determination of GHRL Gene Expression and Protein Production
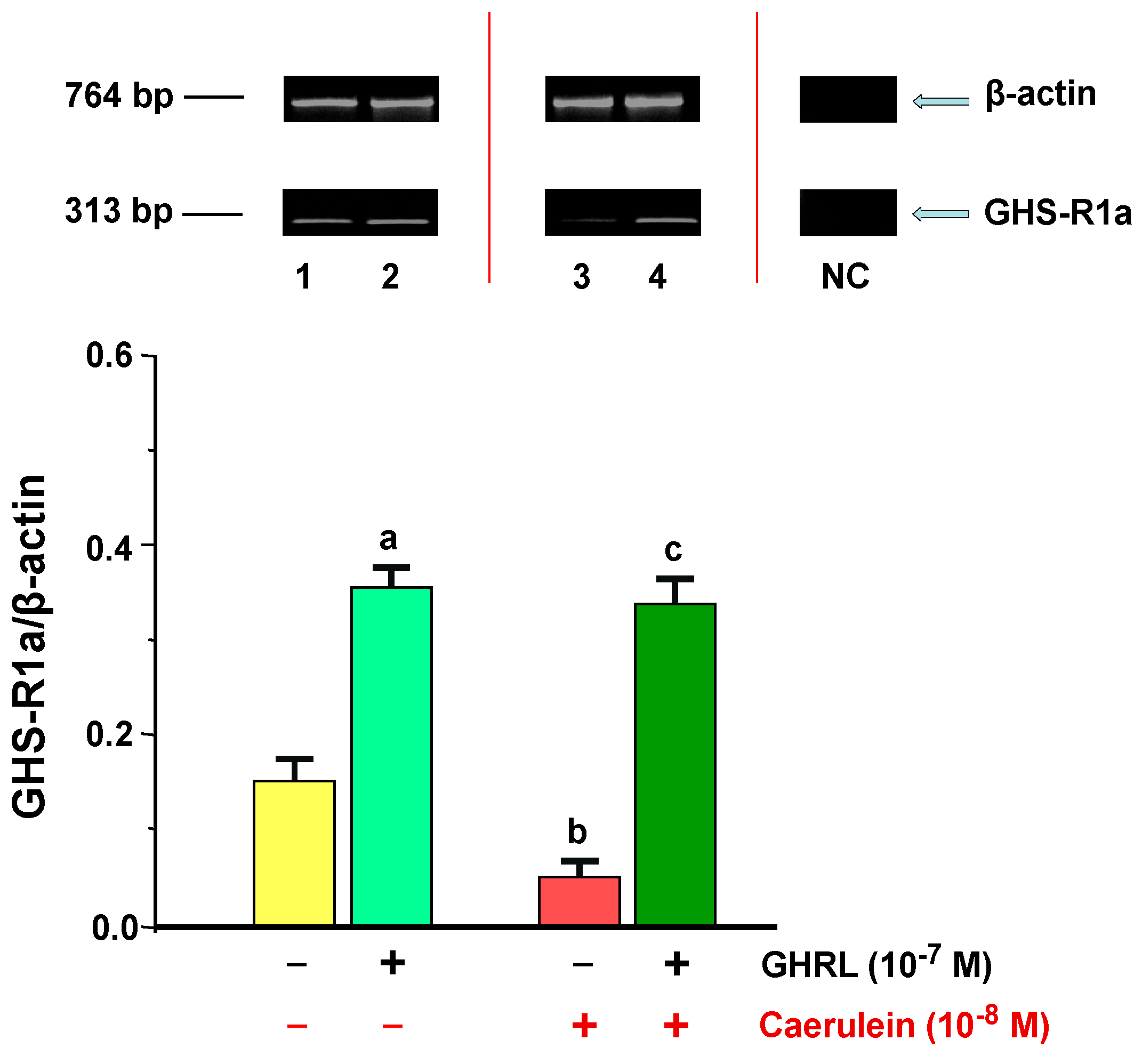
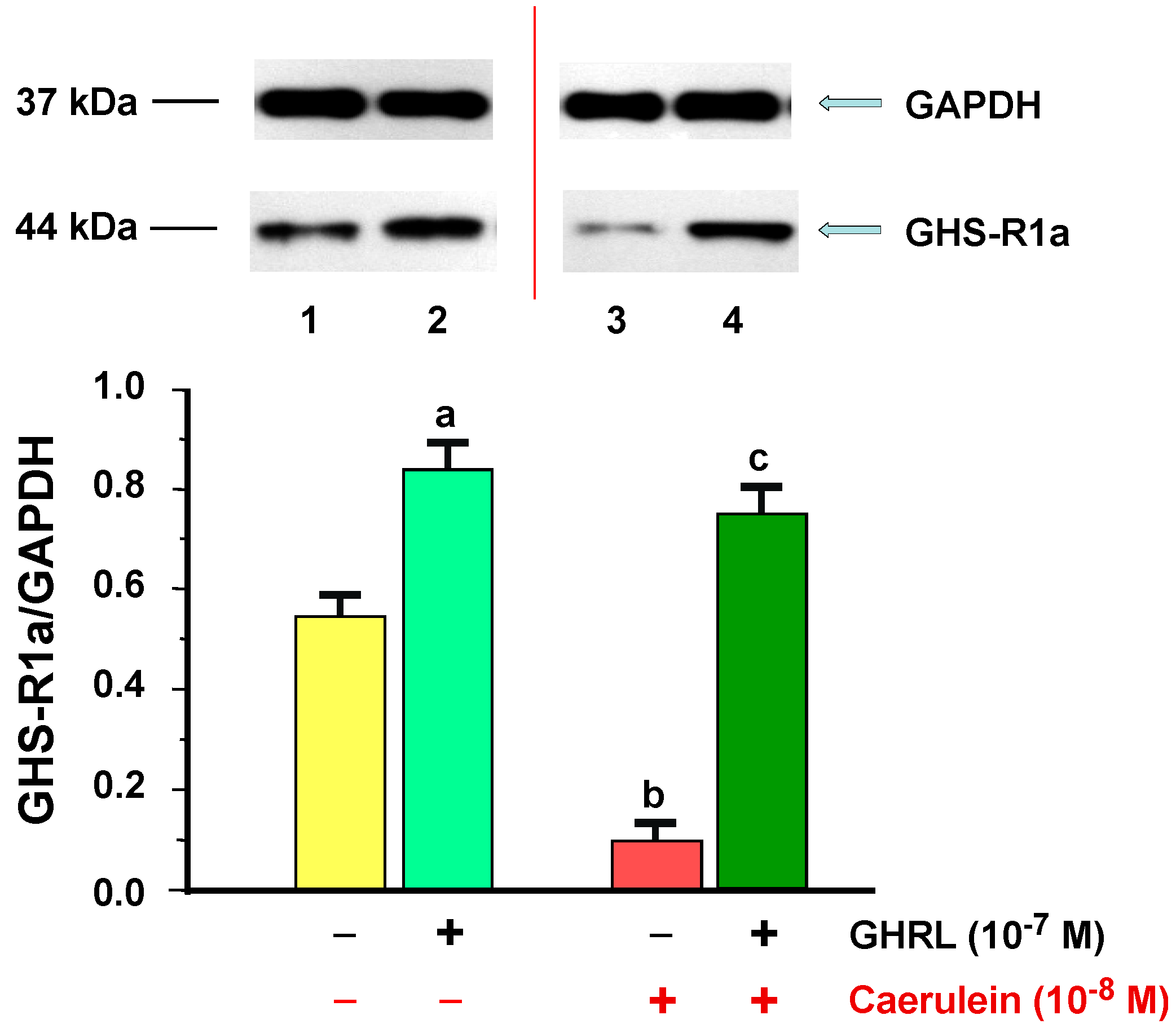
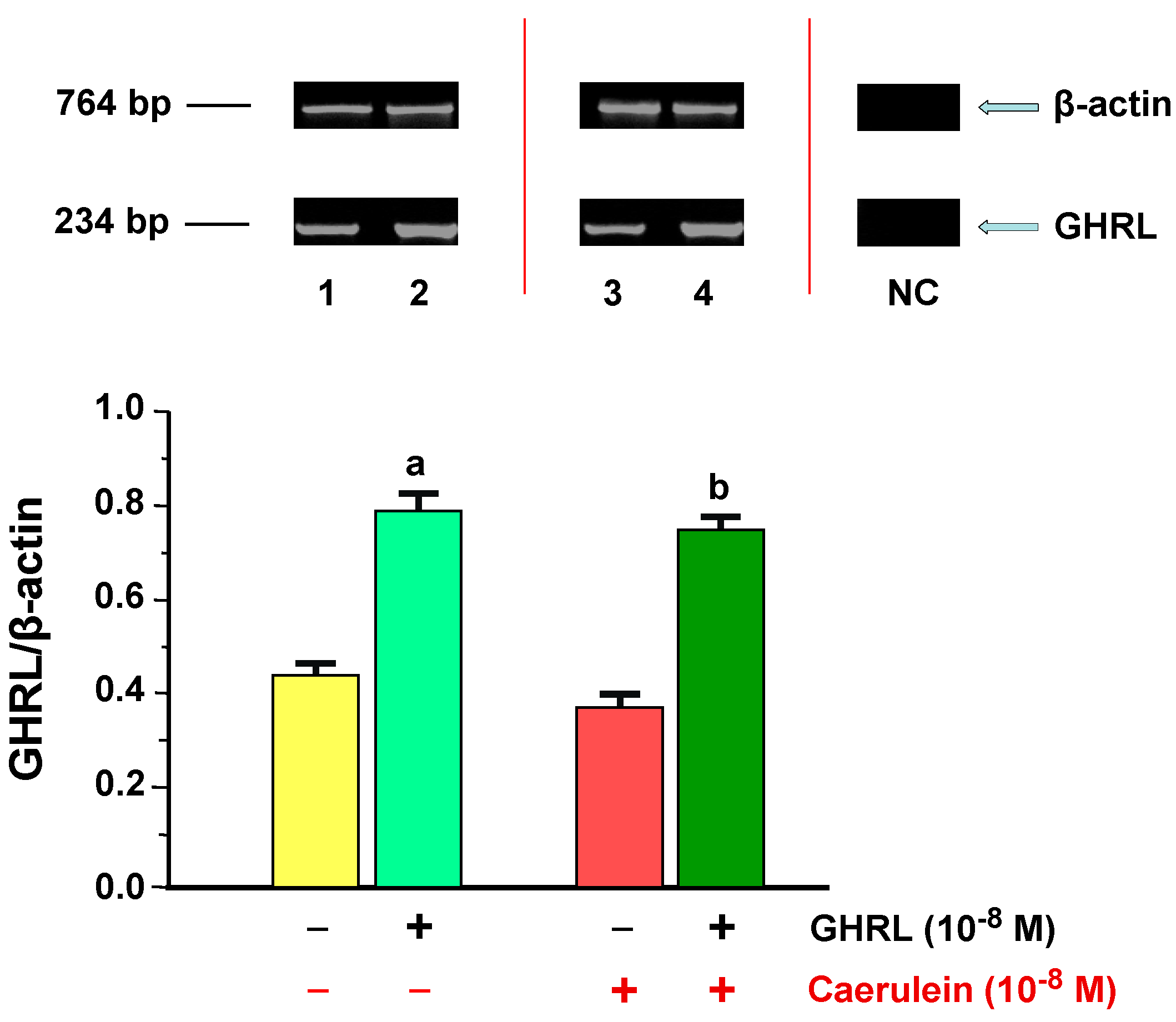
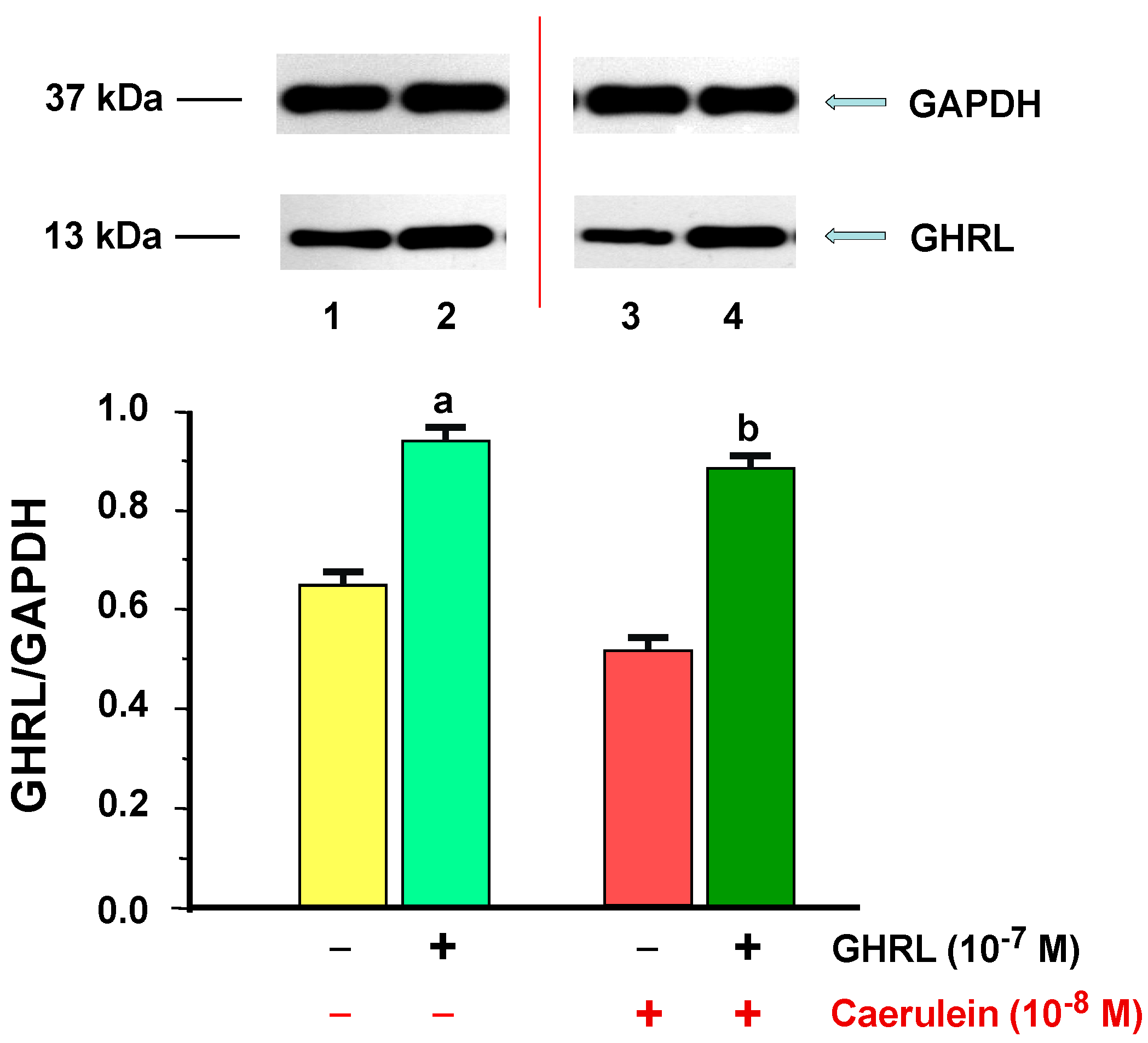
2.2. Influence of Ghrelin on the GHS-R1a and GHRL Level of Gene Expression and Protein Production in the AR42J Cells in Basic Conditions and after Hyperstimulation with Caerulein In Vitro
2.2.1. Determination of GHS-R1a Gene Expression and Protein Production
2.2.2. Determination of GHRL Gene Expression and Protein Production
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.2.1. In Vivo Experiments
Experimental Protocol and Groups
4.2.2. In Vitro Experiments
Rat Pancreatic Acinar Cells Experimental Protocol and Groups
AR42J Cells Experimental Protocol and Groups
4.3. Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation
Immunoblotting
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: Structure and function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.G.; van der Ploeg, L.H.; Howard, A.D.; Feighner, S.D.; Cheng, K.; Hickey, G.J.; Wyvratt, M.J., Jr.; Fisher, M.H.; Nargund, R.P.; Patchett, A.A. Peptidomimetic regulation of growth hormone secretion. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Hayashida, Y.; Iguchi, T.; Nakao, N.; Nakai, N.; Nakashima, K. Organization of the mouse ghrelin gene and promoter: Occurrence of a short noncoding first exon. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 3697–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamoto, N.; Akamizu, T.; Tagami, T.; Hataya, Y.; Moriyama, K.; Takaya, K.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Nakao, K. Genomic structure and characterizaiton of the 5′-flanking region of the human ghrelin gene. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4144–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbonits, M.; Goldstone, A.P.; Gueorguiev, M.; Grossman, A.B. Ghrelin–A hormone with multiple functions. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 25, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, T.R.; Tong, J.; Datta, R.; Culler, M.; Tschöp, M.H. Ghrelin in the regulation of body weight and metabolism. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 31, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: More than endogenous growth hormone secretagogue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1200, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolopoulos, D.; Theocharis, S.; Kouraklis, G. Ghrelin: A potential therapeutic target for cancer. Regul. Pept. 2010, 163, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G.; Grishin, N.V.; Goldstein, J.L. Identification of the acyltransferase that octanoylates ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone. Cell 2008, 132, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.V.; Ren, P.G.; Avsian-Kretchmer, O.; Luo, C.W.; Rauch, R.; Klein, C.; Hsueh, A.J. Obestatin, a peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene, opposes ghrelin’s effects on food intake. Science 2005, 310, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Tschöp, M.; Robinson, S.M.; Heiman, M.L. Extent and direction of ghrelin transport across the blood–brain barrier is determined by its unique primary structure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Burney, B.O.; Robinson, S.M. Effects of triglycerides, obesity, and starvation on ghrelin transport across the blood–brain barrier. Peptides 2008, 29, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Sawaguchi, A.; Mondal, M.S.; Suganuma, T.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: Two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shiimura, Y.; Ohgusu, H.; Kangawa, K.; Kojima, M. Structure, regulation and function of ghrelin. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Solenberg, P.J.; Perkins, D.R.; Willency, J.A.; Knierman, M.D.; Jin, Z.; Witcher, D.R.; Luo, S.; Onyia, J.E.; Hale, J.E. Ghrelin octanoylation mediated by an orphan lipid transferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6320–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, T.J.