Soluble (Pro)renin Receptor and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Oxidative Stress in Brain?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Plasma Concentrations of s(P)RR in Various Pathological Conditions
3. Plasma Concentrations of s(P)RR in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome
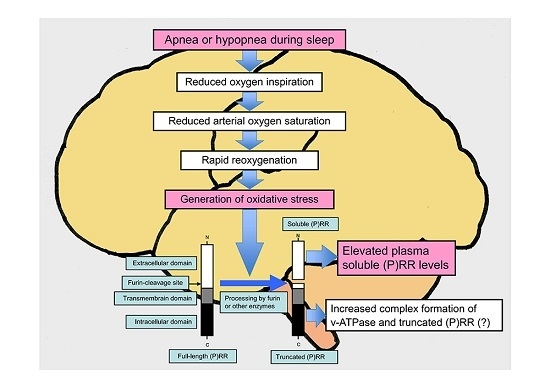
4. Oxidative Stress and (P)RR
5. Relationship between (P)RR Mutations and Brain Function
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | Apnea-hypopnea index |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CPAP | Continuous positive airway pressure |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| OSAS | Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| (P)RR | (Pro)renin receptor |
| RAS | Renin-angiotensin system |
| s(P)RR | Soluble (pro)renin receptor |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| v-ATPase | Vacuolar H+-ATPase |
References
- Nguyen, G.; Delarue, F.; Burcklé, C.; Bouzhir, L.; Giller, T.; Sraer, J.D. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.; Muller, D.N. The biology of the (pro)renin receptor. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G. Renin, (pro)renin and receptor: An update. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, A.H.; Kageshima, A.; Uddin, M.N.; Nakagawa, T.; Park, E.Y.; Suzuki, F. Binding properties of rat prorenin and renin to the recombinant rat renin/prorenin receptor prepared by a baculovirus expression system. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wongamorntham, S.; Kasting, J.; McQuillan, D.; Owens, R.T.; Yu, L.; Noble, N.A.; Border, W. Renin increases mesangial cell transforming growth factor-β1 and matrix proteins through receptor-mediated, angiotensin II-independent mechanisms. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihara, A.; Suzuki, F.; Nakagawa, T.; Kaneshiro, Y.; Takemitsu, T.; Sakoda, M.; Nabi, A.H.; Nishiyama, A.; Sugaya, T.; Hayashi, M.; et al. Prorenin receptor blockade inhibits development of glomerulosclerosis in diabetic angiotensin II type 1a receptor-deficient mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1950–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saris, J.J.; ’t Hoen, P.A.; Garrelds, I.M.; Dekkers, D.H.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Lamers, J.M.; Jan Danser, A.H. Prorenin induces intracellular signaling in cardiomyocytes independently of angiotensin II. Hypertension 2006, 48, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Mori, N.; Totsune, K.; Morimoto, R.; Maejima, T.; Kawamura, T.; Metoki, H.; Asayama, K.; Kikuya, M.; Ohkubo, T.; et al. Gene expression of (pro)renin receptor is upregulated in hearts and kidneys of rats with congestive heart failure. Peptides 2009, 30, 2316–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Mori, N.; Totsune, K.; Morimoto, R.; Maejima, T.; Kawamura, T.; Metoki, H.; Asayama, K.; Kikuya, M.; Ohkubo, T.; et al. Increased expression of (pro)renin receptor in the remnant kidneys of 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Regul. Pept. 2010, 159, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Hiraishi, K.; Hirose, T.; Kato, I.; Yamamoto, H.; Shoji, I.; Shibasaki, A.; Kaneko, K.; Satoh, F.; Totsune, K. Expression of (pro)renin receptor in the human brain and pituitary, and co-localisation with arginine vasopressin and oxytocin in the hypothalamus. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 22, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Hirose, T.; Hiraishi, K.; Shoji, I.; Shibasaki, A.; Kato, I.; Kaneko, K.; Sasano, H.; Satoh, F.; et al. Expression of (pro)renin receptor in human kidneys with end-stage kidney disease due to diabetic nephropathy. Peptides 2010, 31, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yatabe, M.; Fujiwara, K.; Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Yashiro, T. In situ hybridization method reveals (pro)renin receptor expressing cells in the pituitary gland of rats: Correlation with anterior pituitary hormones. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2013, 46, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Ohba, K.; Kaneko, K. Ubiquitous expression and multiple functions of biologically active peptides. Peptides 2015, 72, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousin, C.; Bracquart, D.; Contrepas, A.; Corvol, P.; Muller, L.; Nguyen, G. Soluble form of the (pro)renin receptor generated by intracellular cleavage by furin is secreted in plasma. Hypertension 2009, 53, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, A.; Aizaki, Y.; Kusano, K.; Kishi, F.; Susumu, T.; Iida, S.; Ishiura, S.; Nishimura, S.; Shichiri, M.; Senbonmatsu, T. The (pro)renin receptor is cleaved by ADAM19 in the Golgi leading to its secretion into extracellular space. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Suzuki-Nakagawa, C.; Watanabe, A.; Asami, E.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakano, M.; Ebihara, A.; Uddin, M.N.; Suzuki, F. Site-1 protease is required for the generation of soluble (pro)renin receptor. J. Biochem. 2017, 161, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, J.; Kerscher, S.; Brandt, U.; Pfeiffer, K.; Getlawi, F.; Apps, D.K.; Schägger, H. Identification and characterization of a novel 9.2-kDa membrane sector-associated protein of vacuolar proton-ATPase from chromaffin granules. