Role of Disulfide Bonds in Activity and Stability of Tigerinin-1R
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
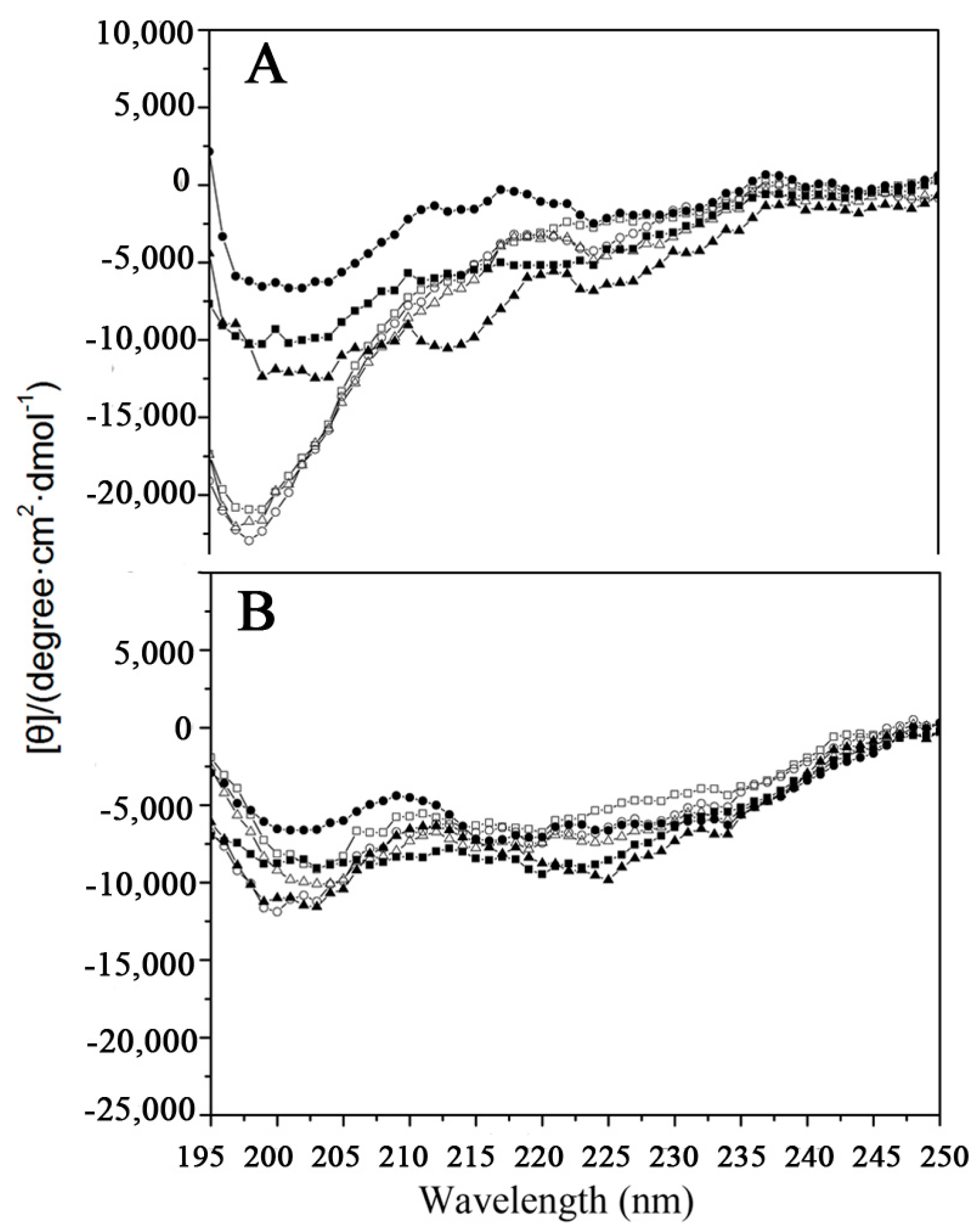
2.1. Peptide Design and Structure
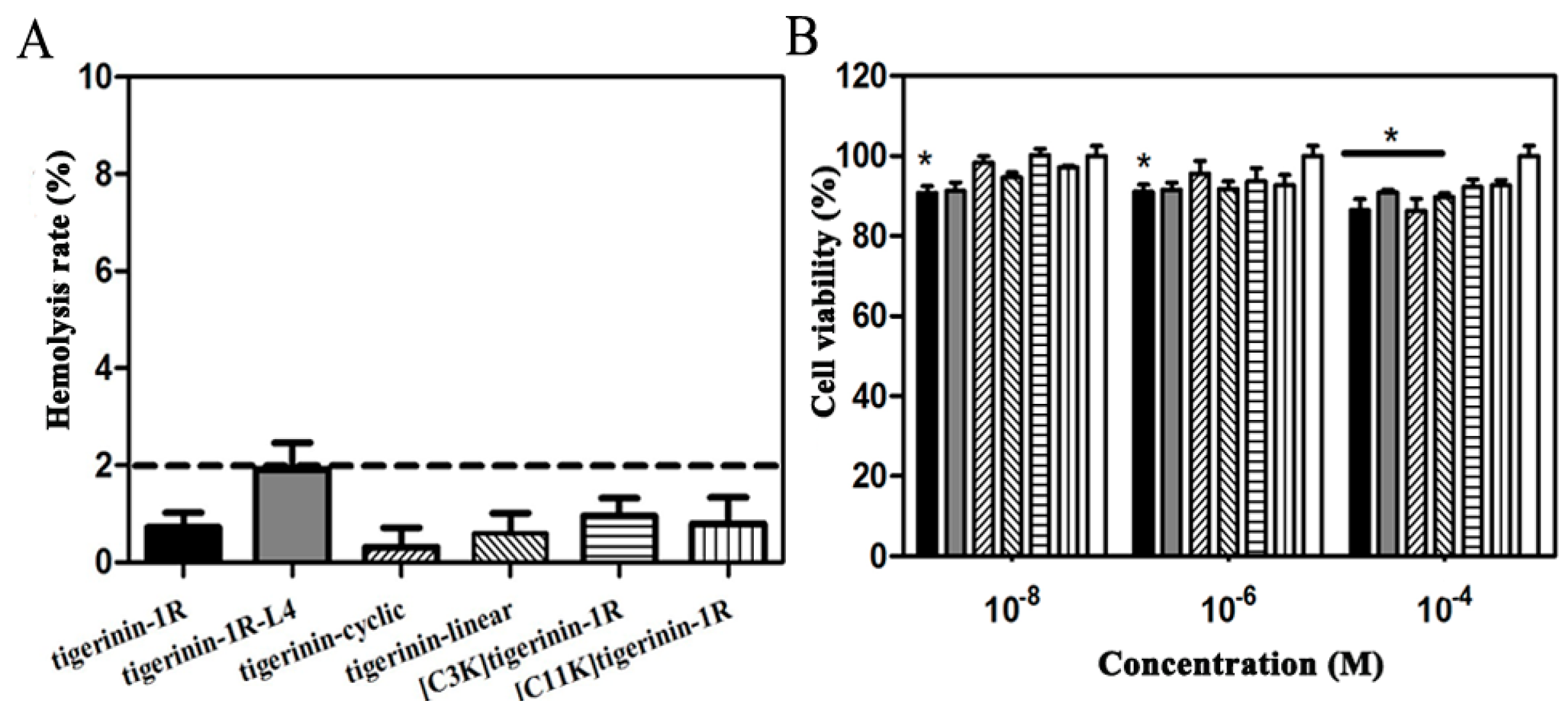
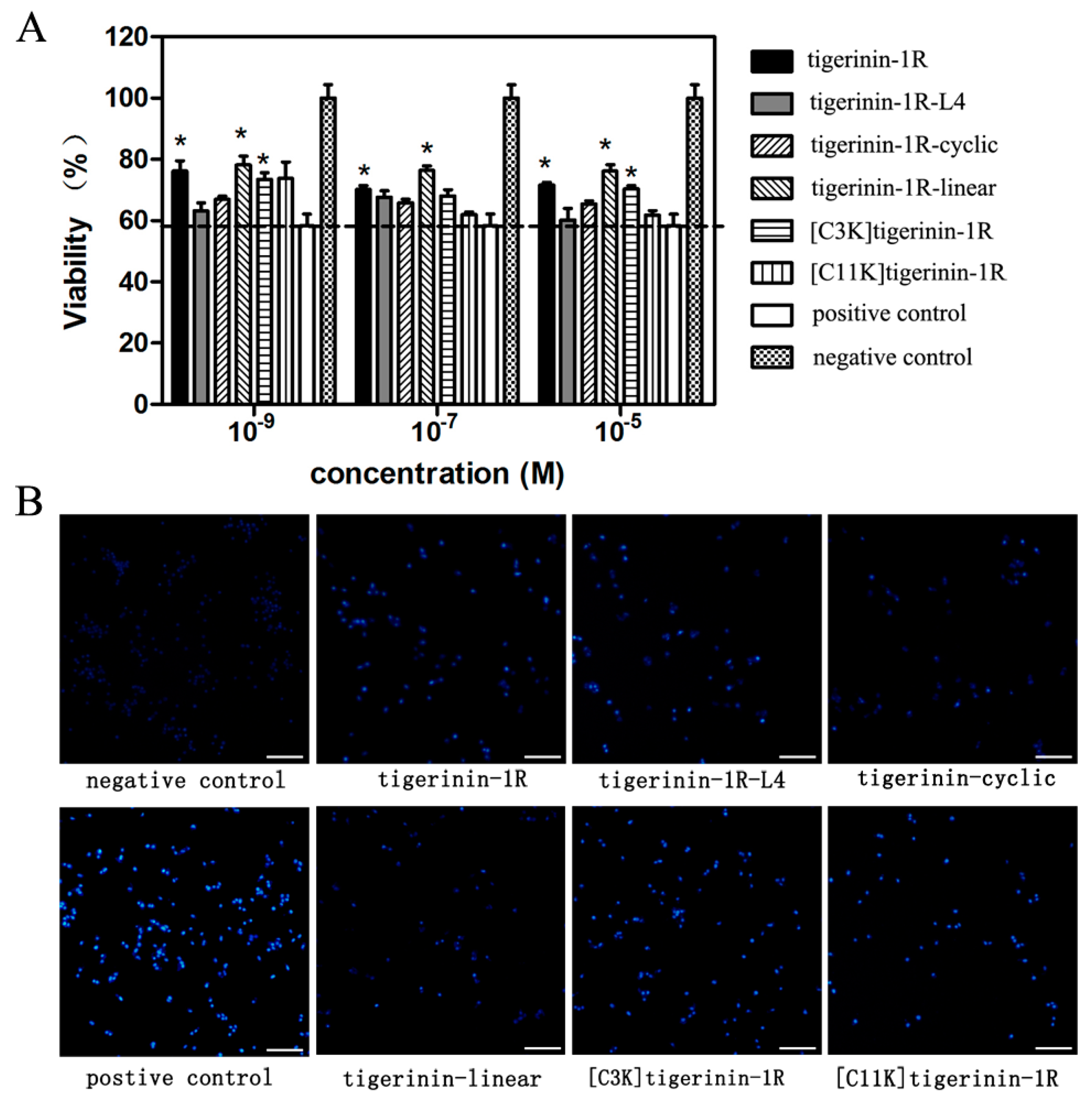
2.2. Cellular Toxicity of Peptides
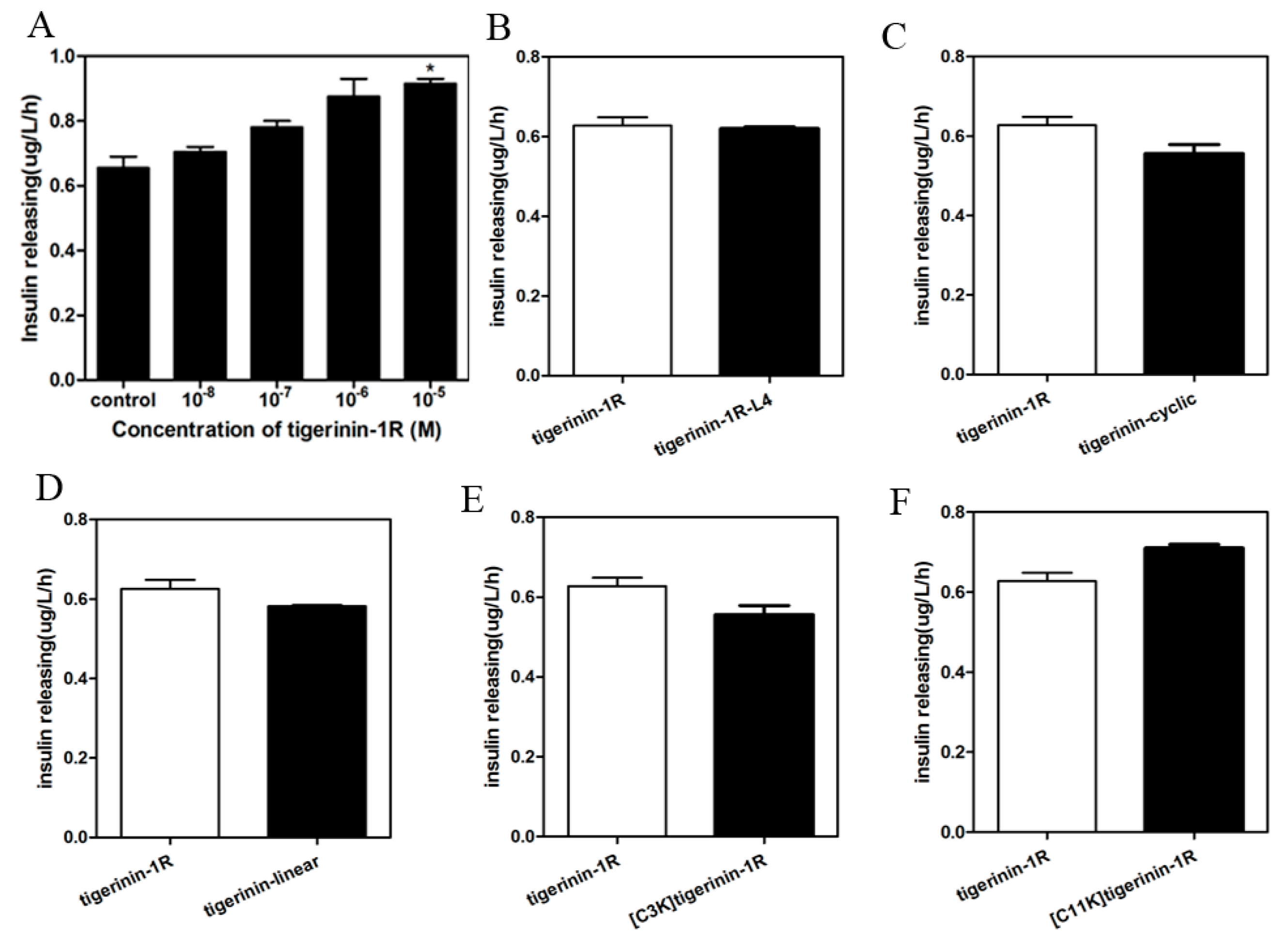
2.3. Insulin-Release Activity of Peptides In Vitro
2.4. Mechanism of Stimulation of Insulin Release
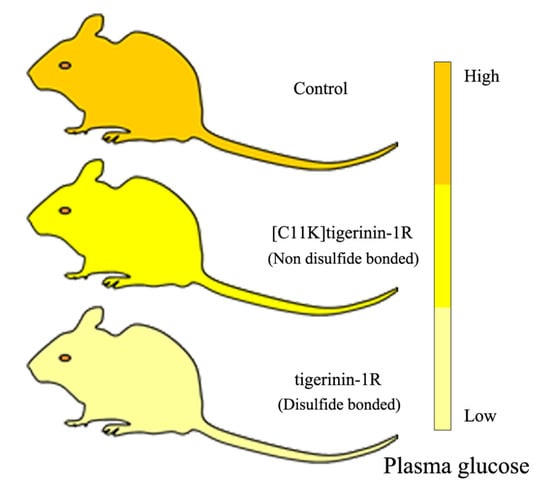
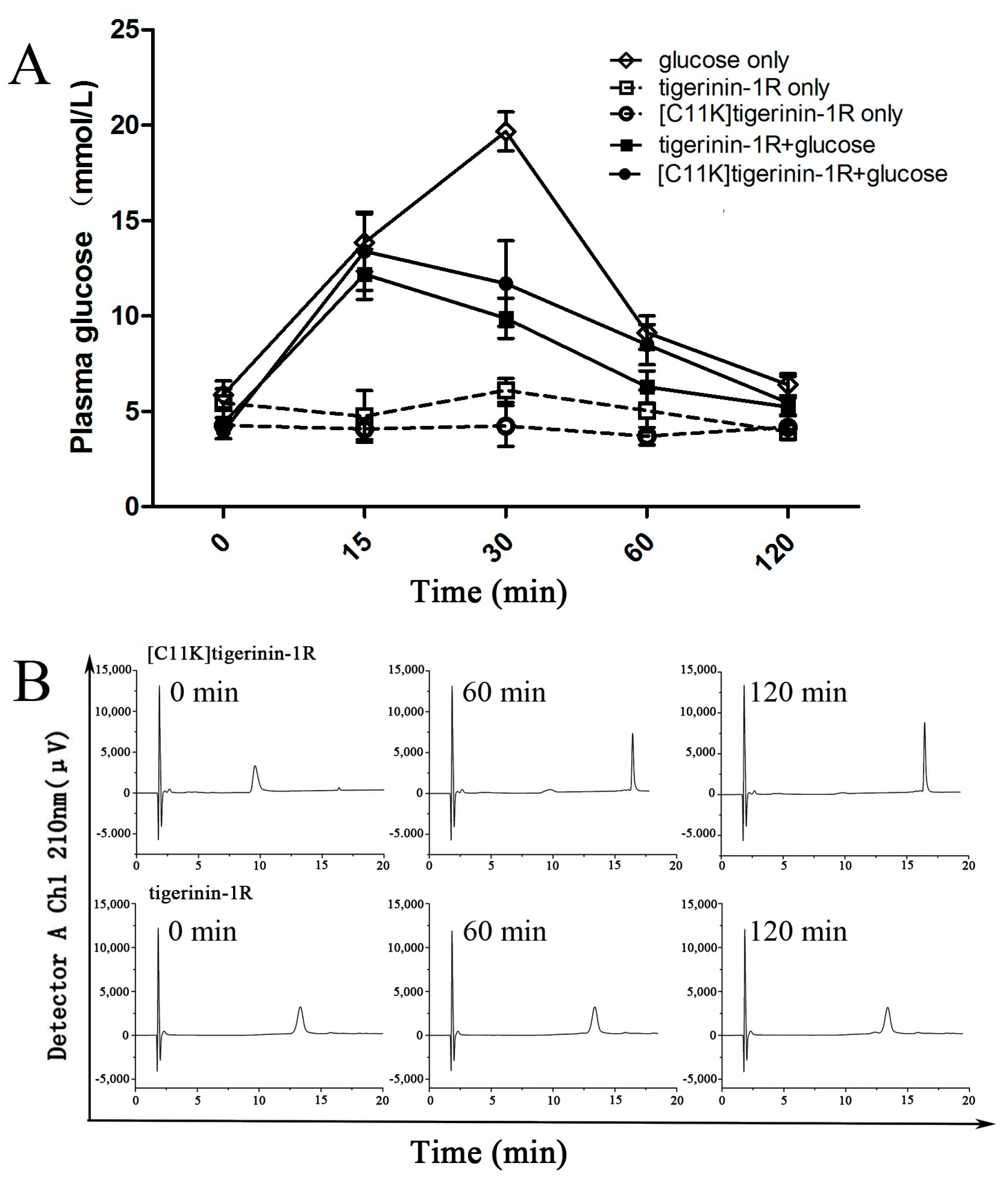
2.5. Effect of Tigerinin-1R and [C11K]Tigerinin-1R on Glucose Tolerance In Vivo
2.6. Protective Effects against Apoptosis Induced by Palmitic Acid
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis and Purification
4.2. Circular Dichroism
4.3. Measurement of Hemolytic Activity
4.4. Cell Culture and Cytoxicity Assays
4.5. Determination of Insulin-Releasing Activity In Vitro
4.6. Lactate Dehydrogenase Leakage Assay
4.7. Measurement of [Ca2+]
4.8. In Vivo Studies
4.9. Peptide Degradation Assays
4.10. Apoptosis Induction and Cell-Viability Assay
4.11. Hoechst 33258 Staining
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, E.M.; Styblo, M.; Fry, R.C. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms underlying arsenic-associated diabetes mellitus: A perspective of the current evidence. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, S.B.; Mehmood, Z.; Akhter, N.; Kauser, A.; Hussain, I.; Rashid, A.; Akram, M.; Tahir, I.M.; Munir, N.; Riaz, M.; et al. Review-medicinal plants and management of diabetes mellitus: A review. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 29, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.; Magliano, D.J.; Bennett, P.H. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: Facts and fallacies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, O.; Buss, J.; Thomas, E. Type 2 diabetes and hearing loss. Dis. Mon. 2013, 59, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Pradeepa, R.; Joshi, S.R.; Mohan, V. Type 2 diabetes: Demystifying the global epidemic. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, M.E. Pharmacological agents that directly modulate insulin secretion. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Sun, P.; Chen, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, K.; Jia, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Cinnamtannin D-1 protects pancreatic β-cells from palmitic acid-induced apoptosis by attenuating oxidative stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5038–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing Yin, J.; Bo Li, Y.; Ming Cao, M.; Wang, Y. Liraglutide improves the survival of INS-1 cells by promoting macroautophagy. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 11, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Tiedge, M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, J.J. The medicinal chemistry of peptides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 4399–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.W. Peptide antibiotics. Lancet 1997, 349, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilor, C.; Rudinsky, A.J.; Hall, M.J. New approaches to feline diabetes mellitus: Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, C.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.; Hucking, K.; Holst, J.J. Degradation of endogenous and exogenous gastric inhibitory polypeptide in healthy and in type 2 diabetic subjects as revealed using a new assay for the intact peptide. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, S.; Hamada, T.; Chisaki, I.; Andou, T.; Sano, N.; Furuta, A.; Amano, N. Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exenatide to characterize its antiobesity effects in diet-induced obese mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 362, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anholm, C.; Kumarathurai, P.; Pedersen, L.R.; Nielsen, O.W.; Kristiansen, O.P.; Fenger, M.; Madsbad, S.; Sajadieh, A.; Haugaard, S.B. Liraglutide effects on β-cell, insulin sensitivity and glucose effectiveness in patients with stable coronary artery disease and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, J.M.; Mechkarska, M.; Lukic, M.L.; Flatt, P.R. Potential therapeutic applications of multifunctional host-defense peptides from frog skin as anti-cancer, anti-viral, immunomodulatory, and anti-diabetic agents. Peptides 2014, 57, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.W.; Lee, W.H.; Zhang, Y. Extremely abundant antimicrobial peptides existed in the skins of nine kinds of chinese odorous frogs. J. Proteom. Res. 2012, 11, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.; Marenah, L.; Flatt, P.R.; Conlon, J.M. Insulin releasing properties of the temporin family of antimicrobial peptides. Protein Pept. Lett. 2007, 14, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenah, L.; Flatt, P.R.; Orr, D.F.; Shaw, C.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H. Skin secretions of rana saharica frogs reveal antimicrobial peptides esculentins-1 and -1B and brevinins-1E and -2EC with novel insulin releasing activity. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 188, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, D.; Ojo, O.O.