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Inhibition of ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) by octanoylated pentapeptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10750–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, J.B.; Leite-Moreira, A.F. Ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin: Three pieces of the same puzzle. Peptides 2008, 29, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauna, C.; Meyler, F.M.; Janssen, JA.; Delhanty, P.J.; Abribat, T.; van Koetsveld, P.; Hofland, L.J.; Broglio, F.; Ghigo, E.; van der Lely, A.J. Administration of acylated ghrelin reduces insulin sensitivity, whereas the combination of acylated plus unacylated ghrelin strongly improves insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; Nagai, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Blockade of pancreatic islet-derived ghrelin enhances insulin secretion to prevent high-fat diet-induced glucose intolerance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Biancone, L.; Trovato, L.; Nano, R.; Bertuzzi, F.; Destefanis, S.; Annunziata, M.; Martinetti, M.; Catapano, F.; et al. Acylated and unacylated ghrelin promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells and human islets: Involvement of 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, and phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase/akt signaling. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González, C.R.; Vázquez, M.J.; López, M.; Diéguez, C. Influence of chronic undernutrition and leptin on GOAT mRNA levels in rat stomach mucosa. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 41, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanapavan, S.; Kola, B.; Bustin, S.A.; Morris, D.G.; McGee, P.; Fairclough, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carpenter, R.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2988–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, I.; Nakamura, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Matsubara, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Kangawa, K.; Sakai, T. Ghrelin-producing cells exist as two types of cells, closed- and opened-type cells, in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Peptides 2002, 23, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Dezaki, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Arima, T.; Matsuo, H.; et al. Ghrelin is present in pancreatic α-cells of humans and rats and stimulates insulin secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volante, M.; Allìa, E.; Gugliotta, P.; Funaro, A.; Broglio, F.; Deghenghi, R.; Muccioli, G.; Ghigo, E.; Papotti, M. Expression of ghrelin and of the GH secretagogue receptor by pancreatic islet cells and related endocrine tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierup, N.; Svensson, H.; Mulder, H.; Sundler, F. The ghrelin cell: A novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2002, 107, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.L.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Elghazi, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B.; Sussel, L. Ghrelin cells replace insulin-producing β cells in two mouse models of pancreas development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Elghazi, L.; Parker, S.E.; Kizilocak, H.; Asano, M.; Sussel, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B. The concerted activities of Pax4 and Nkx2.2 are essential to initiate pancreatic β-cell differentiation. Dev. Biol. 2004, 266, 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, J.T.; Chao, C.S.; Anderson, K.R.; Kaufman, F.; Johnson, C.W.; Sussel, L. Nkx2.2 activates the ghrelin promoter in pancreatic islet cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.K.; Cheng, C.H.; Ko, W.H.; Leung, P.S. Ghrelin system in pancreatic AR42J cells: Its ligand stimulation evokes calcium signalling through ghrelin receptors. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Leung, P.S. The ghrelin system in acinar cells: Localization, expression, and regulation in the exocrine pancreas. Pancreas 2007, 35, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamoto, N.; Akamizu, T.; Hosoda, H.; Hataya, Y.; Ariyasu, H.; Takaya, K.; Hosoda, K.; Saijo, M.; Moriyama, K.; Shimatsu, A.; et al. Substantial production of ghrelin by a human medullary thyroid carcinoma cell line. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4984–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Yoshimoto, A.; Takaya, K.; Hosoda, K.; Ariyasu, H.; Yahata, K.; Mukoyama, M.; Sugawara, A.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; et al. Kidney produces a novel acylated peptide, ghrelin. FEBS Lett. 2000, 486, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuki, A.; Taharaguchi, S.; Ichii, O.; Kojima, M.; Nishi, Y.; Mifune, H.; Kamimura, R.; Matsumoto, M.; Suzuki, S. Immunohistochemical localization of ghrelin in rodent kidneys. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, M.J.; Piñeiro, R.; Blanco, M.; Gallego, R.; Diéguez, C.; Gualillo, O.; Gonzále-Juanatey, J.R.; Lago, F. Growth hormone releasing peptide (ghrelin) is synthesized and secreted by cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, M.; Okimura, Y.; Nakata, H.; Kudo, T.; Iguchi, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Kaji, H.; Chihara, K. Cloning and characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the human ghrelin gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, H.; Li, Y.; Ariyasu, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kanamoto, N.; Bando, M.; Yamada, G.; Hosoda, K.; Nakao, K.; Kangawa, K.; et al. Establishment of a novel ghrelin–producing cell line. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 940–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A. Experimental models of acute pancreatitis. Postepy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2015, 69, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, M.L. Search for the trigger mechanism of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steer, M.L.; Meldolesi, J.; Figarella, C. Pancreatitis. The role of lysosomes. Dig. Dis Sci. 1984, 29, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, M.L. Workshop on experimental pancreatitis. Dig. Dis Sci. 1985, 30, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Dembiński, A. The beginnings of pancreatology as a field of experimental and clinical medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 128095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, S.J. Physiology of pancreatic secretion. J. Physiol. Pharm. 1998, 49, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.; Klar, E. Etiology and pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Ther. Umsch. 1996, 53, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.; Garcia, R.; Solomon, T.E. A simple model for acute pancteatitis: High dose caerulein injection in rat. Gastroenterology 1982, 82, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, G.; Rohr, G.; Kern, H.F. Alternation of membrane fusion as a cause of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1982, 27, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulis, A.K.; Murray, W.R.; Galloway, D.; McCartney, A.C.; Lang, E.; Veitch, J.; Whaley, K. Endotoxaemia and complement activation in acute pancreatitis in man. Gut 1982, 23, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, N.; Pitchumoni, C.S. Acute pancreatitis: A multisystem disease. Gastroenterologist 1993, 1, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Closa, D.; Hotter, G.; Prats, N.; Gelpi, E.; Rosello-Catafau, J. A bradykinin antagonist inhibited nitric oxide generation and thromboxane biosynthesis in acute pancreatitis. Prostaglandins 1995, 49, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumnicka, P.; Maduzia, D.; Ceranowicz, P.; Olszanecki, R.; Drożdż, R.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B. The interplay between inflammation, coagulation and endothelial injury in the early phase of acute pancreatitis: Clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, M.; Cieszkowski, J.; Rembisz, K.; Konturek, S.J.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Pawlik, W.W. Protective and therapeutic effect of heparin in acute pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 59, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Sendur, P.; Ceranowicz, P.; Dembiński, M.