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10939–10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinouchi, K.; Ichihara, A.; Sano, M.; Sun-Wada, G.H.; Wada, Y.; Kurauchi-Mito, A.; Bokuda, K.; Narita, T.; Oshima, Y.; Sakoda, M.; et al. The (pro)renin receptor/ATP6AP2 is essential for vacuolar H+-ATPase assembly in murine cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, Y.; Kinouchi, K.; Ichihara, A.; Sakoda, M.; Kurauchi-Mito, A.; Bokuda, K.; Narita, T.; Kurosawa, H.; Sun-Wada, G.H.; Wada, Y.; et al. Prorenin receptor is essential for normal podocyte structure and function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riediger, F.; Quack, I.; Qadri, F.; Hartleben, B.; Park, J.K.; Potthoff, S.A.; Sohn, D.; Sihn, G.; Rousselle, A.; Fokuhl, V.; et al. Prorenin receptor is essential for podocyte autophagy and survival. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruciat, C.M.; Ohkawara, B.; Acebron, S.P.; Karaulanov, E.; Reinhard, C.; Ingelfinger, D.; Boutros, M.; Niehrs, C. Requirement of prorenin receptor and vacuolar H+-ATPase-mediated acidification for Wnt signaling. Science 2010, 327, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, T.; Tajima, K.; Takahashi, K.; Sakurai, S. Elevated plasma levels of soluble (pro)renin receptor in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: Association with polysomnographic parameters. Peptides 2014, 56, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, T.; Tajima, K.; Yamashiro, Y.; Hosokawa, K.; Suwabe, A.; Takahashi, K.; Sakurai, S. Elevated plasma levels of soluble (pro)renin receptor in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in parallel with the disease severity. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2016, 238, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Shimamura, Y.; Inoue, K.; Ogata, K.; Ishihara, M.; Horino, T.; Fujimoto, S.; Ohguro, T.; Yoshimoto, Y.; et al. Serum level of soluble (pro)renin receptor is modulated in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2013, 17, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, A.; Kinugawa, S.; Homma, T.; Masaki, Y.; Furihata, T.; Abe, T.; Suga, T.; Takada, S.; Kadoguchi, T.; Okita, K.; et al. Increased plasma soluble (pro)renin receptor levels are correlated with renal dysfunction in patients with heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amari, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Nakajima, F.; Ando, T.; Ichihara, A. Serum soluble (pro)renin receptor levels in maintenance hemodialysis patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Bokuda, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Mito, A.; Morimoto, S.; Jwa, S.C.; Egawa, M.; Arai, Y.; Suzuki, F.; et al. Soluble (pro)renin receptor and blood pressure during pregnancy: A prospective cohort study. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Morimoto, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Mori, F.; Ando, T.; Watanabe, D.; Kimura, T.; Sago, H.; et al. Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus by soluble (pro)renin receptor during the first trimester. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2528–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Morimoto, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Ando, T.; Kimura, T.; Sago, H.; Ichihara, A. Association between soluble (pro)renin receptor concentration in cord blood and small for gestational age birth: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kaneko, K.; Ohba, K.; Morimoto, R.; Hirose, T.; Satoh, F.; Totsune, K.; Takahashi, K. Increased expression of (pro)renin receptor in aldosterone-producing adenomas. Peptides 2013, 49, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohba, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nishiyama, H.; Kaneko, K.; Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Sasano, S.; Takahashi, K. Expression of (pro)renin receptor in breast cancers and its effect on cancer cell proliferation. Biomed. Res. 2014, 35, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, Y.; Fujimori, T.; Nguyen, G.; Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Ichihara, A.; Kitada, K.; Nakano, D.; Kobori, H.; Kohno, M.; et al. (Pro)renin receptor is crucial for Wnt/β-catenin-dependent genesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, Y.; Mori, N.; Xu, B.; Nakamura, T.; Yamakoshi, S.; Hirose, T.; Ito, O.; Totsune, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kohzuki, M. Water deprivation increases (pro)renin receptor levels in the kidney and decreases plasma concentrations of soluble (pro)renin receptor. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2016, 239, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.; Blanchard, A.; Curis, E.; Bergerot, D.; Chambon, Y.; Hirose, T.; Caumont-Prim, A.; Tabard, S.B.; Baron, S.; Frank, M.; et al. Plasma Soluble (pro)renin receptor is independent of plasma renin, prorenin, and aldosterone concentrations but is affected by ethnicity. Hypertension 2014, 63, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; Palta, M.; Dempsey, J.; Skatrud, J.; Weber, S.; Badr, S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzer, S.; Charuzi, I. Obstructive sleep apnea in the obese. World J. Surg. 1998, 22, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Skatrud, J. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichmuth, K.J.; Austin, D.; Skatrud, J.B.; Young, T. Association of sleep apnea and type II diabetes: A population-based study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, R.J.; Pasirstein, M.; Pierson, R.; Mackley, A.; Hachadoorian, R.; Arens, R.; Maislin, G.; Pack, A.I. Identification of upper airway anatomic risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea with volumetric magnetic resonance imaging. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calhoun, D.A.; Nishizaka, M.K.; Zaman, M.A.; Harding, S.M. Aldosterone excretion among subjects with resistant hypertension and symptoms of sleep apnea. Chest 2004, 125, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, D.S.; Lind, P.; Strunge, B.; Pedersen, E.B. Abnormal vasoactive hormones and 24-hour blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Hypertens. 