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.; Flatt, P.R.; Guilhaudis, L.; Conlon, J.M. Insulin-releasing and cytotoxic properties of the frog skin peptide, tigerinin-1R: A structure-activity study. Peptides 2014, 55, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.O.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.; Flatt, P.R.; Conlon, J.M. Insulinotropic actions of the frog skin host-defense peptide alyteserin-2A: A structure-activity study. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 82, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.O.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.; Flatt, P.R.; Mechkarska, M.; Conlon, J.M. Tigerinin-1R: A potent, non-toxic insulin-releasing peptide isolated from the skin of the asian frog, hoplobatrachus rugulosus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.O.; Srinivasan, D.K.; Owolabi, B.O.; Flatt, P.R.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A. Beneficial effects of tigerinin-1R on glucose homeostasis and β cell function in mice with diet-induced obesity-diabetes. Biochimie 2015, 109, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, D.K.; Ojo, O.O.; Owolabi, B.O.; Conlon, J.M.; Flatt, P.R.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A. [I10W]tigerinin-1R enhances both insulin sensitivity and pancreatic β cell function and decreases adiposity and plasma triglycerides in high-fat mice. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilotta, F.L.; Arcidiacono, B.; Messineo, S.; Greco, M.; Chiefari, E.; Britti, D.; Nakanishi, T.; Foti, D.P.; Brunetti, A. Insulin and osteocalcin: Further evidence for a mutual cross-talk. Endocrine 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlbauer, E.; Albrecht, E.; Bazwinsky-Wutschke, I.; Peschke, E. Melatonin influences insulin secretion primarily via mt1 receptors in rat insulinoma cells (INS-1) and mouse pancreatic islets. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verspohl, E.J. Effect of PAO (phenylarsine oxide) on the inhibitory effect of insulin and IGF-1 on insulin release from INS-1 cells. Endocrinol. J. 2006, 53, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Luo, F.; Feng, Y.M.; Wei, X.; Miao, H.; Lu, Y.B.; Tang, Y.; Ding, D.F.; Jin, J.F.; Zhu, Q. Neutral ceramidase secreted via exosome protects against palmitate-induced apoptosis in INS-1 cells. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 125, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysham, C.H.; Rosenstock, J.; Vetter, M.L.; Dong, F.; Ohman, P.; Iqbal, N. Efficacy and tolerability of the new autoinjected suspension of exenatide once weekly versus exenatide twice daily in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, S.; Mannucci, E.; Ceriello, A. A review of the long-term efficacy, tolerability, and safety of exenatide once weekly for type 2 diabetes. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 1791–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.O.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; You, G.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Gaegurin-6 stimulates insulin secretion through calcium influx in pancreatic β Rin5mf cells. Regul. Pept. 2010, 159, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.; Patterson, S.; Flatt, P.R.; Conlon, J.M. Brevinin-2-related peptide and its [D4K] analogue stimulate insulin release in vitro and improve glucose tolerance in mice fed a high fat diet. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.O.; Conlon, J.M.; Flatt, P.R.