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Olszanecki, R.; Tomaszewska, R.; Ambroży, T.; Dembiński, A. Protective effect of pretreatment with acenocoumarol in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumnicka, P.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Sporek, M.; Mazur-Laskowska, M.; Gil, K.; Kuźniewski, M.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A.; Bonior, J.; et al. Serum concentrations of angiopoietin-2 and soluble FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) are associated with coagulopathy among patients with acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, H.; Tai, S.; Okimura, Y.; Iguchi, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Abe, H.; Chihara, K. Cloning and characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the human growth hormone secretagogue receptor gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33885–33888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.D.; Feighner, S.D.; Cully, D.F.; Arena, J.P.; Liberator, P.A.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Hamelin, M.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Palyha, O.C.; Anderson, J.; et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 1996, 273, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Lely, A.J.; Tschöp, M.; Heiman, M.L.; Ghigo, E. Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 426–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A. Peptidyl hormones of endocrine cells origin in the gut—Their discovery and physiological relevance. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujii, R.; Hosoya, M.; Fukusumi, S.; Kawamata, Y.; Habata, Y.; Hinuma, S.; Onda, H.; Nishimura, O.; Fujino, M. Identification of neuromedin U as the cognate ligand of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor FM-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21068–21074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.P.; Mazella, J.; Kitabgi, P. Neurotensin and neurotensin receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feighner, S.D.; Tan, C.P.; McKee, K.K.; Palyha, O.C.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Pong, S.S.; Austin, C.P.; Figueroa, D.; MacNeil, D.; Cascieri, M.A.; et al. Receptor for motilin identified in the human gastrointestinal system. Science 1999, 284, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dass, N.B.; Hill, J.; Muir, A.; Testa, T.; Wise, A.; Sanger, G.J. The rabbit motilin receptor: Molecular characterisation and pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 140, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palyha, O.C.; Feighner, S.D.; Tan, C.P.; McKee, K.K.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Gao, Y.D.; Schleim, K.D.; Yang, L.; Morriello, G.J.; Nargund, R.; et al. Ligand activation domain of human orphan growth hormone (GH) secretagogue receptor (GHS-R) conserved from Pufferfish to humans. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.G.; Leonard, R.; Bailey, A.R.; Palyha, O.; Feighner, S.; Tan, C.; McKee, K.K.; Pong, S.S.; Griffin, P.; Howard, A. Growth hormone secretagogue receptor family members and ligands. Endocrine 2001, 14, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Lin, T.R.; Chai, B.; Fan, Y.; Gantz, I.; Mulholland, M.W. Inhibition of adipogenesis by ghrelin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 2484–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldanzi, G.; Filigheddu, N.; Cutrupi, S.; Catapano, F.; Bonissoni, S.; Fubini, A.; Malan, D.; Baj, G.; Granata, R.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lear, P.V.; Iglesias, M.J.; Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Rodríguez-Penas, D.; Mosquera-Leal, A.; García-Rúa, V.; Gualillo, O.; Ghè, C.; Arnoletti, E.; Muccioli, G.; et al. Des-acyl ghrelin has specific binding sites and different metabolic effects from ghrelin in cardiomyocytes. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3286–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.M.; Yu, H.; Palyha, O.C.; McKee, K.K.; Feighner, S.D.; Sirinathsinghji, D.J.; Smith, R.G.