2003, 16, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, D.; Fineyre, F.; Dreyfuss, D.; Djedaini, K.; Blanchet, F.; Paycha, F.; Dussaule, J.C.; Nitenberg, A. Pressure-heart rate responses to alpha-adrenergic stimulation and hormonal regulation in normotensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997, 10, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorup, P.H.; Sadauskiene, L.; Wessels, J.; Nyvad, O.; Strunge, B.; Pedersen, E.B. Abnormally increased endothelin-1 in plasma during the night in obstructive sleep apnea: Relation to blood pressure and severity of disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imagawa, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Neichi, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Mukai, H.Y.; Suzuki, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagasawa, T. Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor are elevated in patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Blood 2001, 98, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnicki, M.; Shamsuzzaman, A.; Lanfranchi, P.; Accurso, V.; Olson, E.; Davison, D.; Somers, V.K. Erythropoietin and obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, T.; Sakurai, S.; Arihara, Z.; Takahashi, K. Plasma orexin-A-like immunoreactivity in patients with sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Peptides 2003, 24, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, S.; Nishijima, T.; Takahashi, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Arihara, Z.; Takahashi, K. Low plasma orexin-A levels were improved by continuous positive airway pressure treatment in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Chest 2005, 127, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svatikova, A.; Olson, L.J.; Wolk, R.; Phillips, B.G.; Adachi, T.; Schwartz, G.L.; Somers, V.K. Obstructive sleep apnea and aldosterone. Sleep 2009, 32, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, L. Oxidative stress in obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia–revisited—The bad ugly and good: Implications to the heart and brain. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 20, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.M.; Mehra, R. Obstructive sleep apnea: Role of intermittent hypoxia and inflammation. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 35, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almendros, I.; Farré, R.; Planas, A.M.; Torres, M.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Navajas, D.; Montserrat, J.M. Tissue oxygenation in brain, muscle, and fat in a rat model of sleep apnea: Differential effect of obstructive apneas and intermittent hypoxia. Sleep 2011, 34, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milgrom, E.; Diab, H.; Middleton, F.; Kane, P.M. Loss of vacuolar proton-translocating ATPase activity in yeast results in chronic oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7125–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Ohba, K.; Hirose, T.; Totsune, K.; Furuyama, K.; Takahashi, K. Elevated expression of (pro)renin receptor during rapamycin-induced erythropoiesis in K562 erythroleukemia cells and its possible dual actions on erythropoiesis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 241, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Totsune, K.; Metoki, H.; Asayama, K.; Kikuya, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Katsuya, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hashimoto, J.; et al. Association of (pro)renin receptor gene polymorphism with blood pressure in Japanese men: The Ohasama study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2009, 22, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Totsune, K.; Metoki, H.; Hara, A.; Satoh, M.; Kikuya, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Asayama, K.; Kondo, T.; et al. Association of (pro)renin receptor gene polymorphisms with lacunar infarction and left ventricular hypertrophy in Japanese women: The Ohasama study. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramser, J.; Abidi, F.E.; Burckle, C.A.; Lenski, C.; Toriello, H.; Wen, G.; Lubs, H.A.; Engert, S.; Stevenson, R.E.; et al. A unique exonic splice enhancer mutation in a family with X-linked mental retardation and epilepsy points to a novel role of the renin receptor. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korvatska, O.; Strand, N.S.; Berndt, J.D.; Strovas, T.; Chen, D.H.; Leverenz, J.B.; Kiianitsa, K.; Mata, I.F.; Karakoc, E.; Greenup, J.L.; et al. Altered splicing of ATP6AP2 causes X-linked parkinsonism with spasticity (XPDS). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3259–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, K.; Ohba, K.; Tajima, K.; Nishijima, T.; Sakurai, S. Soluble (Pro)renin Receptor and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Oxidative Stress in Brain? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061313
Takahashi K, Ohba K, Tajima K, Nishijima T, Sakurai S. Soluble (Pro)renin Receptor and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Oxidative Stress in Brain? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061313
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Kazuhiro, Koji Ohba, Kazuki Tajima, Tsuguo Nishijima, and Shigeru Sakurai. 2017. "Soluble (Pro)renin Receptor and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Oxidative Stress in Brain?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061313
APA StyleTakahashi, K., Ohba, K., Tajima, K., Nishijima, T., & Sakurai, S. (2017). Soluble (Pro)renin Receptor and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Oxidative Stress in Brain? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061313