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A. Frog skin peptides (tigerinin-1R, magainin-AM1,-AM2, CPF-AM1, and PGla-AM1) stimulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) by GLUTag cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res Commun. 2013, 431, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Yan, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Tat modification of α-helical anticancer peptides to improve specificity and efficacy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, G.X.; Bai, X.W.; Li, Z.J.; Yan, X.W.; He, X.Q.; Rong, M.Q. A novel insulinotropic peptide from the skin secretions of amolops loloensis frog. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2014, 4, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxin, A.; Zheng, G. Flexible or fixed: A comparative review of linear and cyclic cancer-targeting peptides. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1601–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemazar, M.; Kwon, S.; Mahatmanto, T.; Ravipati, A.S.; Craik, D.J. Discovery and applications of disulfide-rich cyclic peptides. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wan, X.; Su, Q. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibition ameliorates palmitate-induced INS-1 β cell death. Endocrine 2012, 42, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.B.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.X. Studies on mechanism of action of anticancer peptides by modulation of hydrophobicity within a defined structural framework. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Temperature selectivity effects in reversed-phase liquid chromatography due to conformation differences between helical and non-helical peptides. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1010, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Power, G.J.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A.; Flatt, P.R.; Jiansheng, H.; Coquet, L.; Leprince, J.; Jouenne, T.; Vaudry, H. A potent, non-toxic insulin-releasing peptide isolated from an extract of the skin of the asian frog, hylarana guntheri (anura:Ranidae). Regul. Pept. 2008, 151, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Peptide | Amino Acid Sequence a | Mw | tR (min) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tigerinin-1R | RVCSAIPLPICH-amide (C–C) | 1035.65 | 19.465 |
| 2 | tigerinin-1R-L4 | RVCSLLPLPLCH-amide (C–C) | 1347.73 | 23.608 |
| 3 | tigerinin-cyclic | CSAIPLPIC-amide (C–C) | 955.23 | 19.647 |
| 4 | tigerinin-linear | Ac-RVASAIPLPIAH-amide | 1285.56 | 11.590 |
| 5 | [C3K]tigerinin-1R | Ac-RVKSAIPLPICH-amide | 1374.72 | 10.818 |
| 6 | [C11K]tigerinin-1R | Ac-RVCSAIPLPIKH-amide | 1374.72 | 8.835 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Hu, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Role of Disulfide Bonds in Activity and Stability of Tigerinin-1R. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020288
Chen X, Hu C, Huang Y, Chen Y. Role of Disulfide Bonds in Activity and Stability of Tigerinin-1R. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020288
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaolong, Cuihua Hu, Yibing Huang, and Yuxin Chen. 2018. "Role of Disulfide Bonds in Activity and Stability of Tigerinin-1R" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020288
APA StyleChen, X., Hu, C., Huang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2018). Role of Disulfide Bonds in Activity and Stability of Tigerinin-1R. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020288