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.; Howard, A.D. Distribution of mRNA encoding the growth hormone secretagogue receptor in brain and peripheral tissues. Brain Res. 1997, 48, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazato, M.; Murakami, N.; Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 2001, 409, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, N.; Saito, T.; Yagyu, T.; Jiang, B.H.; Kitagawa, K.; Inagaki, C. GH, GH receptor, GH secretagogue receptor, and ghrelin expression in human T cells, B cells, and neutrophils. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K. Purification and distribution of ghrelin: The natural endogenous ligand for the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Horm. Res. 2001, 56, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueberberg, B.; Unger, N.; Saeger, W.; Mann, K.; Petersenn, S. Expression of ghrelin and its receptor in human tissues. Horm. Metab. Res. 2009, 41, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, H.; Funahashi, H.; Hirayama, M.; Takenoya, F.; Kita, T.; Kato, S.; Sakurai, J.; Lee, E.Y.; Inoue, S.; Date, Y.; et al. Morphological analysis of ghrelin and its receptor distribution in the rat pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2005, 126, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, F.; Gottero, C.; Arvat, E.; Ghigo, E. Endocrine and non-endocrine actions of ghrelin. Horm. Res. 2003, 59, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Kot, M.; Macko, M.; Tomaszewska, R.; Stachura, J.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W. Protective effect of ghrelin in experimental acute pancreatitis. Clin. Exp. Med. Lett. 2005, 46, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Kong, Y.H.; Han, K.H.; Jeong, W.J.; Lee, S.J.; Cheon, G.J. The relevance of serum ghrelin concentration to severity of acute pancreatitis. Gut Liver 2010, 4, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Tang, C. Change of plasma ghrelin level in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, P.; Leśniowski, B.; Jasińska, A.; Pietruczuk, M.; Małecka-Panas, E. Usefulness of assessing circulating levels of resistin, ghrelin, and IL-18 in alcoholic acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis Sci. 2010, 55, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panek, J.; Bonior, J.; Pieton, J.; Jaworek, J. Serum leptin and ghrelin levels in patients in the early stages of acute biliary pancreatitis and different degrees of severity. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 2014, 86, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerem, M.; Bedirli, A.; Pasaoglu, H.; Unsal, C.; Yilmaz, T.U.; Ofluoglu, E.; Sahin, T.T. Role of ghrelin and leptin in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J. Ghrelin and melatonin in the regulation of pancreatic exocrine secretion and maintaining of integrity. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Tomaszewska, R.; Stachura, J.; Konturek, S.J.; Konturek, P.C. Ghrelin attenuates the development of acute pancreatitis in rat. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Pawlik, W.W.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Naskalski, J.W.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Role of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in the protective effect of ghrelin in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute pancreatitis. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2006, 16, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, D.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Role of hormonal axis, growth hormone—IGF-1, in the therapeutic effect of ghrelin in the course of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Dembinski, A.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Therapeutic effect of ghrelin in the course of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bukowczan, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Dembinski, A. Therapeutic effect of ghrelin in the course of ischemia/reperfusion induced acute pancreatitis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xue, C. Ghrelin inhibits the development of acute pancreatitis and nuclear factor kappaB activation in pancreas and liver. Pancreas 2009, 38, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xue, C. Ghrelin attenuates acute pancreatitis-induced lung injury and inhibits substance P expression. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 339, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Bonior, J.; Nawrot, K.; Leja, A.; Sendur, R.; Stachura, J.; Pawlik, W.; Konturek, S.J. Intracerebroventricular administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide prevents the development of acute experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Med. Sci. Monit. 2002, 8, BR136–BR143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Bonior, J.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Nawrot, K.; Tomaszewska, M.R.; Stachura, J.; Pawlik, W.W.; Konturek, S.J. Sensory nerves in central and peripheral control of pancreatic integrity by leptin and melatonin. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Konturek, P.J.; Ceranowicz, P.; Konturek, S.J. Influence of capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons and nitric oxide (NO) on caerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. Int. J. Pancreatol. 1996, 19, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Jaworek, J.; Ceranowicz, P.; Szlachcic, A.; Walocha, J.; Konturek, S.J. Role of sensory nerves in pancreatic secretion and caerulein-induced pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 48, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Stachura, J.; Tomaszewska, R.; Konturek, S.J. Effect of sensory nerves and CGRP on the development of caerulein-induced pancreatitis and pancreatic recovery. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 52, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Dembinski, A.; Tomaszewska, R.; Szklarczyk, J.; Kot, M.; Nawrot-Porabka, K.; Bonior, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Pawlik, W.W. Involvement of sensory nerves in the protective effect of growth hormone on acute pancreatitis. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2009, 19, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P. Capsaicin as a tool for studying neuron functions. In Sensory Nerves and Neuropeptides in Gastroenterology: From Basis Science to Clinical Perspectives; Costa, M., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ligh, A.R. The initial processing of pain and its descending control: Spinal and trigeminal system. In Pain and Headache; Gildenberg, P.L., Ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland; New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 12, pp. 51–74. [Google Scholar]
- Holzer, P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: Involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience 1988, 24, 739–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raybould, H.E.; Li, D.S.; Guth, P.H. Calcitonin gene-related peptide mediates the gastric hyperemic response to acid back-diffusion. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 657, 536–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyorfi, A.; Fazekas, A.; Rosivall, L. Neurogenic inflammation and the oral mucosa. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1992, 19, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokfelt, T.; Pernow, B.; Wahren, J. Substance P: A pioneer amongst neuropeptides. J. Intern. Med. 2001, 249, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Senba, E.; Ueda, Y.; Tohyama, M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide containing sensory neurons innervating tooth pulp and buccal mucosa of the rat: An immunohistochemical analysis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1990, 3, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caterina, M.J.; Schumacher, M.A.; Tominaga, M.; Rosen, T.A.; Levine, J.D.; Julius, D. The capsaicin receptor: A heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 1997, 389, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cromer, B.A.; McIntyre, P. Painful toxins acting at TRPV1. Toxicon 2008, 51, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Uddman, R.; Tajti, J.; Kanje, M.; Edvinsson, L. Capsaicin receptor immunoreactivity in the human trigeminal ganglion. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 330, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, P. Capsaicin: Cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity from sensory neurons. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 143–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Jaworek, J.; Sendur, R.; Knafel, A.; Dembinski, M.; Bilski, J.; Pawlik, W.W.; Tomaszewska, R.; et al. Stimulation of sensory nerves and CGRP attenuate pancreatic damage in ischemia/reperfusion induced pancreatitis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2003, 9, BR418–BR425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Konturek, P.C.; Stachura, J.; Konturek, S.J.; Niemiec, J. Protective effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide against caerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 48, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, A.M.; Pawlik, W.W.; Dembinski, M.; Rembiasz, K.; Sendur, P.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; et al. Dual, time-dependent deleterious and protective effect of anandamide on the course of cerulean-induced acute pancreatitis. Role of sensory nerves. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Konturek, P.C.; Stachura, J.; Tomaszewska, R.; Konturek, S.J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide can attenuate or augment pancreatic damage in caerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 50, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Konturek, PC.; Niemiec, J.; Stachura, J.; Tomaszewska, R.; Konturek, S.J. The influence of sensory nerves and CGRP on the pancreatic regeneration after repeated episodes of acute pancreatitis in rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2000, 51, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.Y.; Winston, J.H.; Shenoy, M.; Yin, H.; Pendyala, S.; Pasricha, P.J. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 mediates hyperalgesia and is up-regulated in rats with chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Bonior, J.; Pierzchalski, P.; Tomaszewska, R.; Stachura, J.; Sendur, R.; Leja, A.; Jachimczak, B.; Konturek, P.C.; Bielański, W.; et al. Leptin protects the pancreas from damage induced by caerulein overstimulation by modulating cytokine production. Pancreatology 2002, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leja-Szpak, A.; Jaworek, J.; Tomaszewska, R.; Nawrot, K.; Bonior, J.; Kot, M.; Palonek, M.; Stachura, J.; Czupryna, A.; Konturek, S.J.; et al. Melatonin precursor; l-tryptophan protects the pancreas from development of acute pancreatitis through the central site of action. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 55, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adeghate, E.; Ponery, A.S. Ghrelin stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas of normal and diabetic rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egido, E.M.; Rodriguez-Gallardo, J.; Silvestre, R.A.; Marco, J. Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on insulin and pancreatic somatostatin secretion. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 146, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Wang, G.; Englander, E.W.; Kojima, M.; Greeley, G.H., Jr. Ghrelin, a new gastrointestinal endocrine peptide that stimulates insulin secretion: Enteric distribution, ontogeny, influence of endocrine, and dietary manipulations. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Segura, B.J.; Mulholland, M.W. Inhibition of pancreatic protein secretion by ghrelin in the rat. J. Physiol. 2001, 537, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Kanai, S.; Takano, S.; Kurosawa, M.; Funakoshi, A.; Miyasaka, K. Central administration of ghrelin stimulates pancreatic exocrine secretion via the vagus in conscious rats. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2003, 53, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrot-Porabka, K.; Jaworek, J.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Szklarczyk, J.; Macko, M.; Kot, M.; Mitis-Musioł, M.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W. The effect of luminal ghrelin on pancreatic enzyme secretion in the rat. Regul. Pept. 2007, 143, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Nawrot-Porabka, K.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Konturek, S.J. Brain-gut axis in the modulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dezaki, K.; Hosoda, H.; Kakei, M.; Hashiguchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Endogenous ghrelin in pancreatic islets restricts insulin release by attenuating Ca2+ signaling in β-cells: Implication in the glycemic control in rodents. Diabetes 2004, 53, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeone, D.M.; Yule, D.I.; Logsdon, C.D.; Williams, J.A. Ca2+ signaling through secretagogue and growth factor receptors on pancreatic AR42J cells. Regul. Pept. 1995, 55, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, L.; Dahlén, H.G.; Lund, P.E.; Gylfe, E. Stimulation of pancreatic amylase release is associated with a parallel sustained increase of cytoplasmic calcium. Regul. Pept. 1990, 30, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsterdam, A.; Solomon, T.E.; Jamieson, J.D. Sequential dissocation of the exocrine pancreas into lobules, acini and individual cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1978, 20, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaninovic, V.; Gukovskaya, A.S.; Gukovsky, I.; Mouria, M.; Pandol, S.J. Cerulein upregulates ICAM-1 in pancreatic acinar cells, which mediates neutrophil adhesion to these cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G666–G676. [Google Scholar]
- Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Kot, M.; Konturek, S.J.; Pierzchalski, P. Long-lasting effect of infant rats endotoxemia on heat shock protein 60 in the pancreatic acinar cells: Involvement of toll-like receptor 4. Int. J. Inflam. 2012, 2012, 354904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W. Increase of heat shock protein gene expression by melatonin in AR42J cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 56, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W. Leptin is the modulator of HSP60 gene expression in AR42J cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Kot, M.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W. Endotoxemia in the infant rats modulates HSP60 protein level in the pancreatic acinar cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chomczyński, P.; Sacchi, N. Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinum thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudel, U.; Zakut, R.; Shani, M.; Neuman, S.; Levy, S.; Vaffe, D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic β-actin gene. Nucleic Acid. Res. 1983, 11, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T.; Nolan, C. Molecular Clonng, A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]

| Gene | Sequence 5’ > 3’ | Product | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | S: TTG TAA CCA ACT GGG ACG ATA TGG A: GAT CTT GAT CTT CAT GGT GCT AGG | 764 bp | 60 | [132] |
| GHS-R1a | S: GAG ATC GCT CAG ATC AGC CAG ATC AGC CAG TAC A: TAA TCC CCA AAC TGA GGT TCT GC | 313 bp | 60.7 | [32] |
| GHRL | S: CAG AGG ACA GAG GAC AAG CAG AAG A A: GCT GGA TGT GAG TTC TTG CTT AGG A | 234 bp | 59.5 | [32] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonior, J.; Ceranowicz, P.; Gajdosz, R.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Pierzchalski, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Kot, M.; Leja-Szpak, A.; et al. Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050929
Bonior J, Ceranowicz P, Gajdosz R, Kuśnierz-Cabala B, Pierzchalski P, Warzecha Z, Dembiński A, Pędziwiatr M, Kot M, Leja-Szpak A, et al. Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(5):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050929
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonior, Joanna, Piotr Ceranowicz, Ryszard Gajdosz, Beata Kuśnierz-Cabala, Piotr Pierzchalski, Zygmunt Warzecha, Artur Dembiński, Michał Pędziwiatr, Michalina Kot, Anna Leja-Szpak, and et al. 2017. "Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 5: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050929
APA StyleBonior, J., Ceranowicz, P., Gajdosz, R., Kuśnierz-Cabala, B., Pierzchalski, P., Warzecha, Z., Dembiński, A., Pędziwiatr, M., Kot, M., Leja-Szpak, A., Nawrot-Porąbka, K., Link-Lenczowski, P., Olszanecki, R., Bartuś, K., & Jaworek, J. (2017). Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(5), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050929








